CB2 Question Bank
Quiz-summary
0 of 999 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
- 568
- 569
- 570
- 571
- 572
- 573
- 574
- 575
- 576
- 577
- 578
- 579
- 580
- 581
- 582
- 583
- 584
- 585
- 586
- 587
- 588
- 589
- 590
- 591
- 592
- 593
- 594
- 595
- 596
- 597
- 598
- 599
- 600
- 601
- 602
- 603
- 604
- 605
- 606
- 607
- 608
- 609
- 610
- 611
- 612
- 613
- 614
- 615
- 616
- 617
- 618
- 619
- 620
- 621
- 622
- 623
- 624
- 625
- 626
- 627
- 628
- 629
- 630
- 631
- 632
- 633
- 634
- 635
- 636
- 637
- 638
- 639
- 640
- 641
- 642
- 643
- 644
- 645
- 646
- 647
- 648
- 649
- 650
- 651
- 652
- 653
- 654
- 655
- 656
- 657
- 658
- 659
- 660
- 661
- 662
- 663
- 664
- 665
- 666
- 667
- 668
- 669
- 670
- 671
- 672
- 673
- 674
- 675
- 676
- 677
- 678
- 679
- 680
- 681
- 682
- 683
- 684
- 685
- 686
- 687
- 688
- 689
- 690
- 691
- 692
- 693
- 694
- 695
- 696
- 697
- 698
- 699
- 700
- 701
- 702
- 703
- 704
- 705
- 706
- 707
- 708
- 709
- 710
- 711
- 712
- 713
- 714
- 715
- 716
- 717
- 718
- 719
- 720
- 721
- 722
- 723
- 724
- 725
- 726
- 727
- 728
- 729
- 730
- 731
- 732
- 733
- 734
- 735
- 736
- 737
- 738
- 739
- 740
- 741
- 742
- 743
- 744
- 745
- 746
- 747
- 748
- 749
- 750
- 751
- 752
- 753
- 754
- 755
- 756
- 757
- 758
- 759
- 760
- 761
- 762
- 763
- 764
- 765
- 766
- 767
- 768
- 769
- 770
- 771
- 772
- 773
- 774
- 775
- 776
- 777
- 778
- 779
- 780
- 781
- 782
- 783
- 784
- 785
- 786
- 787
- 788
- 789
- 790
- 791
- 792
- 793
- 794
- 795
- 796
- 797
- 798
- 799
- 800
- 801
- 802
- 803
- 804
- 805
- 806
- 807
- 808
- 809
- 810
- 811
- 812
- 813
- 814
- 815
- 816
- 817
- 818
- 819
- 820
- 821
- 822
- 823
- 824
- 825
- 826
- 827
- 828
- 829
- 830
- 831
- 832
- 833
- 834
- 835
- 836
- 837
- 838
- 839
- 840
- 841
- 842
- 843
- 844
- 845
- 846
- 847
- 848
- 849
- 850
- 851
- 852
- 853
- 854
- 855
- 856
- 857
- 858
- 859
- 860
- 861
- 862
- 863
- 864
- 865
- 866
- 867
- 868
- 869
- 870
- 871
- 872
- 873
- 874
- 875
- 876
- 877
- 878
- 879
- 880
- 881
- 882
- 883
- 884
- 885
- 886
- 887
- 888
- 889
- 890
- 891
- 892
- 893
- 894
- 895
- 896
- 897
- 898
- 899
- 900
- 901
- 902
- 903
- 904
- 905
- 906
- 907
- 908
- 909
- 910
- 911
- 912
- 913
- 914
- 915
- 916
- 917
- 918
- 919
- 920
- 921
- 922
- 923
- 924
- 925
- 926
- 927
- 928
- 929
- 930
- 931
- 932
- 933
- 934
- 935
- 936
- 937
- 938
- 939
- 940
- 941
- 942
- 943
- 944
- 945
- 946
- 947
- 948
- 949
- 950
- 951
- 952
- 953
- 954
- 955
- 956
- 957
- 958
- 959
- 960
- 961
- 962
- 963
- 964
- 965
- 966
- 967
- 968
- 969
- 970
- 971
- 972
- 973
- 974
- 975
- 976
- 977
- 978
- 979
- 980
- 981
- 982
- 983
- 984
- 985
- 986
- 987
- 988
- 989
- 990
- 991
- 992
- 993
- 994
- 995
- 996
- 997
- 998
- 999
Information
CB2 Question Bank
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Your Result
You scored 0 of 0 points, (0)0 of 999 questions answered correctly
Time Taken:
Time has elapsed
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- CB2 IAI FEB 2025 DIET 0%
- CB2- CB2 M4 0%
- CB2- CB2 M5 0%
- CB2- CB2 X1 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X2 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X3 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X4 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X5 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X6 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X7 Mock 0%
- CB2- CB2 X8 Mock 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Background to demand 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Background to supply 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Balance of payments and exchange rates 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Classical and keynesian theory 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Debates on theory and policy 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Demand-side policy 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Economic concepts and systems 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Exchange rate policy 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Global harmonisation / union 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 International trade 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Macroeconomic objectives 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Main strands of economic thinking 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Market failure and government intervention 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Monetarist and new classical schools, keynesian responses 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Monopolistic competition and oligopoly 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Perfect competition and monopoly 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Pricing strategies 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Relationship between the goods and the money markets 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Supply and demand(1) 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Supply and demand(2) 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 Supply-side policy 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 The financial system 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 The macroeconomic environment 0%
- Cb2- TV CB2 The money market and monetary policy 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
- 568
- 569
- 570
- 571
- 572
- 573
- 574
- 575
- 576
- 577
- 578
- 579
- 580
- 581
- 582
- 583
- 584
- 585
- 586
- 587
- 588
- 589
- 590
- 591
- 592
- 593
- 594
- 595
- 596
- 597
- 598
- 599
- 600
- 601
- 602
- 603
- 604
- 605
- 606
- 607
- 608
- 609
- 610
- 611
- 612
- 613
- 614
- 615
- 616
- 617
- 618
- 619
- 620
- 621
- 622
- 623
- 624
- 625
- 626
- 627
- 628
- 629
- 630
- 631
- 632
- 633
- 634
- 635
- 636
- 637
- 638
- 639
- 640
- 641
- 642
- 643
- 644
- 645
- 646
- 647
- 648
- 649
- 650
- 651
- 652
- 653
- 654
- 655
- 656
- 657
- 658
- 659
- 660
- 661
- 662
- 663
- 664
- 665
- 666
- 667
- 668
- 669
- 670
- 671
- 672
- 673
- 674
- 675
- 676
- 677
- 678
- 679
- 680
- 681
- 682
- 683
- 684
- 685
- 686
- 687
- 688
- 689
- 690
- 691
- 692
- 693
- 694
- 695
- 696
- 697
- 698
- 699
- 700
- 701
- 702
- 703
- 704
- 705
- 706
- 707
- 708
- 709
- 710
- 711
- 712
- 713
- 714
- 715
- 716
- 717
- 718
- 719
- 720
- 721
- 722
- 723
- 724
- 725
- 726
- 727
- 728
- 729
- 730
- 731
- 732
- 733
- 734
- 735
- 736
- 737
- 738
- 739
- 740
- 741
- 742
- 743
- 744
- 745
- 746
- 747
- 748
- 749
- 750
- 751
- 752
- 753
- 754
- 755
- 756
- 757
- 758
- 759
- 760
- 761
- 762
- 763
- 764
- 765
- 766
- 767
- 768
- 769
- 770
- 771
- 772
- 773
- 774
- 775
- 776
- 777
- 778
- 779
- 780
- 781
- 782
- 783
- 784
- 785
- 786
- 787
- 788
- 789
- 790
- 791
- 792
- 793
- 794
- 795
- 796
- 797
- 798
- 799
- 800
- 801
- 802
- 803
- 804
- 805
- 806
- 807
- 808
- 809
- 810
- 811
- 812
- 813
- 814
- 815
- 816
- 817
- 818
- 819
- 820
- 821
- 822
- 823
- 824
- 825
- 826
- 827
- 828
- 829
- 830
- 831
- 832
- 833
- 834
- 835
- 836
- 837
- 838
- 839
- 840
- 841
- 842
- 843
- 844
- 845
- 846
- 847
- 848
- 849
- 850
- 851
- 852
- 853
- 854
- 855
- 856
- 857
- 858
- 859
- 860
- 861
- 862
- 863
- 864
- 865
- 866
- 867
- 868
- 869
- 870
- 871
- 872
- 873
- 874
- 875
- 876
- 877
- 878
- 879
- 880
- 881
- 882
- 883
- 884
- 885
- 886
- 887
- 888
- 889
- 890
- 891
- 892
- 893
- 894
- 895
- 896
- 897
- 898
- 899
- 900
- 901
- 902
- 903
- 904
- 905
- 906
- 907
- 908
- 909
- 910
- 911
- 912
- 913
- 914
- 915
- 916
- 917
- 918
- 919
- 920
- 921
- 922
- 923
- 924
- 925
- 926
- 927
- 928
- 929
- 930
- 931
- 932
- 933
- 934
- 935
- 936
- 937
- 938
- 939
- 940
- 941
- 942
- 943
- 944
- 945
- 946
- 947
- 948
- 949
- 950
- 951
- 952
- 953
- 954
- 955
- 956
- 957
- 958
- 959
- 960
- 961
- 962
- 963
- 964
- 965
- 966
- 967
- 968
- 969
- 970
- 971
- 972
- 973
- 974
- 975
- 976
- 977
- 978
- 979
- 980
- 981
- 982
- 983
- 984
- 985
- 986
- 987
- 988
- 989
- 990
- 991
- 992
- 993
- 994
- 995
- 996
- 997
- 998
- 999
-
Question 1 of 999CB2023165
Question 1
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is FALSE?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONPerfect competition is a market structure characterized by many buyers and sellers engaged in the production and
exchange of homogeneous products. Each firm is so small relative to the whole industry that it has no power to
influence price. Firms are price takers meaning that they accept the prevailing market price. Also, there is complete
freedom of entry into the industry for new firms. In the long run, if typical firms are making supernormal profits,
new firms will be attracted into the industry to take advantage of the profitable conditions. As more firms enter, the
market or industry supply increases, leading to a decrease in price. This decrease in price reduces the profitability of
individual firms, eventually eroding supernormal profits until firms make only normal profits.
Monopolistic competition is a market structure where, as with perfect competition, there are many firms and freedom
of entry into the industry, but where each firm produces a differentiated product and thus has some control over its
price. As a result, it can raise its price without losing all its customers.
An oligopoly is a market that is dominated by a small number of firms. In contrast to the situation under
monopolistic competition, there are various barriers to the entry of new firms. Also, the firms are interdependent, and
each firm is affected by its rivals’ actions.
A monopoly exists when there is only one firm in the industry. Compared with other market structures, demand
under monopoly will be relatively inelastic at each price. A monopolist will maximise profit where MR= MC.
Hence, the FALSE statement is that, firms under monopolistic competition produce homogeneous products.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONPerfect competition is a market structure characterized by many buyers and sellers engaged in the production and
exchange of homogeneous products. Each firm is so small relative to the whole industry that it has no power to
influence price. Firms are price takers meaning that they accept the prevailing market price. Also, there is complete
freedom of entry into the industry for new firms. In the long run, if typical firms are making supernormal profits,
new firms will be attracted into the industry to take advantage of the profitable conditions. As more firms enter, the
market or industry supply increases, leading to a decrease in price. This decrease in price reduces the profitability of
individual firms, eventually eroding supernormal profits until firms make only normal profits.
Monopolistic competition is a market structure where, as with perfect competition, there are many firms and freedom
of entry into the industry, but where each firm produces a differentiated product and thus has some control over its
price. As a result, it can raise its price without losing all its customers.
An oligopoly is a market that is dominated by a small number of firms. In contrast to the situation under
monopolistic competition, there are various barriers to the entry of new firms. Also, the firms are interdependent, and
each firm is affected by its rivals’ actions.
A monopoly exists when there is only one firm in the industry. Compared with other market structures, demand
under monopoly will be relatively inelastic at each price. A monopolist will maximise profit where MR= MC.
Hence, the FALSE statement is that, firms under monopolistic competition produce homogeneous products. -
Question 2 of 999CB2023166
Question 2
FlagAn economy with a floating exchange rate has a large deficit on the current account of its balance of
payments. Which policy combination would be most likely to reduce this deficit?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWhen a country has current account deficits, it implies the country is importing more than it is exporting to the rest
of the word. Policy combinations should be targeted at reducing imports and encouraging exports. The right answer
is option D. When interest rates are increased, it reduces money demand which leads to a reduction in domestic
demand. This will decrease the demand for imports and improve the current account balance. Also, increasing
income tax rates will decrease domestic demand and hence, the demand for imports.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWhen a country has current account deficits, it implies the country is importing more than it is exporting to the rest
of the word. Policy combinations should be targeted at reducing imports and encouraging exports. The right answer
is option D. When interest rates are increased, it reduces money demand which leads to a reduction in domestic
demand. This will decrease the demand for imports and improve the current account balance. Also, increasing
income tax rates will decrease domestic demand and hence, the demand for imports. -
Question 3 of 999CB2023167
Question 3
FlagVertical product differentiation refers to differences between products which reflect:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONVertical product differentiation is a type of product differentiation that occurs when a firm supplies different products
that have different qualities to the same market, and consumers see the difference in qualities based on their tastes for
the products. Producers employ vertical differentiation because of different costs incurred in producing products with
differing qualities, and as a strategy to charge different prices for their products.
Apple is an example of a company that employs vertical differentiation. This is feasible in the production of different
iPhone models such as the iPhone 14 Mini, iPhone 14 Pro, and iPhone 14 Pro Max, which differ in terms of their
features.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONVertical product differentiation is a type of product differentiation that occurs when a firm supplies different products
that have different qualities to the same market, and consumers see the difference in qualities based on their tastes for
the products. Producers employ vertical differentiation because of different costs incurred in producing products with
differing qualities, and as a strategy to charge different prices for their products.
Apple is an example of a company that employs vertical differentiation. This is feasible in the production of different
iPhone models such as the iPhone 14 Mini, iPhone 14 Pro, and iPhone 14 Pro Max, which differ in terms of their
features. -
Question 4 of 999CB2023168
Question 4
FlagFinancial intermediaries play a crucial role in maintaining a well-functioning and efficient financial
system. The definition below describes the role or service of financial intermediaries. Select the option that best fits
this definition.
“The process whereby banks can spread the risks of lending by having a large number of borrowers.”Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONFinancial intermediaries are the general name for financial institutions (banks, building societies, etc.) that act as a
means of channeling funds from depositors to borrowers. They typically provide five important services/roles:
i. Expert advice, which may include offering an expert opinion on saving and investment activities or information
about other sources of finance.
ii.
0
A
Allocative efficiency, where financial intermediaries offer expertise in how to channel funds into activities that
have higher returns and balance the viability of loans against risks.
iii. Maturity transformation, where financial institutions facilitate the transformation of deposits into loans of longer
maturity.
iv. Risk transformation, which is the process whereby banks can spread the risks of lending by having a large number
of borrowers.
v. Transmission of funds, where money can be transferred from one person or institution to another without having to
rely on cash.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONFinancial intermediaries are the general name for financial institutions (banks, building societies, etc.) that act as a
means of channeling funds from depositors to borrowers. They typically provide five important services/roles:
i. Expert advice, which may include offering an expert opinion on saving and investment activities or information
about other sources of finance.
ii.
0
A
Allocative efficiency, where financial intermediaries offer expertise in how to channel funds into activities that
have higher returns and balance the viability of loans against risks.
iii. Maturity transformation, where financial institutions facilitate the transformation of deposits into loans of longer
maturity.
iv. Risk transformation, which is the process whereby banks can spread the risks of lending by having a large number
of borrowers.
v. Transmission of funds, where money can be transferred from one person or institution to another without having to
rely on cash. -
Question 5 of 999CB2023169
Question 5
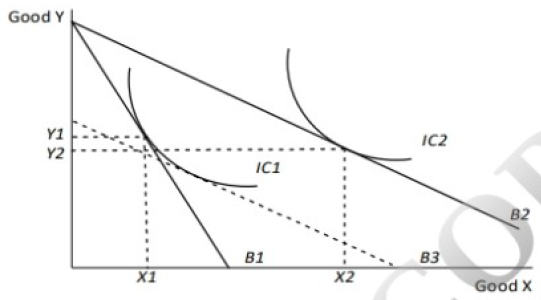
FlagA consumer has 200 rupees of income, which is spent entirely on two goods, Good X and Good Y. Good
X costs 40 rupees per unit and Good Y costs 40 rupees per unit. The relevant marginal utilities (MUs) for the
consumer are:$\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \begin{array}{c}
\text { Good X } \\
\text { Quantity (in units) }
\end{array} & \text { Good X MU } & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Good Y } \\
\text { Quantity (in units) }
\end{array} & \text { Good Y MU } \\
\hline 1 & 100 & 1 & 70 \\
\hline 2 & 80 & 2 & 50 \\
\hline 3 & 50 & 3 & 40 \\
\hline 4 & 25 & 4 & 30 \\
\hline 5 & 10 & 5 & 20 \\
\hline
\end{array}$The optimum combination of units of Good X and Good Y for the consumer to purchase is:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe optimum combination of goods X for Y occurs when the marginal utilities ( MU x / MUy) equal the ratio of the
prices of the two goods (Px /Py). From the question, Px / Py = 40 / 40 = 1. Hence the optimum combination
occurs by purchasing three units of Good X and two units of Good Y, which gives MU x / MUy = 50 / 50 = 1.
Alternatively, the total consumer surplus is given by
Total Consumer Surplus (TCS) = Total Utility- Total Expenditure.
The optimum combination of units of Good X and Good Y for the consumer to purchase is the combination that
gives the highest TCS. From the options, purchasing three units of Good X and two units of Good Y produces
TCS = (100 + 80 + 50) + (70 + 50) – 200 = 150, which is the highest TCS.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe optimum combination of goods X for Y occurs when the marginal utilities ( MU x / MUy) equal the ratio of the
prices of the two goods (Px /Py). From the question, Px / Py = 40 / 40 = 1. Hence the optimum combination
occurs by purchasing three units of Good X and two units of Good Y, which gives MU x / MUy = 50 / 50 = 1.
Alternatively, the total consumer surplus is given by
Total Consumer Surplus (TCS) = Total Utility- Total Expenditure.
The optimum combination of units of Good X and Good Y for the consumer to purchase is the combination that
gives the highest TCS. From the options, purchasing three units of Good X and two units of Good Y produces
TCS = (100 + 80 + 50) + (70 + 50) – 200 = 150, which is the highest TCS. -
Question 6 of 999CB2023171
Question 6
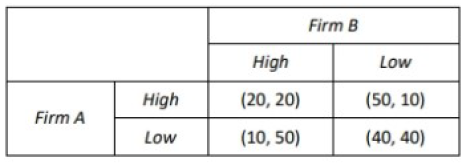
FlagTwo firms operate in a duopoly, but do not collude. Given the profit pay-off matrix of output options to
Firms A and B below, what is the dominant strategy for the firms?
[Note: Profit pay-offs are ‘(profit A, profit B)’, and ‘high’ and ‘low’ refer to the price decision of the firms.]
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIf firm A looks at the pricing decision from firm B’s point of view, it will show that firm B has a dominant strategy. If
firm A charges High, it can see that firm B’s best response is to charge Low (making a profit of 90 rather than 60). If
firm A charges Low, firm B’s best response is also to charge Low (making a profit of 40 rather than 20). Therefore,
firm A can predict with a high level of certainty that firm B will charge Low – its dominant strategy. Firm A’s best
response, therefore, is to charge Low and make a profit of 40 rather than 20. Hence the dominant strategy for the
firms is Firm A-Low; Firm B – Low.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIf firm A looks at the pricing decision from firm B’s point of view, it will show that firm B has a dominant strategy. If
firm A charges High, it can see that firm B’s best response is to charge Low (making a profit of 90 rather than 60). If
firm A charges Low, firm B’s best response is also to charge Low (making a profit of 40 rather than 20). Therefore,
firm A can predict with a high level of certainty that firm B will charge Low – its dominant strategy. Firm A’s best
response, therefore, is to charge Low and make a profit of 40 rather than 20. Hence the dominant strategy for the
firms is Firm A-Low; Firm B – Low. -
Question 7 of 999CB2023172
Question 7
FlagIdentify which one of the following would NOT constitute a demand-side economic policy for reducing
unemployment.Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONEconomic activities can be broadly divided into the supply side and the demand side. The supply side refers to the
level of production or output in an economy, which is determined by resources such as labor, capital, and natural
endowment. The level of supply can also be influenced by factors that affect the availability of these resources, such
as their cost and efficiency. On the other hand, the demand side is typically determined by government spending,
consumption, and private investment. The level of consumption can be influenced by factors such as consumer
preferences, interest rates, and the money supply.
Therefore, policies such as cutting interest rates can increase consumption and private investment, resulting in a
decrease in unemployment and an increase in output. Similarly, when the government implements policies that
increase the money supply or its own spending, the level of economic activity can rise, leading to a decrease in
unemployment.
Privatisation policies involve transferring the ownership of businesses from the government to private citizens and
are generally categorized as supply-side policies. If privatization increases efficiency and leads to an increase in the
production of goods and services, then unemployment can decline. However, this is a supply-side effect, not a
demand-side effect. Therefore, option D is the correct answer.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONEconomic activities can be broadly divided into the supply side and the demand side. The supply side refers to the
level of production or output in an economy, which is determined by resources such as labor, capital, and natural
endowment. The level of supply can also be influenced by factors that affect the availability of these resources, such
as their cost and efficiency. On the other hand, the demand side is typically determined by government spending,
consumption, and private investment. The level of consumption can be influenced by factors such as consumer
preferences, interest rates, and the money supply.
Therefore, policies such as cutting interest rates can increase consumption and private investment, resulting in a
decrease in unemployment and an increase in output. Similarly, when the government implements policies that
increase the money supply or its own spending, the level of economic activity can rise, leading to a decrease in
unemployment.
Privatisation policies involve transferring the ownership of businesses from the government to private citizens and
are generally categorized as supply-side policies. If privatization increases efficiency and leads to an increase in the
production of goods and services, then unemployment can decline. However, this is a supply-side effect, not a
demand-side effect. Therefore, option D is the correct answer. -
Question 8 of 999CB2023173
Question 8
FlagIn Country A, government expenditure is £350 billion, tax revenue is £275 billion, aggregate saving is
£300 billion and aggregate investment is £250 billion. The net exports of Country A are equal to a:Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe national income identity for an open economy can be written in this form
S-l=X-M
Where S – I is the net capital outflow and X – M is the net exports or trade balance.
S is national saving which is a sum of public saving (T-G) and private saving (Y-C-T).
Public saving= 275-350 = -£75 billion.
This implies that National savings= 300-75 = £225 billion.
Now from the identity,225-250 = X-M
X- M = – pounds 25 billion
Net export is a deficit of £25 billion.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe national income identity for an open economy can be written in this form
S-l=X-M
Where S – I is the net capital outflow and X – M is the net exports or trade balance.
S is national saving which is a sum of public saving (T-G) and private saving (Y-C-T).
Public saving= 275-350 = -£75 billion.
This implies that National savings= 300-75 = £225 billion.
Now from the identity,225-250 = X-M
X- M = – pounds 25 billion
Net export is a deficit of £25 billion. -
Question 9 of 999CB2023175
Question 9
FlagIdentify which of the following factors could cause a country’s aggregate demand curve to shift outward
to the right.Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe correct answer is option B. A shift in the aggregate demand curve to the right implies an increase in aggregate
demand. Depreciation in the exchange rate will make exports cheaper and imports more expensive. This improves
the net exports component of GDP and hence causes an increase in aggregate demand. This will cause the aggregate
demand curve to shift to the right. All the other options will cause aggregate demand to decrease.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe correct answer is option B. A shift in the aggregate demand curve to the right implies an increase in aggregate
demand. Depreciation in the exchange rate will make exports cheaper and imports more expensive. This improves
the net exports component of GDP and hence causes an increase in aggregate demand. This will cause the aggregate
demand curve to shift to the right. All the other options will cause aggregate demand to decrease. -
Question 10 of 999CB2023176
Question 10
FlagIn a simple closed economy with no government sector, the consumption function relating consumption
(C) to income (Y) is given by the expression:
C = £80 million + 0. 75Y
Planned investment is constant at £50 million.
Which of the following is TRUE?Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIn a simple closed economy with no government sector, we have:
Y=C+I
where C = consumption function; and I= investment expenditure. Given C = £80million + 0. 75Y and
I = £ 50million, then:
Y = £80million + 0.75Y + I
0.25Y = £80million + £50million
Then, equilibrium income Y = £520million. Therefore, consumption will be
C = £80million + 0.75Y = £80million + 0.75 x £520million = £470million.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIn a simple closed economy with no government sector, we have:
Y=C+I
where C = consumption function; and I= investment expenditure. Given C = £80million + 0. 75Y and
I = £ 50million, then:
Y = £80million + 0.75Y + I
0.25Y = £80million + £50million
Then, equilibrium income Y = £520million. Therefore, consumption will be
C = £80million + 0.75Y = £80million + 0.75 x £520million = £470million. -
Question 11 of 999CB2023177
Question 11
FlagA consumer’s demand curve for Good X is represented by the equation:
Qdx = 50 – 0.2Px
where Q dx is the quantity of Good X demanded and Px is the price of Good X.
A producer’s supply curve for Good X is represented by the equation:
Qsx = 10 + 0.6Px
where Qsx is the quantity of Good X supplied and Px is the price of Good X.
Demand and supply are in equilibrium when:Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONGiven the equations for the supply and demand as:
Qdx = 50 – 0.2Px
Qsx = 10 + 0.6PxWe can find the market equilibrium price by setting the two equations equal to each other, since, in equilibrium, the
quantity supplied (Qsx) equals the quantity demanded (Qdx). Thus:
50 – 0.2Px = 10 + 0.6Px
40 = 0.8Px
which solves for Px = 50.
We can then solve for equilibrium quantity (Qe) by substituting Px = 50 into the demand or supply equations (since Qdx = Qsx). Thus, from the demand equation:
Qe = 50 – 0.2Px = 50 – 0.2(50) = 40
Then demand and supply are in equilibrium when: quantity is 40 and price is 50.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONGiven the equations for the supply and demand as:
Qdx = 50 – 0.2Px
Qsx = 10 + 0.6PxWe can find the market equilibrium price by setting the two equations equal to each other, since, in equilibrium, the
quantity supplied (Qsx) equals the quantity demanded (Qdx). Thus:
50 – 0.2Px = 10 + 0.6Px
40 = 0.8Px
which solves for Px = 50.
We can then solve for equilibrium quantity (Qe) by substituting Px = 50 into the demand or supply equations (since Qdx = Qsx). Thus, from the demand equation:
Qe = 50 – 0.2Px = 50 – 0.2(50) = 40
Then demand and supply are in equilibrium when: quantity is 40 and price is 50. -
Question 12 of 999CB2023179
Question 12
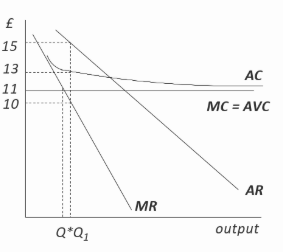
FlagIn the short run, a loss-making firm that seeks to maximise profits will continue to produce if:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONFixed costs have to be paid even if the firm is producing nothing at all, hence we will assume all fixed costs are also
sunk costs. This means that providing the firm is able to cover its variable costs, it is no worse off than it would be if
it temporarily shut down. Therefore, in the short run, a loss making firm that seeks to maximise profits will
continue to produce if: it can charge a price greater than its average variable cost.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONFixed costs have to be paid even if the firm is producing nothing at all, hence we will assume all fixed costs are also
sunk costs. This means that providing the firm is able to cover its variable costs, it is no worse off than it would be if
it temporarily shut down. Therefore, in the short run, a loss making firm that seeks to maximise profits will
continue to produce if: it can charge a price greater than its average variable cost. -
Question 13 of 999CB2023180
Question 13
FlagStructural unemployment is unemployment that:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONStructural unemployment is a type of unemployment that occurs when the skills of workers in certain industries do
not match the available jobs. This type of unemployment is usually caused by changes in the structure of an
economy, such as a change in consumer preferences.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONStructural unemployment is a type of unemployment that occurs when the skills of workers in certain industries do
not match the available jobs. This type of unemployment is usually caused by changes in the structure of an
economy, such as a change in consumer preferences. -
Question 14 of 999CB2023181
Question 14
FlagIf the government imposes a minimum wage that is above the market equilibrium wage, we would expect:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONSuppose the government imposes a minimum wage above the market equilibrium wage. In that case, there will be
an increase in the quantity of labor supplied, which leads to surplus labor. The reason is that more people will be
willing to work (an increase in labor supply) to enjoy the new higher wage.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONSuppose the government imposes a minimum wage above the market equilibrium wage. In that case, there will be
an increase in the quantity of labor supplied, which leads to surplus labor. The reason is that more people will be
willing to work (an increase in labor supply) to enjoy the new higher wage. -
Question 15 of 999CB2023182
Question 15
FlagOne way of reducing the natural rate of unemployment would be to increase:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe natural rate of unemployment is made up of frictional unemployment and structural unemployment. Frictional
unemployment occurs when workers are in transition between jobs. Structural unemployment occurs due to a
mismatch between the skills and qualifications of job seekers and the job opportunities that are available. Policies
targeted at reducing these two types of unemployment will reduce the natural rate of unemployment. Providing
information about job availability will reduce the transition periods between jobs, and hence reduce frictional
unemployment. The correct answer is option C.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe natural rate of unemployment is made up of frictional unemployment and structural unemployment. Frictional
unemployment occurs when workers are in transition between jobs. Structural unemployment occurs due to a
mismatch between the skills and qualifications of job seekers and the job opportunities that are available. Policies
targeted at reducing these two types of unemployment will reduce the natural rate of unemployment. Providing
information about job availability will reduce the transition periods between jobs, and hence reduce frictional
unemployment. The correct answer is option C. -
Question 16 of 999CB2023183
Question 16
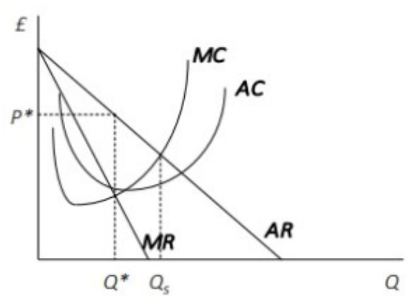
FlagThe socially efficient output for a monopoly is at the point where:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe price is determined in the industry by the intersection of demand and supply. Under perfect competition, the rule
of profit maximization is for each firm to produce the quantity of output where P = MC. The price (P) reflects
demand and as such, is a measure of how much buyers value the good, while the marginal cost (MC) is a measure of
what additional units of output cost society to produce. Following this rule assures allocative efficiency. However, in
the case of the monopoly, at the profit-maximizing level of output, the price is always greater than the marginal cost.
If P > MC, then the marginal benefit to society (as measured by P) is greater than the marginal cost to society of
producing additional units, and a greater quantity should be produced; and yet the the monopolist is deliberately
holding back, so as to keep its profits up.
Hence, the socially efficient output for a monopoly is at the point where: the marginal cost curve cuts the
demand curve.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe price is determined in the industry by the intersection of demand and supply. Under perfect competition, the rule
of profit maximization is for each firm to produce the quantity of output where P = MC. The price (P) reflects
demand and as such, is a measure of how much buyers value the good, while the marginal cost (MC) is a measure of
what additional units of output cost society to produce. Following this rule assures allocative efficiency. However, in
the case of the monopoly, at the profit-maximizing level of output, the price is always greater than the marginal cost.
If P > MC, then the marginal benefit to society (as measured by P) is greater than the marginal cost to society of
producing additional units, and a greater quantity should be produced; and yet the the monopolist is deliberately
holding back, so as to keep its profits up.
Hence, the socially efficient output for a monopoly is at the point where: the marginal cost curve cuts the
demand curve. -
Question 17 of 999CB2023184
Question 17
FlagA profit-maximising monopoly facing a linear demand schedule and having positive marginal costs will
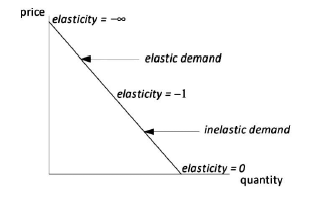
set its price in the region of the demand curve where the absolute price elasticity of demand is:Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONBecause the monopolist is a price maker, prices will always be set in the region where the demand curve is elastic.
When the monopolist starts off on the inelastic part of the demand curve, there is always the possibility that revenues
can be increased by restricting output and charging higher prices. Also, with positive marginal cost, a reduction in
output reduces the total cost of production. This means that for the monopolist, as long as demand is inelastic, the
monopolist will keep reducing output and charging higher prices. Hence the monopolist continues to move up on the
demand curve until he enters the elastic portion of the demand curve. Hence, equilibrium is only possible on the
elastic portion of the demand curve (Elasticity is greater than I).
The right answer is option AIncorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONBecause the monopolist is a price maker, prices will always be set in the region where the demand curve is elastic.
When the monopolist starts off on the inelastic part of the demand curve, there is always the possibility that revenues
can be increased by restricting output and charging higher prices. Also, with positive marginal cost, a reduction in
output reduces the total cost of production. This means that for the monopolist, as long as demand is inelastic, the
monopolist will keep reducing output and charging higher prices. Hence the monopolist continues to move up on the
demand curve until he enters the elastic portion of the demand curve. Hence, equilibrium is only possible on the
elastic portion of the demand curve (Elasticity is greater than I).
The right answer is option A -
Question 18 of 999CB2023185
Question 18
FlagThe introduction of a restrictive monetary policy in an open economy operating with a flexible exchange
rate would most likely lead to:Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA restrictive monetary policy refers to the actions taken by the Fed or the central bank to reduce the money supply in
the economy. One of the primary tools used in restrictive monetary policy is raising interest rates. By increasing the
cost of borrowing (raising interest rates), central banks aim to discourage borrowing and spending, reducing overall
economic demand. In an open economy, an increase in domestic interest rates will lead capital to flow from abroad
to the domestic economy, where investors can earn a higher return on their investments. The inflow of capital from
abroad will lead to an increased demand for domestic currency, resulting in the appreciation of the domestic currency
(or exchange rate appreciation). Therefore, the correct answer is A.
NB: A currency appreciates when its value rises (because of high demand for that currency) relative to other
currencies and depreciates when its value falls (because of low demand for that currency).Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA restrictive monetary policy refers to the actions taken by the Fed or the central bank to reduce the money supply in
the economy. One of the primary tools used in restrictive monetary policy is raising interest rates. By increasing the
cost of borrowing (raising interest rates), central banks aim to discourage borrowing and spending, reducing overall
economic demand. In an open economy, an increase in domestic interest rates will lead capital to flow from abroad
to the domestic economy, where investors can earn a higher return on their investments. The inflow of capital from
abroad will lead to an increased demand for domestic currency, resulting in the appreciation of the domestic currency
(or exchange rate appreciation). Therefore, the correct answer is A.
NB: A currency appreciates when its value rises (because of high demand for that currency) relative to other
currencies and depreciates when its value falls (because of low demand for that currency). -
Question 19 of 999CB2023188
Question 19
FlagThe following data is for a perfectly competitive firm producing Good X in the short run:
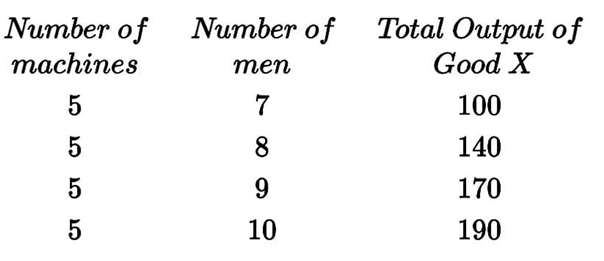
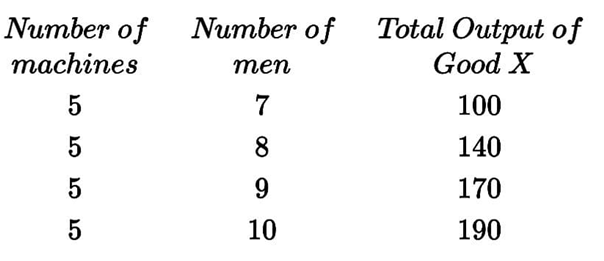
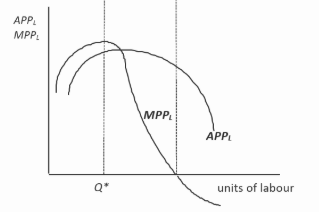
Which of the following statements about the marginal physical product per the table above is correct?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe following data is for a perfectly competitive firm producing Good X in the short run:
$\begin{array}{cccc}
\begin{array}{c}
\text { Number of } \\
\text { machines }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Number of } \\
\text { men }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Total Output of } \\
\text { Good X }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Marginal } \\
\text { Physical Product }
\end{array} \\
5 & 7 & 100 & – \\
5 & 8 & 140 & 40 \\
5 & 9 & 170 & 30 \\
5 & 10 & 190 & 20
\end{array}$Marginal Physical Product = Change in Total Output of Good X from one additional unit of men – ~X.
From the table,
The marginal physical product of the 8th man = 40
The marginal physical product of the 9th man = 30
40>30
Note: Other options are incorrect based on the values in at the table.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe following data is for a perfectly competitive firm producing Good X in the short run:
$\begin{array}{cccc}
\begin{array}{c}
\text { Number of } \\
\text { machines }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Number of } \\
\text { men }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Total Output of } \\
\text { Good X }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Marginal } \\
\text { Physical Product }
\end{array} \\
5 & 7 & 100 & – \\
5 & 8 & 140 & 40 \\
5 & 9 & 170 & 30 \\
5 & 10 & 190 & 20
\end{array}$Marginal Physical Product = Change in Total Output of Good X from one additional unit of men – ~X.
From the table,
The marginal physical product of the 8th man = 40
The marginal physical product of the 9th man = 30
40>30
Note: Other options are incorrect based on the values in at the table. -
Question 20 of 999CB2023189
Question 20
FlagThe global financial crisis of 2007-2009 not only led to a worldwide recession but also a
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONDuring the financial crisis, many European countries experienced significant economic downturns and faced
challenges in managing their public debt. The crisis revealed weaknesses in the financial systems of several
European countries, particularly those with high levels of government debt and fiscal imbalances. These countries
struggled to meet their debt obligations, leading to concerns about their solvency and the stability of the eurozone.
0
A
The sovereign debt crisis in Europe was characterized by escalating borrowing costs for affected countries, declining
investor confidence, and the need for financial assistance from international organizations such as the International
Monetary Fund and the European Central Banlc Several countries, including Greece, Ireland, Portugal, and later
Spain and Italy, faced severe economic and fiscal challenges, which required substantial bailout packages and
austerity measures to address the crisis.
Therefore, the most accurate response is C.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONDuring the financial crisis, many European countries experienced significant economic downturns and faced
challenges in managing their public debt. The crisis revealed weaknesses in the financial systems of several
European countries, particularly those with high levels of government debt and fiscal imbalances. These countries
struggled to meet their debt obligations, leading to concerns about their solvency and the stability of the eurozone.
0
A
The sovereign debt crisis in Europe was characterized by escalating borrowing costs for affected countries, declining
investor confidence, and the need for financial assistance from international organizations such as the International
Monetary Fund and the European Central Banlc Several countries, including Greece, Ireland, Portugal, and later
Spain and Italy, faced severe economic and fiscal challenges, which required substantial bailout packages and
austerity measures to address the crisis.
Therefore, the most accurate response is C. -
Question 21 of 999CB2023190
Question 21
FlagWhich of the following will result in an improvement in the domestic country’s terms of trade?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONTerms of trade refer to the price index of exports divided by the price index of imports and then expressed as
a percentage. This means that the terms of trade will be 100 in the base year. Thus, if the average price of exports
relative to the average price of imports has risen by 20 percent since the base year, the terms of trade will now be
120. If the terms of trade rise (export prices rising relative to import prices), they are said to have ‘improved’, since
fewer exports now have to be sold to purchase any given quantity of imports. Changes in the terms of trade are
caused by changes in the demand for and supply of imports and exports and by changes in the exchange rate.
Hence, an improvement in the domestic country’s terms of trade will result from a rise in the average price of
exports relative to the average price of imports.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONTerms of trade refer to the price index of exports divided by the price index of imports and then expressed as
a percentage. This means that the terms of trade will be 100 in the base year. Thus, if the average price of exports
relative to the average price of imports has risen by 20 percent since the base year, the terms of trade will now be
120. If the terms of trade rise (export prices rising relative to import prices), they are said to have ‘improved’, since
fewer exports now have to be sold to purchase any given quantity of imports. Changes in the terms of trade are
caused by changes in the demand for and supply of imports and exports and by changes in the exchange rate.
Hence, an improvement in the domestic country’s terms of trade will result from a rise in the average price of
exports relative to the average price of imports. -
Question 22 of 999CB2023191
Question 22
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a gain that countries may experience as a result of engaging in
international trade?Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe following are gains that countries may experience as a result of engaging in
international trade:
Decreasing costs – as countries specialise in a particular good they tend to experience economies of scale ( falling
unit costs), this can particularly arise within small countries where the local market is limited and presents no natural
opportunity for falling costs via expansion.
Differences in demand – one country may prefer a particular good to another and find that the demand for their
product is higher in another country. By engaging in trade, demand within both countries can be fulfilled.
Increased competition – imports from overseas can potentially create more
competition within a market and stimulate efficiency within the home market (if such competition were previously
lacking). This could lead to greater R&D and new
product development.
Trade as an engine of growth – increased demand elsewhere leading to a rise in
exports can help to stimulate growth within a country.
Non-economic advantages – other benefits may include political and social/cultural advantages as a result of
exposure to other firms across the world and differing ways of producing goods/services.
One argument for restricting international trade is to prevent Dumping. A country
may engage in dumping by subsidising its exports. The result is that prices may no longer reflect comparative costs .
The correct answer is: A country may engage in dumping by subsidising its exports.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe following are gains that countries may experience as a result of engaging in
international trade:
Decreasing costs – as countries specialise in a particular good they tend to experience economies of scale ( falling
unit costs), this can particularly arise within small countries where the local market is limited and presents no natural
opportunity for falling costs via expansion.
Differences in demand – one country may prefer a particular good to another and find that the demand for their
product is higher in another country. By engaging in trade, demand within both countries can be fulfilled.
Increased competition – imports from overseas can potentially create more
competition within a market and stimulate efficiency within the home market (if such competition were previously
lacking). This could lead to greater R&D and new
product development.
Trade as an engine of growth – increased demand elsewhere leading to a rise in
exports can help to stimulate growth within a country.
Non-economic advantages – other benefits may include political and social/cultural advantages as a result of
exposure to other firms across the world and differing ways of producing goods/services.
One argument for restricting international trade is to prevent Dumping. A country
may engage in dumping by subsidising its exports. The result is that prices may no longer reflect comparative costs .
The correct answer is: A country may engage in dumping by subsidising its exports. -
Question 23 of 999CB2023192
Question 23
FlagWhich one of the following will NOT happen following a devaluation of the domestic currency on the
foreign exchange market?Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONDevaluation refers to fall in the value of a domestic currency relative to other country’s currencies. Devaluation
usually causes exports to be cheaper and imports to be more expensive for the domestic country. Since exports
become cheaper relative to other countries, the domestic country’s export volume will rise and import volume will
fall.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONDevaluation refers to fall in the value of a domestic currency relative to other country’s currencies. Devaluation
usually causes exports to be cheaper and imports to be more expensive for the domestic country. Since exports
become cheaper relative to other countries, the domestic country’s export volume will rise and import volume will
fall. -
Question 24 of 999CB2023193
Question 24
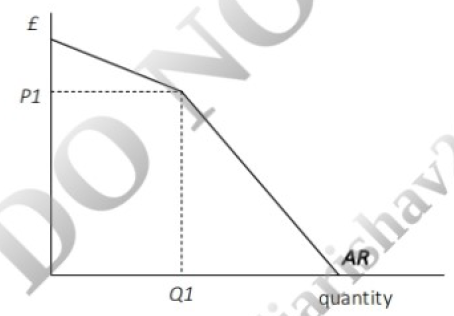
FlagAll the following are economic costs of imposing an import tariff, EXCEPT?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
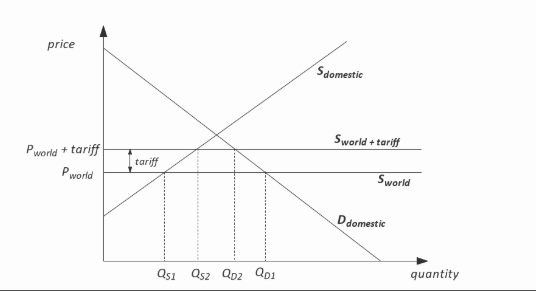
EXPLANATION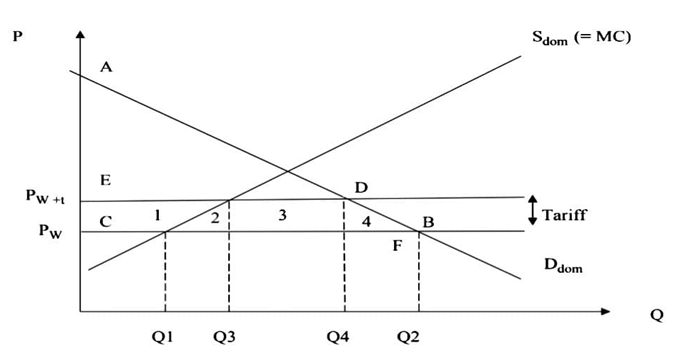
The cost of imposing a tariff is that consumers pay more as illustrated by the higher world price which now includes
the tariff and the resulting fall in consumer surplus. Before the tariff, consumer surplus is represented by the area
ABC. It falls to area ADE which represents a fall ofEDBC. The price rises from Pw to Pw+t. Domestic production
which was previously Q 1 increases to Q3 but consumption falls to Q4. Imports also fall to the difference between
Q4-Q3. Firms receive a higher price and therefore generate higher profits, represented by area 1. The government
receives income from the tariff represented by area 3. There are deadweight losses to society that are not recouped
anywhere and these losses are represented by areas 2 and 4 .
Therefore, the correct answer is: Rise in consumer surplus.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATION
The cost of imposing a tariff is that consumers pay more as illustrated by the higher world price which now includes
the tariff and the resulting fall in consumer surplus. Before the tariff, consumer surplus is represented by the area
ABC. It falls to area ADE which represents a fall ofEDBC. The price rises from Pw to Pw+t. Domestic production
which was previously Q 1 increases to Q3 but consumption falls to Q4. Imports also fall to the difference between
Q4-Q3. Firms receive a higher price and therefore generate higher profits, represented by area 1. The government
receives income from the tariff represented by area 3. There are deadweight losses to society that are not recouped
anywhere and these losses are represented by areas 2 and 4 .
Therefore, the correct answer is: Rise in consumer surplus. -
Question 25 of 999CB2023194
Question 25
FlagThe following transactions take place in a simple closed economy. A company producing Good X sells its
output for £2 million. In producing Good X, the company buys raw materials for £800,000, uses £200,000 worth
of electricity, and has labour costs of £ 400, 000. What is the contribution of the company to the country’s Gross
Domestic Product (GDP)?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONTo find the contribution of the company to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), we use the value-added
approach. That is,
GDP using the value-added method= Value of sales – Cost of intermediate goods
= £2,000,000 – (£800,000 + £200,000 + £400,000) = £600,000Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONTo find the contribution of the company to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), we use the value-added
approach. That is,
GDP using the value-added method= Value of sales – Cost of intermediate goods
= £2,000,000 – (£800,000 + £200,000 + £400,000) = £600,000 -
Question 26 of 999CB2023196
Question 26
FlagThe marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, the rate of income tax is 25% of all income, and government
expenditure is £50 million. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONConsider a simple Keynesian model: GDP= C + G with T = 0.25GDP such that C = 0.B(GDP- 0.25GDP)
where C = aggregate consumption function; G = government expenditure; T = taxes and GDP= income.
This implies that,
GDP= 0.B(GDP- 0.25GDP) + G
GDP= 0.6GDP + G
GDP-0.6GDP = G
0.4GDP = G
GDP= 2.5G
: . The government expenditure multiplier is 2.5, i.e., an increase in government expenditure of £10 million will
increase the national income by £25 million.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONConsider a simple Keynesian model: GDP= C + G with T = 0.25GDP such that C = 0.B(GDP- 0.25GDP)
where C = aggregate consumption function; G = government expenditure; T = taxes and GDP= income.
This implies that,
GDP= 0.B(GDP- 0.25GDP) + G
GDP= 0.6GDP + G
GDP-0.6GDP = G
0.4GDP = G
GDP= 2.5G
: . The government expenditure multiplier is 2.5, i.e., an increase in government expenditure of £10 million will
increase the national income by £25 million. -
Question 27 of 999CB2023197
Question 27
FlagWhich of the following is most likely to lead to a rise in aggregate demand?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAggregate Demand (AD) is normally referred to as aggregate expenditure (E). Aggregate expenditure consists of the
consumption of domestically produced goods Cd plus the three injections (J): investment in the domestic economy
(I), government purchases in the domestic economy (G) and expenditure from abroad on the country’s exports (X).
AD=E=Cd+J
An increase in the income tax rate will reduce the disposable income for people to spend on consumption; therefore,
aggregate demand reduces
A decrease in government expenditure reduces injections therefore, aggregate demand reduces
A decrease in the value of exports reduces reduces injections therefore, aggregate demand reduces
A decrease in the rate of interest means people will be encouraged to borrow to invest in production at a lower
cost which increases aggregate demand.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAggregate Demand (AD) is normally referred to as aggregate expenditure (E). Aggregate expenditure consists of the
consumption of domestically produced goods Cd plus the three injections (J): investment in the domestic economy
(I), government purchases in the domestic economy (G) and expenditure from abroad on the country’s exports (X).
AD=E=Cd+J
An increase in the income tax rate will reduce the disposable income for people to spend on consumption; therefore,
aggregate demand reduces
A decrease in government expenditure reduces injections therefore, aggregate demand reduces
A decrease in the value of exports reduces reduces injections therefore, aggregate demand reduces
A decrease in the rate of interest means people will be encouraged to borrow to invest in production at a lower
cost which increases aggregate demand. -
Question 28 of 999CB2023198
Question 28
FlagThe conventional Phillips Curve illustrates the inverse relationship between:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
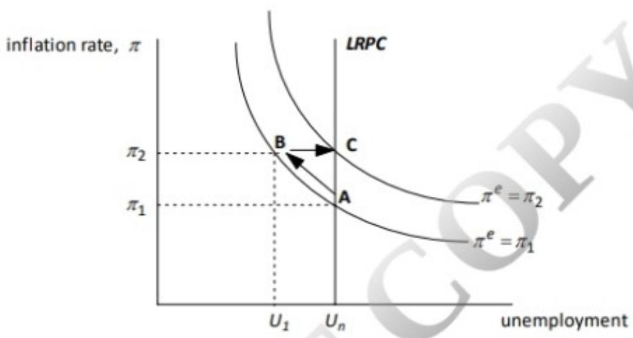
EXPLANATIONThe conventional Phillips Curve demonstrates an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation,
suggesting that lower unemployment rates are associated with higher inflation, and vice versa. Therefore, the
correct answer is option CIncorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe conventional Phillips Curve demonstrates an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation,
suggesting that lower unemployment rates are associated with higher inflation, and vice versa. Therefore, the
correct answer is option C -
Question 29 of 999CB2023199
Question 29
FlagAssume that the public holds 50% of deposits as cash, and banks hold 50% of deposits as reserves. If the
broad money supply is 300 million rupees, what is the value of the narrow money supply?Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe currency-deposit ratio is the proportion of deposits held as cash= 0.5
The reserve-deposit ratio is the proportion of deposits held by the banks for reserves = 0.5
Hence, the money multiplier (m) is computed as:
$\frac {0.5+1}{0.5+0.5} = 1.5$The narrow money supply (B) is the sum of currency held by the public and the bank reserves.
The broad money supply (M) depends on the narrow money supply in the following way:
M=m x BThis implies that the narrow money supply can be expressed as:
$B = \frac {M}{m} = \frac {300}{1.5} = 200 \text {rupees}$Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe currency-deposit ratio is the proportion of deposits held as cash= 0.5
The reserve-deposit ratio is the proportion of deposits held by the banks for reserves = 0.5
Hence, the money multiplier (m) is computed as:
$\frac {0.5+1}{0.5+0.5} = 1.5$The narrow money supply (B) is the sum of currency held by the public and the bank reserves.
The broad money supply (M) depends on the narrow money supply in the following way:
M=m x BThis implies that the narrow money supply can be expressed as:
$B = \frac {M}{m} = \frac {300}{1.5} = 200 \text {rupees}$ -
Question 30 of 999CB2023200
Question 30
FlagWhich of the following is a potential source of cost-push inflation?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONCost-push inflation is caused by factors that increase the cost of production. The right answer is Option A. A
depreciation of the domestic currency will increase the cost of imported raw materials. This increases the cost of
production which is passed on to the consumer in the form of higher prices.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONCost-push inflation is caused by factors that increase the cost of production. The right answer is Option A. A
depreciation of the domestic currency will increase the cost of imported raw materials. This increases the cost of
production which is passed on to the consumer in the form of higher prices. -
Question 31 of 999CB2023202
Question 31
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a ‘crowding out’ effect resulting from a fiscal expansion?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONCrowding out: Where increased public expenditure diverts money or resources away from the private sector. If the
government relies on pure fiscal policy. It will have to borrow the money from the non-bank private sector. It will
thus be competing with the private sector for finance and will have to offer higher interest rates. Which may
discourage firms from investing and individuals from buying on credit. Hence, there will be a fall in investment due
to the associated rise in interest rates.
Also, because the high-interest rates discourage consumers from buying on credit, then it will lead to a fall in
consumer demand. In addition, fear of higher future taxes due to a high budget deficit as a result of an increase in
government expenditure discourages consumer demand.
Further, the increase in interest rates, as a result of an increase in government expenditure, will lead to an inflow of
finance from abroad, which in tum will lead to an appreciation of the exchange rate. The higher exchange rate will
reduce the level of exports and increase the level of imports.
Therefore, reduced import expenditure due to increased government demand for domestically produced
goods is NOT a ‘crowding out’ effect resulting from a fiscal expansion.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONCrowding out: Where increased public expenditure diverts money or resources away from the private sector. If the
government relies on pure fiscal policy. It will have to borrow the money from the non-bank private sector. It will
thus be competing with the private sector for finance and will have to offer higher interest rates. Which may
discourage firms from investing and individuals from buying on credit. Hence, there will be a fall in investment due
to the associated rise in interest rates.
Also, because the high-interest rates discourage consumers from buying on credit, then it will lead to a fall in
consumer demand. In addition, fear of higher future taxes due to a high budget deficit as a result of an increase in
government expenditure discourages consumer demand.
Further, the increase in interest rates, as a result of an increase in government expenditure, will lead to an inflow of
finance from abroad, which in tum will lead to an appreciation of the exchange rate. The higher exchange rate will
reduce the level of exports and increase the level of imports.
Therefore, reduced import expenditure due to increased government demand for domestically produced
goods is NOT a ‘crowding out’ effect resulting from a fiscal expansion. -
Question 32 of 999CB2023203
Question 32
FlagWhich of the following are the correct responses for the missing words (i) and (ii) in the following
statement?
Automatic stabilisers act to (i) ____ government expenditures and (ii) ____ government revenues during a
recessionary period.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAutomatic stabilizers are mechanisms that are built into government budgets to adjust government expenditures and
taxation in response to different states of the economy. When the economy is in a recession, the government needs to
stimulate demand, hence, automatic stabilizers will increase government expenditure and decrease taxation or
government revenues.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAutomatic stabilizers are mechanisms that are built into government budgets to adjust government expenditures and
taxation in response to different states of the economy. When the economy is in a recession, the government needs to
stimulate demand, hence, automatic stabilizers will increase government expenditure and decrease taxation or
government revenues. -
Question 33 of 999CB2023204
Question 33
FlagIf the money supply decreases due to a contractionary open market operation by the central bank then the
price of treasury bills will:Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONIf the central bank conducts a contractionary open market operation (OMO), it means government sells securities,
such as treasury bills, to the public in exchange for cash. This policy, therefore, causes a decline in supply of money
in the economy. Given that the demand for money remains the same, fall in money supply will give rise to shortage
of credit in the financial market, thereby leading to a rise in interest rate.
On the other hand, increase in sales of government securities would cause the supply for securites to increase in the
market, based on the theory of demand and supply, the price of treasury bills will fall. The fall in price of treasury
bills and a rise in interest rate due to fiscal contractionary policy is plausible because the relationship between price
of securities and interest rate is negative.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONIf the central bank conducts a contractionary open market operation (OMO), it means government sells securities,
such as treasury bills, to the public in exchange for cash. This policy, therefore, causes a decline in supply of money
in the economy. Given that the demand for money remains the same, fall in money supply will give rise to shortage
of credit in the financial market, thereby leading to a rise in interest rate.
On the other hand, increase in sales of government securities would cause the supply for securites to increase in the
market, based on the theory of demand and supply, the price of treasury bills will fall. The fall in price of treasury
bills and a rise in interest rate due to fiscal contractionary policy is plausible because the relationship between price
of securities and interest rate is negative. -
Question 34 of 999CB2023205
Question 34
FlagThe Chief Operating Officer (COO) of a monopoly firm knows that the firm’s profits are higher when the
demand curve is less elastic. Given that the firm operates under the profit-maximizing rule-where marginal revenue
equals marginal cost, both at 14 rupees-and that the price elasticity of demand is -2 (indicating elastic demand),
what is the profit-maximizing price?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAs with firms in other market structures, a monopolist will maximise profit where MR= MC= 14 rupees. The less
elastic the demand at the output level where MC equals MR, the larger the gap between average revenue (AR) and
MR. Consequently, the price will be higher relative to MR. The relationship between price, MR ( or MC), and the
price elasticity of demand (PeD) can be expressed using the following formula:
$P = \frac {MR}{1+(1/P_{E_{D}})}
Plugging in the values we get:
$P = \frac {14}{1-(1/2)} = 28 \text {rupees}$Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAs with firms in other market structures, a monopolist will maximise profit where MR= MC= 14 rupees. The less
elastic the demand at the output level where MC equals MR, the larger the gap between average revenue (AR) and
MR. Consequently, the price will be higher relative to MR. The relationship between price, MR ( or MC), and the
price elasticity of demand (PeD) can be expressed using the following formula:
$P = \frac {MR}{1+(1/P_{E_{D}})}
Plugging in the values we get:
$P = \frac {14}{1-(1/2)} = 28 \text {rupees}$ -
Question 35 of 999CB2023206
Question 35
FlagThe Delhi Transport Corporation (DTC) offers eight main types of concessional passes at different prices,
including student passes, senior citizen passes (for those above 60 years), and disabled person passes. What type of
price discrimination does this represent?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThere are three types of price discrimination: first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree. First-degree price
discrimination occurs when the seller charges each consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay for each
unit of the product. Second-degree price discrimination involves offering consumers a variety of pricing options for
the same or similar product. Third-degree price discrimination entails categorizing consumers into different groups
based on observable characteristics that provide information about their willingness to pay. The firm then charges
different prices to consumers in different groups, while keeping the price uniform within each group.
DTC’s practice of offering bus passes based on observable characteristics is a clear example of third-degree price
discrimination.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThere are three types of price discrimination: first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree. First-degree price
discrimination occurs when the seller charges each consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay for each
unit of the product. Second-degree price discrimination involves offering consumers a variety of pricing options for
the same or similar product. Third-degree price discrimination entails categorizing consumers into different groups
based on observable characteristics that provide information about their willingness to pay. The firm then charges
different prices to consumers in different groups, while keeping the price uniform within each group.
DTC’s practice of offering bus passes based on observable characteristics is a clear example of third-degree price
discrimination. -
Question 36 of 999CB2023207
Question 36
FlagWhich of the below option is incorrect with regards to the monopolistic competition and monopoly.
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA monopoly market structure is a market that is characterized by a sole seller of a product without any competition.
In a monopolistic competition, there are several firms each producing slightly differentiated products. There are
barriers to entry in a monopoly but not in the case of a monopolistic competition. Because of this, firms in
monopolistic competition can only make normal profits in the long run while a monopoly can make supernormal
profits in the long run. Also, because of the presence of competition, the demand curve for a firm under monopolistic
competition is relatively more price elastic compared to the case of a monopoly. Notice that all options except option
A states the difference between a monopolistic competition and a monopoly.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA monopoly market structure is a market that is characterized by a sole seller of a product without any competition.
In a monopolistic competition, there are several firms each producing slightly differentiated products. There are
barriers to entry in a monopoly but not in the case of a monopolistic competition. Because of this, firms in
monopolistic competition can only make normal profits in the long run while a monopoly can make supernormal
profits in the long run. Also, because of the presence of competition, the demand curve for a firm under monopolistic
competition is relatively more price elastic compared to the case of a monopoly. Notice that all options except option
A states the difference between a monopolistic competition and a monopoly. -
Question 37 of 999CB2023210
Question 37
FlagWhich of the following factor( s) does not contribute to economies of scale? Select all that apply.
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONEconomies of scale refers to how costs change in proportion to the output produced. A firm experiences economies
of scale if costs per unit of output fall as the scale of production increases, i.e., the proportionate increase in total
costs is lower than the proportionate increase in output. Other things being equal, this means that it will be producing
at a lower unit cost. There are several reasons why firms are likely to experience economies of scale.
Specialisation and division of labour: In large-scale plants, workers can often do simple, repetitive jobs. With this
specialisation and division of labour, less training is needed; workers can become highly efficient in their particular
job, especially with long production runs; there is less time lost in workers switching from one operation to another;
and supervision is easier.
Indivisibilities: Some inputs are of a minimum size: they are indivisible. The most obvious example is machinery.
Take the case of a combine harvester. A small-scale farmer could not make full use of one. They only become
economical to use, therefore, on farms above a certain size.
Spreading overheads: Some expenditures are economic only when the firm is large: for example, research and
development – only a large firm can afford to set up a research laboratory. This is another example of indivisibilities,
only this time at the level of the firm rather than the plant. The greater the firm’s output, the more these overhead
costs are spread.
Therefore, Dilution of ownership does NOT contribute to economies of scale.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONEconomies of scale refers to how costs change in proportion to the output produced. A firm experiences economies
of scale if costs per unit of output fall as the scale of production increases, i.e., the proportionate increase in total
costs is lower than the proportionate increase in output. Other things being equal, this means that it will be producing
at a lower unit cost. There are several reasons why firms are likely to experience economies of scale.
Specialisation and division of labour: In large-scale plants, workers can often do simple, repetitive jobs. With this
specialisation and division of labour, less training is needed; workers can become highly efficient in their particular
job, especially with long production runs; there is less time lost in workers switching from one operation to another;
and supervision is easier.
Indivisibilities: Some inputs are of a minimum size: they are indivisible. The most obvious example is machinery.
Take the case of a combine harvester. A small-scale farmer could not make full use of one. They only become
economical to use, therefore, on farms above a certain size.
Spreading overheads: Some expenditures are economic only when the firm is large: for example, research and
development – only a large firm can afford to set up a research laboratory. This is another example of indivisibilities,
only this time at the level of the firm rather than the plant. The greater the firm’s output, the more these overhead
costs are spread.
Therefore, Dilution of ownership does NOT contribute to economies of scale. -
Question 38 of 999CB2023211
Question 38
FlagIf an economy moves from producing 10 units of Good X and 5 units of Good Y to producing 8 units of
Good X and 6 units of Good Y, the opportunity cost of the 6th unit of Good Y is:Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe opportunity cost of producing the 6th unit of good Y is how much of good X that has to be given up in order to
produce the 6th unit of good Y. Initially, the economy was producing 10 units of Good X and 5 units of good Y. To
increase the production of good Y to 6 units, the economy had to give up 2 units of good X. This means that the
opportunity cost of producing the 6th unit of Good Y is 2 units of good X.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe opportunity cost of producing the 6th unit of good Y is how much of good X that has to be given up in order to
produce the 6th unit of good Y. Initially, the economy was producing 10 units of Good X and 5 units of good Y. To
increase the production of good Y to 6 units, the economy had to give up 2 units of good X. This means that the
opportunity cost of producing the 6th unit of Good Y is 2 units of good X. -
Question 39 of 999CB2023212
Question 39
FlagIf Good Y has a cross elasticity of demand with respect to Good X calculated using the average method of -1 and initially 100 units of Good Y are demanded when Good X costs 20 pence. Then a rise in the price of Good X
to 25 pence will result in a new level of demand for Good Y of _____ units.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe average method for computing the cross-price elasticity of demand is stated below:
$
\epsilon_{Y X}=\frac{Q_2^Y-Q_1^Y}{Q_2^Y+Q_1^Y} \times \frac{P_2^X+P_1^X}{P_2^X-P_1^X}
$Where $\epsilon_{Y X}=-1, Q_1^Y=100, P_1^X=20$ cents, $P_2^X=25$ cents. You are required to find the new level of demand for $\operatorname{good} \mathrm{Y}\left(Q_2^Y\right)$.
$
\begin{gathered}
-1=\frac{Q_2^Y-100}{Q_2^Y+100} \times \frac{25+20}{25-20} \\
-1=\left(\frac{Q_2^Y-100}{Q_2^Y+100}\right) \times 9 \\
-Q_2^Y-100=9 Q_2^Y-900 \\
-10 Q_2^Y=-800 \\
Q_2^Y=\frac{-800}{-10}=80 \text { units }
\end{gathered}
$Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe average method for computing the cross-price elasticity of demand is stated below:
$
\epsilon_{Y X}=\frac{Q_2^Y-Q_1^Y}{Q_2^Y+Q_1^Y} \times \frac{P_2^X+P_1^X}{P_2^X-P_1^X}
$Where $\epsilon_{Y X}=-1, Q_1^Y=100, P_1^X=20$ cents, $P_2^X=25$ cents. You are required to find the new level of demand for $\operatorname{good} \mathrm{Y}\left(Q_2^Y\right)$.
$
\begin{gathered}
-1=\frac{Q_2^Y-100}{Q_2^Y+100} \times \frac{25+20}{25-20} \\
-1=\left(\frac{Q_2^Y-100}{Q_2^Y+100}\right) \times 9 \\
-Q_2^Y-100=9 Q_2^Y-900 \\
-10 Q_2^Y=-800 \\
Q_2^Y=\frac{-800}{-10}=80 \text { units }
\end{gathered}
$ -
Question 40 of 999CB2023214
Question 40
FlagThe demand equation for Good X is Q d = 15 – 0.5P and the supply equation for Good X is
Q s
= 3 + 2P, where P is the price. When the price is £6 there will be a ______ of Good X and the price will ______.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONDemand: Q d = 15 – 0.5P
Supply: Qs = 3 + 2P
Substitute P into the equations for supply and demand.
Demand: Qd = 15 – 0.5(6) = 12
Supply: Qs = 3 + 2(6) – 15When the price is £6, the supply of Good X is greater than the demand for Good X ( Q s> Q d)- This means there is
surplus in the market, which will result in a fall in price.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONDemand: Q d = 15 – 0.5P
Supply: Qs = 3 + 2P
Substitute P into the equations for supply and demand.
Demand: Qd = 15 – 0.5(6) = 12
Supply: Qs = 3 + 2(6) – 15When the price is £6, the supply of Good X is greater than the demand for Good X ( Q s> Q d)- This means there is
surplus in the market, which will result in a fall in price. -
Question 41 of 999CB2023215
Question 41
FlagFor a normal good, the combined effect of an increase in the cost of production and a rise in consumer income is ________ in the equilibrium price. The effect on equilibrium quantity is __________.
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the cost of production will cause a decrease in supply, shifting the supply curve to the left. This
causes the price to rise and the quantity to fall. Also, a rise in consumer incomes will increase the demand for the
commodity since it is a normal good. This will cause the demand curve to shift to the right, resulting in an
increase in the price and quantity. When both changes are combined, we see that the equilibrium price will
increase unambiguously, but the equilibrium quantity change is indeterminate. This is because the increase in
the cost of production causes quantity to decline while the increase in consumer incomes causes the quantity to
increase. The resulting effect will depend on the relative size of the shifts.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the cost of production will cause a decrease in supply, shifting the supply curve to the left. This
causes the price to rise and the quantity to fall. Also, a rise in consumer incomes will increase the demand for the
commodity since it is a normal good. This will cause the demand curve to shift to the right, resulting in an
increase in the price and quantity. When both changes are combined, we see that the equilibrium price will
increase unambiguously, but the equilibrium quantity change is indeterminate. This is because the increase in
the cost of production causes quantity to decline while the increase in consumer incomes causes the quantity to
increase. The resulting effect will depend on the relative size of the shifts. -
Question 42 of 999CB2023219
Question 42
FlagA student studying a one-year Master’s degree in Actuarial Science has course fees of £12,000 and could
otherwise have had a job paying an after-tax income of £20,000. The cost of her accommodation is £7,000 whether
she studies or works and the food bill is £3,000 whether she studies or works. What is the opportunity cost of
studying for the Masters degree?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONOpportunity cost: The cost of any activity measured in terms of the best alternative forgone.
A
With this question, the opportunity cost is the sacrifice entailed by going for one year Masters’s degree in Actuarial
Science rather than taking the job. The correct list of opportunity costs of the one-year Masters degree would include
income from the job of £20,000 and tuition fees of £12,000. Hence the total is £32,000.
Note that we do not include the cost of her accommodation and the food bill because the student will incur that cost
whether she studies or works.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONOpportunity cost: The cost of any activity measured in terms of the best alternative forgone.
A
With this question, the opportunity cost is the sacrifice entailed by going for one year Masters’s degree in Actuarial
Science rather than taking the job. The correct list of opportunity costs of the one-year Masters degree would include
income from the job of £20,000 and tuition fees of £12,000. Hence the total is £32,000.
Note that we do not include the cost of her accommodation and the food bill because the student will incur that cost
whether she studies or works. -
Question 43 of 999CB2023220
Question 43
FlagA situation when firms in an oligopoly agree to limit competition between themselves by such practices as
agreeing on each keeping its market share, price fixing, setting output quota or limiting advertising is known as: __________________________
A situation where oligopolists cooperate without any formal agreement between themselves, formal, informal, or
tacit.____________________
A few firms dominate the industry, but there are variations in the products or services offered by these firms.________________________Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFormal Collusive oligopoly is a situation when firms in an oligopoly agree formally to limit competition between
themselves by such practices as agreeing on each keeping its market share, price fixing, setting output quota or
limiting advertising.
Tacit collusive oligopoly is where oligopolists have no agreement between themselves, formal, informal or tacit.
Imperfect Oligopoly is a type of oligopoly where a few firms dominate the industry, but each firm produces a
slightly differentiated product. This contrasts with the case of a pure oligopoly where there is no product
differentiation.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFormal Collusive oligopoly is a situation when firms in an oligopoly agree formally to limit competition between
themselves by such practices as agreeing on each keeping its market share, price fixing, setting output quota or
limiting advertising.
Tacit collusive oligopoly is where oligopolists have no agreement between themselves, formal, informal or tacit.
Imperfect Oligopoly is a type of oligopoly where a few firms dominate the industry, but each firm produces a
slightly differentiated product. This contrasts with the case of a pure oligopoly where there is no product
differentiation. -
Question 44 of 999CB2023221
Question 44
FlagWhat is the number of units of Good X consumed if the consumption of Good Y rises to 7 units due to a
50% fall in its price?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONNote that the initial budget line is:
5X + l0Y = 100
A 50% fall in the price of Y means the price falls to £5. The new budget line is:
5X +5Y= 100
If 7 units of good Y are consumed, then the units of good X consumed is computed as follows:
5X + 5(7) = 100
5X +35 = 100
5X= 65
X= 13Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONNote that the initial budget line is:
5X + l0Y = 100
A 50% fall in the price of Y means the price falls to £5. The new budget line is:
5X +5Y= 100
If 7 units of good Y are consumed, then the units of good X consumed is computed as follows:
5X + 5(7) = 100
5X +35 = 100
5X= 65
X= 13 -
Question 45 of 999CB2023223
Question 45
FlagYou are given the following data on a simple closed economy:
C = £ 40 million + 0. 75Y d
I= £30 million
G = £50 million
T = 0.2Y
where C is consumer expenditure, Y is national income, Yd is disposable national income, G is government
expenditure on goods and services, I is investment expenditure and T is total taxes.
Which of the following statements is true?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONIn a simple closed economy, the equilibrium level of national income Y is given by:
Y = C +I+ G = £40 million + 0.75Yd + £30 million + £50 million
Given total taxes T, the disposable income Yd= Y – T = Y – 0.2Y = Y(l – 0.2). Then we have
Y = 40 + 0. 75(1 – 0.2)Y + 30 + 50 ===} Y = 120 + 0.6Y
Then:
$Y = \frac {120}{0.4} =$ pounds 300 million.
The equilibrium national income is £300 million
The fiscal deficit is computed as T – G = 0.2(300) – 50 so there is a fiscal surplus of +£10 millionIncorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONIn a simple closed economy, the equilibrium level of national income Y is given by:
Y = C +I+ G = £40 million + 0.75Yd + £30 million + £50 million
Given total taxes T, the disposable income Yd= Y – T = Y – 0.2Y = Y(l – 0.2). Then we have
Y = 40 + 0. 75(1 – 0.2)Y + 30 + 50 ===} Y = 120 + 0.6Y
Then:
$Y = \frac {120}{0.4} =$ pounds 300 million.
The equilibrium national income is £300 million
The fiscal deficit is computed as T – G = 0.2(300) – 50 so there is a fiscal surplus of +£10 million -
Question 46 of 999CB2023226
Question 46
FlagThe main targets of competition policy are the following, EXCEPT?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe main targets of competition policy are the following:
Abuse of power by existing oligopolies and monopolies – monopoly policy. Monopoly policy is designed to
prevent existing oligopolies and monopolies from exploiting their dominant powers. Firms could, if they had the
opportunity, use this dominant power to raise prices and restrict output so as to make supernormal profits and also try
and increase barriers to entry. Therefore, the aim of monopoly policy is to ensure that there are caps on the prices
such firms can charge and to ensure, where possible, that there is competition between firms and sufficient consumer
choice and also sufficient investment for the future.
One target is to stop oligopolistic collusion: restrictive practices. The aim is to prevent firms colluding to exploit
their joint power to make larger profits. This could take numerous forms such as raising prices and/or restricting
output, dividing up the market or agreeing not to encroach on other firms’ established markets. The target is to
reduce the possibility of restrictive practices by use of fines, prosecution if collusion is found and other legal
remedies.
Limiting growth of power through mergers and acquisitions – merger policy. The aim of merger policy is to
provide oversight of mergers. This will involve analysing the potential gains and losses that may occur as a result of
a merger. As such, the impact on consumers, the public interest and the broader economy could be considered. The
policy may aim to limit the adverse impacts of the merger or prevent it going ahead .Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe main targets of competition policy are the following:
Abuse of power by existing oligopolies and monopolies – monopoly policy. Monopoly policy is designed to
prevent existing oligopolies and monopolies from exploiting their dominant powers. Firms could, if they had the
opportunity, use this dominant power to raise prices and restrict output so as to make supernormal profits and also try
and increase barriers to entry. Therefore, the aim of monopoly policy is to ensure that there are caps on the prices
such firms can charge and to ensure, where possible, that there is competition between firms and sufficient consumer
choice and also sufficient investment for the future.
One target is to stop oligopolistic collusion: restrictive practices. The aim is to prevent firms colluding to exploit
their joint power to make larger profits. This could take numerous forms such as raising prices and/or restricting
output, dividing up the market or agreeing not to encroach on other firms’ established markets. The target is to
reduce the possibility of restrictive practices by use of fines, prosecution if collusion is found and other legal
remedies.
Limiting growth of power through mergers and acquisitions – merger policy. The aim of merger policy is to
provide oversight of mergers. This will involve analysing the potential gains and losses that may occur as a result of
a merger. As such, the impact on consumers, the public interest and the broader economy could be considered. The
policy may aim to limit the adverse impacts of the merger or prevent it going ahead . -
Question 47 of 999CB2023460
Question 47
FlagThe minimum wage is currently above the equilibrium wage. Which one of the following policies will
increase voluntary unemployment?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWith the minimum wage currently above the equilibrium wage, a reduction in unemployment benefit, better
dissemination of information about job vacancies, and an extension of job retraining programmes will lead to a
reduction in unemployment as the supply of labor will increase. However, reducing the minimum wage will have the
opposite effect, where the unemployed are not desperate to get a job encouraging voluntary unemploymentIncorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWith the minimum wage currently above the equilibrium wage, a reduction in unemployment benefit, better
dissemination of information about job vacancies, and an extension of job retraining programmes will lead to a
reduction in unemployment as the supply of labor will increase. However, reducing the minimum wage will have the
opposite effect, where the unemployed are not desperate to get a job encouraging voluntary unemployment -
Question 48 of 999CB2023461
Question 48
FlagSuppose a firm’s production costs are given by MC= 10 + 20Q. The firm’s production process
generates chemical waste that is dumped in a nearby river. The surrounding community bears the additional costs to
those borne by the firm. The marginal external cost associated with Qth unit of production is given by 6Q. What is
the marginal social cost of producing the 10th unit?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe scenario above presents a case of a negative externality in production. Here, the marginal social cost (MSC) of
chemical production equals the marginal private costs (MPG) plus the marginal external costs (MECp)- That is,
MSC=MPC+MECp.
The marginal private cost is: MPG= 10 + 20(10) = 210.
The external cost of the 10th unit is: MECp = 6(10) = 60.
⇒ The marginal social cost of producing the 10th unit is: MSC= 210 + 60 = 270.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe scenario above presents a case of a negative externality in production. Here, the marginal social cost (MSC) of
chemical production equals the marginal private costs (MPG) plus the marginal external costs (MECp)- That is,
MSC=MPC+MECp.
The marginal private cost is: MPG= 10 + 20(10) = 210.
The external cost of the 10th unit is: MECp = 6(10) = 60.
⇒ The marginal social cost of producing the 10th unit is: MSC= 210 + 60 = 270. -
Question 49 of 999CB2023462
Question 49
FlagFor a simple closed economy with no government taxes:
C= 10+0.75Y
I= 20
G=40
where C is consumption expenditure, Y is national income, G is government
expenditure on goods and services, I is investment expenditure ( all measured in
millions of pounds).
Calculate the new level of national income if government expenditure is increased by £ 10 million.Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIn a simple closed economy, the equilibrium level of national income Y is given by:
Y = C +I+ G = £10 million + 0.75Y + £20 million + £40 million
Then we have
Y= 70+0.75Y
Then:
$Y = \frac {70}{0.25}$ = pounds 280 million
The multiplier k is given by:
$k = \frac {1}{1-\text {mpc}} =\frac {1}{1-0.75} = 4,$
where mpc is marginal propensity to consume. Then, if government expenditure is increased by £ 10 million, the
national income will increase by:
4 x £ 10 million = £ 40 million
Hence the new level of national income= £40 million +£280 million =£320 million.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIn a simple closed economy, the equilibrium level of national income Y is given by:
Y = C +I+ G = £10 million + 0.75Y + £20 million + £40 million
Then we have
Y= 70+0.75Y
Then:
$Y = \frac {70}{0.25}$ = pounds 280 million
The multiplier k is given by:
$k = \frac {1}{1-\text {mpc}} =\frac {1}{1-0.75} = 4,$
where mpc is marginal propensity to consume. Then, if government expenditure is increased by £ 10 million, the
national income will increase by:
4 x £ 10 million = £ 40 million
Hence the new level of national income= £40 million +£280 million =£320 million. -
Question 50 of 999CB2023463
Question 50
FlagWhich of the following is a potential challenge for businesses resulting from a policy of tax cuts?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA potential drawback or challenge for businesses resulting from a policy of tax cuts is the potential reduction in
government spending on public infrastructure projects. Tax cuts can lead to lower government revenues, which may
result in reduced funding for public investments in areas such as transportation, education, and healthcare. This
reduction in public spending can have indirect consequences for businesses, such as limited infrastructure
development, decreased public services, and potential constraints on economic growth.
Options B, C, and D represent other potential challenges or impacts that businesses may face due to tax cuts, but they
are generally considered less directly related to the policy itself.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA potential drawback or challenge for businesses resulting from a policy of tax cuts is the potential reduction in
government spending on public infrastructure projects. Tax cuts can lead to lower government revenues, which may
result in reduced funding for public investments in areas such as transportation, education, and healthcare. This
reduction in public spending can have indirect consequences for businesses, such as limited infrastructure
development, decreased public services, and potential constraints on economic growth.
Options B, C, and D represent other potential challenges or impacts that businesses may face due to tax cuts, but they
are generally considered less directly related to the policy itself. -
Question 51 of 999CB2023464
Question 51
FlagAssertion (Statement 1): Suppose the cost of production increases and consumer income rises. In that case, the combined effect on an inferior good’s equilibrium price and quantity is indeterminate on price, but quantity will fall.
Reason (Statement 2): Given the commodity is an inferior good, the demand rises as the consumer incomes rise. This shifts the demand curve to the left. Increases in the cost of production shift the supply curve to the left.Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe equilibrium price is the price where demand equals supply. Also, an inferior good is a good whose demand falls
as people’s incomes rise. A rise in consumer income shifts the demand curve to the left for an inferior good. Further,
the higher the costs of production, the less profit will be made at any price. As costs rise, firms will cut back on
production, probably switching to alternative products whose costs have not risen so much. This shifts the supply
curve to the left.
Hence, the combined effect of an increase in the cost of production and a rise in consumer income on the
equilibrium price and quantity of an inferior good is that the effect on price is indeterminate, but quantity will
fall. The correct answer is option C.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe equilibrium price is the price where demand equals supply. Also, an inferior good is a good whose demand falls
as people’s incomes rise. A rise in consumer income shifts the demand curve to the left for an inferior good. Further,
the higher the costs of production, the less profit will be made at any price. As costs rise, firms will cut back on
production, probably switching to alternative products whose costs have not risen so much. This shifts the supply
curve to the left.
Hence, the combined effect of an increase in the cost of production and a rise in consumer income on the
equilibrium price and quantity of an inferior good is that the effect on price is indeterminate, but quantity will
fall. The correct answer is option C. -
Question 52 of 999CB2023465
Question 52
FlagConsider the following options A to E. Each option relates to an individual firm operating under a certain
market structure in the short run.
Which of the options indicate that the firm could increase its output and increase its profits?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe most straightforward way to approach this question is to recall the profit-maximising rule, which states that the
level of output produced when MC=MR maximizes profit. In other words, as long as MR exceeds MC, profit can be
increased by increasing production ( output). Option E best represents this and thus options B, D and E are not
chosen.
For option A, MC= 25 >MR= 10, so profit could be increased, but by cutting back on production.
Therefore, the option that indicates that the firm could increase its output and increase its profits is E.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe most straightforward way to approach this question is to recall the profit-maximising rule, which states that the
level of output produced when MC=MR maximizes profit. In other words, as long as MR exceeds MC, profit can be
increased by increasing production ( output). Option E best represents this and thus options B, D and E are not
chosen.
For option A, MC= 25 >MR= 10, so profit could be increased, but by cutting back on production.
Therefore, the option that indicates that the firm could increase its output and increase its profits is E. -
Question 53 of 999CB2023466
Question 53
FlagAs of 2023, India has the largest population in the world, totaling 1,438,069,596. Use the labor force
indicators shown in the table below to calculate India’s unemployment rate for 2023.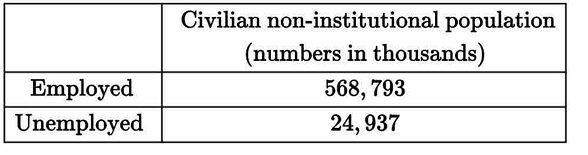 Correct
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe unemployment rate is the percent of the labor force who are currently unemployed but are available for work
and have been actively seeking work for the previous four weeks.
Labor force: This is the total number of those who are either employed or unemployed (Unemployed + Employed).
Unemployment rate: This is the number of unemployed divided by the labor force, expressed as a percent.
From the question,16 million are employed, and 2 million are unemployed, the unemployment rate would be:
$\frac {\text {Unemployed}}{\text {Labor force}} \times 100 = \frac {24937}{24937+568793} \times 100 = 4.2 \%$Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe unemployment rate is the percent of the labor force who are currently unemployed but are available for work
and have been actively seeking work for the previous four weeks.
Labor force: This is the total number of those who are either employed or unemployed (Unemployed + Employed).
Unemployment rate: This is the number of unemployed divided by the labor force, expressed as a percent.
From the question,16 million are employed, and 2 million are unemployed, the unemployment rate would be:
$\frac {\text {Unemployed}}{\text {Labor force}} \times 100 = \frac {24937}{24937+568793} \times 100 = 4.2 \%$ -
Question 54 of 999CB2023467
Question 54
FlagIn an economy, investment spending is £240 billion, savings are £160 billion, government spending is £80
billion, imports are £120 billion and tax is £80 billion.
What is the value of exports in this economy?Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe national income identity for an open economy can be written in this form:
S-I=X-M
Where S – I is the net capital outflow and X – M is the net exports or trade balance.
Sis national saving which is a sum of public saving (T – G) and private saving (Y – C – T).
Public saving = 80 – 80 = £0 billion.
This implies that National savings= 160 + 0 = £160 billion.
Now from the identity,
160 – 240 = X – M
X – M = -80 billion pounds
Given M = £120 billion => M = £40 billion.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe national income identity for an open economy can be written in this form:
S-I=X-M
Where S – I is the net capital outflow and X – M is the net exports or trade balance.
Sis national saving which is a sum of public saving (T – G) and private saving (Y – C – T).
Public saving = 80 – 80 = £0 billion.
This implies that National savings= 160 + 0 = £160 billion.
Now from the identity,
160 – 240 = X – M
X – M = -80 billion pounds
Given M = £120 billion => M = £40 billion. -
Question 55 of 999CB2023468
Question 55
FlagIn the aggregate demand and aggregate supply framework, which of the following summarizes the short
run and long-run impact of a monetary expansion?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIn the short run, an expansionary monetary policy will cause an increase in the money supply, thereby lowering
short-term interest rates, which leads to increasing aggregate demand. An increase in aggregate demand is
represented by a rightward shift of the aggregate demand. The increase in aggregate demand will push up the price
level and level of real income in the short run. In the long run, the rise in the aggregate price level will mean that
workers will seek to get wage increments which will shift the aggregate supply curve to the left, somewhat reducing
the increase in the real level of real output, possibly even back to its original level.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIn the short run, an expansionary monetary policy will cause an increase in the money supply, thereby lowering
short-term interest rates, which leads to increasing aggregate demand. An increase in aggregate demand is
represented by a rightward shift of the aggregate demand. The increase in aggregate demand will push up the price
level and level of real income in the short run. In the long run, the rise in the aggregate price level will mean that
workers will seek to get wage increments which will shift the aggregate supply curve to the left, somewhat reducing
the increase in the real level of real output, possibly even back to its original level. -
Question 56 of 999CB2023469
Question 56
FlagIn his second run for President of the United States, former President Donald Trump plans to implement tariffs as part of his economic policy. Consider a simplified scenario where the world consists of two countries engaged in trade: the United States and India. Based on the statement provided on the left and the reason given on the right, select the option below that is most accurate.
Statement 1: If the United States imposes import tariffs on certain goods from India, the Indian Rupee will appreciate.
Statement 2: American consumers will likely decrease their purchases of goods from India if a tariff is imposed on these goods. As a result, there will be a reduced demand for the Rupee, leading to a decrease in the supply of US dollars in exchange for Rupees.Is Statement 2 a valid explanation for Statement 1?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONIf the United States imposes import tariffs, American consumers will likely decrease their purchases of goods from
India. As a result, there will be a reduced demand for the Rupee, leading to a decrease in the supply of US dollars in
exchange for rupees–a leftward shift of the supply curve for US dollars. This, in turn, will cause the US dollar to
appreciate, i.e., the Rupee will decpreciate.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONIf the United States imposes import tariffs, American consumers will likely decrease their purchases of goods from
India. As a result, there will be a reduced demand for the Rupee, leading to a decrease in the supply of US dollars in
exchange for rupees–a leftward shift of the supply curve for US dollars. This, in turn, will cause the US dollar to
appreciate, i.e., the Rupee will decpreciate. -
Question 57 of 999CB2023470
Question 57
FlagThe direct impact of open market operations, where the central bank purchases government securities, is
to:Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWhen the central bank purchases government securities from commercial banks, this transaction expands their cash
reserves, which they can now use to create additional loans. Since the monetary base is the sum of cash (notes and
coins) in circulation and bank reserves, an open market purchase also increases the monetary base.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWhen the central bank purchases government securities from commercial banks, this transaction expands their cash
reserves, which they can now use to create additional loans. Since the monetary base is the sum of cash (notes and
coins) in circulation and bank reserves, an open market purchase also increases the monetary base. -
Question 58 of 999CB2023471
Question 58
FlagIn a simple economy, assume that banks have just one type of liability, deposits, and two types of assets,
balances with the central bank, and advances to customers. Assume that banks choose to operate a 25% liquidity
ratio and receive extra cash deposits of £10 million. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONLet’s carefully consider each of the options given:
– Option A: Firstly, we need to calculate the bank deposits multiplier, which measures the extent to which bank deposits expand in relation to the additional liquidity introduced into the banks. In other words, it is the reciprocal of the liquidity ratio ( $l$ ), which is $25 \%$. So,
Bank deposits multiplier $=\frac{1}{l}=\frac{1}{0.25}=4 \rightarrow$ Option A is False.
– Option B: The total increase in the money supply resulting from an additional deposit of $£ 10$ million is determined by multiplying the bank deposits multiplier by the initial deposit. That is, the total increase in the money supply is $£ 40$ million (4* $£ 10$ million) $\rightarrow$ Option B is False.
– Option C: Given an initial additional deposit of $£ 10$ million and a liquidity requirement of 0.25 (implying a minimum balance of $£ 2.5$ billion with the central bank), the remaining $75 \%$ ( $£ 7.5$ billion) is available as surplus funds for banks to lend to customers. If all of this surplus liquidity is used for advances to customers, the process of credit creation would expand loans to customers by $£ 30$ billion ( $£ 2.5$ billion * 4) $\rightarrow$ Option C is also false.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONLet’s carefully consider each of the options given:
– Option A: Firstly, we need to calculate the bank deposits multiplier, which measures the extent to which bank deposits expand in relation to the additional liquidity introduced into the banks. In other words, it is the reciprocal of the liquidity ratio ( $l$ ), which is $25 \%$. So,
Bank deposits multiplier $=\frac{1}{l}=\frac{1}{0.25}=4 \rightarrow$ Option A is False.
– Option B: The total increase in the money supply resulting from an additional deposit of $£ 10$ million is determined by multiplying the bank deposits multiplier by the initial deposit. That is, the total increase in the money supply is $£ 40$ million (4* $£ 10$ million) $\rightarrow$ Option B is False.
– Option C: Given an initial additional deposit of $£ 10$ million and a liquidity requirement of 0.25 (implying a minimum balance of $£ 2.5$ billion with the central bank), the remaining $75 \%$ ( $£ 7.5$ billion) is available as surplus funds for banks to lend to customers. If all of this surplus liquidity is used for advances to customers, the process of credit creation would expand loans to customers by $£ 30$ billion ( $£ 2.5$ billion * 4) $\rightarrow$ Option C is also false. -
Question 59 of 999CB2023472
Question 59
FlagIf a household’s income increases from £20,000 to £25,000 and, as a result, consumption increases from
£17,000 to £21,000, what is the household’s marginal propensity to save?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe marginal propensity to consume,
$
\text { MPC }=\frac{\text { Change in Consumption }}{\text { Change in Disposable Income }}=\frac{£ 21,000-£ 17,000}{£ 25,000-£ 20,000}=0.8
$Since a household’s only two options are to spend income or to save it, MPC + MPS $=1,1-$ MPC $=$ MPS, then MPS $=0.2$.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe marginal propensity to consume,
$
\text { MPC }=\frac{\text { Change in Consumption }}{\text { Change in Disposable Income }}=\frac{£ 21,000-£ 17,000}{£ 25,000-£ 20,000}=0.8
$Since a household’s only two options are to spend income or to save it, MPC + MPS $=1,1-$ MPC $=$ MPS, then MPS $=0.2$.
-
Question 60 of 999CB2023473
Question 60
FlagDuring an economic boom, the government fiscal position is likely to:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONDuring economic boom or expansion, the citizens who are able and willing to work find jobs and earn income. By
implication, the welfare of the average working population improves and lesser government intervention on the
ecomomy would be needed. Additionally, the government’s budget improves because it is able to balance its budget
and reduce debts.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONDuring economic boom or expansion, the citizens who are able and willing to work find jobs and earn income. By
implication, the welfare of the average working population improves and lesser government intervention on the
ecomomy would be needed. Additionally, the government’s budget improves because it is able to balance its budget
and reduce debts. -
Question 61 of 999CB2023474
Question 61
FlagWhich of the following would constitute a supply side economic policy for raising employment?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONFactors affecting the supply side of the economy contribute to expansion in production of outputs in the economy.
These factors include natural endowments, increases in labour force, and government policies that cause people to
work and invest. Therefore, reducing social security benefits by the government will cause people to increase the
number of work hours and/or increase labour supply in order to make up for the fall in income received from the
government.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONFactors affecting the supply side of the economy contribute to expansion in production of outputs in the economy.
These factors include natural endowments, increases in labour force, and government policies that cause people to
work and invest. Therefore, reducing social security benefits by the government will cause people to increase the
number of work hours and/or increase labour supply in order to make up for the fall in income received from the
government. -
Question 62 of 999CB2023475
Question 62
FlagAs a result of a change in economic policy, interest rates and consumption rise but investment falls. The
new policy is most likely to have been:Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe question prompt contains interest rates and two components of aggregate demand: consumption and investment
spending. This suggests we can approach this question using the AS-AD framework and the liquidity preference
model. For consumption to rise, all else constant, the policy must have been a fiscal stimulus, implying that the
aggregate demand shifted rightward such that real GDP increases relative to its potential output level. It could not
have been an expansionary monetary policy, as investments would rise due to the lower opportunity cost of the
spending.
From the liquidity preference model, an increase in the level of real output will shift the money demand curve to the
right since households and firms will demand a larger quantity of money to facilitate purchases at any given interest
rate. All else equal, a rightward shift of the MD curve results in a rise in the rate of interest. The higher rate of
interest would lower investment demand.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe question prompt contains interest rates and two components of aggregate demand: consumption and investment
spending. This suggests we can approach this question using the AS-AD framework and the liquidity preference
model. For consumption to rise, all else constant, the policy must have been a fiscal stimulus, implying that the
aggregate demand shifted rightward such that real GDP increases relative to its potential output level. It could not
have been an expansionary monetary policy, as investments would rise due to the lower opportunity cost of the
spending.
From the liquidity preference model, an increase in the level of real output will shift the money demand curve to the
right since households and firms will demand a larger quantity of money to facilitate purchases at any given interest
rate. All else equal, a rightward shift of the MD curve results in a rise in the rate of interest. The higher rate of
interest would lower investment demand. -
Question 63 of 999CB2023476
Question 63
FlagWhich of the following is a supply-side economic policy aimed at promoting economic growth?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONSupply-side policies are policies designed to increase the quantity and/or productivity of the inputs used in
production. These policies attempt to influence aggregate supply directly rather than through aggregate demand, and
if effective, will increase potential output. We can evaluate each option to check for the correct answer.
l. increases in social security benefits designed to increase expenditures of unemployed workers ➔ This a type of
government spending (transfer payments to households), which will impact aggregate demand through
consumption.
2. measures designed to increase trade union powers so that real wage rises can increase expenditures of employed
workers ➔ This option is misleading since supply-side policies are usually designed to reduce the monopoly
power of trade unions so as to encourage greater flexibility in both wages and working practices and to allow
labour markets to clear.
3. increases in tariffs designed to increase production of domestic goods ➔ This type of tariff is a trade barrier that
will increase net exports, thus affecting aggregate demand.
4. reduction in corporate taxation ➔ This increases incentives for firms to take risks and develop new products
and new techniques, thus increasing aggregate supply and long-run growth.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONSupply-side policies are policies designed to increase the quantity and/or productivity of the inputs used in
production. These policies attempt to influence aggregate supply directly rather than through aggregate demand, and
if effective, will increase potential output. We can evaluate each option to check for the correct answer.
l. increases in social security benefits designed to increase expenditures of unemployed workers ➔ This a type of
government spending (transfer payments to households), which will impact aggregate demand through
consumption.
2. measures designed to increase trade union powers so that real wage rises can increase expenditures of employed
workers ➔ This option is misleading since supply-side policies are usually designed to reduce the monopoly
power of trade unions so as to encourage greater flexibility in both wages and working practices and to allow
labour markets to clear.
3. increases in tariffs designed to increase production of domestic goods ➔ This type of tariff is a trade barrier that
will increase net exports, thus affecting aggregate demand.
4. reduction in corporate taxation ➔ This increases incentives for firms to take risks and develop new products
and new techniques, thus increasing aggregate supply and long-run growth. -
Question 64 of 999CB2023477
Question 64
FlagIn general, increased investment in capital goods will lead to:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCapital goods are the assets used by businesses in the course of producing their products and services, such as
buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles, and tools. By investing in new equipment or technology, companies can
improve their efficiency, thus lower costs and increasing output. Hence investment leads to increased future capital
goods.
However, increased investment in capital goods reduces consumption in the short-term as there is generally a
trade-off between consumption and investing in capital goods.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCapital goods are the assets used by businesses in the course of producing their products and services, such as
buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles, and tools. By investing in new equipment or technology, companies can
improve their efficiency, thus lower costs and increasing output. Hence investment leads to increased future capital
goods.
However, increased investment in capital goods reduces consumption in the short-term as there is generally a
trade-off between consumption and investing in capital goods. -
Question 65 of 999CB2023478
Question 65
FlagIdentify the statement that is NOT correct regarding the Austrian school of thought.
Economists of the Austrian school:
(i) Emphasize individual subjective preferences.
(ii) Focus on market forces determining prices.
(iii) Believe in a centrally planned economic system.Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe Austrian school of thought emphasizes that the value of a product is in the utility it provides a consumer. This
makes the value of a product completely subjective and depends solely on its ability to satisfy wants. This makes the
concept of marginal utility a central part of the thinking of Austrian economics. Proponents of this school of thought
are generally in support of a laissez-faire economy, hence market forces are key in driving the prices of goods and
services. Proponents of this school are very critical of centrally planned economies.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe Austrian school of thought emphasizes that the value of a product is in the utility it provides a consumer. This
makes the value of a product completely subjective and depends solely on its ability to satisfy wants. This makes the
concept of marginal utility a central part of the thinking of Austrian economics. Proponents of this school of thought
are generally in support of a laissez-faire economy, hence market forces are key in driving the prices of goods and
services. Proponents of this school are very critical of centrally planned economies. -
Question 66 of 999CB2023479
Question 66
FlagWhich of the following statements defines moral hazard in relation to insurance?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONMoral hard is a situation where one party is more likely to take risks because it does not have to bear the full
consequences of those actions. In insurance, a moral hazard occurs when a policyholder acts in ways that make the
insured even more likely to occur.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONMoral hard is a situation where one party is more likely to take risks because it does not have to bear the full
consequences of those actions. In insurance, a moral hazard occurs when a policyholder acts in ways that make the
insured even more likely to occur. -
Question 67 of 999CB2023480
Question 67
FlagA firm producing carpets has an average variable cost of production of 420 rupees, and a marginal cost of
production of 500 rupees and operates in a perfectly competitive market. A decrease in the demand for carpets that
reduces the price from 600 to 400 rupees will mean that in the short run, the firm will:Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONUnder a perfectly competitive industry, whether the firm is prepared to continue making a loss in the short run or
whether it will close down immediately depends on whether it can cover its variable costs – assuming all fixed costs
are also sunk costs.
With the information provided, the price (400) has been reduced to a point below the average variable cost
(420). Thus, the firm will shut down in the short run.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONUnder a perfectly competitive industry, whether the firm is prepared to continue making a loss in the short run or
whether it will close down immediately depends on whether it can cover its variable costs – assuming all fixed costs
are also sunk costs.
With the information provided, the price (400) has been reduced to a point below the average variable cost
(420). Thus, the firm will shut down in the short run. -
Question 68 of 999CB2023531
Question 68
FlagWhat do economists mean by opportunity cost?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONRecall that the opportunity cost of something is what you have to give up in order to get it. It is often measured in terms of the value of the best alternative foregone.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONRecall that the opportunity cost of something is what you have to give up in order to get it. It is often measured in terms of the value of the best alternative foregone.
-
Question 69 of 999CB2023532
Question 69
FlagPoints to the right of the production possibility curve show combinations of goods:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe production possibility curve shows all the possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce in a specified time period assuming that all resources are fully employed and working to maximum efficiency. It therefore shows the limits to production; only combinations on or inside the frontier curve can be produced. Consequently, combinations of goods on the outside of the curve are unattainable.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe production possibility curve shows all the possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce in a specified time period assuming that all resources are fully employed and working to maximum efficiency. It therefore shows the limits to production; only combinations on or inside the frontier curve can be produced. Consequently, combinations of goods on the outside of the curve are unattainable.
-
Question 70 of 999CB2023533
Question 70
FlagThe marginal revenue curve for a monopoly is:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe marginal revenue curve is the revenue that is realised as quantity of a good sold increases by one unit.
On the other hand, the demand curve (price line) is the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of
that good.
Generally, the demand curve facing a monopolist slopes downward because the quantity demanded increases as the
price of the good decreases. More so, marginal revenue also slopes downwards, but it is below the price because for
monopolist to sell additional units of commodity, the price for additional unit of the product must decrease. This
causes the total revenue to increase at a declining rate.
As a result, the marginal revenue generated from selling an additional unit of a good will be less than the price at
each level of output produced.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe marginal revenue curve is the revenue that is realised as quantity of a good sold increases by one unit.
On the other hand, the demand curve (price line) is the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of
that good.
Generally, the demand curve facing a monopolist slopes downward because the quantity demanded increases as the
price of the good decreases. More so, marginal revenue also slopes downwards, but it is below the price because for
monopolist to sell additional units of commodity, the price for additional unit of the product must decrease. This
causes the total revenue to increase at a declining rate.
As a result, the marginal revenue generated from selling an additional unit of a good will be less than the price at
each level of output produced. -
Question 71 of 999CB2023534
Question 71
FlagA firm’s decision to reduce its expenditure on advertising is most likely to have the following impact on its
demand curve:Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONA reduction in advertising expenditure will reduce the level of public awareness of the product. This will reduce the
demand for the product and cause the demand curve to shift to the left. Also, the low advertisement will reduce the
number of consumers that will develop loyalty to the product. Hence, consumers will be more willing to substitute
other products for the product in question. This implies that the demand curve will be more elastic. The correct
answer is option C.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONA reduction in advertising expenditure will reduce the level of public awareness of the product. This will reduce the
demand for the product and cause the demand curve to shift to the left. Also, the low advertisement will reduce the
number of consumers that will develop loyalty to the product. Hence, consumers will be more willing to substitute
other products for the product in question. This implies that the demand curve will be more elastic. The correct
answer is option C. -
Question 72 of 999CB2023535
Question 72
FlagAssume that Sunshine sunflower spread, a well-known brand, launched a successful heart-health
campaign, with the slogan “It lowers cholesterol”. What is the likely effect of this advertising campaign on the
demand for Sunshine sunflower spread?Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONAdvertising campaigns generally have two main objectives: (i) to shift the product’s demand curve to the right and
(ii) to make it less price elastic. If successful, these campaigns increase people’s awareness of the product, which
increases the market for the good and the demand curve shifts to the right. Additionally, effective advertising can
enhance consumers’ desire for the product, making them more willing to pay a higher price for each unit purchased.
Advertising can impact the elasticity of demand by fostering greater brand loyalty. By emphasizing the product’s
superiority and positioning competitors’ brands as inferior or lacking comparable alternatives, advertising can create
a perception that no other product can compete. As a result, the firm can potentially raise its price without
experiencing a significant decline in sales, i.e., demand becomes less elastic. This is because consumers are
convinced that there are no close substitutes available, reducing the substitution effect.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONAdvertising campaigns generally have two main objectives: (i) to shift the product’s demand curve to the right and
(ii) to make it less price elastic. If successful, these campaigns increase people’s awareness of the product, which
increases the market for the good and the demand curve shifts to the right. Additionally, effective advertising can
enhance consumers’ desire for the product, making them more willing to pay a higher price for each unit purchased.
Advertising can impact the elasticity of demand by fostering greater brand loyalty. By emphasizing the product’s
superiority and positioning competitors’ brands as inferior or lacking comparable alternatives, advertising can create
a perception that no other product can compete. As a result, the firm can potentially raise its price without
experiencing a significant decline in sales, i.e., demand becomes less elastic. This is because consumers are
convinced that there are no close substitutes available, reducing the substitution effect. -
Question 73 of 999CB2023536
Question 73
FlagA firm operates in two markets, Market 1 and Market 2, and price discriminates when profit maximising.
In such circumstances, its marginal revenue in Market 1 is equal to the:Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIn market 1 the profit-maximising firm should produce where MR1 =MC. In market 2 the profit-maximising firm
should produce where MR2 =MC.Then, when profit maximising, marginal revenue in Market 1 is equal to
the marginal revenue in Market 2.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIn market 1 the profit-maximising firm should produce where MR1 =MC. In market 2 the profit-maximising firm
should produce where MR2 =MC.Then, when profit maximising, marginal revenue in Market 1 is equal to
the marginal revenue in Market 2. -
Question 74 of 999CB2023537
Question 74
FlagIn a free-market economy, allocation decisions are made by:the government and suppliers only.
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONA free-market economy is one in which there is no government intervention. Instead, all allocation decisions are made by the interaction of demand and supply, driven by consumers (aiming to maximise their utility) and suppliers (aiming to maximise their profits).
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONA free-market economy is one in which there is no government intervention. Instead, all allocation decisions are made by the interaction of demand and supply, driven by consumers (aiming to maximise their utility) and suppliers (aiming to maximise their profits).
-
Question 75 of 999CB2023538
Question 75
FlagThe kinked demand curve model of an oligopoly is based upon the assumption that:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONOne of the major characteristics of an oligopoly is the price war among the firms in the market. The kinked demand
curve model of an oligopoly is based on this price rivalry among the firms, which causes them to react differently to
price increases and decreases. In an oligopoly market, if one firm increases its price, other firms will not, but will
instead maintain their current prices in order to gain a larger market share. On the other hand, if the firm lowers its
price, other firms will also decrease their prices in order to avoid losing market share to the firm that decreases the
price of its product. This behaviour causes the demand curve facing oligopoly firms to be kinked.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONOne of the major characteristics of an oligopoly is the price war among the firms in the market. The kinked demand
curve model of an oligopoly is based on this price rivalry among the firms, which causes them to react differently to
price increases and decreases. In an oligopoly market, if one firm increases its price, other firms will not, but will
instead maintain their current prices in order to gain a larger market share. On the other hand, if the firm lowers its
price, other firms will also decrease their prices in order to avoid losing market share to the firm that decreases the
price of its product. This behaviour causes the demand curve facing oligopoly firms to be kinked. -
Question 76 of 999CB2023539
Question 76
FlagWhich of the following scenarios represents a liquidity risk exposure for a bank’s loan portfolio?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONLiquidity risk refers to the risk that a bank may not be able to meet its short-term funding obligations or have
sufficient cash to honor customer withdrawals. A sudden increase in customer withdrawals can strain the bank’s
liquidity position, potentially leading to a shortage of available cash. This represents a liquidity risk exposure for the
bank.
Options A, B, and D are more related to interest rate risk, market risk, and credit risk, respectively, rather than
liquidity risk.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONLiquidity risk refers to the risk that a bank may not be able to meet its short-term funding obligations or have
sufficient cash to honor customer withdrawals. A sudden increase in customer withdrawals can strain the bank’s
liquidity position, potentially leading to a shortage of available cash. This represents a liquidity risk exposure for the
bank.
Options A, B, and D are more related to interest rate risk, market risk, and credit risk, respectively, rather than
liquidity risk. -
Question 77 of 999CB2023540
Question 77
FlagIf the rate of income tax is cut from 30% to 25% while the marginal propensity to import falls from 20%
to 15%, the effect on the open economy fiscal multiplier will be:Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe size of the multiplier depends on the slope of the Withdrawal (W) function. The slope of the W function is given
by the marginal propensity to withdraw (mpw), $\Delta W /\Delta Y$. The lower the mpw, the bigger will be the rise in national
income: the bigger will be the multiplier.
Since W = S + T + M, where S is net savings, T is net taxes, and M is import spending. Then mpw=mps + mpt +
mpm.
Given, the rate of income tax is cut from 30% to 25% while the marginal propensity to import falls from 20% to
15%, this implies that mpt and mpm reduce, which reduces mpw, then the multiplier will rise.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe size of the multiplier depends on the slope of the Withdrawal (W) function. The slope of the W function is given
by the marginal propensity to withdraw (mpw), $\Delta W /\Delta Y$. The lower the mpw, the bigger will be the rise in national
income: the bigger will be the multiplier.
Since W = S + T + M, where S is net savings, T is net taxes, and M is import spending. Then mpw=mps + mpt +
mpm.
Given, the rate of income tax is cut from 30% to 25% while the marginal propensity to import falls from 20% to
15%, this implies that mpt and mpm reduce, which reduces mpw, then the multiplier will rise. -
Question 78 of 999CB2023541
Question 78
FlagPrices are most volatile when:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONDraw a diagram to prove this to yourself. Prices move a lot when supply and demand curves are both steep, ie relatively inelastic. When both are elastic, quantity would change a lot.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONDraw a diagram to prove this to yourself. Prices move a lot when supply and demand curves are both steep, ie relatively inelastic. When both are elastic, quantity would change a lot.
-
Question 79 of 999CB2023542
Question 79
FlagWhich one of the following is most likely to be the best method of reducing long term structural
unemployment?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONStructural unemployment occurs due to the mismatch between the skills labour posses and the skills demanded in the
labour market. This is usually caused by major shifts in the structure of the economy such as technological
advancements. The best way to reduce long-term structural unemployment is to retrain workers and restructure the
educational system to meet the demands of the market. The right answer is option C.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONStructural unemployment occurs due to the mismatch between the skills labour posses and the skills demanded in the
labour market. This is usually caused by major shifts in the structure of the economy such as technological
advancements. The best way to reduce long-term structural unemployment is to retrain workers and restructure the
educational system to meet the demands of the market. The right answer is option C. -
Question 80 of 999CB2023543
Question 80
FlagThe adoption of an expansionary fiscal policy will result in
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONExpansionary fiscal policy involves an increase in government spending, a decrease in taxes, or a combination of
both. Government spending can be directed towards consumption or investment, or it can provide a stimulus to
citizens.
The formula for aggregate demand is:
AD = C +I+ G + NX
This formula shows that aggregate demand rises when government spending (G) increases. As a result, real output
(Y) also increases, since an increase in government spending usually has a trickle-down effect on consumption and
the purchasing power of citizens.
In addition, if the government cuts taxes for businesses, it reduces their operational costs, which stimulates them to
employ more laborers to produce goods and services.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONExpansionary fiscal policy involves an increase in government spending, a decrease in taxes, or a combination of
both. Government spending can be directed towards consumption or investment, or it can provide a stimulus to
citizens.
The formula for aggregate demand is:
AD = C +I+ G + NX
This formula shows that aggregate demand rises when government spending (G) increases. As a result, real output
(Y) also increases, since an increase in government spending usually has a trickle-down effect on consumption and
the purchasing power of citizens.
In addition, if the government cuts taxes for businesses, it reduces their operational costs, which stimulates them to
employ more laborers to produce goods and services. -
Question 81 of 999CB2023544
Question 81
FlagGood X has an income elasticity of demand of-0.5 and a cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to Good Y of +0.6. Good X is:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONGood X is an inferior good because it has a negative income elasticity of demand, indicating that demand for the good decreases as consumer income increases.
Good X is a substitute for Good Y because it has a positive cross-price elasticity of demand. This indicates that an increase in the price of Good Y will lead to an increase in the demand for Good X , as consumers switch from buying Good Y to buying Good X instead.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONGood X is an inferior good because it has a negative income elasticity of demand, indicating that demand for the good decreases as consumer income increases.
Good X is a substitute for Good Y because it has a positive cross-price elasticity of demand. This indicates that an increase in the price of Good Y will lead to an increase in the demand for Good X , as consumers switch from buying Good Y to buying Good X instead.
-
Question 82 of 999CB2023545
Question 82
FlagA central bank’s use of the “Taylor Rule” attempts to take which of the following two macroeconomic
objectives into account?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONA Taylor rule takes two objectives into account- (1) inflation and (2) either real national income or unemployment – and seeks to get the optimum degree of stability of the two. The degree of importance attached to each of the two objectives can be decided by the government or central bank. The central bank adjusts interest rates when either the rate of inflation diverges from its target or the level of real national income ( or unemployment) diverges from its potential ( or natural) level.
Hence, a central bank’s use of the “Taylor Rule” attempts to take inflation and economic growth into account.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONA Taylor rule takes two objectives into account- (1) inflation and (2) either real national income or unemployment – and seeks to get the optimum degree of stability of the two. The degree of importance attached to each of the two objectives can be decided by the government or central bank. The central bank adjusts interest rates when either the rate of inflation diverges from its target or the level of real national income ( or unemployment) diverges from its potential ( or natural) level.
Hence, a central bank’s use of the “Taylor Rule” attempts to take inflation and economic growth into account. -
Question 83 of 999CB2023546
Question 83
FlagWhich of the following is a potential challenge for businesses resulting from a policy of tax cuts?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA potential drawback or challenge for businesses resulting from a policy of tax cuts is the potential reduction in
government spending on public infrastructure projects. Tax cuts can lead to lower government revenues, which may
result in reduced funding for public investments in areas such as transportation, education, and healthcare. This
reduction in public spending can have indirect consequences for businesses, such as limited infrastructure
development, decreased public services, and potential constraints on economic growth.
Options B, C, and D represent other potential challenges or impacts that businesses may face due to tax cuts, but they
are generally considered less directly related to the policy itself.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA potential drawback or challenge for businesses resulting from a policy of tax cuts is the potential reduction in
government spending on public infrastructure projects. Tax cuts can lead to lower government revenues, which may
result in reduced funding for public investments in areas such as transportation, education, and healthcare. This
reduction in public spending can have indirect consequences for businesses, such as limited infrastructure
development, decreased public services, and potential constraints on economic growth.
Options B, C, and D represent other potential challenges or impacts that businesses may face due to tax cuts, but they
are generally considered less directly related to the policy itself. -
Question 84 of 999CB2023547
Question 84
FlagA consumer has £4.50 to spend on Mars and Twix chocolate bars. Mars chocolate bars cost
90 pence. Twix bars cost 90 pence. The relevant marginal utilities for the consumer are:$\begin{array}{cccc}
\begin{array}{c}
\text { Quantity of } \\
\text { Mars }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Marginal utility } \\
\text { of Mars }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Quantity of } \\
\text { Twix }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Marginal utility } \\
\text { of Twix }
\end{array} \\
1 & 90 & 1 & 50 \\
2 & 60 & 2 & 40 \\
3 & 40 & 3 & 30 \\
4 & 20 & 4 & 20 \\
5 & 10 & 5 & 10
\end{array}$The optimal combination of Mars bars and Twix bars for the consumer to purchase is:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONWe need to add together the marginal utilities of each extra Twix or Mars bar to find out which combination of chocolate bars maximises the consumer’s utility. Because the consumer’s budget is $£ 4.50$ and all chocolate bars cost 90 pence, we know that they can only buy a total of five chocolate bars.
For 3 Mars and 2 Twix bars, the consumer’s total utility is $90+60+40+50+40=280$. Any other combination gives a lower level of utility.
An alternative method is to equate the ratio of the prices of the two goods with the ratios of their marginal utilities. Here, we need:
$$
\frac{M U_{\text {Mars }}}{M U_{\text {Twix }}}=\frac{P_{\text {Mars }}}{P_{\text {Twix }}}
$$Because the prices are the same, we need to find the levels of consumption where the marginal utilities are equal, bearing in mind the total cost constraint. This occurs where:
$$
M U_{\text {Mars }}=M U_{\text {Twix }}=40
$$
$i e$ three Mars bars and two Twix bars.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONWe need to add together the marginal utilities of each extra Twix or Mars bar to find out which combination of chocolate bars maximises the consumer’s utility. Because the consumer’s budget is $£ 4.50$ and all chocolate bars cost 90 pence, we know that they can only buy a total of five chocolate bars.
For 3 Mars and 2 Twix bars, the consumer’s total utility is $90+60+40+50+40=280$. Any other combination gives a lower level of utility.
An alternative method is to equate the ratio of the prices of the two goods with the ratios of their marginal utilities. Here, we need:
$$
\frac{M U_{\text {Mars }}}{M U_{\text {Twix }}}=\frac{P_{\text {Mars }}}{P_{\text {Twix }}}
$$Because the prices are the same, we need to find the levels of consumption where the marginal utilities are equal, bearing in mind the total cost constraint. This occurs where:
$$
M U_{\text {Mars }}=M U_{\text {Twix }}=40
$$
$i e$ three Mars bars and two Twix bars. -
Question 85 of 999CB2023548
Question 85
FlagThe principle of diminishing marginal utility of wealth implies that a risk-averse individual will be prepared to insure themself against an event:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA risk-averse individual will be prepared to pay more for insurance than the long-run average value of claims that will be made. Consequently, they will on average be less well off in monetary terms. However, insurance will be bought if it makes the individual better off in terms of expected utility.
While a risk-averse investor might buy insurance if the expected return is negative, zero or positive, a risk-neutral investor will buy insurance only if the expected return is zero or positive. A risk-seeking investor will buy insurance only if the expected return is positive.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA risk-averse individual will be prepared to pay more for insurance than the long-run average value of claims that will be made. Consequently, they will on average be less well off in monetary terms. However, insurance will be bought if it makes the individual better off in terms of expected utility.
While a risk-averse investor might buy insurance if the expected return is negative, zero or positive, a risk-neutral investor will buy insurance only if the expected return is zero or positive. A risk-seeking investor will buy insurance only if the expected return is positive.
-
Question 86 of 999CB2023549
Question 86
FlagA firm is selling 1,000 units of output at a price of £20, with a marginal cost of £5 and average variable
cost of £8 at that level of output. What is the supernormal profit that the monopoly firm is making?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONProfit is the difference between total revenue and total cost. From the information given, the total revenue can be
computed as
Total revenue= 20 x £1000 = £20,000
Total cost is computed as the product of the average cost and the units of output. Since the average cost is not given,
the total cost cannot be determined. Notice that what is given is the average variable cost which can be used to
compute the total variable cost. However, the total cost is the sum of variable cost and fixed cost. There is no
information about the fixed cost, so the total cost cannot be determined. The correct answer is option DIncorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONProfit is the difference between total revenue and total cost. From the information given, the total revenue can be
computed as
Total revenue= 20 x £1000 = £20,000
Total cost is computed as the product of the average cost and the units of output. Since the average cost is not given,
the total cost cannot be determined. Notice that what is given is the average variable cost which can be used to
compute the total variable cost. However, the total cost is the sum of variable cost and fixed cost. There is no
information about the fixed cost, so the total cost cannot be determined. The correct answer is option D -
Question 87 of 999CB2023550
Question 87
FlagWhich one of the following statements concerning advertising is FALSE?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe main goal of advertisements is to raise the revenues of the firm by increasing the customer base. When a
product is more price elastic, revenues fall as the price increases. To increase revenues, advertisements should aim at
developing some level of customer loyalty to the firm’s product and make the demand for the product more price
inelastic to increase revenuesIncorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe main goal of advertisements is to raise the revenues of the firm by increasing the customer base. When a
product is more price elastic, revenues fall as the price increases. To increase revenues, advertisements should aim at
developing some level of customer loyalty to the firm’s product and make the demand for the product more price
inelastic to increase revenues -
Question 88 of 999CB2023551
Question 88
FlagA necessary condition for a firm being able to engage in price discrimination is that:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFor a firm to be able to undertake price discrimination, the necessary condition is that it must have considerable
market power. That is, the firm must be a price maker for it to be able to discriminate. This implies that it must
face a downward-sloping demand curve, similar to what is faced by a monopolist.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFor a firm to be able to undertake price discrimination, the necessary condition is that it must have considerable
market power. That is, the firm must be a price maker for it to be able to discriminate. This implies that it must
face a downward-sloping demand curve, similar to what is faced by a monopolist. -
Question 89 of 999CB2023552
Question 89
FlagThe terms of trade index is initially set at 100. If the average price of exports has risen by 50% since the
base year and the average price of imports has risen by 20% since the base year, what is the current figure for the
terms of trade index to the nearest whole number?Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONTerms of trade refer to the price index of exports divided by the price index of imports and then expressed as a
percentage. This means that the terms of trade will be l 00 in the base year. Thus if the average price of exports
relative to the average price of imports has risen by 20 percent since the base year, the terms of trade will now be
120.
In the question at hand, the terms of trade are given by:
$\frac {\text {Average price of exports}}{\text {Average price of imports}} = \frac {150}{125} = 1.25 \, \text {expressed as a percentage}$
Hence, the current figure for the terms of trade index is 125.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONTerms of trade refer to the price index of exports divided by the price index of imports and then expressed as a
percentage. This means that the terms of trade will be l 00 in the base year. Thus if the average price of exports
relative to the average price of imports has risen by 20 percent since the base year, the terms of trade will now be
120.
In the question at hand, the terms of trade are given by:
$\frac {\text {Average price of exports}}{\text {Average price of imports}} = \frac {150}{125} = 1.25 \, \text {expressed as a percentage}$
Hence, the current figure for the terms of trade index is 125. -
Question 90 of 999CB2023553
Question 90
FlagThe endowment effect suggests that:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe value of a product to a person who owns the product can be considered in terms of the amount he is willing to accept (WTA) for the product, whereas the value to a person who does not have the product can be considered in terms of the amount he is willing to pay (WTP) to obtain it. Many studies have shown that the WTA is greater than the WTP, showing that ownership endows additional value to the product. This is known as the endowment effect or divestiture aversion, $i e$ the aversion to losing what is owned.
Present payoffs being endowed with more appeal relative to future payoffs refers to present bias, ie a form of time-inconsistent behaviour, which involves the giving of greater weight to present payoffs relative to future payoffs than would be predicted by standard discounting techniques.
The utility from a product increasing if other people buy it refers to the effect that other people have on a consumer’s perception of a product. This herding effect can lead to price bubbles.
The perceived value of a product and how it relates to the presentation refers to the effect of framing on a consumer’s choice.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe value of a product to a person who owns the product can be considered in terms of the amount he is willing to accept (WTA) for the product, whereas the value to a person who does not have the product can be considered in terms of the amount he is willing to pay (WTP) to obtain it. Many studies have shown that the WTA is greater than the WTP, showing that ownership endows additional value to the product. This is known as the endowment effect or divestiture aversion, $i e$ the aversion to losing what is owned.
Present payoffs being endowed with more appeal relative to future payoffs refers to present bias, ie a form of time-inconsistent behaviour, which involves the giving of greater weight to present payoffs relative to future payoffs than would be predicted by standard discounting techniques.
The utility from a product increasing if other people buy it refers to the effect that other people have on a consumer’s perception of a product. This herding effect can lead to price bubbles.
The perceived value of a product and how it relates to the presentation refers to the effect of framing on a consumer’s choice.
-
Question 91 of 999CB2023554
Question 91
FlagWith a given amount of resources (labour, land and capital) two countries, A and B, can produce either
Good X or Good Y according to the production possibilities set out in the table below:$\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Country } & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Units of } \\
\text { Good X }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Units of } \\
\text { Good Y }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { A } & 500 & 1,500 \\
\hline \text { B } & 200 & 1,000 \\
\hline
\end{array}$State which Good will be exported by Country A if trade is opened up between the two countries.
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONComparative advantage exists when one country has a lower opportunity cost of producing a good than another
country. The table below contains the opportunity cost of producing goods X and Y for countries A and B
respectively.
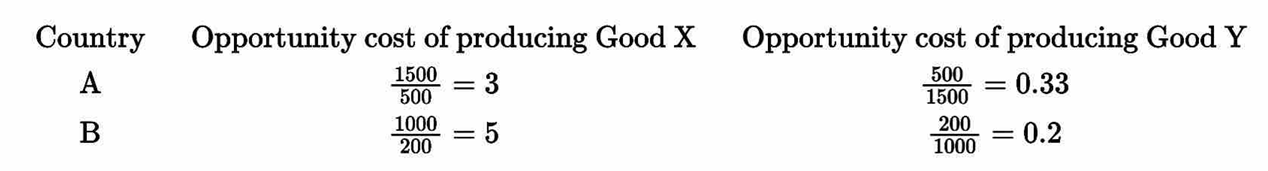
We can see that Country A has a comparative advantage in producing good X because its opportunity cost is
lower than Country B. Similarly, country B has a comparative advantage in producing good Y.
The reasons for international trade are really only an extension of the reasons for trade within a nation. Rather than
people trying to be self-sufficient and do everything for themselves, it makes sense to specialize. Firms specialize in
producing goods in which it has a comparative advantage. This allows them to gain economies of scale and to exploit
their entrepreneurial and management skills and the skills of their labor force.
Since Country A has a comparative advantage in producing good X, it will export good X.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONComparative advantage exists when one country has a lower opportunity cost of producing a good than another
country. The table below contains the opportunity cost of producing goods X and Y for countries A and B
respectively.
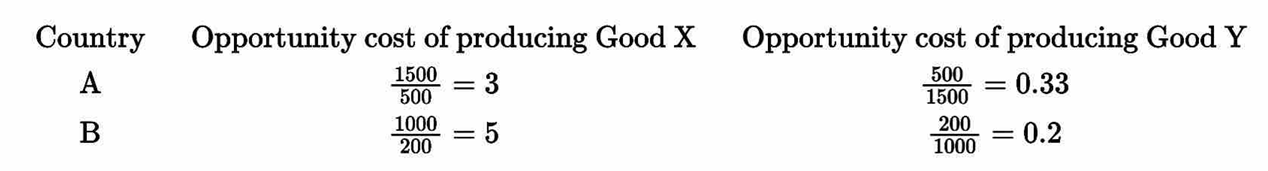
We can see that Country A has a comparative advantage in producing good X because its opportunity cost is
lower than Country B. Similarly, country B has a comparative advantage in producing good Y.
The reasons for international trade are really only an extension of the reasons for trade within a nation. Rather than
people trying to be self-sufficient and do everything for themselves, it makes sense to specialize. Firms specialize in
producing goods in which it has a comparative advantage. This allows them to gain economies of scale and to exploit
their entrepreneurial and management skills and the skills of their labor force.
Since Country A has a comparative advantage in producing good X, it will export good X. -
Question 92 of 999CB2023555
Question 92
FlagIn the table below, consider the assertion and decide whether it is a true statement.
Consider the reason and decide whether it is a true statement.
If you decide that both the assertion and the reason are true, decide whether the reason provides a true explanation of the assertion.$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{Penalties for the late arrival of } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{Train companies might } \\
\text{trains, intended to be an } && \text{re-timetable journeys, allowing }\\
\text{incentive to minimise delays, } && \text{them ‘catch-up time’ at a number }\\
\text{might be classified as a perverse } && \text{of stations along the routes.}\\
\text{incentive. } && \\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe penalties might have undesirable effects, so might be classified as a perverse incentive.
In order to reduce the risk of the penalties being imposed, the train companies might re-timetable the journeys.This scheduled catch-up time, implemented in response to the penalties, might then result in longer journey times – which is the opposite of what was originally intended.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe penalties might have undesirable effects, so might be classified as a perverse incentive.
In order to reduce the risk of the penalties being imposed, the train companies might re-timetable the journeys.This scheduled catch-up time, implemented in response to the penalties, might then result in longer journey times – which is the opposite of what was originally intended.
-
Question 93 of 999CB2023556
Question 93
FlagWhich THREE of the following actions could be taken to reduce a fruit farmer’s risk or uncertainty over income?
Correct
The correct answer is B, C & E.
EXPLANATIONA farmer could reduce the risk or uncertainty concerning income by:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ gaining better information about the likely state of the market at harvest time
$\bullet$ $\quad$ selling fruit to a range of wholesalers to reduce the risk of bad debts
$\bullet$ $\quad$ planting different types of fruit to reduce the risk that any one fruit fails
$\bullet$ $\quad$ storing stocks of the harvested crops, which can be sold at the most appropriate times, rather than selling the crops all at once.Buying (rather than avoiding) insurance products (costly or otherwise) can help protect the farmer against financial loss, eg from poor weather ruining the crops, and so should reduce the uncertainty over income.
Keeping costs low might help to maximise profits, but not reduce uncertainty concerning income.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B, C & E.
EXPLANATIONA farmer could reduce the risk or uncertainty concerning income by:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ gaining better information about the likely state of the market at harvest time
$\bullet$ $\quad$ selling fruit to a range of wholesalers to reduce the risk of bad debts
$\bullet$ $\quad$ planting different types of fruit to reduce the risk that any one fruit fails
$\bullet$ $\quad$ storing stocks of the harvested crops, which can be sold at the most appropriate times, rather than selling the crops all at once.Buying (rather than avoiding) insurance products (costly or otherwise) can help protect the farmer against financial loss, eg from poor weather ruining the crops, and so should reduce the uncertainty over income.
Keeping costs low might help to maximise profits, but not reduce uncertainty concerning income.
-
Question 94 of 999CB2023557
Question 94
FlagA firm produces paper and plants a forest, the additional trees create natural beauty, an area for walking,
and reduce air pollution. Which is the following best describes this example?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAn external benefit is where there is a positive spillover effect from an activity to a third party who is not involved
in the activity in question. The marginal social cost of producion is less than the marginal private cost to the firm.
Hence the example describes an external benefit. Below is a diagram to illustrate the external benefits of
production.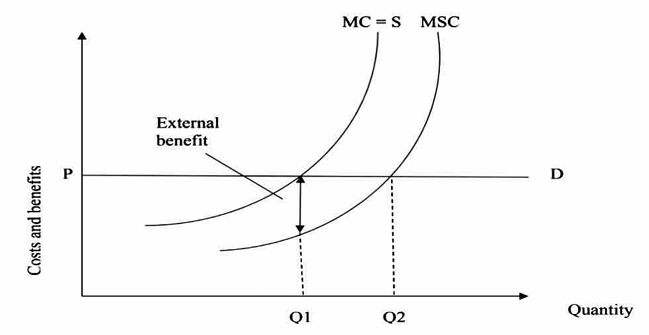
Similarly, A firm produces an external cost if its marginal social cost of production is greater than the marginal
private cost.
Pigouvian tax (or subsidy) A tax (or subsidy): designed to ‘internalise’ an extemality. The marginal rate of a
Pigouvian tax (or subsidy) should be equal to the marginal external cost (or benefit).Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAn external benefit is where there is a positive spillover effect from an activity to a third party who is not involved
in the activity in question. The marginal social cost of producion is less than the marginal private cost to the firm.
Hence the example describes an external benefit. Below is a diagram to illustrate the external benefits of
production.
Similarly, A firm produces an external cost if its marginal social cost of production is greater than the marginal
private cost.
Pigouvian tax (or subsidy) A tax (or subsidy): designed to ‘internalise’ an extemality. The marginal rate of a
Pigouvian tax (or subsidy) should be equal to the marginal external cost (or benefit). -
Question 95 of 999CB2023558
Question 95
FlagIn the table below, consider the assertion and decide whether it is a true statement.
Consider the reason and decide whether it is a true statement.
If you decide that both the assertion and the reason are true, decide whether the reason provides a true explanation of the assertion.$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{An indifference curve is typically } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{Individuals will gain increasingly } \\
\text{bow shaped towards the origin.} && \text{less additional satisfaction from a }\\
&& \text{good the more of the good they }\\
&& \text{consume (the principle of }\\
&&\text{diminishing marginal utility).} \\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONBoth statements are true. These are described in the textbook. Statement 2 explains Statement 1.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONBoth statements are true. These are described in the textbook. Statement 2 explains Statement 1.
-
Question 96 of 999CB2023559
Question 96
FlagThe following diagram shows the effect of a fall in price of Good X when the price of Good Y and the consumer’s income remain unchanged. IC1, Bl, X I and Y1 show the indifference curve, budget line and optimal consumption quantities of Goods X and Y before the price change, and IC2, B2, X2 and Y2 show the corresponding items after the price change. B3 shows a hypothetical budget line, which has the same gradient as B2 and is drawn at a tangent to IC1.
Which TWO statements about Good X are illustrated in the diagram?
Correct
The correct answer is C & E.
EXPLANATIONThe substitution effect is shown by the movement from $X 1$ to the point on the $x$-axis directly below the point of tangency between IC1 and B3 and the income effect is shown by the movement from this intermediate point to $X 2$. These are both negative, ie a fall in the price of Good X leads to a rise in the quantity demanded of Good X . The substitution effect is always negative as consumers will always switch towards the cheaper good. The negative income effect demonstrates that Good X is a normal good: the fall in the price of Good X leads to a rise in the real income of the consumer, and for a normal good, a rise in income leads to a rise in quantity demanded; so a fall in price has led to a rise in quantity demanded. For an inferior good, the income effect is positive, ie a fall in the price of the good would lead to a rise in the real income of the consumer and so a fall in quantity demanded.
These goods are substitutes because the price decrease of one good results in more of that good but less of the other being consumed. The convexity reflects the diminishing marginal rate of substitution (ie the more a person consumes of Good X , the less additional units of Good Y will that person be prepared to give up in order to obtain an extra unit of Good X).
It is not possible to say anything about the relative prices of Good $X$ and Good $Y$ without a scale.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C & E.
EXPLANATIONThe substitution effect is shown by the movement from $X 1$ to the point on the $x$-axis directly below the point of tangency between IC1 and B3 and the income effect is shown by the movement from this intermediate point to $X 2$. These are both negative, ie a fall in the price of Good X leads to a rise in the quantity demanded of Good X . The substitution effect is always negative as consumers will always switch towards the cheaper good. The negative income effect demonstrates that Good X is a normal good: the fall in the price of Good X leads to a rise in the real income of the consumer, and for a normal good, a rise in income leads to a rise in quantity demanded; so a fall in price has led to a rise in quantity demanded. For an inferior good, the income effect is positive, ie a fall in the price of the good would lead to a rise in the real income of the consumer and so a fall in quantity demanded.
These goods are substitutes because the price decrease of one good results in more of that good but less of the other being consumed. The convexity reflects the diminishing marginal rate of substitution (ie the more a person consumes of Good X , the less additional units of Good Y will that person be prepared to give up in order to obtain an extra unit of Good X).
It is not possible to say anything about the relative prices of Good $X$ and Good $Y$ without a scale.
-
Question 97 of 999CB2023560
Question 97
FlagThe diagram below shows the marginal social benefit (MSB) curve and marginal private benefit (MB)
curve.
Which of the following exists based on the diagram?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAn external cost of consumption is the cost experienced by people other than the consumer of the product or service.
A negative externality in consumption occurs when the marginal social benefit (MSB) of consuming something
is less than the marginal private benefit (MB). Examples include: pollution from air travel, noise from night clubs
suffered by local residents, adverse health effects on other people from individuals that smoke.
From the diagram MSB<MB, therefore, a negative externality in consumption exists.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAn external cost of consumption is the cost experienced by people other than the consumer of the product or service.
A negative externality in consumption occurs when the marginal social benefit (MSB) of consuming something
is less than the marginal private benefit (MB). Examples include: pollution from air travel, noise from night clubs
suffered by local residents, adverse health effects on other people from individuals that smoke.
From the diagram MSB<MB, therefore, a negative externality in consumption exists. -
Question 98 of 999CB2023561
Question 98
FlagThe following table contains output and expenditure data for an economy:
$\begin{array}{|l|c|}
\hline & £ \text { billions } \\
\hline \text { Consumption (at market prices) } & 300 \\
\hline \text { Investment (at market prices) } & 80 \\
\hline \text { Government spending (at market prices) } & 85 \\
\hline \text { Net exports (at market prices) } & -10 \\
\hline \text { Net income from abroad } & 5 \\
\hline \text { Indirect taxes } & 60 \\
\hline
\end{array}$Determine the GDP at basic prices and the gross national income at market prices, respectively, (in£ billions):
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONGDP at basic price= GDP at market price – indirect taxes
But:
GDP at market price = Consumption (at market prices)+ Investment(at market prices)
+ Government spending( at market prices) + Net Exports (at market prices)
=> GDP at market price= 300 + 80 + 85 -10 = 455.
Then:
GDP at basic price = £( 455 – 60) = £395 billion
Also:
GNI at market price = GDP at market price + net income received from abroad
GNI at market price= £455 + £5 = £460 billionIncorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONGDP at basic price= GDP at market price – indirect taxes
But:
GDP at market price = Consumption (at market prices)+ Investment(at market prices)
+ Government spending( at market prices) + Net Exports (at market prices)
=> GDP at market price= 300 + 80 + 85 -10 = 455.
Then:
GDP at basic price = £( 455 – 60) = £395 billion
Also:
GNI at market price = GDP at market price + net income received from abroad
GNI at market price= £455 + £5 = £460 billion -
Question 99 of 999CB2023562
Question 99
FlagThe aggregate demand curve slopes downwards because at higher price levels the real money supply:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONReal money supply and price level have an inverse relationship. Real money supply is the money in the
circulation after nominal money supply is adjusted for inflation. Therefore, an increase in general price level would
cause real money supply to decline, vice versa. In addition, when real money supply decreases, consumers and firms
have less purchasing power, which could lead to fall in consumption and investment, and finally, fall in aggerate
income.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONReal money supply and price level have an inverse relationship. Real money supply is the money in the
circulation after nominal money supply is adjusted for inflation. Therefore, an increase in general price level would
cause real money supply to decline, vice versa. In addition, when real money supply decreases, consumers and firms
have less purchasing power, which could lead to fall in consumption and investment, and finally, fall in aggerate
income. -
Question 100 of 999CB2023563
Question 100
FlagIf the rate of inflation is lower than the anticipated rate used for negotiating interest rates and wages:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWhen the actual inflation is lower than the anticipated rate inflation, lenders gain at the expense of borrowers. This is
because the real interest rate increases as actual inflation is lower than the anticipated inflation. Further, workers tend
to gain at the expense of employers because the real value or purchasing power of already negotiated wages paid to
workers increases with lower inflation.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONWhen the actual inflation is lower than the anticipated rate inflation, lenders gain at the expense of borrowers. This is
because the real interest rate increases as actual inflation is lower than the anticipated inflation. Further, workers tend
to gain at the expense of employers because the real value or purchasing power of already negotiated wages paid to
workers increases with lower inflation. -
Question 101 of 999CB2023576
Question 101
FlagIn a closed economy with no government sector, the marginal propensity to save is 0.1, investment is
£500 million, and autonomous consumption is £200 million. Which of the following statements is true at the
equilibrium level of national income?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONWith the information given, the national income identity can be written as :
Y = 200 + 0.9Y + 500
0.1Y = 700
Y = £7,000 million
Consumption = 200 + 0.9(7000) = £6,500 millionIncorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONWith the information given, the national income identity can be written as :
Y = 200 + 0.9Y + 500
0.1Y = 700
Y = £7,000 million
Consumption = 200 + 0.9(7000) = £6,500 million -
Question 102 of 999CB2023577
Question 102
FlagIn an open economy with a government sector, the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75 and the
marginal propensity to import is 0.25. The open economy multiplier will equal:Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATION$\begin{aligned}
& \text { Marginal Propensity to Import }=M P I=0.25 \\
& \text { Marginal Propensity to Consume }=M P C=0.75 \\
& \text { Marginal Propensity to Save }=M P S \\
& \qquad \text { Open Economy Multiplier }=\frac{1}{M P S+M P I} \\
& \qquad M P S=(1-M P C)=1-0.75=0.25 \\
& \text { Open Economy Multiplier }=\frac{1}{0.25+0.25}=2
\end{aligned}$Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATION$\begin{aligned}
& \text { Marginal Propensity to Import }=M P I=0.25 \\
& \text { Marginal Propensity to Consume }=M P C=0.75 \\
& \text { Marginal Propensity to Save }=M P S \\
& \qquad \text { Open Economy Multiplier }=\frac{1}{M P S+M P I} \\
& \qquad M P S=(1-M P C)=1-0.75=0.25 \\
& \text { Open Economy Multiplier }=\frac{1}{0.25+0.25}=2
\end{aligned}$ -
Question 103 of 999CB2023578
Question 103
FlagIf the central bank has to intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent the home currency from
depreciating, then its foreign exchange reserves will:Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONForeign exchange reserves are the central bank’s assets in the form of foreign currencies. If a central bank has to
intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent the home currency from depreciating, it will sell foreign
currencies to the public and buy the home currency. As a result, foreign exchange reserves will decrease. Since the
central bank buys the home currency from the public, the domestic money in circulation will fall.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONForeign exchange reserves are the central bank’s assets in the form of foreign currencies. If a central bank has to
intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent the home currency from depreciating, it will sell foreign
currencies to the public and buy the home currency. As a result, foreign exchange reserves will decrease. Since the
central bank buys the home currency from the public, the domestic money in circulation will fall. -
Question 104 of 999CB2023579
Question 104
FlagThe US has been running a large current account deficit, and China has a large current account surplus. If
their exchange rates were both flexible, how could such imbalances be eliminated?Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONForeign exchange rate depreciation makes a country’s currency weaker relative to other countries of world and
causes the country’s exports to be relatively cheaper. Foreign exchange rate appreciation, on the other hand, causes a
country’s currency to be stronger relative to other countries and causes country’s export to be relatively expensive.
Therefore, the imbalance in current account deficit could be be eliminated if U.S dollar depreciates against Chinese
renminbi. In this scenario, the U.S would be able to export and sell more goods in the international market and
improve its balance of payment.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONForeign exchange rate depreciation makes a country’s currency weaker relative to other countries of world and
causes the country’s exports to be relatively cheaper. Foreign exchange rate appreciation, on the other hand, causes a
country’s currency to be stronger relative to other countries and causes country’s export to be relatively expensive.
Therefore, the imbalance in current account deficit could be be eliminated if U.S dollar depreciates against Chinese
renminbi. In this scenario, the U.S would be able to export and sell more goods in the international market and
improve its balance of payment. -
Question 105 of 999CB2023580
Question 105
FlagUnder a fixed exchange rate system, the following approaches might be considered by governments to
correct a balance of payments deficit:
I. Discouraging imports
II. Support for exporters
Ill. Increasing the level of aggregate demand
Which of the above are most likely to achieve this objective?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONBalance of payment deficit is a situation when a country imports more goods, services, and capital than it
exports.
A fixed exchange rate system is a system adopted by the central bank to make dometic currency exchange for foreign
currency at a fixed rate. In this situation, the exchange rate can neither appreciate or depreciate.
If the government wants to reduce the balance of payment deficit under a fixed exchange rate system, the domestic
residents must reduce goods imported from abroad and the government must deliberately encourage exports.
An increase in aggregate demand may worsen the balance of payment deficit if citizens spend more money on
importable goods than goods produced domestically.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONBalance of payment deficit is a situation when a country imports more goods, services, and capital than it
exports.
A fixed exchange rate system is a system adopted by the central bank to make dometic currency exchange for foreign
currency at a fixed rate. In this situation, the exchange rate can neither appreciate or depreciate.
If the government wants to reduce the balance of payment deficit under a fixed exchange rate system, the domestic
residents must reduce goods imported from abroad and the government must deliberately encourage exports.
An increase in aggregate demand may worsen the balance of payment deficit if citizens spend more money on
importable goods than goods produced domestically. -
Question 106 of 999CB2023581
Question 106
FlagMarginal cost is:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONMarginal cost is usually defined as the change in total costs when output is expanded by one unit. Total costs are made up of fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are fixed. So, the change in total costs as output expands is the same as the change in variable costs as output expands.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONMarginal cost is usually defined as the change in total costs when output is expanded by one unit. Total costs are made up of fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are fixed. So, the change in total costs as output expands is the same as the change in variable costs as output expands.
-
Question 107 of 999CB2023582
Question 107
FlagIf the real rate of interest is 5% and the expected inflation rate is 4%, then the nominal rate of interest is
approximatelyCorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe relationship between real interest rate r, nominal interest rates i, and inflation rate $\pi$ is given as:
$(1+i) = (1+r)(1+\pi)$
Then, given r = 5% and $\pi$ = 0.04, we have
1 + i = (1.05)(1.04) = 1.092 => i = 1.092 – 1 = 0.092
Then, i approx = 9%.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe relationship between real interest rate r, nominal interest rates i, and inflation rate $\pi$ is given as:
$(1+i) = (1+r)(1+\pi)$
Then, given r = 5% and $\pi$ = 0.04, we have
1 + i = (1.05)(1.04) = 1.092 => i = 1.092 – 1 = 0.092
Then, i approx = 9%. -
Question 108 of 999CB2023583
Question 108
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for real money balances is interest inelastic and the demand for
investment is interest elastic. A change in the money supply will result in a relatively:Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONWhen the demand for real money balances is interest rate inelastic, the money demand curve is steeper. With a
steeper money demand curve, a small change in the money supply will cause the interest rate to change by a larger
value. For example, consider a small increase in the money supply. With a steep money demand curve, this will
result in a large decrease in the interest rate. Given that investment is interest rate elastic, the investment curve is
flatter. This implies that the decrease in the interest rate will cause a proportionately larger increase in investment.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONWhen the demand for real money balances is interest rate inelastic, the money demand curve is steeper. With a
steeper money demand curve, a small change in the money supply will cause the interest rate to change by a larger
value. For example, consider a small increase in the money supply. With a steep money demand curve, this will
result in a large decrease in the interest rate. Given that investment is interest rate elastic, the investment curve is
flatter. This implies that the decrease in the interest rate will cause a proportionately larger increase in investment. -
Question 109 of 999CB2023584
Question 109
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for real money balances and the demand for investment are both
highly interest elastic. A change in the money supply will give:Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONTo approach this question, we can use the liquidity preference model, which combines a downward-sloping money
demand (MD) curve with a vertical money supply curve (fixed by the Central Bank). If the demand for real money
balances is highly interest elastic, then the MD curve will be relatively flat, and any change in money supply will
lead to only a small change in the real rate of interest. However, if demand for investment is highly responsive to
changes in interest rates, then a small change in the rate of interest results in a bigger fall in investment. Therefore,
the correct answer is D.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONTo approach this question, we can use the liquidity preference model, which combines a downward-sloping money
demand (MD) curve with a vertical money supply curve (fixed by the Central Bank). If the demand for real money
balances is highly interest elastic, then the MD curve will be relatively flat, and any change in money supply will
lead to only a small change in the real rate of interest. However, if demand for investment is highly responsive to
changes in interest rates, then a small change in the rate of interest results in a bigger fall in investment. Therefore,
the correct answer is D. -
Question 110 of 999CB2023585
Question 110
FlagConsider the scenario below and determine its effect on the official unemployment rate.
Scenario: Previously unemployed persons find part-time jobs even though they need full-time work.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe official unemployment rate would decrease because these individuals are now counted as employed, regardless
of their part-time status or desire for full-time work. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of the labor
force that is jobless and actively seeking employment, so once individuals gain employment (even if part-time), they
no longer count as unemployed.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe official unemployment rate would decrease because these individuals are now counted as employed, regardless
of their part-time status or desire for full-time work. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of the labor
force that is jobless and actively seeking employment, so once individuals gain employment (even if part-time), they
no longer count as unemployed. -
Question 111 of 999CB2023586
Question 111
Flag
The figure above illustrates
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe law of diminishing returns applies to the short run production process. It states that as you add increasing
amounts of a variable factor of production to a given amount of a fixed factor of production, after a certain point the
marginal product of the variable factors will decline.
The law of diminishing marginal utility applies to consumption. It states that as a consumer consumes increasing
amounts of a given product then the marginal utility derived from the product will decline.
Constant returns to scale is where a given percentage increase in inputs leads to the same percentage increase in
output.
Specialisation and division of labour is where production is broken down into a number of simpler, more
specialised tasks, thus allowing workers to acquire a high degree of efficiency.
The graph illustrates marginal product curve for Good X that you would expect from the laws of diminishing
returns.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe law of diminishing returns applies to the short run production process. It states that as you add increasing
amounts of a variable factor of production to a given amount of a fixed factor of production, after a certain point the
marginal product of the variable factors will decline.
The law of diminishing marginal utility applies to consumption. It states that as a consumer consumes increasing
amounts of a given product then the marginal utility derived from the product will decline.
Constant returns to scale is where a given percentage increase in inputs leads to the same percentage increase in
output.
Specialisation and division of labour is where production is broken down into a number of simpler, more
specialised tasks, thus allowing workers to acquire a high degree of efficiency.
The graph illustrates marginal product curve for Good X that you would expect from the laws of diminishing
returns. -
Question 112 of 999CB2023587
Question 112
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a reason why economies of scale may exist?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONEconomies of scale refer to changes in the scale of production, not time.
Indivisibilities and the division of labour are both examples of plant economies of scale, which arise because of the large size of the factory; economies of scope is not.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONEconomies of scale refer to changes in the scale of production, not time.
Indivisibilities and the division of labour are both examples of plant economies of scale, which arise because of the large size of the factory; economies of scope is not. -
Question 113 of 999CB2023588
Question 113
FlagWhich of the following conditions produces normal profits?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIf a firm is making normal profits, this means that supernormal profits, ie economic profits, are zero. Thus total economic costs equal total revenue, and average costs equal average revenue. Setting MR = MC maximises profit, whichmay mean that profits are a lot more (or a lot less) than normal profits.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIf a firm is making normal profits, this means that supernormal profits, ie economic profits, are zero. Thus total economic costs equal total revenue, and average costs equal average revenue. Setting MR = MC maximises profit, whichmay mean that profits are a lot more (or a lot less) than normal profits.
-
Question 114 of 999CB2023589
Question 114
FlagWhich of the following changes would most likely cause the Phillips Curve to shift to the right, indicating
a higher rate of unemployment for a given level of inflation?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATION$\bullet \quad$ Option A: An increase in labor productivity due to technological advancements.
Increased labor productivity typically reduces production costs and can lead to lower inflation for a given level
of output, potentially shifting the Phillips Curve to the left rather than to the right. This results in lower
unemployment without putting upward pressure on inflation.
$\bullet \quad$ Option B: A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment due to improved job matching in the labor market.
A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment means the economy can sustain lower unemployment without
triggering higher inflation, shifting the Phillips Curve to the left. This option implies improved efficiency in the
labor market, which lowers the natural rate of unemployment.
$\bullet \quad$ Option D: A fiscal expansion that boosts aggregate demand in the economy.
Fiscal expansion increases aggregate demand, leading to lower unemployment and higher inflation in the short
run, but it does not shift the Phillips Curve itself. Instead, it moves along the Phillips Curve, reflecting the
inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
In contrast, Option C involves changes in inflation expectations, which directly shifts the Phillips Curve to the right,
as workers and firms anticipate higher future inflation, leading to higher wage demands and price-setting behavior.
This raises inflation even at higher levels of unemployment, thus shifting the curve to the right, reflecting a higher
unemployment rate for any given level of inflation.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATION$\bullet \quad$ Option A: An increase in labor productivity due to technological advancements.
Increased labor productivity typically reduces production costs and can lead to lower inflation for a given level
of output, potentially shifting the Phillips Curve to the left rather than to the right. This results in lower
unemployment without putting upward pressure on inflation.
$\bullet \quad$ Option B: A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment due to improved job matching in the labor market.
A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment means the economy can sustain lower unemployment without
triggering higher inflation, shifting the Phillips Curve to the left. This option implies improved efficiency in the
labor market, which lowers the natural rate of unemployment.
$\bullet \quad$ Option D: A fiscal expansion that boosts aggregate demand in the economy.
Fiscal expansion increases aggregate demand, leading to lower unemployment and higher inflation in the short
run, but it does not shift the Phillips Curve itself. Instead, it moves along the Phillips Curve, reflecting the
inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
In contrast, Option C involves changes in inflation expectations, which directly shifts the Phillips Curve to the right,
as workers and firms anticipate higher future inflation, leading to higher wage demands and price-setting behavior.
This raises inflation even at higher levels of unemployment, thus shifting the curve to the right, reflecting a higher
unemployment rate for any given level of inflation. -
Question 115 of 999CB2023590
Question 115
FlagA profit-maximising firm should keep producing in the short run:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONA profit-maximising firm should keep producing in the short run provided that it is able to cover its variable costs – in the short run it has to pay its fixed costs come what may. This is the case when average revenue exceeds average variable cost.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONA profit-maximising firm should keep producing in the short run provided that it is able to cover its variable costs – in the short run it has to pay its fixed costs come what may. This is the case when average revenue exceeds average variable cost.
-
Question 116 of 999CB2023591
Question 116
FlagThe market structure in which producers must take account of the reactions of competitors in the industry when making decisions is known as:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe need to consider the reactions of competitors is a key difference distinguishing oligopoly from other types of market structure.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe need to consider the reactions of competitors is a key difference distinguishing oligopoly from other types of market structure.
-
Question 117 of 999CB2023592
Question 117
FlagConsumer behaviour can be influenced by small suggestions and positive reinforcements ________________.
Under limited information and cognitive capacity, individuals make satisfactory rather than optimal choices ______________.
The tendency for individuals to not consider only their our own material gains but also the well-being of others ___________________.Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONNudge theory suggests consumer behaviour can be influenced by small suggestions and positive reinforcements.
Proponents of nudge theory suggest that well-placed ‘nudges’ can reduce market failure, save the government
money, encourage desirable actions, and help increase the efficiency of resource use.
Bounded rationality is a concept that suggests that rationality is limited. Individual decision-making is influenced
by limited knowledge and cognitive capacity. Acquiring information may be time-consuming and costly. So
consumers’ rationality is ‘bounded’ by their circumstances. In making their choices, therefore, they would resort to
past experience, best guess, or similar choices that turned out to be good in the past. Hence individuals make
satisfactory rather than optimal decisions.
Social preferences theory suggests the human tendency to consider not only our own material well-being but also
the well-being of others.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONNudge theory suggests consumer behaviour can be influenced by small suggestions and positive reinforcements.
Proponents of nudge theory suggest that well-placed ‘nudges’ can reduce market failure, save the government
money, encourage desirable actions, and help increase the efficiency of resource use.
Bounded rationality is a concept that suggests that rationality is limited. Individual decision-making is influenced
by limited knowledge and cognitive capacity. Acquiring information may be time-consuming and costly. So
consumers’ rationality is ‘bounded’ by their circumstances. In making their choices, therefore, they would resort to
past experience, best guess, or similar choices that turned out to be good in the past. Hence individuals make
satisfactory rather than optimal decisions.
Social preferences theory suggests the human tendency to consider not only our own material well-being but also
the well-being of others. -
Question 118 of 999CB2023593
Question 118
FlagHigh entry and exit costs:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONHigh entry and exit costs make it easier for firms to collude, since other firms are less likely to enter the industry and interfere with collusive agreements.
The main features of perfectly contestable markets are low entry and exit costs.
Competitive markets (ie not those with high entry and exit costs) tend to improve efficiency and benefit consumers, who typically pay lower prices and enjoy greater product choice.
A hit and run strategy in which a firm enters a market, makes short-term profits and then leaves again when the existing firms cut prices, is more likely when entry costs are low.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONHigh entry and exit costs make it easier for firms to collude, since other firms are less likely to enter the industry and interfere with collusive agreements.
The main features of perfectly contestable markets are low entry and exit costs.
Competitive markets (ie not those with high entry and exit costs) tend to improve efficiency and benefit consumers, who typically pay lower prices and enjoy greater product choice.
A hit and run strategy in which a firm enters a market, makes short-term profits and then leaves again when the existing firms cut prices, is more likely when entry costs are low.
-
Question 119 of 999CB2023594
Question 119
FlagA hotel will set the prices of its rooms in the region where the demand is
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONSince the hotel is a profit-maximizing firm, it will set its room prices in the region where the demand is price elastic,
The reason is that when the demand is inelastic, raising the prices will cause a less than proportionate decrease in
quantity demanded. This would mean that total revenue will increase. It is, therefore, profitable for the firm to keep
increasing prices until it fully exhausts the profit-making incentive. Whereas, when the demand is price elastic the
firms lose revenue when raising their prices because quantity demand decreases more than proportionate to the price
increase. Hence it is profitable for the hotel to stop raising prices when demand is price elastic. Therefore, the hotel
will operate in a region where demand is price-elastic because there is no further profit incentive to increase prices.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONSince the hotel is a profit-maximizing firm, it will set its room prices in the region where the demand is price elastic,
The reason is that when the demand is inelastic, raising the prices will cause a less than proportionate decrease in
quantity demanded. This would mean that total revenue will increase. It is, therefore, profitable for the firm to keep
increasing prices until it fully exhausts the profit-making incentive. Whereas, when the demand is price elastic the
firms lose revenue when raising their prices because quantity demand decreases more than proportionate to the price
increase. Hence it is profitable for the hotel to stop raising prices when demand is price elastic. Therefore, the hotel
will operate in a region where demand is price-elastic because there is no further profit incentive to increase prices. -
Question 120 of 999CB2023595
Question 120
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONPotential competitors are those that could enter the market, as opposed to those other firms that are actually in the market at present. (A contestable market is one in which the threat of competition is a key determinant of prices and output. The actual existence of competition is not necessary.)
A perfectly competitive market produces at the level of output where average revenue is equal to marginal cost. In the absence of external costs and benefits, this corresponds to the socially optimal output level, ie where welfare is maximised.
Competition for corporate control refers to the threat of a potential takeover, which should encourage a monopoly to produce efficiently.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONPotential competitors are those that could enter the market, as opposed to those other firms that are actually in the market at present. (A contestable market is one in which the threat of competition is a key determinant of prices and output. The actual existence of competition is not necessary.)
A perfectly competitive market produces at the level of output where average revenue is equal to marginal cost. In the absence of external costs and benefits, this corresponds to the socially optimal output level, ie where welfare is maximised.
Competition for corporate control refers to the threat of a potential takeover, which should encourage a monopoly to produce efficiently.
-
Question 121 of 999CB2023596
Question 121
FlagWhich of the following statements are true about the potential effects of advertising on the market for
laptops?
i) Advertising increases firm profit by making the demand curve more price elastic.
ii) Advertising increases firm profit by shifting the demand curve to the right.
iii) Advertising increases firm profit by reducing economies of scale.
iv) Advertising increases firm profit by making the demand curve less price elasticCorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAdvertising can increase sales and profits by shifting the firm’s demand curve to the right and it can help create
longer-term brand awareness and increase customer loyalty to the brand in the longer run. Brand loyalty will cause
the demand curve to be less price-elastic, allowing firms to raise the prices of laptops without losing too many
customers. This increases firm revenues and profits. Advertising also enables firms to expand production in line
with the increased demand, enabling them to gain economies of scale which reduce their long-run average costs of
producing each laptop and increase their longer-term profitability. From this, you can see that ii and iv are the only
true statements.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAdvertising can increase sales and profits by shifting the firm’s demand curve to the right and it can help create
longer-term brand awareness and increase customer loyalty to the brand in the longer run. Brand loyalty will cause
the demand curve to be less price-elastic, allowing firms to raise the prices of laptops without losing too many
customers. This increases firm revenues and profits. Advertising also enables firms to expand production in line
with the increased demand, enabling them to gain economies of scale which reduce their long-run average costs of
producing each laptop and increase their longer-term profitability. From this, you can see that ii and iv are the only
true statements. -
Question 122 of 999CB2023597
Question 122
FlagThe price of a product in perfect competition is always equal to:
I $\quad$ the marginal cost of all firms
II $\quad$ the average revenue of all firms
III $\quad$ the short-run average cost of all firmsCorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAll firms are assumed to maximise profits, therefore all firms set marginal revenue (and hence price in perfect competition) equal to marginal cost. So Option I is correct.
Option II is correct because average revenue is always equal to price, whatever the market structure. (This assumes that all customers pay the same price, which is the case under perfect competition, as all the firms are price takers and so have no control over the price they charge.)
Option III is incorrect, because in the short run, price can be greater than, equal to, or less than average cost.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAll firms are assumed to maximise profits, therefore all firms set marginal revenue (and hence price in perfect competition) equal to marginal cost. So Option I is correct.
Option II is correct because average revenue is always equal to price, whatever the market structure. (This assumes that all customers pay the same price, which is the case under perfect competition, as all the firms are price takers and so have no control over the price they charge.)
Option III is incorrect, because in the short run, price can be greater than, equal to, or less than average cost.
-
Question 123 of 999CB2023598
Question 123
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an example of a barrier to entry?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONConstant returns to scale (whereby an $x \%$ increase in all inputs leads to an $x \%$ increase in output) mean that large firms do not have a cost advantage through being larger than small firms. This means that small firms can enter the market and not be at a severe disadvantage.
Termination fees for consumers who wish to leave a contract before the end of the contract period are a type of switching cost, which is an additional cost that deters consumers from buying a product from a different firm. Producing a range of products means that there are no gaps, or niches, in the market for new firms to exploit. Excessive spending on advertising is an aggressive tactic to establish brand loyalty, and also increase the costs of entering the market, making it harder for new entrants to gain market share.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONConstant returns to scale (whereby an $x \%$ increase in all inputs leads to an $x \%$ increase in output) mean that large firms do not have a cost advantage through being larger than small firms. This means that small firms can enter the market and not be at a severe disadvantage.
Termination fees for consumers who wish to leave a contract before the end of the contract period are a type of switching cost, which is an additional cost that deters consumers from buying a product from a different firm. Producing a range of products means that there are no gaps, or niches, in the market for new firms to exploit. Excessive spending on advertising is an aggressive tactic to establish brand loyalty, and also increase the costs of entering the market, making it harder for new entrants to gain market share.
-
Question 124 of 999CB2023599
Question 124
FlagUnder average cost pricing, how would firms most likely adjust their prices if their average costs increase
due to a rise in raw material prices?
Option A: Firms will keep prices constant to maintain customer loyalty, absorbing the increased costs.
Option B: Firm~ will raise prices by the same percentage as the increase in average costs, maintaining their profit margins.
Option C: Firms will decrease prices slightly to increase market share and offset the higher costs with higher sales volume.
Option D: Firms will raise prices proportionally to the increase in average costs, following a straightforward pricing rule.
Option E: Firms will switch to marginal cost pricing to better align with competitive market practices.Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONOptions B and D correctly reflect the practice of average cost pricing, where firms adjust their prices
proportionally to changes in average costs, ensuring that they continue to cover their costs and maintain their profit
margins. This approach involves a simple rule of thumb that adjusts prices automatically based on cost fluctuations,
making it easy for firms to implement without complex calculations or strategic considerations.
$\bullet \quad$ Option A is incorrect because keeping prices constant would mean absorbing the increased costs, which
contradicts the principles of average cost pricing aimed at maintaining profitability.
$\bullet \quad$ Option C is incorrect because decreasing prices to gain market share would not cover the higher costs and is not
typical of average cost pricing behavior.
$\bullet \quad$ Option E is incorrect because marginal cost pricing differs from average cost pricing and involves setting prices
equal to the marginal cost of production, not average cost plus a markup.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONOptions B and D correctly reflect the practice of average cost pricing, where firms adjust their prices
proportionally to changes in average costs, ensuring that they continue to cover their costs and maintain their profit
margins. This approach involves a simple rule of thumb that adjusts prices automatically based on cost fluctuations,
making it easy for firms to implement without complex calculations or strategic considerations.
$\bullet \quad$ Option A is incorrect because keeping prices constant would mean absorbing the increased costs, which
contradicts the principles of average cost pricing aimed at maintaining profitability.
$\bullet \quad$ Option C is incorrect because decreasing prices to gain market share would not cover the higher costs and is not
typical of average cost pricing behavior.
$\bullet \quad$ Option E is incorrect because marginal cost pricing differs from average cost pricing and involves setting prices
equal to the marginal cost of production, not average cost plus a markup. -
Question 125 of 999CB2023600
Question 125
FlagWhich of the following best explains how average cost pricing could lead to tacit collusion among firms in
a competitive market?Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAverage cost pricing can lead to tacit collusion because firms independently adopt similar pricing strategies, such as
adding a standard markup to their average costs. When all firms in an industry follow this simple rule, they adjust
prices similarly in response to changes in costs ( e.g., rising raw material prices). This behavior stabilizes prices
across the market without the need for explicit agreements or communication among firms, effectively creating a
form of collusion where price competition is minimized.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAverage cost pricing can lead to tacit collusion because firms independently adopt similar pricing strategies, such as
adding a standard markup to their average costs. When all firms in an industry follow this simple rule, they adjust
prices similarly in response to changes in costs ( e.g., rising raw material prices). This behavior stabilizes prices
across the market without the need for explicit agreements or communication among firms, effectively creating a
form of collusion where price competition is minimized. -
Question 126 of 999CB2023601
Question 126
FlagWhy might a company choose penetration pricing during the introduction stage of a product?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONPenetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to attract a large number of customers quickly. This strategy is
used to build market share rapidly and create broad market acceptance. The low price encourages mass adoption and
generates buzz, helping the company establish a strong market presence before potentially increasing prices later to
improve profitability.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONPenetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to attract a large number of customers quickly. This strategy is
used to build market share rapidly and create broad market acceptance. The low price encourages mass adoption and
generates buzz, helping the company establish a strong market presence before potentially increasing prices later to
improve profitability. -
Question 127 of 999CB2023602
Question 127
FlagA managing director of a monopoly firm is given the following data:
$\begin{array}{lr}
\text { Marginal revenue } & £ 9 \\
\text { Marginal cost } & £ 10 \\
\text { Average cost } & £ 11 \\
\text { Average revenue } & £ 15
\end{array}$To maximise profits the firm should:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONProfits are maximised at the output level where $M C=M R$. If $M C>M R$, then by producing one fewer unit, the firm can reduce its costs by more than it reduces its revenue and so increase its profits. Hence, the firm should reduce its output and in doing so will be’able to increase its price since it faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONProfits are maximised at the output level where $M C=M R$. If $M C>M R$, then by producing one fewer unit, the firm can reduce its costs by more than it reduces its revenue and so increase its profits. Hence, the firm should reduce its output and in doing so will be’able to increase its price since it faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
-
Question 128 of 999CB2023662
Question 128
FlagFirms operating under monopolistic competition will:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONFirms operating under monopolistic competition produce different goods, which is why they are able to raise their prices without losing all of their sales. In addition, the lack of barriers to entry means that any supernormal profits will typically be competed away by the entry of new firms into the industry, so that only normal profits will be earned in the long run.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONFirms operating under monopolistic competition produce different goods, which is why they are able to raise their prices without losing all of their sales. In addition, the lack of barriers to entry means that any supernormal profits will typically be competed away by the entry of new firms into the industry, so that only normal profits will be earned in the long run.
-
Question 129 of 999CB2023663
Question 129
FlagTwo firms operate in a duopoly, but do not collude. Given the payoff matrix of output options to Firms A and B below, what is the dominant strategy for the firms?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONA dominant strategy is the best strategy for one player, no matter what the other player does.
Suppose Firm B goes high. If Firm A goes high, it will get a payoff of 20. If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 10. So Firm A should go high. Suppose Firm B goes low. If Firm A goes high, it will get a payoff of 50. If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 40 . So Firm A should go high. Since Firm A should go high no matter what Firm B does, high is a dominant strategy for Firm A.As the two firms have symmetrical profits, high is also a dominant strategy for Firm B.
The combination (High, High) is a dominant equilibrium and a Nash equilibrium.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONA dominant strategy is the best strategy for one player, no matter what the other player does.
Suppose Firm B goes high. If Firm A goes high, it will get a payoff of 20. If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 10. So Firm A should go high. Suppose Firm B goes low. If Firm A goes high, it will get a payoff of 50. If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 40 . So Firm A should go high. Since Firm A should go high no matter what Firm B does, high is a dominant strategy for Firm A.As the two firms have symmetrical profits, high is also a dominant strategy for Firm B.
The combination (High, High) is a dominant equilibrium and a Nash equilibrium. -
Question 130 of 999CB2023664
Question 130
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an example of collusion between firms?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCollusion involves firms agreeing to limit competition between themselves. The following are examples of collusion:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ horizontal price fixing, where firms agree to set their prices at a level above the competitive price
$\bullet$ $\quad$ agreements to limit production to keep supply low, which should result in higher prices
$\bullet$ $\quad$ sharing out sources of supply, which involves the firms agreeing who will use which suppliers and should avoid situations in which input prices are bid up as a result of competition for raw materials / other inputs.In contrast, if a firm increases its R&D, it will benefit from improved products and/or lower production costs, which is to the detriment of other firms.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCollusion involves firms agreeing to limit competition between themselves. The following are examples of collusion:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ horizontal price fixing, where firms agree to set their prices at a level above the competitive price
$\bullet$ $\quad$ agreements to limit production to keep supply low, which should result in higher prices
$\bullet$ $\quad$ sharing out sources of supply, which involves the firms agreeing who will use which suppliers and should avoid situations in which input prices are bid up as a result of competition for raw materials / other inputs.In contrast, if a firm increases its R&D, it will benefit from improved products and/or lower production costs, which is to the detriment of other firms.
-
Question 131 of 999CB2023665
Question 131
FlagThe following diagram shows an average revenue (AR) curve for a firm.
Which TWO of the following firms are most likely to be subject to such an AR curve?
Correct
The correct answer is B & D.
EXPLANATIONThe $A R$ curve is the same as the demand curve for firms that offer a single price to all customers.
The kinked demand curve model is associated with oligopoly, where there would be a small number of large firms that dominate the market. Examples of this are major automobile manufacturers and mobile phone network operators.A hotel group and legal firm are likely to be in competition with many other competing firms, all offering slightly different levels of service and different prices. This is monopolistic competition and is associated with a non-kinked downward-sloping demand curve.
An online currency exchange firm is in competition with many other providers that offer an indistinguishable service. This is close to perfect competition and is associated with a horizontal demand curve.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B & D.
EXPLANATIONThe $A R$ curve is the same as the demand curve for firms that offer a single price to all customers.
The kinked demand curve model is associated with oligopoly, where there would be a small number of large firms that dominate the market. Examples of this are major automobile manufacturers and mobile phone network operators.A hotel group and legal firm are likely to be in competition with many other competing firms, all offering slightly different levels of service and different prices. This is monopolistic competition and is associated with a non-kinked downward-sloping demand curve.
An online currency exchange firm is in competition with many other providers that offer an indistinguishable service. This is close to perfect competition and is associated with a horizontal demand curve.
-
Question 132 of 999CB2023666
Question 132
FlagIn the table below, consider the assertion and decide whether it is a true statement.
Consider the reason and decide whether it is a true statement.
If you decide that both the assertion and the reason are true, decide whether the reason provides a true explanation of the assertion.$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{Non-price competition is a } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{Under the kinked demand curve} \\
\text{feature of perfectly competitive } && \text{model, the price elasticity of }\\
\text{markets.}&& \text{equilibrium price disincentivises }\\
&& \text{price changes.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONUnder the assumptions of the kinked demand curve model, firms are disincentivised from making price changes:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The demand curve is relatively elastic (ie flat) above the equilibrium price, because it is assumed that if the firm raises its prices, other firms will not respond, and therefore the firm will suffer a large fall in sales (or a fall in market share).
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The demand curve is less elastic (ie steeper) below the equilibrium price, because it is assumed that if the firm lowers its prices, other firms will respond by lowering their prices, and therefore the firm will gain few extra sales (and no increase in market share).Therefore Statement 2 is true, and because of this, non-price competition can be very important within an oligopolistic market. However, this model is associated with oligopoly, not perfect competition.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONUnder the assumptions of the kinked demand curve model, firms are disincentivised from making price changes:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The demand curve is relatively elastic (ie flat) above the equilibrium price, because it is assumed that if the firm raises its prices, other firms will not respond, and therefore the firm will suffer a large fall in sales (or a fall in market share).
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The demand curve is less elastic (ie steeper) below the equilibrium price, because it is assumed that if the firm lowers its prices, other firms will respond by lowering their prices, and therefore the firm will gain few extra sales (and no increase in market share).Therefore Statement 2 is true, and because of this, non-price competition can be very important within an oligopolistic market. However, this model is associated with oligopoly, not perfect competition.
-
Question 133 of 999CB2023667
Question 133
FlagMatch the statements:
I $\quad$ In a monopoly market…
II $\quad$ In a perfectly competitive market…
Ill $\quad$ In a monopolistically competitive market …
IV In an oligopoly market …
A $\quad$ … there is likely to be relevant government competition policy to prevent practices that are harmful to consumers.
B $\quad$ … firms compete on quality and price.
C $\quad$ … collusion between incumbent firms may make it hard for a new entrant to gain a foothold.
D $\quad$ … market share has no influence on prices.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONI-A, II-D, III-B, IV -C
Monopolists are the most likely target of competition policy because the extreme market power of monopolies may allow them to abuse their position.
Collusion is a feature of oligopoly and can be a barrier to entry.
For firms to compete on quality and price, they must be price makers (ie subject to a sloping demand curve), hence this cannot apply in perfect competition. This could also apply to oligopoly, however oligopoly is often associated with price stability and hence there is a greater focus on non-price competition.Under perfect competition all firms are price takers, hence market share has no effect on prices.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONI-A, II-D, III-B, IV -C
Monopolists are the most likely target of competition policy because the extreme market power of monopolies may allow them to abuse their position.
Collusion is a feature of oligopoly and can be a barrier to entry.
For firms to compete on quality and price, they must be price makers (ie subject to a sloping demand curve), hence this cannot apply in perfect competition. This could also apply to oligopoly, however oligopoly is often associated with price stability and hence there is a greater focus on non-price competition.Under perfect competition all firms are price takers, hence market share has no effect on prices.
-
Question 134 of 999CB2023668
Question 134
FlagWhich THREE of the following are characteristics of both perfect competition and monopolistic competition?
Correct
The correct answer is A, B & F.
EXPLANATIONThere is a large number of small firms and no barriers to entry into perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive markets, so new firms can enter easily.
Although all firms in a perfectly competitive market sell identical products, firms operating under monopolistic competition can sell differentiated products. Firms operating under monopolistic competition also have control over their prices, however, firms operating under perfect competition are assumed to be price takers.
Firms operating in any market structure can make supernormal profits in the short run, however, in perfect competition and monopolistic competition, only normal profits can be made in the long run (because new firms can enter the market and compete the supernormal profits away).
Incorrect
The correct answer is A, B & F.
EXPLANATIONThere is a large number of small firms and no barriers to entry into perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive markets, so new firms can enter easily.
Although all firms in a perfectly competitive market sell identical products, firms operating under monopolistic competition can sell differentiated products. Firms operating under monopolistic competition also have control over their prices, however, firms operating under perfect competition are assumed to be price takers.
Firms operating in any market structure can make supernormal profits in the short run, however, in perfect competition and monopolistic competition, only normal profits can be made in the long run (because new firms can enter the market and compete the supernormal profits away).
-
Question 135 of 999CB2023686
Question 135
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a condition required for first-degree price discrimination?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA firm operating under perfect competition will not be able to exercise price discrimination, as it is a price taker and has no control over the price that it sets.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA firm operating under perfect competition will not be able to exercise price discrimination, as it is a price taker and has no control over the price that it sets.
-
Question 136 of 999CB2023687
Question 136
FlagA loss leader may be used as part of which of the following pncing strategies’
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONRecall that full-range pricing is where the firm sets the price on each individual product so as to maximise total profits across its full product range, rather than just to maximise the profit made on each individual product in isolation.
Predatory pricing is where a firm sets its price below its average cost in order to drive other firms out of business. Cost-based pricing is a simple pricing approach where firms apply a fixed percentage markup to average cost. First-degree price discrimination is where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that they are prepared to pay for a good or service.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONRecall that full-range pricing is where the firm sets the price on each individual product so as to maximise total profits across its full product range, rather than just to maximise the profit made on each individual product in isolation.
Predatory pricing is where a firm sets its price below its average cost in order to drive other firms out of business. Cost-based pricing is a simple pricing approach where firms apply a fixed percentage markup to average cost. First-degree price discrimination is where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that they are prepared to pay for a good or service.
-
Question 137 of 999CB2023688
Question 137
FlagWhich of the following describes social efficiency?
I $\quad$ a situation of Pareto optimality
II $\quad$ a situation in which changes in production or consumption can only make one person better off if they make another worse off
III $\quad$ a situation in which marginal social benefit equals marginal social costCorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONSocial efficiency is a situation of Pareto optimality by definition. Statement II describes a situation where no Pareto improvements can be made, which in turn describes a/situation of Pareto optimality. Statement III describes the output level at which social efficiency is achieved.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONSocial efficiency is a situation of Pareto optimality by definition. Statement II describes a situation where no Pareto improvements can be made, which in turn describes a/situation of Pareto optimality. Statement III describes the output level at which social efficiency is achieved.
-
Question 138 of 999CB2023689
Question 138
FlagA key difference between a public good and a merit good is that:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe two key characteristics of public goods are that they are non-rival and non-excludable. Merit goods can be private goods in that they canbe both rival and excludable.
The correct option describes the non-rivalry characteristic of public goods. The option ‘it is possible to provide … available to others’ attributes non-excludability to merit goods rather than public goods.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe two key characteristics of public goods are that they are non-rival and non-excludable. Merit goods can be private goods in that they canbe both rival and excludable.
The correct option describes the non-rivalry characteristic of public goods. The option ‘it is possible to provide … available to others’ attributes non-excludability to merit goods rather than public goods.
-
Question 139 of 999CB2023690
Question 139
FlagThe demand and supply functions for Good A are as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Q_d=40-2 P \\\\
& Q_s=\frac{1}{2} p
\end{aligned}
$$The government now introduces a subsidy of 5 per unit, payable to firms, in order to encou consumption of Good A. The cost of this subsidy will be:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe effect of the subsidy paid to firms is to shift the supply curve vertically downwards by the amount of the subsidy, ie 5. We would therefore expect the market price to fall and the quantity traded to increase.
Consumers are not affected directly by the subsidy paid to firms and so the demand function doesn’t change. However, if $P$ is the market price, then the effect of the subsidy is that firms will now base their supply decision on the market price plus the subsidy, ie $P+5$, rather than $P$.
So, to find the new equilibrium market price and quantity we equate the original demand curve with the revised supply based on $P+5$ :
$$
\frac{1}{2}(P+5)=40-2 P
$$From which the market price is:
$$
P^*=15
$$Substituting this into the demand function gives the equilibrium quantity as:
$$
Q^*=10
$$Given that the subsidy is 5 per unit on each of these 10 units, the overall cost of the subsidy must be:
$$
\text { cost }=10 \times 5=50
$$Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe effect of the subsidy paid to firms is to shift the supply curve vertically downwards by the amount of the subsidy, ie 5. We would therefore expect the market price to fall and the quantity traded to increase.
Consumers are not affected directly by the subsidy paid to firms and so the demand function doesn’t change. However, if $P$ is the market price, then the effect of the subsidy is that firms will now base their supply decision on the market price plus the subsidy, ie $P+5$, rather than $P$.
So, to find the new equilibrium market price and quantity we equate the original demand curve with the revised supply based on $P+5$ :
$$
\frac{1}{2}(P+5)=40-2 P
$$From which the market price is:
$$
P^*=15
$$Substituting this into the demand function gives the equilibrium quantity as:
$$
Q^*=10
$$Given that the subsidy is 5 per unit on each of these 10 units, the overall cost of the subsidy must be:
$$
\text { cost }=10 \times 5=50
$$ -
Question 140 of 999CB2023691
Question 140
FlagWhich of the following are examples of third-degree price discrimination?
I $\quad$ an auction house invites sealed bids for a work of art
II $\quad$ a firm offers a discount to students
III $\quad$ a market trader charges higher prices to tourists than to localsCorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThird-degree price discrimination is where a firm divides consumers into different groups based on an observable and informative characteristic about how much customers are willing to pay. The firm can then charge a different price to members of the different groups. Students and tourists are examples of suchgroups.
A sealed-bid auction prevents bidders from being able to obserye how much others are prepared to pay. This is an attempt to gain the benefits of first-degree price discrimination, by encouraging bidders to submit a bid equal to the maximum they are prepared to pay.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThird-degree price discrimination is where a firm divides consumers into different groups based on an observable and informative characteristic about how much customers are willing to pay. The firm can then charge a different price to members of the different groups. Students and tourists are examples of suchgroups.
A sealed-bid auction prevents bidders from being able to obserye how much others are prepared to pay. This is an attempt to gain the benefits of first-degree price discrimination, by encouraging bidders to submit a bid equal to the maximum they are prepared to pay.
-
Question 141 of 999CB2023692
Question 141
FlagA firm that operates perfect first-degree price discrimination will be:
I $\quad$ productively efficient
II $\quad$ socially efficient
II $\quad$ economically efficientCorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIn order to maximise profits, a firm charging a single price should produce where marginal revenue $(M R)=$ marginal cost $(M C)$, ie at $P^{*}$ and $Q^{*}$ on the diagram below. However, since a firm practising first-degree price discrimination need not drop its prices to existing customers in order to sell more, the firm’s MR curve is the same as its average revenue (AR) curve, and hence its profit-maximising condition is ( $M R=$ ) $A R=M C$, ie at a quantity of $Q s$ on the diagram below. $A R=M C$ is also the condition for social efficiency in the absence of externalities.
Productive efficiency (or technical efficiency) occurs when production is at minimum cost (eg at the bottom of the $A C$ curve). Economic efficiency occurs when we have both social and productive efficiency.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIn order to maximise profits, a firm charging a single price should produce where marginal revenue $(M R)=$ marginal cost $(M C)$, ie at $P^{*}$ and $Q^{*}$ on the diagram below. However, since a firm practising first-degree price discrimination need not drop its prices to existing customers in order to sell more, the firm’s MR curve is the same as its average revenue (AR) curve, and hence its profit-maximising condition is ( $M R=$ ) $A R=M C$, ie at a quantity of $Q s$ on the diagram below. $A R=M C$ is also the condition for social efficiency in the absence of externalities.
Productive efficiency (or technical efficiency) occurs when production is at minimum cost (eg at the bottom of the $A C$ curve). Economic efficiency occurs when we have both social and productive efficiency.
-
Question 142 of 999CB2023693
Question 142
FlagThe next three questions relate to the cost-benefit diagram below, which relates to a particular good.
Which TWO of the following statements are TRUE in relation to the diagram?
Correct
The correct answer is A & D.
EXPLANATIONThe diagram shows an example of an external cost of production, ie where there are external costs to third parties of the production process. In the absence of government intervention, the free market would result in an output level of $Q_{f}$. However, if external costs are considered, the optimal output from the point of view of society is $Q_{5}$. Since $Q_{F}$ exceeds $Q_{5}$, there is overproduction of this good, and so the government might discourage production to reduce the quantity produced. The cost of the overproduction is the additional social cost net of additional benefits, which is the shaded area.
External costs of production occur in oil refinery because it produces significant air pollution. Vaccination is unlikely to lead to significant external costs of production and is more likely to be an example of a good with external benefits of consumption.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A & D.
EXPLANATIONThe diagram shows an example of an external cost of production, ie where there are external costs to third parties of the production process. In the absence of government intervention, the free market would result in an output level of $Q_{f}$. However, if external costs are considered, the optimal output from the point of view of society is $Q_{5}$. Since $Q_{F}$ exceeds $Q_{5}$, there is overproduction of this good, and so the government might discourage production to reduce the quantity produced. The cost of the overproduction is the additional social cost net of additional benefits, which is the shaded area.
External costs of production occur in oil refinery because it produces significant air pollution. Vaccination is unlikely to lead to significant external costs of production and is more likely to be an example of a good with external benefits of consumption.
-
Question 143 of 999CB2023694
Question 143
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{A government wishing to address } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{A change in taxation that cancels } \\
\text{this market failure QUICKLY } && \text{out externalities will result in the }\\
\text{should alter taxation rather than }&& \text{socially optimal level of output.}\\
\text{legislation.}&&\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONBoth taxation and legislation could be used to limit production of this particular good. However, for a quick effect, the government should legislate rather than use taxation since it takes time for the full effect of a taxation change to propagate through the system, and firms may find ways to avoid or minimise the intended impact of the change.
Statement 2 is true – if externalities are cancelled out using taxation, then there will no longer be any difference between the social and private costs / benefits, and so $Q_{F}$ and $Q_{S}$ will become the same on the diagram. However, this doesn’t explain the assertion.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONBoth taxation and legislation could be used to limit production of this particular good. However, for a quick effect, the government should legislate rather than use taxation since it takes time for the full effect of a taxation change to propagate through the system, and firms may find ways to avoid or minimise the intended impact of the change.
Statement 2 is true – if externalities are cancelled out using taxation, then there will no longer be any difference between the social and private costs / benefits, and so $Q_{F}$ and $Q_{S}$ will become the same on the diagram. However, this doesn’t explain the assertion.
-
Question 144 of 999CB2023695
Question 144
FlagWhich line on the diagram would equal the amount of a Pigouvian tax collected that is designed to ‘internalise the externality’?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA Pigouvian tax is said to ‘internalise the externality’, which in this case means the producer will be taxed the difference between the private and social costs of production in order to bring production down to the socially optimal level. This is equal to the $M E C_{p}$ line on the diagram (the marginal external cost of production), which is equal to the difference between the MSC (marginal social cost) and MPC (marginal private cost) lines.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA Pigouvian tax is said to ‘internalise the externality’, which in this case means the producer will be taxed the difference between the private and social costs of production in order to bring production down to the socially optimal level. This is equal to the $M E C_{p}$ line on the diagram (the marginal external cost of production), which is equal to the difference between the MSC (marginal social cost) and MPC (marginal private cost) lines.
-
Question 145 of 999CB2023696
Question 145
FlagWhich TWO of the following policies could be used to remove the welfare cost of overproduction where the burning of fossil fuels is required for the production of a good?
Correct
The correct answer is B & E.
EXPLANATIONThe deadweight welfare loss from overproduction could be removed by shifting the supply curve up until it coincides with the marginal social cost curve. This can be achieved by increasing sales taxes, which increase the private cost of production to allow for the externality (this is an example of a Pigouvian tax). Another way to ensure production at the socially optimal level would be to impose limits on production, though this relies on knowing what the target level of production should be.
Subsidising the production of cleaner substitute goods would affect both the supply and demand of the good. Consumers would be attracted to the cheaper alternatives, shifting the demand curve to the left, and suppliers may also switch to producing the subsidised alternative since it would become more profitable, shifting the supply curve to the left. Both of these effects would reduce the market equilibrium quantity sold for the good but would also reduce the social optimum position, leaving a residual welfare loss from overproduction.
Providing information to consumers is most likely to affect the demand for goods involving the burning of fossil fuels – and the demand curve might shift to the left. This would reduce both the market equilibrium quantity sold and the social optimum quantity, so there would still be a welfare loss from overproduction.
Collusion between firms can be harmful to customers, though this will tend to relate to pricing rather than externalities.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B & E.
EXPLANATIONThe deadweight welfare loss from overproduction could be removed by shifting the supply curve up until it coincides with the marginal social cost curve. This can be achieved by increasing sales taxes, which increase the private cost of production to allow for the externality (this is an example of a Pigouvian tax). Another way to ensure production at the socially optimal level would be to impose limits on production, though this relies on knowing what the target level of production should be.
Subsidising the production of cleaner substitute goods would affect both the supply and demand of the good. Consumers would be attracted to the cheaper alternatives, shifting the demand curve to the left, and suppliers may also switch to producing the subsidised alternative since it would become more profitable, shifting the supply curve to the left. Both of these effects would reduce the market equilibrium quantity sold for the good but would also reduce the social optimum position, leaving a residual welfare loss from overproduction.
Providing information to consumers is most likely to affect the demand for goods involving the burning of fossil fuels – and the demand curve might shift to the left. This would reduce both the market equilibrium quantity sold and the social optimum quantity, so there would still be a welfare loss from overproduction.
Collusion between firms can be harmful to customers, though this will tend to relate to pricing rather than externalities.
-
Question 146 of 999CB2023697
Question 146
FlagWhich TWO of the following are NOT proposals from the Financial Conduct Authority in the UK designed to reduce excessive cross-subsidies between groups of customers?
Correct
The correct answer is B & C.
EXPLANATIONOn savings accounts, a basic savings rate is intended to prevent the practice of offering an attractive rate on new deposits that declines over time. On current accounts, the banning of charges can be targeted at those charges that are only paid by a small number of customers, including those who might be seen as vulnerable. On insurance products, renewal prices can be capped at the price for an equivalent new customer to prevent inertia pricing.
The prohibiting of eligibility criteria for short-term loans may ensure wider access to loans, but it doesn’t prevent some groups being charged more than others nor excess cross-subsidies. A maximum interest rate on mortgages might help to prevent excessive cross subsidies, however it is not a proposal from the Financial Conduct Authority. Higher interest rates are usually charged for higher risk customers, eg those with a lower credit rating or lower loan-to-value ratio, and this practice isn’t deemed as excessive or unfair.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B & C.
EXPLANATIONOn savings accounts, a basic savings rate is intended to prevent the practice of offering an attractive rate on new deposits that declines over time. On current accounts, the banning of charges can be targeted at those charges that are only paid by a small number of customers, including those who might be seen as vulnerable. On insurance products, renewal prices can be capped at the price for an equivalent new customer to prevent inertia pricing.
The prohibiting of eligibility criteria for short-term loans may ensure wider access to loans, but it doesn’t prevent some groups being charged more than others nor excess cross-subsidies. A maximum interest rate on mortgages might help to prevent excessive cross subsidies, however it is not a proposal from the Financial Conduct Authority. Higher interest rates are usually charged for higher risk customers, eg those with a lower credit rating or lower loan-to-value ratio, and this practice isn’t deemed as excessive or unfair.
-
Question 147 of 999CB2023698
Question 147
FlagWhich THREE of the following pricing strategies are examples of second-degree price discrimination?
Correct
The correct answer is A, C & F.
EXPLANATIONSecond-degree price discrimination is where consumers are offered a range of prices. Lower prices can be achieved by purchasing a greater quantity, using coupons or vouchers, or buying the product at certain times.
Charging different prices for different groups based on observable characteristics (such as residents vs tourists, pensioners vs hon pensioners and business travellers vs tourists) is consistent with third-degree price discrimination.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A, C & F.
EXPLANATIONSecond-degree price discrimination is where consumers are offered a range of prices. Lower prices can be achieved by purchasing a greater quantity, using coupons or vouchers, or buying the product at certain times.
Charging different prices for different groups based on observable characteristics (such as residents vs tourists, pensioners vs hon pensioners and business travellers vs tourists) is consistent with third-degree price discrimination.
-
Question 148 of 999CB2023699
Question 148
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{Price discrimination only benefits } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{Price discrimination enables firms } \\
\text{the firms who engage in it. } && \text{to maximise their revenues and }\\
&& \text{profits, but consumers always }\\
&&\text{end up paying more.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is E.
EXPLANATIONFirms often benefit from price discrimination by earning higher revenues and profits. However, consumers can also benefit. For example, some customers will pay a lower price under price discrimination than if a single price were charged to all customers. Also, a good may become affordable for some people under price discrimination who might not be able to afford the single equilibrium price, ie price discrimination might lead to wider access of a good. Price discrimination can also increase output (close) to the social optimum level, which should be beneficial to society as a whole.
Incorrect
The correct answer is E.
EXPLANATIONFirms often benefit from price discrimination by earning higher revenues and profits. However, consumers can also benefit. For example, some customers will pay a lower price under price discrimination than if a single price were charged to all customers. Also, a good may become affordable for some people under price discrimination who might not be able to afford the single equilibrium price, ie price discrimination might lead to wider access of a good. Price discrimination can also increase output (close) to the social optimum level, which should be beneficial to society as a whole.
-
Question 149 of 999CB2023700
Question 149
FlagWhich THREE of the following are examples of club goods?
Correct
The correct answer is A, D & E.
EXPLANATIONClub goods are excludable but non-rival.
A toll road during off-peak hours is excludable as only drivers who have paid the toll are allowed to use it, but non-rival at quiet times. A music subscription service is excludable (as only those who pay can use it) but non-rival, as one person listening doesn’t prevent others. A golf course is excludable as only those with a membership or pass can use it, but non-rival at quiet times.National security is both non-rival and non-excludable and so is a public good. Fishing in a private lake is excludable and rival and so is a private good. Fishing in international waters is non-excludable butrival and so is a common good.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A, D & E.
EXPLANATIONClub goods are excludable but non-rival.
A toll road during off-peak hours is excludable as only drivers who have paid the toll are allowed to use it, but non-rival at quiet times. A music subscription service is excludable (as only those who pay can use it) but non-rival, as one person listening doesn’t prevent others. A golf course is excludable as only those with a membership or pass can use it, but non-rival at quiet times.National security is both non-rival and non-excludable and so is a public good. Fishing in a private lake is excludable and rival and so is a private good. Fishing in international waters is non-excludable butrival and so is a common good.
-
Question 150 of 999CB2023701
Question 150
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{Public goods will not be provided } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{The free-rider problem means } \\
\text{at the socially optimal level if left } && \text{people will be unwilling to buy }\\
\text{to the free market.} && \text{goods that are non-rival and non-}\\
&&\text{excludable because they can }\\
&&\text{make use of these goods if other }\\
&&\text{people buy them.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONPublic goods will not be provided at all if left to the free market because of the free-rider problem. The free-rider problem is where people avoid paying for things themselves if they can make use of things other people have bought and leads to items not being purchased privately even if they would benefit society.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONPublic goods will not be provided at all if left to the free market because of the free-rider problem. The free-rider problem is where people avoid paying for things themselves if they can make use of things other people have bought and leads to items not being purchased privately even if they would benefit society.
-
Question 151 of 999CB2023702
Question 151
FlagWhich of the following can cause the breakdown of the Coase theorem in practice, which states that with well-defined property rights, negotiations between the parties affected by an externality can bring about the socially efficient output?
I $\quad$ property rights being extended to the party that benefits from the externality rather than the party that suffers V * 7
II $\quad$ enforcement of the outcome of the negotiation may be costly or difficult
III $\quad$ the number of parties involved may make it impossible to reach an agreementCorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe Coase theorem relies on all parties affected by the externality being involved in the negotiation, and there being zero bargaining costs. The theorem also depends on the relevant property rights being fully assigned between the parties, but it does not depend on who the property rights are assigned to.
In practical terms, the greater the number of parties, the harder it will be to reach agreement, and the legal costs of negotiation and enforcement may be out of reach for some parties, especially if they have significantly less legal clout than the other parties involved.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe Coase theorem relies on all parties affected by the externality being involved in the negotiation, and there being zero bargaining costs. The theorem also depends on the relevant property rights being fully assigned between the parties, but it does not depend on who the property rights are assigned to.
In practical terms, the greater the number of parties, the harder it will be to reach agreement, and the legal costs of negotiation and enforcement may be out of reach for some parties, especially if they have significantly less legal clout than the other parties involved.
-
Question 152 of 999CB2023703
Question 152
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONSuppose $P^{*}$ is the price the firm would charge to all consumers in the absence of price discrimination.
Under first-degree price discrimination, those consumers who would have purchased the good anyway in the absence of price discrimination do end up paying at least $P^{*}$ for the good. However, the extra consumers who would not have been prepared to pay the market price in the absence of price discrimination, actually end up paying less than $P^{*}$. (The reason they did not buy the good at price $P^{*}$ in the absence of price discrimination is precisely because they were not prepared to pay as much as $P^{*}$.)
First-degree price discrimination does enable the firm to increase its profits (as do the other forms of price discrimination). It also means that there is no consumer surplus, as each consumer pays exactly the maximum they are prepared to pay for the good. Finally, first-degree price discrimination implies that $M R=$ price, so it enables the firm to produce at the socially efficient output level, where price is equal to marginal cost.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONSuppose $P^{*}$ is the price the firm would charge to all consumers in the absence of price discrimination.
Under first-degree price discrimination, those consumers who would have purchased the good anyway in the absence of price discrimination do end up paying at least $P^{*}$ for the good. However, the extra consumers who would not have been prepared to pay the market price in the absence of price discrimination, actually end up paying less than $P^{*}$. (The reason they did not buy the good at price $P^{*}$ in the absence of price discrimination is precisely because they were not prepared to pay as much as $P^{*}$.)
First-degree price discrimination does enable the firm to increase its profits (as do the other forms of price discrimination). It also means that there is no consumer surplus, as each consumer pays exactly the maximum they are prepared to pay for the good. Finally, first-degree price discrimination implies that $M R=$ price, so it enables the firm to produce at the socially efficient output level, where price is equal to marginal cost.
-
Question 153 of 999CB2023704
Question 153
FlagA firm engaged in producing a certain good has private costs that are not equal to social costs. In order to increase economic welfare, the government could:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONWelfare is maximised when the marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal social cost.
We are told that private costs are not equal to social costs. If social costs exceed private costs, then the free market will overproduce compared with the socially optimal level of output. In this case, a Pigouvian tax (ie a tax per unit set equal to the marginal external cost at the socially optimal output level) will increase marginal private costs to the level of marginal social costs and output will be reduced to the socially optimal output level.If private costs exceed social costs, then the free market will underproduce compared with the socially optimal level of output. In this case, a Pigouvian subsidy (ie a subsidy per unit set equal to the marginal external benefit at the socially optimal output level) will increase output to the socially optimal level of output.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONWelfare is maximised when the marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal social cost.
We are told that private costs are not equal to social costs. If social costs exceed private costs, then the free market will overproduce compared with the socially optimal level of output. In this case, a Pigouvian tax (ie a tax per unit set equal to the marginal external cost at the socially optimal output level) will increase marginal private costs to the level of marginal social costs and output will be reduced to the socially optimal output level.If private costs exceed social costs, then the free market will underproduce compared with the socially optimal level of output. In this case, a Pigouvian subsidy (ie a subsidy per unit set equal to the marginal external benefit at the socially optimal output level) will increase output to the socially optimal level of output.
-
Question 154 of 999CB2023725
Question 154
FlagAggregate demand in France is:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFrench aggregate demand (ie $C+I+G+X-M$ ) refers to demand from anyone for French goods and services. The ${ }^{\prime}-M^{\prime}$ term means that aggregate demand includes only demand for French goods and services (ie it excludes the demand for goods from other countries), and the inclusion of the $X$ term means that aggregate demand measures demand from both France and other countries.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFrench aggregate demand (ie $C+I+G+X-M$ ) refers to demand from anyone for French goods and services. The ${ }^{\prime}-M^{\prime}$ term means that aggregate demand includes only demand for French goods and services (ie it excludes the demand for goods from other countries), and the inclusion of the $X$ term means that aggregate demand measures demand from both France and other countries.
-
Question 155 of 999CB2023726
Question 155
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a substitution effect on aggregate demand as a result of a rise in the price level?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe aggregate demand $(A D)$ curve is downward sloping, $i e$ as the price level increases, $A D$ falls. This reflects:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ three substitution effects (the inter-temporal substitution effect, the real balance effect, and the international substitution effect (each of the three incorrect options)) as consumers and firms switch from domestic consumption and investment to savings and/or imports
$\bullet$ $\quad$ an income effect as consumers’ purchasing power falls – assuming incomes do not increase in line with prices (the correct option). (Although firms’ profit might benefit from falling real wages, investment is unlikely to increase while consumer spending is falling.)Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe aggregate demand $(A D)$ curve is downward sloping, $i e$ as the price level increases, $A D$ falls. This reflects:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ three substitution effects (the inter-temporal substitution effect, the real balance effect, and the international substitution effect (each of the three incorrect options)) as consumers and firms switch from domestic consumption and investment to savings and/or imports
$\bullet$ $\quad$ an income effect as consumers’ purchasing power falls – assuming incomes do not increase in line with prices (the correct option). (Although firms’ profit might benefit from falling real wages, investment is unlikely to increase while consumer spending is falling.) -
Question 156 of 999CB2023727
Question 156
FlagFor an economy in equilibrium, savings = 300, investment = 200, exports = 100, imports = 150 and government spending is 250. Taxation is therefore:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONFor equilibrium, planned injections must be equal to planned withdrawals, so:
$\begin{aligned}
&J=W\\\\
&I+G+X=S+T+M\\\\
&200+250+100=300+T+150\\\\
&550=450+T\\\\
&T=100
\end{aligned}$Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONFor equilibrium, planned injections must be equal to planned withdrawals, so:
$\begin{aligned}
&J=W\\\\
&I+G+X=S+T+M\\\\
&200+250+100=300+T+150\\\\
&550=450+T\\\\
&T=100
\end{aligned}$ -
Question 157 of 999CB2023728
Question 157
FlagWhich one of the following is best suited to reducing the level of structural unemployment?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONStructural unemployment occurs when there is a change in the structure of the economy. This may arise from changes in demand, eg a decline in the demand for coal, or a change in the method of production. People find themselves out of work and lacking the skills they need to get a new job in a different area of work. More government funds for retraining of the unemployed would help to overcome these problems and hence might reduce the level of structural unemployment.
Although raising the rate of unemployment benefit and / or higher voluntary redundancy payments for workers in declining industries would ease the monetary circumstances of the unemployed, it would not help them to find new jobs. In fact, raising unemployment benefit is likely to reduce the incentive to work and so increase unemployment.
Lowering the rate of interest would increase aggregate demand and hence reduce demand-deficient unemployment.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONStructural unemployment occurs when there is a change in the structure of the economy. This may arise from changes in demand, eg a decline in the demand for coal, or a change in the method of production. People find themselves out of work and lacking the skills they need to get a new job in a different area of work. More government funds for retraining of the unemployed would help to overcome these problems and hence might reduce the level of structural unemployment.
Although raising the rate of unemployment benefit and / or higher voluntary redundancy payments for workers in declining industries would ease the monetary circumstances of the unemployed, it would not help them to find new jobs. In fact, raising unemployment benefit is likely to reduce the incentive to work and so increase unemployment.
Lowering the rate of interest would increase aggregate demand and hence reduce demand-deficient unemployment.
-
Question 158 of 999CB2023729
Question 158
FlagA consumer prices index is a measure of changes in:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA consumer prices index measures changes in the average level of the retail prices paid by consumers. It therefore measures changes in the average cost of living. It does not méasure changes in the standard of living because it does not take into account other factors that affect the standard of living such as income and the quality of life.
Consumer spending relates to the total quantity of goods consumed, rather than just the prices of those goods, and changes in average earnings would be measured by an earnings index.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA consumer prices index measures changes in the average level of the retail prices paid by consumers. It therefore measures changes in the average cost of living. It does not méasure changes in the standard of living because it does not take into account other factors that affect the standard of living such as income and the quality of life.
Consumer spending relates to the total quantity of goods consumed, rather than just the prices of those goods, and changes in average earnings would be measured by an earnings index.
-
Question 159 of 999CB2023730
Question 159
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a method of measuring the output gap?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONDe-trending techniques smooth the actual GDP figures to try to estimate potential output and hence the output gap.
Businesses can be surveyed in order to create estimates of rates of capacity utilisation and hence potential output and the output gap.
A production function approach estimates potential output and hence the output gap using statistics on capital stock, labour and productivity.
However, a production possibility curve shows the possible combinations of two goods that can be produced by a country in a given time period and does not relate to output gaps.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONDe-trending techniques smooth the actual GDP figures to try to estimate potential output and hence the output gap.
Businesses can be surveyed in order to create estimates of rates of capacity utilisation and hence potential output and the output gap.
A production function approach estimates potential output and hence the output gap using statistics on capital stock, labour and productivity.
However, a production possibility curve shows the possible combinations of two goods that can be produced by a country in a given time period and does not relate to output gaps.
-
Question 160 of 999CB2023731
Question 160
FlagCountry A exports Good X to Country B and imports Good Y from Country B. If the price of Good X rises by 40% and the price of Good Y falls by 30%, what can be said about Country A’s terms of trade?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=100 \times \frac{\text { average price of exports }}{\text { average price of imports }}
$$One way to tackle a question like this is to think of a simple numerical example. Here, let’s say that we start with the prices of Good $X$ and Good $Y$ both being $£ 100$. The terms of trade will then be 100 .
A $40 \%$ increase in the price of Good X gives a new average price of exports of $£ 140$.
A $30 \%$ fall in the price of Good $Y$ gives a new average price of imports of $£ 70$.
The terms of trade for Country A is now 200, which is an increase of $100 \%$.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThe terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=100 \times \frac{\text { average price of exports }}{\text { average price of imports }}
$$One way to tackle a question like this is to think of a simple numerical example. Here, let’s say that we start with the prices of Good $X$ and Good $Y$ both being $£ 100$. The terms of trade will then be 100 .
A $40 \%$ increase in the price of Good X gives a new average price of exports of $£ 140$.
A $30 \%$ fall in the price of Good $Y$ gives a new average price of imports of $£ 70$.
The terms of trade for Country A is now 200, which is an increase of $100 \%$. -
Question 161 of 999CB2023732
Question 161
FlagIf, with one hour of labour, Country A can produce 10 units of Good X or S units of Good Y; and Country B can produce 6 units of Good X or 2 units of Good Y,t hen:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCountry A has an absolute advantage in both goods as it can produce more of both goods with the same resources, ie one hour of labour.
The opportunity cost of producing 10 units of Good X for Country A is the 5 units of Good Y it could have produced instead. Therefore the opportunity cost of 1 unit of Good $X$ for Country A is $1 / 2$ a unit of Good $Y$. Similarly, the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good $X$ for Country $B$ is $1 / 3$ of a unit of Good $Y$. This is lower, so Country B has the comparative advantage in producing Good X.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCountry A has an absolute advantage in both goods as it can produce more of both goods with the same resources, ie one hour of labour.
The opportunity cost of producing 10 units of Good X for Country A is the 5 units of Good Y it could have produced instead. Therefore the opportunity cost of 1 unit of Good $X$ for Country A is $1 / 2$ a unit of Good $Y$. Similarly, the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good $X$ for Country $B$ is $1 / 3$ of a unit of Good $Y$. This is lower, so Country B has the comparative advantage in producing Good X.
-
Question 162 of 999CB2023733
Question 162
FlagAn increase in the value of the pound sterling will
I $\quad$ increase the price of imports into the UK.
II $\quad$ increase the volume of exports from the UK.
Ill $\quad$ improve the UK’s terms of trade.Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAnincrease in the value of sterling makes imports cheaper in pound terms (so Statement I is not true), improving the UK’s terms of trade(so Statement III is true). The volume of exports is likely to fall as they will now be more expensive (so Statement II is not true).
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAnincrease in the value of sterling makes imports cheaper in pound terms (so Statement I is not true), improving the UK’s terms of trade(so Statement III is true). The volume of exports is likely to fall as they will now be more expensive (so Statement II is not true).
-
Question 163 of 999CB2023734
Question 163
FlagWhich of the following is NOT one of the four limits to trade?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONStrategy, structure and rivalry of firms is one of Porter’s four key determinants of why nations have a competitive advantage in some products. The other determinants are available resources, demand conditions in the home market, related and supporting industries.
The fourth limit to trade is that factors of production rather than goods may move from country to country.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONStrategy, structure and rivalry of firms is one of Porter’s four key determinants of why nations have a competitive advantage in some products. The other determinants are available resources, demand conditions in the home market, related and supporting industries.
The fourth limit to trade is that factors of production rather than goods may move from country to country.
-
Question 164 of 999CB2023735
Question 164
FlagConsider the following information about Country A, Country B and Country C for the year 2022.
$\begin{array}{|l|c|c|}
\hline & \text { Country B } & \text { Country C } \\
\hline \text { GDP (Country } \mathrm{A}=100) & 120 & 80 \\
\hline \text { GDP per head (Country } \mathrm{A}=100) & 110 & 90 \\
\hline \text { GDP }\left(\text { PPS }^* \text { ) per head (Country } \mathrm{A}=100\right) & 105 & 95 \\
\hline \text { Index of well-being (Country } \mathrm{A}=100) & 85 & 105 \\
\hline
\end{array}$* PPS (Purchasing Power Standard) is GDP measured at a country’s PPP (Purchasing Power Parity) exchange rate.
Which TWO of the following statements must be TRUE about Countries A, B and C?Correct
The correct answer is A & C.
EXPLANATIONThe question asks which options MUST be true, so only options that are the only possible explanation should be selected as TRUE.
GDP is an absolute measure, so GDP figures can be added together (even though the figures here appear to have been rebased). Therefore, the output of Countries A and C combined is 180, which is more than the output of Country B of 120 .
GDP per head is a measure of output per head of population. This includes non-workers such as children and the elderly. Therefore the table doesn’t give enough information to determine the output of the average worker.
Relative population sizes can be determined by comparing GDP divided by GDP per head in each country. This gives a higher population for Country B than Country C.
The low index of wellbeing in Country B suggests that people are relatively unhappy, however this could be down to a number of factors such as the weather and environment, which are unconnected to working hours. This index will also reflect the wellbeing of the non-working population.
The difference between the level of output per person (GDP (PPS*) per head) and happiness (Index of well-being) is greater for Country B than it is for Country C. However, it is not possible to conclude from this whether output is more or less important to citizens of either country given no information is given about the other factors considered when calculating the index of well-being.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A & C.
EXPLANATIONThe question asks which options MUST be true, so only options that are the only possible explanation should be selected as TRUE.
GDP is an absolute measure, so GDP figures can be added together (even though the figures here appear to have been rebased). Therefore, the output of Countries A and C combined is 180, which is more than the output of Country B of 120 .
GDP per head is a measure of output per head of population. This includes non-workers such as children and the elderly. Therefore the table doesn’t give enough information to determine the output of the average worker.
Relative population sizes can be determined by comparing GDP divided by GDP per head in each country. This gives a higher population for Country B than Country C.
The low index of wellbeing in Country B suggests that people are relatively unhappy, however this could be down to a number of factors such as the weather and environment, which are unconnected to working hours. This index will also reflect the wellbeing of the non-working population.
The difference between the level of output per person (GDP (PPS*) per head) and happiness (Index of well-being) is greater for Country B than it is for Country C. However, it is not possible to conclude from this whether output is more or less important to citizens of either country given no information is given about the other factors considered when calculating the index of well-being.
-
Question 165 of 999CB2023736
Question 165
FlagWhich THREE of the following could be caused by a failure to control inflation?
Correct
The correct answer is A, B & E.
EXPLANATIONInflation causes uncertainty for businesses, especially if it fluctuates. This discourages investment since it becomes harder to predict revenues. This uncertainty also leads to firms needing to divert more resources towards managing the inflationary environment itself, and away from more productive uses.
Exports will become more expensive to other countries (as long as they are not subject to an even greater increase in inflation), which will cause the exchange rate to fall and the balance of trade to deteriorate.
Consumer confidence generally falls when inflation is high. However, consumers tend to forego luxury items and big purchases first and could end up spending more on necessities to fulfil their basic needs as prices rise.
Wealth will be redistributed towards owners of real assets and those with the greatest bargaining power. This group is unlikely to include the poorest members of society.
Employment is not immediately at risk due to inflation – in fact it may even be helped as real wages fall by reducing real-wage unemployment.Incorrect
The correct answer is A, B & E.
EXPLANATIONInflation causes uncertainty for businesses, especially if it fluctuates. This discourages investment since it becomes harder to predict revenues. This uncertainty also leads to firms needing to divert more resources towards managing the inflationary environment itself, and away from more productive uses.
Exports will become more expensive to other countries (as long as they are not subject to an even greater increase in inflation), which will cause the exchange rate to fall and the balance of trade to deteriorate.
Consumer confidence generally falls when inflation is high. However, consumers tend to forego luxury items and big purchases first and could end up spending more on necessities to fulfil their basic needs as prices rise.
Wealth will be redistributed towards owners of real assets and those with the greatest bargaining power. This group is unlikely to include the poorest members of society.
Employment is not immediately at risk due to inflation – in fact it may even be helped as real wages fall by reducing real-wage unemployment. -
Question 166 of 999CB2023737
Question 166
FlagMatch the examples to the definitions:
I $\quad$ a seasonal farm worker whose work becomes mechanised
II $\quad$ a recent graduate who hasn’t yet found a job
III $\quad$ an inhabitant of a holiday island who can’t find work during the off season
IV $\quad$ an unskilled worker laid off due to an increase in the mandated minimum wage
V $\quad$ a car salesman laid off during a recessionA $\quad$ demand-deficient unemployment
B $\quad$ technological unemployment
C $\quad$ frictional unemployment
D $\quad$ seasonal unemploymentCorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATION$\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{V}, \mathrm{B}-\mathrm{I}, \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{II}, \mathrm{D}-\mathrm{III}$.
The unmatched option ‘an unskilled worker laid off due to an increase in the mandated minimum wage’ is an example of real-wage unemployment.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATION$\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{V}, \mathrm{B}-\mathrm{I}, \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{II}, \mathrm{D}-\mathrm{III}$.
The unmatched option ‘an unskilled worker laid off due to an increase in the mandated minimum wage’ is an example of real-wage unemployment. -
Question 167 of 999CB2023738
Question 167
FlagThe world consists of two countries, A and B, and the only factor of production is labour. In Country A it takes 20 hours to produce one unit of Good x and 5 hours to produce one unit of Good Y. in Country B it takes 30 hours to produce one unit of Good X and IS hours to produce one unit of Good Y.r
A country might have a comparative advantage in the production of a particular good because the factors of production of the good:
I $\quad$ are abundant in the country.
II $\quad$ are easily traded between countries.
Ill $\quad$ have many suitable substitutes,Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAbundance of the factors of production makes it easier to produce the good domestically, leading to a comparative advantage in the production of the good. This effect is increased if it is hard to trade the factors of production, or if there are no substitutes that can be used instead.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAbundance of the factors of production makes it easier to produce the good domestically, leading to a comparative advantage in the production of the good. This effect is increased if it is hard to trade the factors of production, or if there are no substitutes that can be used instead.
-
Question 168 of 999CB2023739
Question 168
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONInternational trade leads to increased competition and this should result in lower prices.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONInternational trade leads to increased competition and this should result in lower prices.
-
Question 169 of 999CB2023740
Question 169
FlagWhich of the following statements about national income is always true in a country in which taxes on goods exceed subsidies?
I $\quad$ GNY>GDP
II $\quad$ GNY > NNY
III $\quad$ NNY at market prices > NNY at basic pricesCorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe difference between net national income (NNY) and gross national income (GNY) is depreciation (ie the reduction in value of capital goods due to wear and tear and obsolescence), which must always be positive. Thus Statement II is always true. NNY at basic prices is obtained from NNY at market prices by deducting taxes on goods and adding on subsidies. So Statement III is true in this case. GNY is obtained from gross domestic product (GDP) by adding on net income from abroad, so Statement I may or may not be true, depending whether net income from abroad is negative or positive.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe difference between net national income (NNY) and gross national income (GNY) is depreciation (ie the reduction in value of capital goods due to wear and tear and obsolescence), which must always be positive. Thus Statement II is always true. NNY at basic prices is obtained from NNY at market prices by deducting taxes on goods and adding on subsidies. So Statement III is true in this case. GNY is obtained from gross domestic product (GDP) by adding on net income from abroad, so Statement I may or may not be true, depending whether net income from abroad is negative or positive.
-
Question 170 of 999CB2023741
Question 170
FlagNet worth is defined as:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe net worth of each sector (household, corporate and government) can be found by adding together its net financial assets (ie financial assets less its financial liabilities) and its non-financial wealth (ie its physical wealth such as property and machinery). The country’s net worth is the sum of the net worth of the three sectors.
The income available for households to spend is households’ disposable income. The nation’s stock of financial and physical assets is the value of the nation’s assets. Financial liabilities must be deducted from this to arrive at the nation’s net worth. The value of output produced within a country over a 12 -month period is GDP.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe net worth of each sector (household, corporate and government) can be found by adding together its net financial assets (ie financial assets less its financial liabilities) and its non-financial wealth (ie its physical wealth such as property and machinery). The country’s net worth is the sum of the net worth of the three sectors.
The income available for households to spend is households’ disposable income. The nation’s stock of financial and physical assets is the value of the nation’s assets. Financial liabilities must be deducted from this to arrive at the nation’s net worth. The value of output produced within a country over a 12 -month period is GDP.
-
Question 171 of 999CB2023742
Question 171
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a problem associated with trade restrictions used to protect domestic industries?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe potential problem is that other countries may increase their tariffs in retaliation.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe potential problem is that other countries may increase their tariffs in retaliation.
-
Question 172 of 999CB2023761
Question 172
FlagThe record of a country’s transactions in goods and services and assets with the rest of the world is referred to as its:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONBalance of trade refers to the balance of imports and exports of both goods and services and covers two of the four subdivisions of the current account. The other two subdivisions of the current account are income flows and current transfers of money. The capital account records the flows of funds into (credits) and out of (debits) the country in relation to fixed assets, the transfer of funds by migrants, government grants for overseas projects, government debt forgiveness and the receipt of money for capital projects. The current account and the capital account are two of the three main parts of the balance of payments account. The third main part is the financial account.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONBalance of trade refers to the balance of imports and exports of both goods and services and covers two of the four subdivisions of the current account. The other two subdivisions of the current account are income flows and current transfers of money. The capital account records the flows of funds into (credits) and out of (debits) the country in relation to fixed assets, the transfer of funds by migrants, government grants for overseas projects, government debt forgiveness and the receipt of money for capital projects. The current account and the capital account are two of the three main parts of the balance of payments account. The third main part is the financial account.
-
Question 173 of 999CB2023762
Question 173
FlagWhich of the following is recorded as a plus in the balance of payments accounts of Country A?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATION‘Short-term lending by Country A to the rest of the world’ and ‘the purchase of foreign shares by residents of Country A’ are outflows on the financial account. ‘The payments of interest by residents of Country $A$ to residents of other countries’ is an outflow on the current account. These are recorded as minuses. ‘The export of goods by Country A to the rest of the world’ is an inflow on the current account and is therefore recorded as a plus.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATION‘Short-term lending by Country A to the rest of the world’ and ‘the purchase of foreign shares by residents of Country A’ are outflows on the financial account. ‘The payments of interest by residents of Country $A$ to residents of other countries’ is an outflow on the current account. These are recorded as minuses. ‘The export of goods by Country A to the rest of the world’ is an inflow on the current account and is therefore recorded as a plus.
-
Question 174 of 999CB2023763
Question 174
FlagWhich one of the following is a high-earning but relatively illiquid asset of banks?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONLoans and advances to customers are amongst the most profitable of banks’ assets. However, they are relatively illiquid. The other assets mentioned in the question are all liquid assets of banks that typically offer low returns.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONLoans and advances to customers are amongst the most profitable of banks’ assets. However, they are relatively illiquid. The other assets mentioned in the question are all liquid assets of banks that typically offer low returns.
-
Question 175 of 999CB2023764
Question 175
FlagThe process of repackaging assets into marketable securities is known as:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONSecuritisation is the process of pooling assets such as loans and mortgages into marketable securities such as bonds. It is a form of secondary marketing, ie the sale of assets before maturity.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONSecuritisation is the process of pooling assets such as loans and mortgages into marketable securities such as bonds. It is a form of secondary marketing, ie the sale of assets before maturity.
-
Question 176 of 999CB2023765
Question 176
FlagAn increase in the average riskiness of a bank’s assets, assuming that nothing else changes, will result in;
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe capital adequacy ratio (CAR) is the ratio of a bank’s capital (shares and reserves) to its risk-weighted assets. So, an increase in the riskiness of a bank’s assets will result in an increase in its risk-weighted assets and a decrease in its CAR.
The liquidity ratio, which is the proportion of a bank’s total assets held in liquid form, will be unaffected. (In practice, banks might decide to hold a higher liquidity ratio if they feel there is increased danger of bad debt.)
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe capital adequacy ratio (CAR) is the ratio of a bank’s capital (shares and reserves) to its risk-weighted assets. So, an increase in the riskiness of a bank’s assets will result in an increase in its risk-weighted assets and a decrease in its CAR.
The liquidity ratio, which is the proportion of a bank’s total assets held in liquid form, will be unaffected. (In practice, banks might decide to hold a higher liquidity ratio if they feel there is increased danger of bad debt.)
-
Question 177 of 999CB2023766
Question 177
FlagPrudential control:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONPrudential control refers to the insistence by the Bank of England that each individual bank maintains sufficient liquidity. It applies to all banks, including those deemed to be global systemically important, ie so large that their failure could impact the global financial system.
Macro-prudential regulation is concerned with the financial health of the banking system as a whole, ie with ensuring that the banking system as whole has sufficient liquidity and capital, and so doesn’t impact adversely on the wider economy.
The ratio of a bank’s share capital and reserves to its risk-weighted assets is its capital adequacy ratio. This is intended to ensure that the bank has sufficient capital to withstand defaults on its assets (bank loans, personal loans, mortgages etc).
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONPrudential control refers to the insistence by the Bank of England that each individual bank maintains sufficient liquidity. It applies to all banks, including those deemed to be global systemically important, ie so large that their failure could impact the global financial system.
Macro-prudential regulation is concerned with the financial health of the banking system as a whole, ie with ensuring that the banking system as whole has sufficient liquidity and capital, and so doesn’t impact adversely on the wider economy.
The ratio of a bank’s share capital and reserves to its risk-weighted assets is its capital adequacy ratio. This is intended to ensure that the bank has sufficient capital to withstand defaults on its assets (bank loans, personal loans, mortgages etc).
-
Question 178 of 999CB2023767
Question 178
FlagTo improve the cash position of banks, the central bank could do any of the following EXCEPT:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONUnlike government bonds, Treasury bills form part of the liquid assets of banks and are therefore used as a basis for credit creation. So, if the government chooses to fund its borrowing by issuing more bonds and fewer Treasury bills, this is likely to restrict the banks’ ability to create credit and hence worsen the cash position of banks.
If the central bank buys government bonds or Treasury bills before maturity from banks, this provides them with cash. Buying Treasury bills before maturity is also known as rediscounting.Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONUnlike government bonds, Treasury bills form part of the liquid assets of banks and are therefore used as a basis for credit creation. So, if the government chooses to fund its borrowing by issuing more bonds and fewer Treasury bills, this is likely to restrict the banks’ ability to create credit and hence worsen the cash position of banks.
If the central bank buys government bonds or Treasury bills before maturity from banks, this provides them with cash. Buying Treasury bills before maturity is also known as rediscounting. -
Question 179 of 999CB2023768
Question 179
FlagWhich of the following will lead to a decrease in the demand for money?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATION‘Increased expectations of price rises’ mean that consumers and firms will want to bring forward their purchases so as to buy goods and assets before their prices increase. Hence, they will be left holding lower money balances now.
‘An increase in actual prices’ means consumers and firms will need higher money balances in order to buy the (same volume of) more expensive goods.
‘A reduction in the use of credit cards’ means people will be paying for goods and services more frequently, as opposed to once at the end of each month, and consequently will need higher money balances in order to do so. In addition, more money will need to be held for precautionary purposes.A switch from weekly payment to the monthly payment of wages means people will need to hold higher money balances to cover outgoings until the next payment of wages.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATION‘Increased expectations of price rises’ mean that consumers and firms will want to bring forward their purchases so as to buy goods and assets before their prices increase. Hence, they will be left holding lower money balances now.
‘An increase in actual prices’ means consumers and firms will need higher money balances in order to buy the (same volume of) more expensive goods.
‘A reduction in the use of credit cards’ means people will be paying for goods and services more frequently, as opposed to once at the end of each month, and consequently will need higher money balances in order to do so. In addition, more money will need to be held for precautionary purposes.A switch from weekly payment to the monthly payment of wages means people will need to hold higher money balances to cover outgoings until the next payment of wages.
-
Question 180 of 999CB2023769
Question 180
FlagThe central bank is concerned about rising domestic inflation. Which of the following monetary measures would NOT be suitable as a means to try and reduce inflation?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIn order to try and reduce inflation, the central bank will want to try and reduce the money supply. (In practice, it will likely aim to reduce the rate of growth of the money supply.)
‘Buying government bonds from banks’, as part of a programme of open market operations, would increase the cash in the banking system, enabling banks to increase their lending, resulting in an increase in the money supply.In contrast, each of the other three measures will reduce the money supply. For example, introducing a minimum reserve, or liquidity, ratio for banks (that is higher than the reserve, or liquidity, ratio they would choose themselves) would reduce the amount of credit they could create from a given amount of cash and hence would reduce the broad money supply.
Likewise, knowing that the central bank is less willing to lend to them should they run short of cash would encourage banks to hold more cash themselves, ie to choose to operate with higher liquidity ratios, leading to less credit creation.
Funding government borrowing by selling more long-term, illiquid government bonds and fewer short-term, liquid Treasury bills means banks would hold fewer liquid assets that could be used as the basis for credit creation. This would again lead to less bank lending and a lower money supply.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIn order to try and reduce inflation, the central bank will want to try and reduce the money supply. (In practice, it will likely aim to reduce the rate of growth of the money supply.)
‘Buying government bonds from banks’, as part of a programme of open market operations, would increase the cash in the banking system, enabling banks to increase their lending, resulting in an increase in the money supply.In contrast, each of the other three measures will reduce the money supply. For example, introducing a minimum reserve, or liquidity, ratio for banks (that is higher than the reserve, or liquidity, ratio they would choose themselves) would reduce the amount of credit they could create from a given amount of cash and hence would reduce the broad money supply.
Likewise, knowing that the central bank is less willing to lend to them should they run short of cash would encourage banks to hold more cash themselves, ie to choose to operate with higher liquidity ratios, leading to less credit creation.
Funding government borrowing by selling more long-term, illiquid government bonds and fewer short-term, liquid Treasury bills means banks would hold fewer liquid assets that could be used as the basis for credit creation. This would again lead to less bank lending and a lower money supply.
-
Question 181 of 999CB2023770
Question 181
FlagThe policy remit of the European Central Bank is to:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONOption C is the policy remit of the US Federal Reserve Bank.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONOption C is the policy remit of the US Federal Reserve Bank.
-
Question 182 of 999CB2023771
Question 182
FlagYou are given the following data on Country E’s international transactions for the year 2018 with the rest of the world (ROW):
$\begin{array}{lc}
& £ \text { million } \\
\text { Exports of goods and services (paid for in cash) } & 120 \\
\text { Imports of goods and services } & 140 \\
\text { Interest, profits and dividends received from ROW } & 30 \\
\text { Interest, profits and dividends paid to ROW } & 20 \\
\text { Export of goods on trade credit } & 40 \\
\text { Loans received from ROW } & 30 \\
\text { Capital balance } & -10 \\
\text { Net errors and omissions } & ? \\
\text { Increase in official reserves } & 20
\end{array}$Provide your answers to the questions below in $£$ millions. Use a positive number to indicate a surplus and a negative to identify a deficit.
Calculate the current account balance.
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONCurrent account balance:
$\begin{aligned}
& =\quad \text {net exports of goods and services } \\
& \quad\quad\text { plus net income flows from abroad } \\
& =\quad 120-140+40+30-20 \\
& =\quad £ 30 \mathrm{~m} \text { surplus }
\end{aligned}$Exports of goods on trade credit should be included as an export in the current account balance, however, it should also be included as a negative item in the financial account (see below), so that its total contribution to the overall balance of payment account is zero.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONCurrent account balance:
$\begin{aligned}
& =\quad \text {net exports of goods and services } \\
& \quad\quad\text { plus net income flows from abroad } \\
& =\quad 120-140+40+30-20 \\
& =\quad £ 30 \mathrm{~m} \text { surplus }
\end{aligned}$Exports of goods on trade credit should be included as an export in the current account balance, however, it should also be included as a negative item in the financial account (see below), so that its total contribution to the overall balance of payment account is zero.
-
Question 183 of 999CB2023772
Question 183
FlagYou are given the following data on Country E’s international transactions for the year 2018 with the rest of the world (ROW):
$\begin{array}{lc}
& £ \text { million } \\
\text { Exports of goods and services (paid for in cash) } & 120 \\
\text { Imports of goods and services } & 140 \\
\text { Interest, profits and dividends received from ROW } & 30 \\
\text { Interest, profits and dividends paid to ROW } & 20 \\
\text { Export of goods on trade credit } & 40 \\
\text { Loans received from ROW } & 30 \\
\text { Capital balance } & -10 \\
\text { Net errors and omissions } & ? \\
\text { Increase in official reserves } & 20
\end{array}$Provide your answers to the questions below in £ millions. Use a positive rto indicate a surplus and a negative to identify a deficit.
Calculate the financial account balance.Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFinancial account balance:
$
\begin{aligned}
& =\quad \text { net inflow of investments and loans and flows to and from the reserves } \\
& =\quad-40+30-20 \\
& =\quad £ 30 \text { m deficit }
\end{aligned}
$Remember that an increase in official reserves means an increase in the supply of the country’s currency, ie a ‘negative’ in the financial account. Also trade credit is recorded as a negative item since it is effectively a loan to the purchasing countries, which enables them to buy the exported goods.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONFinancial account balance:
$
\begin{aligned}
& =\quad \text { net inflow of investments and loans and flows to and from the reserves } \\
& =\quad-40+30-20 \\
& =\quad £ 30 \text { m deficit }
\end{aligned}
$Remember that an increase in official reserves means an increase in the supply of the country’s currency, ie a ‘negative’ in the financial account. Also trade credit is recorded as a negative item since it is effectively a loan to the purchasing countries, which enables them to buy the exported goods.
-
Question 184 of 999CB2023773
Question 184
FlagYou are given the following data on Country E’s international transactions for the year 2018 with the rest of the world (ROW):
$\begin{array}{lc}
& £ \text { million } \\
\text { Exports of goods and services (paid for in cash) } & 120 \\
\text { Imports of goods and services } & 140 \\
\text { Interest, profits and dividends received from ROW } & 30 \\
\text { Interest, profits and dividends paid to ROW } & 20 \\
\text { Export of goods on trade credit } & 40 \\
\text { Loans received from ROW } & 30 \\
\text { Capital balance } & -10 \\
\text { Net errors and omissions } & ? \\
\text { Increase in official reserves } & 20
\end{array}$Provide your answers to the questions below in £ millions. Use a positive number to indicate a surplus and a negative to identify a deficit. V
Calculate the value of the net errors and omissions item.Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONUsing:
current account + capital account + financial account + net errors and omissions
$\begin{array}{ll}
& =0 \\
30-10-30+\text { net errors and omissions } & =0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad \text { Net errors and omissions } & =+£ 10 \mathrm{~m}
\end{array}$Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONUsing:
current account + capital account + financial account + net errors and omissions
$\begin{array}{ll}
& =0 \\
30-10-30+\text { net errors and omissions } & =0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad \text { Net errors and omissions } & =+£ 10 \mathrm{~m}
\end{array}$ -
Question 185 of 999CB2023774
Question 185
FlagAssume that the public holds all of its money in bank accounts, the banks’ liquidity ratio is 12.5% and the monetary base is $100 million.
You may find it useful to write down your answers for later use as you go through this case study.Calculate the money multiplier to the nearest whole number.
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe money multiplier, $m$, is equal to:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}
$where $r$ is the banks’ reserve (or liquidity) ratio and $c$ is the cash-to-deposits ratio, ie the cash held by the public outside the banking system, expressed as a proportion of their bank deposits. Initially $r=0.125$ and $c=0$.
The value of the money multiplier is:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}=\frac{1+0}{0.125+0}=8
$Alternatively, if the public holds all its money in bank accounts, the money multiplier, $m$, is the same as the bank deposits multiplier, $b$ :
\section*{Therefore:}
$$
m=b=\frac{1}{L}=\frac{1}{0.125}=8
$$
where $L=0.125$ is the banks’ reserve (or liquidity) ratio.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe money multiplier, $m$, is equal to:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}
$where $r$ is the banks’ reserve (or liquidity) ratio and $c$ is the cash-to-deposits ratio, ie the cash held by the public outside the banking system, expressed as a proportion of their bank deposits. Initially $r=0.125$ and $c=0$.
The value of the money multiplier is:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}=\frac{1+0}{0.125+0}=8
$Alternatively, if the public holds all its money in bank accounts, the money multiplier, $m$, is the same as the bank deposits multiplier, $b$ :
\section*{Therefore:}
$$
m=b=\frac{1}{L}=\frac{1}{0.125}=8
$$
where $L=0.125$ is the banks’ reserve (or liquidity) ratio. -
Question 186 of 999CB2023775
Question 186
FlagAssume that the public holds all of its money in bank accounts, the banks’ liquidity ratio is 12.5% and the monetary base is $100 million.
You may find it useful to write down your answers for later use as you go through this case study.Calculate the value of the broad money supply to the nearest $\$1$ million Give your answer in $\$$millions
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONUsing the definition ‘broad money supply $=$ monetary base $\times$ money multiplier’ we have:
$
\begin{aligned}
\text { broad money supply } & =100 \times 8 \\
& =\$ 800 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}
$Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONUsing the definition ‘broad money supply $=$ monetary base $\times$ money multiplier’ we have:
$
\begin{aligned}
\text { broad money supply } & =100 \times 8 \\
& =\$ 800 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}
$ -
Question 187 of 999CB2023776
Question 187
FlagAssume that the public holds all of its money in bank accounts, the banks’ liquidity ratio is 12.5% and the monetary base is $100 million.
You may find it useful to write down your answers for later use as you go through this case study.Suppose banks reduce their proportion of liquid reserves to deposits from 12.5% to 10%.
Calculate the revised value of the broad money supply to the nearest $\$1$ million. Give your answer in $\$$millions.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe value of the money multiplier is:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}=\frac{1+0}{0.10+0}=10
$and the revised value of the broad money supply:
$
\begin{aligned}
\text { broad money supply } & =100 \times 10 \\
& =\$ 1,000 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}
$Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe value of the money multiplier is:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}=\frac{1+0}{0.10+0}=10
$and the revised value of the broad money supply:
$
\begin{aligned}
\text { broad money supply } & =100 \times 10 \\
& =\$ 1,000 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}
$ -
Question 188 of 999CB2023777
Question 188
FlagAssume that the public holds all of its money in bank accounts, the banks’ liquidity ratio is 12.5% and the monetary base is $100 million.
You may find it useful to write down your answers for later use as you go through this case study.Suppose the public instead decide to hold cash equal in value to 20% of the value of their bank deposits, rather than deposit all their money in the banks.
Calculate the revised value of the broad money supply to the nearest $\$1$ million, assuming that the banks’ ratio of liquid reserves to deposits is still 10%. Give your answer in $\$$millions.Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe revised value of the money multiplier is:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}=\frac{1+0.20}{0.10+0.20}=4
$and the revised value of the broad money supply is:
$
4 \times 100=\$ 400 \mathrm{~m}
$Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe revised value of the money multiplier is:
$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}=\frac{1+0.20}{0.10+0.20}=4
$and the revised value of the broad money supply is:
$
4 \times 100=\$ 400 \mathrm{~m}
$ -
Question 189 of 999CB2023778
Question 189
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{The exogenous money supply } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{An increase in interest rates both } \\
\text{curve is vertical.} && \text{encourages banks to lend more }\\
&& \text{money for a given level of }\\
&&\text{liquidity and attracts additional }\\
&&\text{deposits from other countries, }\\
&&\text{and so leads to an increase in the }\\
&&\text{money supply.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONAn exogenous money supply, which is assumed to be determined solely by the authorities, is illustrated by a vertical money supply curve and so Statement 1 is true.
The endogenous money supply curve is upward sloping because an increase in interest rates:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ will typically increase banks’ profit margins (the differential between lending and borrowing rates) and encourage banks to lend more for a given level of liquidity
$\bullet$ $\quad$ may lead depositors to switch savings from liquid sight accounts to less liquid time accounts, enabling banks to operate with less liquidity
$\bullet$ $\quad$ may attract additional deposits from other countries, allowing banks to lend more.As the endogenous money supply curve typically slopes upwards (rather than being vertical), Statement 2 is also true. However, Statement 2 does not explain the Statement 1.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONAn exogenous money supply, which is assumed to be determined solely by the authorities, is illustrated by a vertical money supply curve and so Statement 1 is true.
The endogenous money supply curve is upward sloping because an increase in interest rates:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ will typically increase banks’ profit margins (the differential between lending and borrowing rates) and encourage banks to lend more for a given level of liquidity
$\bullet$ $\quad$ may lead depositors to switch savings from liquid sight accounts to less liquid time accounts, enabling banks to operate with less liquidity
$\bullet$ $\quad$ may attract additional deposits from other countries, allowing banks to lend more.As the endogenous money supply curve typically slopes upwards (rather than being vertical), Statement 2 is also true. However, Statement 2 does not explain the Statement 1.
-
Question 190 of 999CB2023779
Question 190
FlagWhich THREE of the following are likely effects of an increase in the money supply:
Correct
The correct answer is B, C & E.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the money supply is likely to cause a reduction in the domestic exchange rate.
This is for the following three reasons:
1. $\quad$ Part of the excess money balances will be spent on foreign assets, thereby increasing the supply of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange market.
2. $\quad$ Domestic interest rates will fall relative to foreign interest rates, causing a reduction in the demand for the domestic currency.
3. $\quad$ Speculators will expect the domestic currency to fall, so they will sell it and buy foreign currencies.The decrease in the exchange rate should then lead to an increase in exports, a decrease in imports and hence an improvement in the current account of the balance of payments.
The improvement in the current account of the balance of payments requires that export and import volumes are sufficiently elastic with respect to the value of the exchange rate, which is typically the case in practice. However, there may be a short-term worsening in the current account position before it ultimately improves, due to the J-curve effect.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B, C & E.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the money supply is likely to cause a reduction in the domestic exchange rate.
This is for the following three reasons:
1. $\quad$ Part of the excess money balances will be spent on foreign assets, thereby increasing the supply of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange market.
2. $\quad$ Domestic interest rates will fall relative to foreign interest rates, causing a reduction in the demand for the domestic currency.
3. $\quad$ Speculators will expect the domestic currency to fall, so they will sell it and buy foreign currencies.The decrease in the exchange rate should then lead to an increase in exports, a decrease in imports and hence an improvement in the current account of the balance of payments.
The improvement in the current account of the balance of payments requires that export and import volumes are sufficiently elastic with respect to the value of the exchange rate, which is typically the case in practice. However, there may be a short-term worsening in the current account position before it ultimately improves, due to the J-curve effect.
-
Question 191 of 999CB2023780
Question 191
FlagIf the government finances its public sector deficit by selling bonds to the non-bank private sector:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIf the public sector deficit is financed by sales of bonds to the non-bank private sector, there is no effect on the money supply because the money simply changes hands from those buying the bonds to those receiving money from the government.
To sell the bonds, the government will have to reduce the price of the bonds and hence increase the interest rates offered. The way in which the public sector deficit is financed has no immediate or direct effect on taxation.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIf the public sector deficit is financed by sales of bonds to the non-bank private sector, there is no effect on the money supply because the money simply changes hands from those buying the bonds to those receiving money from the government.
To sell the bonds, the government will have to reduce the price of the bonds and hence increase the interest rates offered. The way in which the public sector deficit is financed has no immediate or direct effect on taxation.
-
Question 192 of 999CB2023781
Question 192
FlagWhich of the following statements relating to the banking system are TRUE?
I $\quad$ Tulipmania is an example of a bank run and involved a large number of investors withdrawing their bank deposits in order to purchase tulips.
II $\quad$ Large banks with high levels of capital will not experience problems as a result of a run on another bank.
Ill $\quad$ Large banks are often required to hold additional capital as a systemic risk buffer.Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONTulipmania is an example of an asset bubble but not a run on the bank.
Large banks are often required to hold additional capital as a systemic risk buffer due to the risk of financial contagion they present. However, this additional capital doesn’t mean they will not experience problems as a result of a run on another bank.Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONTulipmania is an example of an asset bubble but not a run on the bank.
Large banks are often required to hold additional capital as a systemic risk buffer due to the risk of financial contagion they present. However, this additional capital doesn’t mean they will not experience problems as a result of a run on another bank. -
Question 193 of 999CB2023803
Question 193
FlagThe theory of surplus value was developed by:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAccording to Marx, surplus value was the value of the output workers have produced in excess of their own labour cost.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAccording to Marx, surplus value was the value of the output workers have produced in excess of their own labour cost.
-
Question 194 of 999CB2023804
Question 194
FlagWhich of the following statements is TRUE?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONIf aggregate demand exceeds actual output, then firms’ stocks will fall, as they are used up to meet the excess demand for goods and services over and above current actual output.
In addition, if aggregate demand exceeds actual output, then factor incomes will increase. This will lead to a further increase in expenditure in subsequent time periods, leading in turn to a further increase in income. The end result will be a multiplied increase in national income.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONIf aggregate demand exceeds actual output, then firms’ stocks will fall, as they are used up to meet the excess demand for goods and services over and above current actual output.
In addition, if aggregate demand exceeds actual output, then factor incomes will increase. This will lead to a further increase in expenditure in subsequent time periods, leading in turn to a further increase in income. The end result will be a multiplied increase in national income.
-
Question 195 of 999CB2023805
Question 195
FlagWhich one of the fol I owing will increase the size of the multiplier?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe multiplier can be written in terms of marginal propensities as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_{d}}=\frac{1}{m p w}=\frac{1}{m p s+m p t+m p m}
$$Hence, it can be seen that the multiplier will increase as a result of an increase in the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods, or equivalently, as a result of a decrease in any of the marginal propensities to withdraw expenditure from the circular flow of income (ie savings, taxes or imports).
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe multiplier can be written in terms of marginal propensities as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_{d}}=\frac{1}{m p w}=\frac{1}{m p s+m p t+m p m}
$$Hence, it can be seen that the multiplier will increase as a result of an increase in the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods, or equivalently, as a result of a decrease in any of the marginal propensities to withdraw expenditure from the circular flow of income (ie savings, taxes or imports).
-
Question 196 of 999CB2023806
Question 196
FlagCorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe inflationary gap is defined as the amount by which aggregate demand (or aggregate expenditure) exceeds national income (or output) at the full-employment level of national income (or output). The recessionary or deflationary gap is defined as the amount by which aggregate demand is deficient (ie is less than national income) at the full-employment level of national income.
At the full-employment level of income $Y_{F}$, the level of aggregate demand or aggregate expenditure $E$ exceeds the level of national income by $a b$, so this must be an inflationary gap.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe inflationary gap is defined as the amount by which aggregate demand (or aggregate expenditure) exceeds national income (or output) at the full-employment level of national income (or output). The recessionary or deflationary gap is defined as the amount by which aggregate demand is deficient (ie is less than national income) at the full-employment level of national income.
At the full-employment level of income $Y_{F}$, the level of aggregate demand or aggregate expenditure $E$ exceeds the level of national income by $a b$, so this must be an inflationary gap.
-
Question 197 of 999CB2023807
Question 197
FlagThe quantity theory of money assumes that the:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe quantity theory of money is based on the equation of exchange, ie $M V=P Y$. The theory assumes that real output ( $Y$ ) and the velocity of circulation $(V)$ are constant, therefore the ratio of the money supply $(M)$ to the price level $(P)$ is fixed.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe quantity theory of money is based on the equation of exchange, ie $M V=P Y$. The theory assumes that real output ( $Y$ ) and the velocity of circulation $(V)$ are constant, therefore the ratio of the money supply $(M)$ to the price level $(P)$ is fixed.
-
Question 198 of 999CB2023808
Question 198
FlagUnder the gold standard:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONUnder the gold standard, currencies were fixed in terms of a certain weight of gold and therefore with each other. If a country experienced an increase in imports causing a balance of payments deficit, it would be paid for in gold from its reserves (hence the correct answer) and there would be an outflow of gold (not an inflow). Similarly, an increase in prices would make exports less competitive and imports more competitive, so would cause an outflow of gold (not an inflow).
The domestic money supply was backed by gold, so an outflow of gold would also lead to a fall in the money supply. As a result of the quantity theory of money, it was believed that if the money supply fell, prices would fall to restore competitiveness (so there was a relationship between the two).
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONUnder the gold standard, currencies were fixed in terms of a certain weight of gold and therefore with each other. If a country experienced an increase in imports causing a balance of payments deficit, it would be paid for in gold from its reserves (hence the correct answer) and there would be an outflow of gold (not an inflow). Similarly, an increase in prices would make exports less competitive and imports more competitive, so would cause an outflow of gold (not an inflow).
The domestic money supply was backed by gold, so an outflow of gold would also lead to a fall in the money supply. As a result of the quantity theory of money, it was believed that if the money supply fell, prices would fall to restore competitiveness (so there was a relationship between the two).
-
Question 199 of 999CB2023809
Question 199
FlagIn the following diagram the initial equilibrium real wage is $w_1$ and the equilibrium level of employment is $Q_1$.
According to the classical economists, a decrease in aggregate demand in the goods market will:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAccording to the classical model, the decrease in aggregate demand in the goods market will shift the $A D$ curve to the left and the price level will fall in the short run. As a’result, the real wage will rise above $w_{1}$. For example, if it rose to $w_{2}$, there would be a movement along the demand and supply curves for labour resulting in an excess supply of labour of $c-b$. In the long run, wages are assumed to be fully flexible, so nominal wages would fall so that real wages return to the original equilibrium of $w_{1}$. Hence the correct option and hence the option ‘increase the real wage to $w_{2}$ and…in the long run’ is not correct.
In the classical model, the outcome described in the option ‘decrease the demand for labour…, unemployment to $i-h^{\prime}$ would occur if there was an exogenous reduction in the demand for labour, eg if there was a decrease in the productivity of labour, (rather than a change in prices causing a change in the real wage rate).
The option ‘decrease the demand for labour… unemployment of $f-e$ ‘ describes the Keynesian view of the effect of a decrease in aggregate demand. The decrease in aggregate demand leads to a decrease in output (not prices) in the goods market. With unchanged prices and wages, real wages are unchanged. The decrease in demand for goods with unchanged real wages results in a shift of the demand curve for labour to the left, resulting in demand-deficient unemployment of $f-e$ to add to the equilibrium unemployment of $g-f$.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAccording to the classical model, the decrease in aggregate demand in the goods market will shift the $A D$ curve to the left and the price level will fall in the short run. As a’result, the real wage will rise above $w_{1}$. For example, if it rose to $w_{2}$, there would be a movement along the demand and supply curves for labour resulting in an excess supply of labour of $c-b$. In the long run, wages are assumed to be fully flexible, so nominal wages would fall so that real wages return to the original equilibrium of $w_{1}$. Hence the correct option and hence the option ‘increase the real wage to $w_{2}$ and…in the long run’ is not correct.
In the classical model, the outcome described in the option ‘decrease the demand for labour…, unemployment to $i-h^{\prime}$ would occur if there was an exogenous reduction in the demand for labour, eg if there was a decrease in the productivity of labour, (rather than a change in prices causing a change in the real wage rate).
The option ‘decrease the demand for labour… unemployment of $f-e$ ‘ describes the Keynesian view of the effect of a decrease in aggregate demand. The decrease in aggregate demand leads to a decrease in output (not prices) in the goods market. With unchanged prices and wages, real wages are unchanged. The decrease in demand for goods with unchanged real wages results in a shift of the demand curve for labour to the left, resulting in demand-deficient unemployment of $f-e$ to add to the equilibrium unemployment of $g-f$.
-
Question 200 of 999CB2023810
Question 200
FlagAn increase in the money supply will have a bigger impact on real output the more:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the money supply will decrease interest rates and the fall in interest rates will increase investment (and aggregate demand and therefore output). An increase in the money supply will have a greater effect on real output the further interest rates fall and the more investment rises in response to the fall in interest rates.
Interest rates will fall further the more interest-inelastic the demand for money (ie the steeper the money demand curve) since a greater drop is needed to encourage people to hold more money. (Try drawing the money market diagram to illustrate this.) The more interest-elastic the demand for investment the greater the increase in investment in response to the fall in interest rates.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the money supply will decrease interest rates and the fall in interest rates will increase investment (and aggregate demand and therefore output). An increase in the money supply will have a greater effect on real output the further interest rates fall and the more investment rises in response to the fall in interest rates.
Interest rates will fall further the more interest-inelastic the demand for money (ie the steeper the money demand curve) since a greater drop is needed to encourage people to hold more money. (Try drawing the money market diagram to illustrate this.) The more interest-elastic the demand for investment the greater the increase in investment in response to the fall in interest rates.
-
Question 201 of 999CB2023811
Question 201
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a ‘crowding out” effect resulting from a fiscal expansion?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCrowding out is a reduction in private sector expenditure following an increase in government borrowing. The main mechanism for this is an increase in interest rates, which is an element of all three of the other options.
The option ‘reduced import expenditure due to increased government demand for domestically produced goods’ appears to make little sense. What we can say about it is that a reduction in import expenditure cannot be a crowding-out effect. To offset an increase in government expenditure we should be looking for a reduction in net exports.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONCrowding out is a reduction in private sector expenditure following an increase in government borrowing. The main mechanism for this is an increase in interest rates, which is an element of all three of the other options.
The option ‘reduced import expenditure due to increased government demand for domestically produced goods’ appears to make little sense. What we can say about it is that a reduction in import expenditure cannot be a crowding-out effect. To offset an increase in government expenditure we should be looking for a reduction in net exports.
-
Question 202 of 999CB2023812
Question 202
FlagOther things remaining the same, the result of moving from a balanced budget to a budget surplus that the government uses to buy back debt from the non-bank private sector, is:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA budget surplus occurs when tax receipts are greater thân government spending, so there will be a net reduction of aggregate demand into the circular flow of income. Thus, there is a multiplied decrease in the level of national income associated with each given interest rate in the market for goods and services. Hence, the IS curve will shift to the left.
The fall in national income will reduce inflationary pressures in the economy, and so the central bank would be likely to reduce interest rates, ie moving down the MP curve. Therefore the equilibrium level of short-term interest rates will decrease – as will equilibrium national income.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA budget surplus occurs when tax receipts are greater thân government spending, so there will be a net reduction of aggregate demand into the circular flow of income. Thus, there is a multiplied decrease in the level of national income associated with each given interest rate in the market for goods and services. Hence, the IS curve will shift to the left.
The fall in national income will reduce inflationary pressures in the economy, and so the central bank would be likely to reduce interest rates, ie moving down the MP curve. Therefore the equilibrium level of short-term interest rates will decrease – as will equilibrium national income.
-
Question 203 of 999CB2023813
Question 203
FlagThe following case study information, regarding the economy of country X:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods out of national income is 0.6
$\bullet$ $\quad$ tax is raised at a fixed rate of $10 \%$ of all income
$\bullet$ $\quad$ imports are a fixed $20 \%$ of income
$\bullet$ $\quad$ autonomous (or exogenous) consumption $=\$ 5,000$
$\bullet$ $\quad$ investment $=\$ 10,000$
$\bullet$ $\quad$ government spending $=\$ 10,000$
$\bullet$ $\quad$ exports $=\$ 25,000$The withdrawals function is of the form $W=a+b Y$, where $Y$ is national income. Which of the following is the correct withdrawals function?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONSince $Y=C_{d}+W$, then:
$
W=Y-C_{d}
$$
C_{d}=5,000+0.6 Y
$Therefore:
$
\begin{aligned}
W & =Y-(5,000+0.6 Y) \\
& =-5,000+0.4 Y
\end{aligned}
$Alternatively:
Since $W=S+T+M$ and we are given that for Country $X T=0.1 Y$ and $M=0.2 Y$, then:$
\begin{aligned}
S & =Y-C_{d}-T-M \\
& =Y-(5,000+0.6 Y)-0.1 Y-0.2 Y \\
& =-5,000+0.1 Y
\end{aligned}
$So $W=S+T+M=-5,000+0.1 Y+0.1 Y+0.2 Y=-5,000+0.4 Y$
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONSince $Y=C_{d}+W$, then:
$
W=Y-C_{d}
$$
C_{d}=5,000+0.6 Y
$Therefore:
$
\begin{aligned}
W & =Y-(5,000+0.6 Y) \\
& =-5,000+0.4 Y
\end{aligned}
$Alternatively:
Since $W=S+T+M$ and we are given that for Country $X T=0.1 Y$ and $M=0.2 Y$, then:$
\begin{aligned}
S & =Y-C_{d}-T-M \\
& =Y-(5,000+0.6 Y)-0.1 Y-0.2 Y \\
& =-5,000+0.1 Y
\end{aligned}
$So $W=S+T+M=-5,000+0.1 Y+0.1 Y+0.2 Y=-5,000+0.4 Y$
-
Question 204 of 999CB2023814
Question 204
FlagWhich THREE of the following are likely to be caused by an increase in the money supply?
Correct
The correct answer is A, D & F.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the money supply will lead to a decrease in interest rates. A decrease in interest rates is likely to cause an increase in borrowing and a decrease in savings, therefore consumption and investment are both likely to increase.
A decrease in interest rates will make saving in the domestic economy less attractive and hot money will flow out of the country resulting in a decrease in the value of the currency. The decrease in the value of the currency will make exports cheaper and imports dearer, leading to a likely increase in the demand for exports and decrease in the demand for imports. Assuming sufficiently elastic export and import elasticities, net exports will increase.
The increase in consumption, investment and net exports will increase aggregate demand which will tend to increase output and/or prices.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A, D & F.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in the money supply will lead to a decrease in interest rates. A decrease in interest rates is likely to cause an increase in borrowing and a decrease in savings, therefore consumption and investment are both likely to increase.
A decrease in interest rates will make saving in the domestic economy less attractive and hot money will flow out of the country resulting in a decrease in the value of the currency. The decrease in the value of the currency will make exports cheaper and imports dearer, leading to a likely increase in the demand for exports and decrease in the demand for imports. Assuming sufficiently elastic export and import elasticities, net exports will increase.
The increase in consumption, investment and net exports will increase aggregate demand which will tend to increase output and/or prices.
-
Question 205 of 999CB2023815
Question 205
FlagIn a free market, the belief that price adjustments will balance supply and demand and clear the markets is most consistent with the views of:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThis is bookwork covered in the additional Core Reading.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThis is bookwork covered in the additional Core Reading.
-
Question 206 of 999CB2023816
Question 206
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{According to Keynesian } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{Under the gold standard, any } \\
\text{economists, an economy will be } && \text{trade deficit or surplus will be }\\
\text{in equilibrium as long as the } && \text{eliminated by movements in the }\\
\text{government were to balance its } &&\text{exchange rate.}\\
\text{budget.} &&\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is E.
EXPLANATIONIt is classical economists who believe that an economy will be in equilibrium as long as the government were to balance its budget, so the assertion is false.
This classical view that the economy will be in equilibrium as long as the government balances its budget is based on the following two beliefs:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ movements in interest rates will clear the market for loanable funds and so ensure that savings equal investments ( $S=I$ )
$\bullet$ $\quad$ movements in the relative prices of exports and imports will ensure that the value of exports equals the value of imports $(X=M)$.Thus, according to classical economists, since $S=I$ and $X=M$, if governments balance their budgets by setting government spending equal to taxation revenues ( $G=T$ ), then the withdrawals $(S, T, M)$ will equal injections ( $I, G, X)$, and hence the economy will be in equilibrium.
The reason is also false since trade deficits or surpluses will be eliminated by movements in relative export and import prices, rather than the exchange rate.
Incorrect
The correct answer is E.
EXPLANATIONIt is classical economists who believe that an economy will be in equilibrium as long as the government were to balance its budget, so the assertion is false.
This classical view that the economy will be in equilibrium as long as the government balances its budget is based on the following two beliefs:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ movements in interest rates will clear the market for loanable funds and so ensure that savings equal investments ( $S=I$ )
$\bullet$ $\quad$ movements in the relative prices of exports and imports will ensure that the value of exports equals the value of imports $(X=M)$.Thus, according to classical economists, since $S=I$ and $X=M$, if governments balance their budgets by setting government spending equal to taxation revenues ( $G=T$ ), then the withdrawals $(S, T, M)$ will equal injections ( $I, G, X)$, and hence the economy will be in equilibrium.
The reason is also false since trade deficits or surpluses will be eliminated by movements in relative export and import prices, rather than the exchange rate.
-
Question 207 of 999CB2023817
Question 207
FlagA country has experienced a year of unexpected price rises, decreases in aggregate demand and increases in unemployment. Match the possible economic changes to the theories / hypotheses.
I $\quad$ adaptative expectations hypothesis
II $\quad$ natural rate hypothesis
III $\quad$ rational expectations
IV $\quad$ misperceptions theory
V $\quad$ efficiency wage hypothesisA $\quad$ Unemployment returns to a long-term rate that is determined by supply-side factors.
B $\quad$ People revise up their estimate of future inflation.
C $\quad$ People adjust their working and spending habits according to nominal price and wage changes only.
D $\quad$ People might revise up or down their estimate of future inflation.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA – II, B-I, C-IV, D-III.
The adaptive expectations hypothesis is that people base their expectations of inflation on past inflation rates, so following a period of higher than expected inflation, people will revise up their inflation expectation for the following year.The natural rate hypothesis is that following a change in aggregate demand, unemployment will return to a natural rate, and that rate is determined by supply-side factors, such as labour mobility.
Rational expectations are expectations based on the current situation and the information that people have to hand, so higher than expected inflation over the last year does not necessarily mean people will revise up their inflation expectation for the following year. Instead, it could be revised up or down depending on the latest information available regarding future prospects.
Misperceptions theory is the theory that changes in economic activity are caused by people confusing changes in general prices with changes in relative prices. This idea can be applied to real and nominal wages, eg workers respond to the size of the change in nominal wages only despite inflation being high.
The efficiency wage hypothesis is the hypothesis that the productivity of workers is affected by the wage rate that they receive and does not correspond to any of the changes provided.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA – II, B-I, C-IV, D-III.
The adaptive expectations hypothesis is that people base their expectations of inflation on past inflation rates, so following a period of higher than expected inflation, people will revise up their inflation expectation for the following year.The natural rate hypothesis is that following a change in aggregate demand, unemployment will return to a natural rate, and that rate is determined by supply-side factors, such as labour mobility.
Rational expectations are expectations based on the current situation and the information that people have to hand, so higher than expected inflation over the last year does not necessarily mean people will revise up their inflation expectation for the following year. Instead, it could be revised up or down depending on the latest information available regarding future prospects.
Misperceptions theory is the theory that changes in economic activity are caused by people confusing changes in general prices with changes in relative prices. This idea can be applied to real and nominal wages, eg workers respond to the size of the change in nominal wages only despite inflation being high.
The efficiency wage hypothesis is the hypothesis that the productivity of workers is affected by the wage rate that they receive and does not correspond to any of the changes provided.
-
Question 208 of 999CB2023818
Question 208
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{Following an increase in demand, } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{If the demand curve is relatively } \\
\text{it is sometimes in a firm’s interest } && \text{price elastic, a price increase will }\\
\text{not to increase the price it } && \text{lead to a relatively large loss of }\\
\text{charges, even if this means } &&\text{sales.}\\
\text{producing at a point where } &&\\
\text{marginal revenue does not equal } &&\\
\text{marginal cost.} &&\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe profit-maximising condition for any firm is $M R=M C$. However, when deciding whether to change prices when demand changes, a firm should also consider the costs of changing prices. These costs are known as menu costs and include the physical cost of updating price lists as well as the costs of deciding what the new prices will be and negotiating new contracts. The firm may decide that the menu costs outweigh the benefit from changing prices, and so will continue to charge the current price rather than update to the new profit-maximising position.
It is true that when prices rise, a more elastic demand curve will result in a larger loss of sales than a less elastic demand curve, so the reason is true. However, it doesn’t explain the assertion, because although a reduction in demand (and the subsequent reduction in quantity and increase in price) might lead to a loss of revenue, it might also lead to a reduction in costs. In the absence of menu costs, a price increase to the level that is consistent with marginal revenue equals marginal cost would increase a firm’s profits, and this is true irrelevant of price elasticity of demand. So it is the presence of menu costs, not a relatively price-elastic demand, that explains the assertion.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe profit-maximising condition for any firm is $M R=M C$. However, when deciding whether to change prices when demand changes, a firm should also consider the costs of changing prices. These costs are known as menu costs and include the physical cost of updating price lists as well as the costs of deciding what the new prices will be and negotiating new contracts. The firm may decide that the menu costs outweigh the benefit from changing prices, and so will continue to charge the current price rather than update to the new profit-maximising position.
It is true that when prices rise, a more elastic demand curve will result in a larger loss of sales than a less elastic demand curve, so the reason is true. However, it doesn’t explain the assertion, because although a reduction in demand (and the subsequent reduction in quantity and increase in price) might lead to a loss of revenue, it might also lead to a reduction in costs. In the absence of menu costs, a price increase to the level that is consistent with marginal revenue equals marginal cost would increase a firm’s profits, and this is true irrelevant of price elasticity of demand. So it is the presence of menu costs, not a relatively price-elastic demand, that explains the assertion.
-
Question 209 of 999CB2023819
Question 209
FlagConsumption smoothing may be explained by:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONConsumption smoothing occurs when consumption is less volatile than disposable incomes. For example, in a boom, when business is good, workers might save some of their increased income for times that are not so good. Similarly, in a recession, those made redundant might use their savings to support their lifestyle – in the short run, at least. Alternatively, they might borrow in anticipation of higher income in the future.
If banks are more willing to lend in a boom, this adds to the increase in consumption that would be expected in a boom and therefore amplifies the boom.
The fact that spending is influenced by wealth could cause consumption smoothing as consumption could be maintained in times of falling disposable incomes but stable asset values. However, as the value of wealth tends to vary with the business cycle, this exacerbates the consumption cycle rather than smooths it. For example, in a boom, debt increases to finance the purchase of more assets, and with these assets, people feel more confident about spending. However, once asset prices begin to fall, confidence falls and households restore their financial well-being by reducing debt, increasing savings and cutting consumption.
Credit-constrained households are households that are limited in their ability to borrow against expected future incomes. An increase in this type of household limits consumption smoothing and means that the growth of consumptign is more dependent on the growth in current incomes.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONConsumption smoothing occurs when consumption is less volatile than disposable incomes. For example, in a boom, when business is good, workers might save some of their increased income for times that are not so good. Similarly, in a recession, those made redundant might use their savings to support their lifestyle – in the short run, at least. Alternatively, they might borrow in anticipation of higher income in the future.
If banks are more willing to lend in a boom, this adds to the increase in consumption that would be expected in a boom and therefore amplifies the boom.
The fact that spending is influenced by wealth could cause consumption smoothing as consumption could be maintained in times of falling disposable incomes but stable asset values. However, as the value of wealth tends to vary with the business cycle, this exacerbates the consumption cycle rather than smooths it. For example, in a boom, debt increases to finance the purchase of more assets, and with these assets, people feel more confident about spending. However, once asset prices begin to fall, confidence falls and households restore their financial well-being by reducing debt, increasing savings and cutting consumption.
Credit-constrained households are households that are limited in their ability to borrow against expected future incomes. An increase in this type of household limits consumption smoothing and means that the growth of consumptign is more dependent on the growth in current incomes.
-
Question 210 of 999CB2023837
Question 210
FlagAssume that the actual rate of unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment because the expected rate of inflation is below the actual rate of inflation. If the expected rate of inflation rises to equal the actual rate of inflation, then:
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThis question describes a situation where actual unemployment is below its natural rate and actual inflation is above the expected level implied by the initial expectations-augmented Phillips curve.
This is represented by position B in the diagram. (The economy is initially at a point on an expectations-augmented Phillips curve to the left of the vertical long-run Phillips curve – perhaps because the government has recently increased the rate of monetary growth (so causing a movement from $A$ to $B$ ) and expectations have yet to fully adjust.)
As expectations of inflation are revised upwards in the light of experience, the expectationsaugmented Phillips curve will shift upwards. Real wages will increase as workers negotiate new wage agreements. Firms’ costs increase and output falls. The economy returns to the long-run vertical Phillips curve (from $B$ to $C$ ) and unemployment returns to its higher natural rate.
In the short run, if real output increases, unemployment will generally decrease and vice versa.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONThis question describes a situation where actual unemployment is below its natural rate and actual inflation is above the expected level implied by the initial expectations-augmented Phillips curve.
This is represented by position B in the diagram. (The economy is initially at a point on an expectations-augmented Phillips curve to the left of the vertical long-run Phillips curve – perhaps because the government has recently increased the rate of monetary growth (so causing a movement from $A$ to $B$ ) and expectations have yet to fully adjust.)
As expectations of inflation are revised upwards in the light of experience, the expectationsaugmented Phillips curve will shift upwards. Real wages will increase as workers negotiate new wage agreements. Firms’ costs increase and output falls. The economy returns to the long-run vertical Phillips curve (from $B$ to $C$ ) and unemployment returns to its higher natural rate.
In the short run, if real output increases, unemployment will generally decrease and vice versa.
-
Question 211 of 999CB2023838
Question 211
FlagWhich of the following factors could lead to an upward shift in the expectations-augmented Phillips curve?
I $\quad$ an increase in expected inflation
II $\quad$ an increase in actual inflation
III $\quad$ an increase in demand-deficient unemploymentCorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe expectations-augmented Phillipscurve models actual price inflation ( $\pi$ ) as a function of:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the inverse of the unemployment rate $(U)$, as higher aggregate demand leads to higher inflation and lower unemployment
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the expected rate of inflation ( $\pi^{e}$ ), which is determined using adaptive expectations (ie it reflects past inflation rates)
$\bullet$ $\quad$ exogenous (ie non-demand-related) cost-push inflation ( $k$ ) due to factors such as commodity price increases.Its equation is:
$
\quad \quad \pi=f(1 / U)+\pi^{e}+k
$Consequently, it will shift upwards if expectations of inflation increase (Option I) and also if actual inflation increases due to cost-push pressures, eg due to a rise in commodity prices (Option II). (An increase in actual inflation could also arise from an increase in aggregate demand. This would lead to a movement along the Phillips curve upwards to the left.)
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve slopes downwards because demand-pull inflation and demand-deficient unemployment are inversely related. Consequently, an increase in demanddeficient unemployment is associated with a fall in demand-pull inflation and a movement downwards along the curve, not a shift of the curve.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe expectations-augmented Phillipscurve models actual price inflation ( $\pi$ ) as a function of:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the inverse of the unemployment rate $(U)$, as higher aggregate demand leads to higher inflation and lower unemployment
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the expected rate of inflation ( $\pi^{e}$ ), which is determined using adaptive expectations (ie it reflects past inflation rates)
$\bullet$ $\quad$ exogenous (ie non-demand-related) cost-push inflation ( $k$ ) due to factors such as commodity price increases.Its equation is:
$
\quad \quad \pi=f(1 / U)+\pi^{e}+k
$Consequently, it will shift upwards if expectations of inflation increase (Option I) and also if actual inflation increases due to cost-push pressures, eg due to a rise in commodity prices (Option II). (An increase in actual inflation could also arise from an increase in aggregate demand. This would lead to a movement along the Phillips curve upwards to the left.)
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve slopes downwards because demand-pull inflation and demand-deficient unemployment are inversely related. Consequently, an increase in demanddeficient unemployment is associated with a fall in demand-pull inflation and a movement downwards along the curve, not a shift of the curve.
-
Question 212 of 999CB2023839
Question 212
FlagWhich of the following statements is NOT true?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONA fall in structural unemployment, and hence in equilibrium unemployment, will shift the Phillips curve to the left and not the right.
Clockwise Phillips loops can be used to explain the existence of stagflation, ie periods when both unemployment and inflation are rising.
The adaptive expectations hypothesis suggests that expected inflation is based on past inflation. So, it will over-estimate inflation when inflation is consistently falling and likewise únder-estimate inflation when inflation is consistently rising.
The vertical long-run Phillips curve suggests that ultimately unemploymentwill always revert to its natural rate. Consequently, whilst a deflationary policy to reduce inflation will increase unemployment in the short run, there will be no long-term increase in unemployment.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONA fall in structural unemployment, and hence in equilibrium unemployment, will shift the Phillips curve to the left and not the right.
Clockwise Phillips loops can be used to explain the existence of stagflation, ie periods when both unemployment and inflation are rising.
The adaptive expectations hypothesis suggests that expected inflation is based on past inflation. So, it will over-estimate inflation when inflation is consistently falling and likewise únder-estimate inflation when inflation is consistently rising.
The vertical long-run Phillips curve suggests that ultimately unemploymentwill always revert to its natural rate. Consequently, whilst a deflationary policy to reduce inflation will increase unemployment in the short run, there will be no long-term increase in unemployment.
-
Question 213 of 999CB2023840
Question 213
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a reason why the power of labour has reduced?
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONNationally negotiated wage contracts tend to increase the power of labour because the entire workforce can take action to increase wages.
Conversely, locally negotiated wage contracts decrease the power of labour as each region is in competition for work. Local unions have less bargaining power than national unions.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONNationally negotiated wage contracts tend to increase the power of labour because the entire workforce can take action to increase wages.
Conversely, locally negotiated wage contracts decrease the power of labour as each region is in competition for work. Local unions have less bargaining power than national unions.
-
Question 214 of 999CB2023841
Question 214
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an interventionist supply-side policy?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe use of public-private partnerships is an example of a market-orientated supply-side policy since it is a way of funding public projects, such as new roads or hospitals, with private capital, following a competitive tendering process. The government pays the private company to run or maintain the facility, or pays it rent for the asset.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe use of public-private partnerships is an example of a market-orientated supply-side policy since it is a way of funding public projects, such as new roads or hospitals, with private capital, following a competitive tendering process. The government pays the private company to run or maintain the facility, or pays it rent for the asset.
-
Question 215 of 999CB2023842
Question 215
FlagAn increase in government spending has:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in government spending, eg on the health service, results in an immediate and direct increase in spending / aggregate demand. This will then be subject to a multiplier effect as part of the new income received by nurses, doctors, pharmaceutical companies etc is spent on domestically produced goods.
However, if the same amount were given in tax cuts, some of the increase in disposable income would be saved and some would be spent on imported goods, so the initial increase in spending (and hence income) would be less than the value of the tax cuts.
Consequently, the tax multiplier is smaller than the government spending multiplier.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in government spending, eg on the health service, results in an immediate and direct increase in spending / aggregate demand. This will then be subject to a multiplier effect as part of the new income received by nurses, doctors, pharmaceutical companies etc is spent on domestically produced goods.
However, if the same amount were given in tax cuts, some of the increase in disposable income would be saved and some would be spent on imported goods, so the initial increase in spending (and hence income) would be less than the value of the tax cuts.
Consequently, the tax multiplier is smaller than the government spending multiplier.
-
Question 216 of 999CB2023843
Question 216
FlagA government wishing to increase aggregate demand might use any of the following measures EXCEPT;
Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIncreasing the tax on consumer goods effectively increases their price to the consumer and is therefore likely to reduce the demand for such goods. Each of the other options will, however, increase aggregate demand.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONIncreasing the tax on consumer goods effectively increases their price to the consumer and is therefore likely to reduce the demand for such goods. Each of the other options will, however, increase aggregate demand.
-
Question 217 of 999CB2023844
Question 217
FlagThe payment of wages to refuse collectors is categorised as both:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONCurrent expenditure refers to the operational expenditures of the public sector, including the wages of public sector staff and the payment of welfare benefits. It therefore includes the payment of wages to refuse collectors.
Capital expenditure refers to spending on public sector investments, eg on new school buildings or transport infrastructure.
Final expenditure is public sector spending on the goods and services that are consumed to meet the needs of firms and/or households, including refuse collections. It therefore includes the payment of wages to refuse collectors for their services.
Transfers refers to transfers of money from taxpayers to the recipients of benefits and subsidies.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONCurrent expenditure refers to the operational expenditures of the public sector, including the wages of public sector staff and the payment of welfare benefits. It therefore includes the payment of wages to refuse collectors.
Capital expenditure refers to spending on public sector investments, eg on new school buildings or transport infrastructure.
Final expenditure is public sector spending on the goods and services that are consumed to meet the needs of firms and/or households, including refuse collections. It therefore includes the payment of wages to refuse collectors for their services.
Transfers refers to transfers of money from taxpayers to the recipients of benefits and subsidies.
-
Question 218 of 999CB2023845
Question 218
FlagWhich THREE of the following statements relating to unemployment hysteresis are TRUE?
Correct
The correct answer is B, C, E.
EXPLANATIONHysteresis is the persistence of unemployment even when the initial demand deficiency that caused it no longer exists, ie the economy fails to ‘spring back’.
According to the new classical group of economists, this should not happen because when a recession occurs in an economy, there is a self-righting mechanism to spring the economy quickly back to its potential level of output.
The mechanism is as follows:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ a fall in aggregate demand leads to a fall in the price level, so real wages rise
$\bullet$ $\quad$ a rise in real wages causes disequilibrium unemployment
$\bullet$ $\quad$ this results in a fall in nominal wages, which causes real wages to fall back to the equilibrium rate and the level of employment to return to its natural rate.Assuming continuous market clearing and rational expectations, new classical economists believe this will happen virtually instantaneously.
Keynesian economists believe that prices and wages tend to be inflexible, and consequently hysteresis is likely.
Keynesians believe that a recession is likely to cause a rise in unemployment that is unlikely to be corrected automatically. This is because they believe that in a recession:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the decrease in aggregate demand will lead to a decrease in output (rather than prices) … … and therefore a decrease in the demand for labour, which causesdemand-deficient or disequilibrium unemployment
$\bullet$ $\quad$ real wages do not fall quickly, and therefore this unemployment persists.In addition, there is a danger that a long recession will cause hysteresis to occur, ie unemployment will persist even if aggregate demand eventually rises. This is because:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the stock of human capital will be reduced as long-term unemployment reduces skills, confidence and motivation
$\bullet$ $\quad$ in an attempt to cut costs in a recession, firms will cut training and investment, which leads to lower productivity
$\bullet$ $\quad$ industrial capital that lies idle in a recession might be impossible or unattractive to re-use when the recovery comes.This means that the potential output of the economy is reduced, and the equilibrium or natural level of unemployment is increased.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B, C, E.
EXPLANATIONHysteresis is the persistence of unemployment even when the initial demand deficiency that caused it no longer exists, ie the economy fails to ‘spring back’.
According to the new classical group of economists, this should not happen because when a recession occurs in an economy, there is a self-righting mechanism to spring the economy quickly back to its potential level of output.
The mechanism is as follows:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ a fall in aggregate demand leads to a fall in the price level, so real wages rise
$\bullet$ $\quad$ a rise in real wages causes disequilibrium unemployment
$\bullet$ $\quad$ this results in a fall in nominal wages, which causes real wages to fall back to the equilibrium rate and the level of employment to return to its natural rate.Assuming continuous market clearing and rational expectations, new classical economists believe this will happen virtually instantaneously.
Keynesian economists believe that prices and wages tend to be inflexible, and consequently hysteresis is likely.
Keynesians believe that a recession is likely to cause a rise in unemployment that is unlikely to be corrected automatically. This is because they believe that in a recession:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the decrease in aggregate demand will lead to a decrease in output (rather than prices) … … and therefore a decrease in the demand for labour, which causesdemand-deficient or disequilibrium unemployment
$\bullet$ $\quad$ real wages do not fall quickly, and therefore this unemployment persists.In addition, there is a danger that a long recession will cause hysteresis to occur, ie unemployment will persist even if aggregate demand eventually rises. This is because:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ the stock of human capital will be reduced as long-term unemployment reduces skills, confidence and motivation
$\bullet$ $\quad$ in an attempt to cut costs in a recession, firms will cut training and investment, which leads to lower productivity
$\bullet$ $\quad$ industrial capital that lies idle in a recession might be impossible or unattractive to re-use when the recovery comes.This means that the potential output of the economy is reduced, and the equilibrium or natural level of unemployment is increased.
-
Question 219 of 999CB2023846
Question 219
FlagWhich TWO of the following statements relating to approaches to demand- and supply-side policies are TRUE?
Correct
The correct answer is B & C.
EXPLANATIONAccording to the new classical economists, demand-side monetary policy is effective at controlling inflation, however, it is not an effective way to increase growth and reduce unemployment. New classical economists argue that supply-side policies should be used to achieve these objectives and increase potential output, and they favour market-orientated supply-side policies.
According to Keynesian economists, demand-side policies should be used to increase aggregate demand in a recession, so as to increase actual output and to reduce (demand-deficient) unemployment.
Modern Keynesians agree that supply-side policy should be used to increase potential output and to reduce equilibrium unemployment over the long term, however, they favour interventionist supply-side policies.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B & C.
EXPLANATIONAccording to the new classical economists, demand-side monetary policy is effective at controlling inflation, however, it is not an effective way to increase growth and reduce unemployment. New classical economists argue that supply-side policies should be used to achieve these objectives and increase potential output, and they favour market-orientated supply-side policies.
According to Keynesian economists, demand-side policies should be used to increase aggregate demand in a recession, so as to increase actual output and to reduce (demand-deficient) unemployment.
Modern Keynesians agree that supply-side policy should be used to increase potential output and to reduce equilibrium unemployment over the long term, however, they favour interventionist supply-side policies.
-
Question 220 of 999CB2023847
Question 220
FlagWhich of the following statements are TRUE according to real business cycle theory?
I $\quad$ Technology shocks have little effect on long-term economic growth.
II $\quad$ The theory supports monetary policy as an effective tool to manage output.
III $\quad$ Agents are assumed to form expectations rationally.Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONReal business cycle theory is a new classical theory that assumes rational expectations and continuous market clearing.
It draws no distinction between business cycles and long-term economic growth, hence supplyside shocks (and in particular technology shocks) permanently affect the path of the economy over time.
A consequence of this is that demand-side policies, such as monetary.policy, have no role to play in explaining business cycles.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONReal business cycle theory is a new classical theory that assumes rational expectations and continuous market clearing.
It draws no distinction between business cycles and long-term economic growth, hence supplyside shocks (and in particular technology shocks) permanently affect the path of the economy over time.
A consequence of this is that demand-side policies, such as monetary.policy, have no role to play in explaining business cycles.
-
Question 221 of 999CB2023848
Question 221
FlagIn the table below, consider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{A reduction in income tax might } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{A reduction in income tax might } \\
\text{lead to an increase in the labour } && \text{cause people to decide to work }\\
\text{supply. } && \text{fewer hours for the same take- }\\
&&\text{home pay.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONTax cuts may encourage people to work more in exchange for less leisure time (ie the substitution effect of the tax cut) as the opportunity cost of leisure increases. Furthermore, the tax cut might encourage more people into the workforce. The labour supply therefore might increase and so the assertion is true.
However, people may decide that they now need to work fewer hours to earn the same takehome pay (the income effect of a tax cut), so the reason is also true.
The reason does not explain the assertion, since people working fewer hours would lead to a reduction, rather than an increase, in the labour supply.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONTax cuts may encourage people to work more in exchange for less leisure time (ie the substitution effect of the tax cut) as the opportunity cost of leisure increases. Furthermore, the tax cut might encourage more people into the workforce. The labour supply therefore might increase and so the assertion is true.
However, people may decide that they now need to work fewer hours to earn the same takehome pay (the income effect of a tax cut), so the reason is also true.
The reason does not explain the assertion, since people working fewer hours would lead to a reduction, rather than an increase, in the labour supply.
-
Question 222 of 999CB2023849
Question 222
FlagMatch the types of deficit / debt to the definitions,
I $\quad$ Structural deficit
II $\quad$ Primary deficit
III $\quad$ Current budget deficit
IV $\quad$ National debt
V $\quad$ Budget deficit
A $\quad$ The excess of government spending over taxation revenue over the current year.
B $\quad$ The excess of government spending over taxation revenue when there is a zero output
C $\quad$ The accumulated excess of government spending over taxation revenue over all years.
D $\quad$ The excess of government spending excluding interest payments on its debt over taxation revenue over the current year.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATION$\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{V}, \mathrm{B}-\mathrm{I}, \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{IV}, \mathrm{D}-\mathrm{II}$.
The current budget deficit is the excess of government spending that is classed as current expenditure over taxation, where current expenditure includes day to day government expenditure and excludes capital expenditure. The current budget deficit was not defined in the question.Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATION$\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{V}, \mathrm{B}-\mathrm{I}, \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{IV}, \mathrm{D}-\mathrm{II}$.
The current budget deficit is the excess of government spending that is classed as current expenditure over taxation, where current expenditure includes day to day government expenditure and excludes capital expenditure. The current budget deficit was not defined in the question. -
Question 223 of 999CB2023850
Question 223
FlagWhich THREE of the following are examples of interventionist supply-side policies that might encourage growth in potential output?
Correct
The correct answer is D, E, & F.
EXPLANATIONInterventionist supply-side policies seek to increase aggregate supply and hence potential output, using government intervention to counteract the deficiencies of the market. Interventionist policies include spending on infrastructure, research and development and relocation packages.
Market-orientated supply-side policies seek to increase aggregate supply and hence potential output, by freeing up the market. They include reducing or removing planning controls and unemployment benefits.
An increase in corporation tax is likely to lead to a decrease in the growth of potential output as firms are likely to respond by decreasing investment.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D, E, & F.
EXPLANATIONInterventionist supply-side policies seek to increase aggregate supply and hence potential output, using government intervention to counteract the deficiencies of the market. Interventionist policies include spending on infrastructure, research and development and relocation packages.
Market-orientated supply-side policies seek to increase aggregate supply and hence potential output, by freeing up the market. They include reducing or removing planning controls and unemployment benefits.
An increase in corporation tax is likely to lead to a decrease in the growth of potential output as firms are likely to respond by decreasing investment.
-
Question 224 of 999CB2023851
Question 224
FlagWhich of the following pairs is most likely to reduce aggregate demand?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA (government) budget surplus occurs when tax revenues exceed government spending. This is a net withdrawal from the economy and hence reduces aggregate demand. In addition, aggregate demand is likely to decrease if interest rates increase, which is likely with a decrease in the money supply.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONA (government) budget surplus occurs when tax revenues exceed government spending. This is a net withdrawal from the economy and hence reduces aggregate demand. In addition, aggregate demand is likely to decrease if interest rates increase, which is likely with a decrease in the money supply.
-
Question 225 of 999CB2023852
Question 225
FlagWhich of the following is most likely to lead to a decrease in the budget deficit as a proportion of GDP?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe budget deficit is defined as the excess of government spending over tax revenues.
A decrease in national income tends to lead an increase in government spending on unemployment and other income-related benefits (as unemployment generally increases) and decreases government tax revenues as household incomes and firms’ profits fall. This leads to an increase in the budget deficit. GDP is one measure of national income, and so when national income falls, the budget deficit as a proportion of GDP rises.Conversely, an increase in national income (eg GDP) decreases the budget deficit, and so the budget deficit as a proportion of GDP falls.
A decrease in the personal income tax rates will be likely to lead to a decrease in tax receipts and so an increase in the budget deficit. However, the decrease in income tax may encourage spending and so increase aggregate demand and national income (eg GDP). The budget deficit as a proportion of GDP might therefore fall or rise.
An increase in government spending increases the budget deficit and increases aggregate demand and national income (eg GDP). The budget deficit as a proportion of GDP might therefore fall or rise.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe budget deficit is defined as the excess of government spending over tax revenues.
A decrease in national income tends to lead an increase in government spending on unemployment and other income-related benefits (as unemployment generally increases) and decreases government tax revenues as household incomes and firms’ profits fall. This leads to an increase in the budget deficit. GDP is one measure of national income, and so when national income falls, the budget deficit as a proportion of GDP rises.Conversely, an increase in national income (eg GDP) decreases the budget deficit, and so the budget deficit as a proportion of GDP falls.
A decrease in the personal income tax rates will be likely to lead to a decrease in tax receipts and so an increase in the budget deficit. However, the decrease in income tax may encourage spending and so increase aggregate demand and national income (eg GDP). The budget deficit as a proportion of GDP might therefore fall or rise.
An increase in government spending increases the budget deficit and increases aggregate demand and national income (eg GDP). The budget deficit as a proportion of GDP might therefore fall or rise.
-
Question 226 of 999CB2023853
Question 226
FlagIn the table below, consider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{A contractionary fiscal policy will } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{A decrease in taxation will be } \\
\text{be likely to lead to an increase in } && \text{likely to encourage more }\\
\text{real output and unemployment.} && \text{spending in the economy.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA contractionary fiscal policy will be likely to lead to an increase in real output and so a decrease in unemployment, and so the assertion is false.
A decrease in taxation is an example of an expansionary, rather than contractionary, fiscal policy. However, it will be likely to encourage more spending in the economy and so the reason in true.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONA contractionary fiscal policy will be likely to lead to an increase in real output and so a decrease in unemployment, and so the assertion is false.
A decrease in taxation is an example of an expansionary, rather than contractionary, fiscal policy. However, it will be likely to encourage more spending in the economy and so the reason in true.
-
Question 227 of 999CB2023871
Question 227
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe neo-Austrian / libertarian school of thought advocates maximum liberty for economic agents to pursue their own interests and to own property.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONThe neo-Austrian / libertarian school of thought advocates maximum liberty for economic agents to pursue their own interests and to own property.
-
Question 228 of 999CB2023872
Question 228
FlagSuppose that in Country A, the budget surplus is 20, investment is equal to SO and savings are equal to 40. Then the trade balance must be equal to:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONRecall that actual injections of spending into the circular flow of income (investment (I), government spending $(G)$ and exports $(X)$ must equal actual withdrawals (net savings ( $S$ ), net taxes (T), imports (M)). In other words:
$
I+G+X=S+T+M
$This can be rearranged to give:
$
(X-M)=(T-G)+(S-I)
$Plugging in the numbers given in the question and remembering that a budget surplus means that $T-G=20$ gives:
$
\begin{aligned}
(X-M) & =20+(40-50) \\
& =+10
\end{aligned}
$So, the trade balance is $X-M=+10$, which represents a surplus, as Country A is exporting more than it is importing.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONRecall that actual injections of spending into the circular flow of income (investment (I), government spending $(G)$ and exports $(X)$ must equal actual withdrawals (net savings ( $S$ ), net taxes (T), imports (M)). In other words:
$
I+G+X=S+T+M
$This can be rearranged to give:
$
(X-M)=(T-G)+(S-I)
$Plugging in the numbers given in the question and remembering that a budget surplus means that $T-G=20$ gives:
$
\begin{aligned}
(X-M) & =20+(40-50) \\
& =+10
\end{aligned}
$So, the trade balance is $X-M=+10$, which represents a surplus, as Country A is exporting more than it is importing.
-
Question 229 of 999CB2023873
Question 229
FlagAn exchange rate system in which rates are fixed for a period of time but may be revalued or devalued in response to a substantial balance of payment surplus or deficit is referred to as:
Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONBy definition, an adjustable peg is an exchange rate system in which rates are pegged (ie fixed) for a period of time but may be revalued or devalued in response to a substantial balance of payment surplus or deficit.
Under a crawling peg system, the exchange rate is pegged, but the peg rate is adjusted by small amounts at frequent intervals.
A joint float is where a group of currencies are pegged against each other but float against all other currencies.
Managed floating is where exchange rates are allowed to float, but central banks may intervene occasionally to prevent excessive fluctuations (such as happened during the financial crisis of 2008-09) or even to achieve an unofficial target.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONBy definition, an adjustable peg is an exchange rate system in which rates are pegged (ie fixed) for a period of time but may be revalued or devalued in response to a substantial balance of payment surplus or deficit.
Under a crawling peg system, the exchange rate is pegged, but the peg rate is adjusted by small amounts at frequent intervals.
A joint float is where a group of currencies are pegged against each other but float against all other currencies.
Managed floating is where exchange rates are allowed to float, but central banks may intervene occasionally to prevent excessive fluctuations (such as happened during the financial crisis of 2008-09) or even to achieve an unofficial target.
-
Question 230 of 999CB2023874
Question 230
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a possible advantage of freely floating exchange rates?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIt is the successful operation of a system of fixed exchange rates that requires sufficient international liquidity, ie a sufficient supply of currencies in the world acceptable for financing international trade and investment. In particular, it is important that international liquidity grows in line with international trade and investment, and hence the resultant current account deficits and surpluses, because countries’ reserves need to be sufficient to maintain the fixed exchange rate.
The greater freedom of governments to implement their chosen domestic macroeconomic policy under freely floating exchange rates follows directly from the fact that they are not constrained by the need to correct current account deficits because they will be corrected automatically.
An example of an external shock is a world recession, which will lead to a fall in exports (and hence aggregate demand and GDP) and a current account deficit. Under a free-floating system, however, the exchange rate will fall, making exports cheaper and imports dearer, thereby boosting net exports, aggregate demand and GDP.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONIt is the successful operation of a system of fixed exchange rates that requires sufficient international liquidity, ie a sufficient supply of currencies in the world acceptable for financing international trade and investment. In particular, it is important that international liquidity grows in line with international trade and investment, and hence the resultant current account deficits and surpluses, because countries’ reserves need to be sufficient to maintain the fixed exchange rate.
The greater freedom of governments to implement their chosen domestic macroeconomic policy under freely floating exchange rates follows directly from the fact that they are not constrained by the need to correct current account deficits because they will be corrected automatically.
An example of an external shock is a world recession, which will lead to a fall in exports (and hence aggregate demand and GDP) and a current account deficit. Under a free-floating system, however, the exchange rate will fall, making exports cheaper and imports dearer, thereby boosting net exports, aggregate demand and GDP.
-
Question 231 of 999CB2023875
Question 231
FlagIn order to adopt the euro, each EU country had to meet convergence criteria that referred to all of the following EXCEPT:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe five convergence criteria that each EU country had to meet in order to adopt the éuro referred to its:
1. $\quad$ inflation rate
2. $\quad$ interest rates
3. $\quad$ budget deficit
4. $\quad$ national debt
5. $\quad$ exchange rates.They did not refer to unemployment.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe five convergence criteria that each EU country had to meet in order to adopt the éuro referred to its:
1. $\quad$ inflation rate
2. $\quad$ interest rates
3. $\quad$ budget deficit
4. $\quad$ national debt
5. $\quad$ exchange rates.They did not refer to unemployment.
-
Question 232 of 999CB2023876
Question 232
FlagThe loss of separate monetary policies within the eurozone is:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONEuropean Monetary Union (EMU) is the adoption by a group of European countries of a single currency, a single central bank and a single monetary policy. Therefore, the loss of separate monetary policies is an inherent feature or principle of EMU. This loss of monetary policy is regarded as a disadvantage because it requires that all of the member countries must have similar interest rates, which may be appropriate for some countries but highly inappropriate for others.
Criticisms of the current design of EMU relate to the operation of monetary and fiscal policy in practice, especially following the financial crisis.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONEuropean Monetary Union (EMU) is the adoption by a group of European countries of a single currency, a single central bank and a single monetary policy. Therefore, the loss of separate monetary policies is an inherent feature or principle of EMU. This loss of monetary policy is regarded as a disadvantage because it requires that all of the member countries must have similar interest rates, which may be appropriate for some countries but highly inappropriate for others.
Criticisms of the current design of EMU relate to the operation of monetary and fiscal policy in practice, especially following the financial crisis.
-
Question 233 of 999CB2023877
Question 233
FlagWhich of the following do you NOT associate with classical economists?
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe paradox of thrift is associated with Keynes. He used it to criticise the classical economists’ loanable funds theory. According to this theory, an increase in savings is good for the nation because its will lead to a fall in interest rates and an increase in investment. Keynes pointed out that, although saving might be good for an individual in that he or she will be able to consume more in the future, if society as a whole increases saving, consumption will fall and national income will fall. This will decrease the incentive to invest and income will fall still further.
This paradox is an example of the paradox of aggregates (or paradox of composition), which is concerned with the dangers of building on microeconomic foundations to develop macroeconomic theory, because what applies in an individual case does not necessarily apply when analysing aggregates.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe paradox of thrift is associated with Keynes. He used it to criticise the classical economists’ loanable funds theory. According to this theory, an increase in savings is good for the nation because its will lead to a fall in interest rates and an increase in investment. Keynes pointed out that, although saving might be good for an individual in that he or she will be able to consume more in the future, if society as a whole increases saving, consumption will fall and national income will fall. This will decrease the incentive to invest and income will fall still further.
This paradox is an example of the paradox of aggregates (or paradox of composition), which is concerned with the dangers of building on microeconomic foundations to develop macroeconomic theory, because what applies in an individual case does not necessarily apply when analysing aggregates.
-
Question 234 of 999CB2023878
Question 234
FlagPossible causes of the financial crisis in 2008 include all of the following EXCEPT:
Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONSub-prime debt is debt that carries a high risk of default, eg because the borrower is on a low income. Throughout the late 1990s and the early 2000s, banks dramatically increased their lending, and some of it, especially in the US, was in the form of sub-prime mortgages. This made the banks very vulnerable to a change in the financial position of the borrowers, eg if incomes or house prices fell.
Traditionally, banks obtained funds from customers in the form of customer deposits. However, as a result of deregulation and financial innovation, banks were able to bbtain wholesale funding, which is funding from other financial institutions. The increased availability of funds led to a dramatic increase in bank lending, and a lot of this was risky lending.
In the case of insurance, moral hazard refers to the danger of a change in behaviour resulting from being insured. In the case of banking, it was feared that banks were adopting risky behaviour partly in the belief that they would not be allowed to fail, $i e$ they felt safe in the expectation that the government would bail them out if they suffered losses.
Counter-cyclical bank lending would involve banks lending more when the economy is in recession and less when the economy is growing. In practice, bank lending tends to be pro-cyclical, ie banks feel optimistic in good times and are more likely to lend. Prior to the crisis, the economy had grown steadily for about 15 years and the expectation was that this would continue.
Consequently bank lending grew rapidly.Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONSub-prime debt is debt that carries a high risk of default, eg because the borrower is on a low income. Throughout the late 1990s and the early 2000s, banks dramatically increased their lending, and some of it, especially in the US, was in the form of sub-prime mortgages. This made the banks very vulnerable to a change in the financial position of the borrowers, eg if incomes or house prices fell.
Traditionally, banks obtained funds from customers in the form of customer deposits. However, as a result of deregulation and financial innovation, banks were able to bbtain wholesale funding, which is funding from other financial institutions. The increased availability of funds led to a dramatic increase in bank lending, and a lot of this was risky lending.
In the case of insurance, moral hazard refers to the danger of a change in behaviour resulting from being insured. In the case of banking, it was feared that banks were adopting risky behaviour partly in the belief that they would not be allowed to fail, $i e$ they felt safe in the expectation that the government would bail them out if they suffered losses.
Counter-cyclical bank lending would involve banks lending more when the economy is in recession and less when the economy is growing. In practice, bank lending tends to be pro-cyclical, ie banks feel optimistic in good times and are more likely to lend. Prior to the crisis, the economy had grown steadily for about 15 years and the expectation was that this would continue.
Consequently bank lending grew rapidly. -
Question 235 of 999CB2023879
Question 235
FlagA long-standing member country of the eurozone has decided to leave the single currency. Which THREE of the following may be TRUE and are in support of this decision?
Correct
The correct answer is A, B & C.
EXPLANATIONReasons for leaving the eurozone
The country might be better off with its own currency, rather than retaining the euro, if this will allow the government to make the country’s domestic goods more competitive.
The eurozone is not an optimal currency area, ie an area that maximises the benefits of having a single currency relative to the costs, eg because labour is relatively immobile and so unemployment could vary significantly across the region.
Governments within the eurozone cannot control monetary policy directly. Leaving the single currency is likely to give the government control of monetary policy. This, when combined with control over its exchange rate, might allow it to better to respond to shocks.
Reasons against leaving the eurozone
If the country has just received a bailout from the ECB, it is more likely that the country will be in favour of remaining in the eurozone.
Countries in the eurozone share a single monetary policy, and although this can result in lower long-term rates of interest, it is more likely to encourage investment in the member countries, since borrowing costs and the opportunity costs of investing are lower.
If the country trades with many other countries in the eurozone, it is likely to benefit from the non-existence of costs of converting currencies.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A, B & C.
EXPLANATIONReasons for leaving the eurozone
The country might be better off with its own currency, rather than retaining the euro, if this will allow the government to make the country’s domestic goods more competitive.
The eurozone is not an optimal currency area, ie an area that maximises the benefits of having a single currency relative to the costs, eg because labour is relatively immobile and so unemployment could vary significantly across the region.
Governments within the eurozone cannot control monetary policy directly. Leaving the single currency is likely to give the government control of monetary policy. This, when combined with control over its exchange rate, might allow it to better to respond to shocks.
Reasons against leaving the eurozone
If the country has just received a bailout from the ECB, it is more likely that the country will be in favour of remaining in the eurozone.
Countries in the eurozone share a single monetary policy, and although this can result in lower long-term rates of interest, it is more likely to encourage investment in the member countries, since borrowing costs and the opportunity costs of investing are lower.
If the country trades with many other countries in the eurozone, it is likely to benefit from the non-existence of costs of converting currencies.
-
Question 236 of 999CB2023880
Question 236
FlagIn the table below, consider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{Under a floating exchange rate, } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{An increase in taxation will lead } \\
\text{an increase In taxation can lead } && \text{to a decrease in the interest rate.}\\
\text{to an appreciation of the } && \\
\text{domestic currency.} &&\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in taxation will reduce consumer and investment spending in the economy and so aggregate demand and real national income will fall. The direct effect of the fall in real national income on the money market will be a decrease in the demand for money, leading to a decrease in the interest rate and so the reason is true.
This has two effects on the balance of payments:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The lower interest rate makes saving in the domestic country less attractive than other countries, so there will be a net flow of money out of the country as investors seek higher returns elsewhere. This creates a deficit on the financial account of the balance of payments.
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The lower level of national income will lead to people buying fewer goods and services, both from domestic producers and those based abroad, ie imports decrease. This creates a surplus on the current account of the balance of payments.Whether the value of the domestic currency falls or rises depends on the overall change in the balance of payments:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ Where the overall balance of payments moves towards a deficit, ie where the financial account deficit outweighs the current account surplus, there will be excess supply of the domestic currency on foreign exchange markets, and so the value of the domestic currency will fall.
$\bullet$ $\quad$ Where the overall balance of payments moves towards a surplus, ie where the current account surplus outweighs the financial account deficit, there will be excess demand for the domestic currency on foreign exchange markets, and so the value of the domestic currency will rise.The relative sizes of the financial account deficit and current account surplus are unknown, and so the overall balance of payments could move to either an overall deficit or surplus, and hence the value of the currency can either fall or rise as a result. The assertion is therefore true. The reason does not explain the assertion though: if the exchange rate were to appreciate, the current account effect needs to be the dominant one, and this effect is not covered in,the reason.
In practice, with the high level of mobility of international finance in today’s world, the financial account deficit is likely to outweigh the current account surplus, and so the value of the currency is most likely to fall.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in taxation will reduce consumer and investment spending in the economy and so aggregate demand and real national income will fall. The direct effect of the fall in real national income on the money market will be a decrease in the demand for money, leading to a decrease in the interest rate and so the reason is true.
This has two effects on the balance of payments:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The lower interest rate makes saving in the domestic country less attractive than other countries, so there will be a net flow of money out of the country as investors seek higher returns elsewhere. This creates a deficit on the financial account of the balance of payments.
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The lower level of national income will lead to people buying fewer goods and services, both from domestic producers and those based abroad, ie imports decrease. This creates a surplus on the current account of the balance of payments.Whether the value of the domestic currency falls or rises depends on the overall change in the balance of payments:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ Where the overall balance of payments moves towards a deficit, ie where the financial account deficit outweighs the current account surplus, there will be excess supply of the domestic currency on foreign exchange markets, and so the value of the domestic currency will fall.
$\bullet$ $\quad$ Where the overall balance of payments moves towards a surplus, ie where the current account surplus outweighs the financial account deficit, there will be excess demand for the domestic currency on foreign exchange markets, and so the value of the domestic currency will rise.The relative sizes of the financial account deficit and current account surplus are unknown, and so the overall balance of payments could move to either an overall deficit or surplus, and hence the value of the currency can either fall or rise as a result. The assertion is therefore true. The reason does not explain the assertion though: if the exchange rate were to appreciate, the current account effect needs to be the dominant one, and this effect is not covered in,the reason.
In practice, with the high level of mobility of international finance in today’s world, the financial account deficit is likely to outweigh the current account surplus, and so the value of the currency is most likely to fall.
-
Question 237 of 999CB2023881
Question 237
FlagThe government of a country is increasing government spending in order to stimulate the economy The country is open to international trade and has a low marginal propensity to import International finance is extremely mobile.
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
I $\quad$ If the country operates a fixed exchange rate, the government or central bank will likely need to add to their reserves of gold and foreign currencies in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate.
II $\quad$ If the currency of the country is left to freely float, the value of the domestic currency is likely to rise.
Ill $\quad$ The increase in government spending is likely to be more effective if the country’s currency is left to freely float in comparison to If it is fixed against another currency.Correct
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in government spending will increase aggregate demand and national income, which in turn will increase the level of money demand and hence the interest rate in the money market. This has two effects on the balance of payments:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The higher interest rate makes saving in the domestic country more attractive than other countries, so there will be a net flow of money into the country as investors seek higher returns. This creates a surplus on the financial account of the balance of payments and is likely to be significant given the high level of mobility of international finance mentioned in the question.$\bullet$ $\quad$ The higher level of national income will lead to people buying more goods and services, both from domestic producers and those based abroad, ie imports increase. This creates a deficit on the current account of the balance of payments. However, as the marginal propensity to import is low, the increase in imports and hence current account deficit is likely to be small.
Overall, the balance of payments will be in surplus, ie the financial account surplus (from the higher interest rate) will outweigh the current account deficit (from the increase in imports).
An overall surplus on the balance of payments is consistent with excess demand for the domestic currency on foreign exchange markets, and so there will be upward pressure on the value of the domestic currency. This pressure will:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ appreciate the currency, if it is left to freely float (Statement II)
$\bullet$ $\quad$ need counteracting if the government and/or central bank do not want it to appreciate (ie if it is to remain fixed). To counteract the excess demand and hence upward pressure on the value of the currency, the central bank will likely need to supply sterling to the foreign exchange markets, and they can do this by purchasing reserves of gold and foreign currencies (Statement I).If the currency does appreciate, ie if it is left to freely float, the higher value of the currency will reduce exports and increase imports, both of which decrease aggregate demand and national income. This decrease in national income offsets some of the initial increase, and herice reduces the effectiveness of the increase in government spending. So, the increase in government spending is likely to be less effective if the country’s currency is left to freely floát and Statement III is false.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in government spending will increase aggregate demand and national income, which in turn will increase the level of money demand and hence the interest rate in the money market. This has two effects on the balance of payments:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ The higher interest rate makes saving in the domestic country more attractive than other countries, so there will be a net flow of money into the country as investors seek higher returns. This creates a surplus on the financial account of the balance of payments and is likely to be significant given the high level of mobility of international finance mentioned in the question.$\bullet$ $\quad$ The higher level of national income will lead to people buying more goods and services, both from domestic producers and those based abroad, ie imports increase. This creates a deficit on the current account of the balance of payments. However, as the marginal propensity to import is low, the increase in imports and hence current account deficit is likely to be small.
Overall, the balance of payments will be in surplus, ie the financial account surplus (from the higher interest rate) will outweigh the current account deficit (from the increase in imports).
An overall surplus on the balance of payments is consistent with excess demand for the domestic currency on foreign exchange markets, and so there will be upward pressure on the value of the domestic currency. This pressure will:
$\bullet$ $\quad$ appreciate the currency, if it is left to freely float (Statement II)
$\bullet$ $\quad$ need counteracting if the government and/or central bank do not want it to appreciate (ie if it is to remain fixed). To counteract the excess demand and hence upward pressure on the value of the currency, the central bank will likely need to supply sterling to the foreign exchange markets, and they can do this by purchasing reserves of gold and foreign currencies (Statement I).If the currency does appreciate, ie if it is left to freely float, the higher value of the currency will reduce exports and increase imports, both of which decrease aggregate demand and national income. This decrease in national income offsets some of the initial increase, and herice reduces the effectiveness of the increase in government spending. So, the increase in government spending is likely to be less effective if the country’s currency is left to freely floát and Statement III is false.
-
Question 238 of 999CB2023882
Question 238
FlagUnder a floating exchange rate regime, which of the following developments would help to explain a fall in the value of Country X’s currency?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONHigher inflation would increase the price of Country X’s exports relative to the price of other countries’ goods, and so decrease demand for Country X’s goods in the long term, and hence decrease demand for its currency on the foreign exchange market. Also, imports would be more price-competitive, so there would be an increase in demand for imports, and hence an increase in the supply of Country X ‘s currency on the foreign exchange market. Together, these two effects would decrease the value of Country X’scurrency.
More competitive exports from Country X will increase the demand for Country X ‘s goods, which increases the demand for its currency on the foreign exchange market and hence increases the value of its currency.
Increased tariffs on imports into Country X will reduce the demand for imports into Country X . This decreases the supply of country X ‘s currency on the foreign exchange market and hence increase its value.
Increased interest rates in Country X relative to other countries will increase the demand for Country $X$ ‘s currency on the foreign exchange market since investors will seek to maximise their return. This increases the value of Country X’s currency.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONHigher inflation would increase the price of Country X’s exports relative to the price of other countries’ goods, and so decrease demand for Country X’s goods in the long term, and hence decrease demand for its currency on the foreign exchange market. Also, imports would be more price-competitive, so there would be an increase in demand for imports, and hence an increase in the supply of Country X ‘s currency on the foreign exchange market. Together, these two effects would decrease the value of Country X’scurrency.
More competitive exports from Country X will increase the demand for Country X ‘s goods, which increases the demand for its currency on the foreign exchange market and hence increases the value of its currency.
Increased tariffs on imports into Country X will reduce the demand for imports into Country X . This decreases the supply of country X ‘s currency on the foreign exchange market and hence increase its value.
Increased interest rates in Country X relative to other countries will increase the demand for Country $X$ ‘s currency on the foreign exchange market since investors will seek to maximise their return. This increases the value of Country X’s currency.
-
Question 239 of 999CB2023883
Question 239
FlagA balance of payments deficit is LEAST likely to be corrected In the long run by:
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe other options will all help to correct a balance of payments deficit. Increasing the value of the domestic currency is likely to have the opposite effect in the long run by making exports less competitive and imports more competitive.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe other options will all help to correct a balance of payments deficit. Increasing the value of the domestic currency is likely to have the opposite effect in the long run by making exports less competitive and imports more competitive.
-
Question 240 of 999CB2023884
Question 240
FlagThe following table summarises the fiscal position in four countries.
$\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Fiscal deficit as % of GDP at } \\
\text { market prices }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { National debt as \% of GDP at } \\
\text { market prices }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Country A } & 2 & 40 \\
\hline \text { Country B } & 3 & 70 \\
\hline \text { Country C } & 3 & 60 \\
\hline \text { Country D } & 4 & 40 \\
\hline
\end{array}$How many of these countries meet the relevant fiscal convergence criteria that were required in order to join the Eurozone initially?
Correct
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe fiscal criteria to be met in order to join the Eurozone required that the fiscal (or budget) deficit be no more than $3 \%$ of GDP at market prices and the national debt be no more than $60 \%$ of GDP at market prices. Hence, two countries in the table meet these criteria, namely Countries A and C .
Incorrect
The correct answer is B.
EXPLANATIONThe fiscal criteria to be met in order to join the Eurozone required that the fiscal (or budget) deficit be no more than $3 \%$ of GDP at market prices and the national debt be no more than $60 \%$ of GDP at market prices. Hence, two countries in the table meet these criteria, namely Countries A and C .
-
Question 241 of 999CB2023885
Question 241
FlagWhich THREE of the following beliefs are more consistent with the views of Keynesian economists than those of new classical economists?
Correct
The correct answer is B, C & E.
EXPLANATIONKeynesians believe that markets clear very slowly because there are market imperfections, eg sticky prices and wages. Keynesians believe that hysteresis (the persistence of unemployment even when the demand-deficiency that caused it is no longer present) is a problem. This is because Keynesians believe that the markets can take a long time to clear, meaning demanddeficient unemployment can persist for a long time, causing unemployment to become embedded in the economy as people lose skills.
New classical economists do not think hysteresis is a problem since they believe that, following a fall in aggregate demand and the price level, workers will accept a nominal wage cut to retain the same real wage and avoid demand-deficient unemployment.
New classicals also believe that people do not suffer from money illusion, so markets are able to clear quickly, and employment is always at its equilibrium level.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B, C & E.
EXPLANATIONKeynesians believe that markets clear very slowly because there are market imperfections, eg sticky prices and wages. Keynesians believe that hysteresis (the persistence of unemployment even when the demand-deficiency that caused it is no longer present) is a problem. This is because Keynesians believe that the markets can take a long time to clear, meaning demanddeficient unemployment can persist for a long time, causing unemployment to become embedded in the economy as people lose skills.
New classical economists do not think hysteresis is a problem since they believe that, following a fall in aggregate demand and the price level, workers will accept a nominal wage cut to retain the same real wage and avoid demand-deficient unemployment.
New classicals also believe that people do not suffer from money illusion, so markets are able to clear quickly, and employment is always at its equilibrium level.
-
Question 242 of 999CB2023886
Question 242
FlagIn the table below, consider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{ Statement 1 (Assertion) } & & \text{ Statement 2 (Reason) } \\
\hline \text{The effect of an increase in } & \text{BECAUSE } & \text{The injections multiplier is the } \\
\text{Country A’s national income on } && \text{number of times greater the }\\
\text{Country B’s national income will } && \text{expansion of bank deposits is }\\
\text{depend on the injections } && \text{than the liquidity injection into }\\
\text{multiplier in Country B.} && \text{banks that caused it.}\\
\hline
\end{array}$Correct
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in Country A’s national income will mean individuals and firms in Country A spend more money, including on goods and services produced in Country B, ie exports from Country B will increase. Increased exports increases AD and national income with a multiplied effect in Country B.
The injections multiplier is the number of times by which a rise in income exceeds the rise in injections that caused it (exports in this case). The reason instead describes the bank deposits multiplier.
Incorrect
The correct answer is C.
EXPLANATIONAn increase in Country A’s national income will mean individuals and firms in Country A spend more money, including on goods and services produced in Country B, ie exports from Country B will increase. Increased exports increases AD and national income with a multiplied effect in Country B.
The injections multiplier is the number of times by which a rise in income exceeds the rise in injections that caused it (exports in this case). The reason instead describes the bank deposits multiplier.
-
Question 243 of 999CB2023887
Question 243
FlagWhich of the following statements relating to the paradox of aggregates are TRUE?
I $\quad$ Macroeconomic models that don’t allow for the interaction of economic agents might give misleading conclusions.
II $\quad$ Group dynamics can affect individual well-being.
Ill $\quad$ What is true for a representative economic agent might not always hold true at an aggregate level.Correct
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe paradox of aggregates refers to the problems with relying on microeconomic foundations to draw macroeconomic conclusions. It considers how the interactions of individuals should be considered for more accurate economic modelling (Statement I). It also considers how group dynamics can affect individual wellbeing (Statement II). For example, during a recession, individuals might attempt to improve their wellbeing by saving more. However, many people saving more (by spending less) can deepen the recession and hence reduce national income. This also demonstrates that what is true for a representative economic agent (higher savings) might not always hold true at an aggregate level (lower national income and hence lower savings) (Statement III).
Incorrect
The correct answer is D.
EXPLANATIONThe paradox of aggregates refers to the problems with relying on microeconomic foundations to draw macroeconomic conclusions. It considers how the interactions of individuals should be considered for more accurate economic modelling (Statement I). It also considers how group dynamics can affect individual wellbeing (Statement II). For example, during a recession, individuals might attempt to improve their wellbeing by saving more. However, many people saving more (by spending less) can deepen the recession and hence reduce national income. This also demonstrates that what is true for a representative economic agent (higher savings) might not always hold true at an aggregate level (lower national income and hence lower savings) (Statement III).
-
Question 244 of 999CB2023888
Question 244
FlagWhich TWO of the following policies can individual countries in the eurozone use to counteract their business cycle?
Correct
The correct answer is A & C.
EXPLANATIONCountries in the eurozone have a common central bank and so common monetary policy, meaning an individual member cannot use monetary policy (eg changing interest rates) to counteract their business cycle.
Each country does have its own government, and so fiscal policy is available, which can be used to influence both aggregate demand (demand-side policy) and aggregate supply (supply-side policy).
No individual country will be able to use the exchange rate to counteract their business cycle since a number of finance ministers (who will be based in a number of different countries) all provide input to exchange rate decisions.
Incorrect
The correct answer is A & C.
EXPLANATIONCountries in the eurozone have a common central bank and so common monetary policy, meaning an individual member cannot use monetary policy (eg changing interest rates) to counteract their business cycle.
Each country does have its own government, and so fiscal policy is available, which can be used to influence both aggregate demand (demand-side policy) and aggregate supply (supply-side policy).
No individual country will be able to use the exchange rate to counteract their business cycle since a number of finance ministers (who will be based in a number of different countries) all provide input to exchange rate decisions.
-
Question 245 of 999CB2025681
Question 245
FlagFor good X, a movement along the demand curve occurs when:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A movement along the demand curve occurs only due to a change in the good’s own price.
A, B, and C refer to factors that shift the entire demand curve, not movement along it.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A movement along the demand curve occurs only due to a change in the good’s own price.
A, B, and C refer to factors that shift the entire demand curve, not movement along it. -
Question 246 of 999CB2025682
Question 246
FlagIf a rise in the price of Good A causes the demand curve for Good B to shift to the left, then:
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Good A and Good B are complements – Correct. When the price of a good rises and the demand for another good falls (demand curve shifts left), they are complements used together (e.g., coffee and sugar).
B. Good A and Good B are substitutes – Incorrect. Substitutes see an increase in demand for one when the other’s price rises.
C. Good A is a normal good and Good B is an inferior good – Incorrect. This concerns income effects, not cross-price relationships.
D. Good A is an inferior good and Good B is a normal good – Incorrect. Again, this relates to income, not complementary or substitute relationships.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Good A and Good B are complements – Correct. When the price of a good rises and the demand for another good falls (demand curve shifts left), they are complements used together (e.g., coffee and sugar).
B. Good A and Good B are substitutes – Incorrect. Substitutes see an increase in demand for one when the other’s price rises.
C. Good A is a normal good and Good B is an inferior good – Incorrect. This concerns income effects, not cross-price relationships.
D. Good A is an inferior good and Good B is a normal good – Incorrect. Again, this relates to income, not complementary or substitute relationships. -
Question 247 of 999CB2025683
Question 247
FlagAll other things being equal, what makes the demand curve for a good more price elastic?
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. A decrease in the number and closeness of substitute goods – Incorrect. Fewer substitutes make it harder to switch, reducing elasticity.
B. An increase in the number and closeness of substitute goods – Correct. More and closer substitutes make consumers more responsive to price changes, increasing price elasticity.
C. Lesser proportion of consumers’ incomes being spent on the good – Incorrect. Goods taking a smaller share of income tend to be less elastic.
D. None of the above – Incorrect. Option B correctly identifies a factor that increases price elasticity.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. A decrease in the number and closeness of substitute goods – Incorrect. Fewer substitutes make it harder to switch, reducing elasticity.
B. An increase in the number and closeness of substitute goods – Correct. More and closer substitutes make consumers more responsive to price changes, increasing price elasticity.
C. Lesser proportion of consumers’ incomes being spent on the good – Incorrect. Goods taking a smaller share of income tend to be less elastic.
D. None of the above – Incorrect. Option B correctly identifies a factor that increases price elasticity. -
Question 248 of 999CB2025684
Question 248
FlagWhich of the following statements is false?
Governments set minimum prices for the following reasons:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. To protect producer’s incomes – Correct. Minimum prices can ensure producers receive a fair income, especially in agriculture.
B. To create a surplus – Correct. Though not a goal, minimum prices often lead to surplus as quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.
C. To deter the consumption of particular goods – Correct. Minimum prices on goods like alcohol can reduce excessive consumption.
D. To encourage consumption of particular goods – Incorrect. Minimum prices make goods more expensive, which discourages rather than encourages consumptionIncorrect
The correct answer is D
A. To protect producer’s incomes – Correct. Minimum prices can ensure producers receive a fair income, especially in agriculture.
B. To create a surplus – Correct. Though not a goal, minimum prices often lead to surplus as quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.
C. To deter the consumption of particular goods – Correct. Minimum prices on goods like alcohol can reduce excessive consumption.
D. To encourage consumption of particular goods – Incorrect. Minimum prices make goods more expensive, which discourages rather than encourages consumption -
Question 249 of 999CB2025685
Question 249
FlagIf tea and coffee are substitute goods, an increase in the price of coffee will
Correct
The correct answer is B
Law of diminishing marginal utility is one of the rationale for the law of demand – the next unit consumed by the individual will not provide them with as much utility as the first commodity which they have consumed, and hence they would be prepared to pay for the next unit will fall.
And, since tea and coffee are substitute goods, increase in price of tea will shift the consumers of tea to coffee.
This will shift the marginal utility from consuming coffee to shift to the right – because users of coffee are now getting more utility from consuming coffee than tea because it is relatively cheaper.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
Law of diminishing marginal utility is one of the rationale for the law of demand – the next unit consumed by the individual will not provide them with as much utility as the first commodity which they have consumed, and hence they would be prepared to pay for the next unit will fall.
And, since tea and coffee are substitute goods, increase in price of tea will shift the consumers of tea to coffee.
This will shift the marginal utility from consuming coffee to shift to the right – because users of coffee are now getting more utility from consuming coffee than tea because it is relatively cheaper. -
Question 250 of 999CB2025686
Question 250
FlagFor a Budget Line showing combinations of two goods, if the price of either of the goods changes, it will:
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. Shift the Budget Line outwards – Incorrect. A price change affects the slope of the budget line, not its position.
B. Shift the Budget Line inwards – Incorrect. A price change affects how much of each good can be bought, but does not directly shift the line inward.
C. Change the slope of the Budget Line – Correct. The slope of the budget line reflects the ratio of the prices of the two goods, so a change in the price of one good changes this ratio.
D. Not have any effect on the Budget Line – Incorrect. A price change always affects the budget line by altering the slope.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. Shift the Budget Line outwards – Incorrect. A price change affects the slope of the budget line, not its position.
B. Shift the Budget Line inwards – Incorrect. A price change affects how much of each good can be bought, but does not directly shift the line inward.
C. Change the slope of the Budget Line – Correct. The slope of the budget line reflects the ratio of the prices of the two goods, so a change in the price of one good changes this ratio.
D. Not have any effect on the Budget Line – Incorrect. A price change always affects the budget line by altering the slope. -
Question 251 of 999CB2025687
Question 251
FlagWhich of the following statements is false?
In the short run:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Production is subject to diminishing returns – Correct. In the short run, as more units of a variable factor are added to fixed factors, diminishing returns generally occur.
B. It is assumed that one or more factors of production are fixed in supply – Correct. In the short run, at least one factor (like capital or land) is fixed, while others (like labor) are variable.
C. Production function assumes technical efficiency in production – Correct. The production function assumes that the maximum output is produced for a given set of inputs, which reflects technical efficiency.
D. None of the Above – Correct, as all the above statements are true in the context of the short run.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Production is subject to diminishing returns – Correct. In the short run, as more units of a variable factor are added to fixed factors, diminishing returns generally occur.
B. It is assumed that one or more factors of production are fixed in supply – Correct. In the short run, at least one factor (like capital or land) is fixed, while others (like labor) are variable.
C. Production function assumes technical efficiency in production – Correct. The production function assumes that the maximum output is produced for a given set of inputs, which reflects technical efficiency.
D. None of the Above – Correct, as all the above statements are true in the context of the short run. -
Question 252 of 999CB2025688
Question 252
FlagThe long run marginal cost curve (LRMC) will be:
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Below the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is falling – Correct. When LRAC is falling, the LRMC curve lies below the LRAC curve because marginal cost pulls the average cost down.
B. Above the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is falling – Incorrect. If LRAC is falling, LRMC would be below LRAC, not above.
C. Equal to the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is falling – Incorrect. LRMC only equals LRAC when LRAC is at its minimum, not necessarily when LRAC is falling.
D. Below the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is rising – Incorrect. When LRAC is rising, LRMC would be above the LRAC curve.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Below the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is falling – Correct. When LRAC is falling, the LRMC curve lies below the LRAC curve because marginal cost pulls the average cost down.
B. Above the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is falling – Incorrect. If LRAC is falling, LRMC would be below LRAC, not above.
C. Equal to the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is falling – Incorrect. LRMC only equals LRAC when LRAC is at its minimum, not necessarily when LRAC is falling.
D. Below the Long run average cost (LRAC) curve when LRAC is rising – Incorrect. When LRAC is rising, LRMC would be above the LRAC curve. -
Question 253 of 999CB2025689
Question 253
FlagFor a price taker firm:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Average revenue is greater than the price charged – Incorrect. For a price taker, average revenue is equal to the price charged.
B. Average revenue curve is above the demand curve – Incorrect. For a price taker, average revenue and the demand curve are the same.
C. Demand curve is sloping – Incorrect. In perfect competition, the demand curve for a price taker is horizontal at the market price.
D. Demand curve is horizontal – Correct. For a price taker, the firm can sell any quantity at the prevailing market price, so the demand curve is horizontal.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Average revenue is greater than the price charged – Incorrect. For a price taker, average revenue is equal to the price charged.
B. Average revenue curve is above the demand curve – Incorrect. For a price taker, average revenue and the demand curve are the same.
C. Demand curve is sloping – Incorrect. In perfect competition, the demand curve for a price taker is horizontal at the market price.
D. Demand curve is horizontal – Correct. For a price taker, the firm can sell any quantity at the prevailing market price, so the demand curve is horizontal. -
Question 254 of 999CB2025690
Question 254
FlagIf demand is price elastic, a decrease in price will lead to:
I. A proportionately larger increase in quantity demanded
II. A proportionately smaller increase in quantity demanded
III. Positive marginal revenue
IV. Negative marginal revenue
Which of the above statements are true?Correct
The correct answer is B
I. A proportionately larger increase in quantity demanded – Correct. When demand is price elastic, a price decrease leads to a larger percentage increase in quantity demanded.
II. A proportionately smaller increase in quantity demanded – Incorrect. This is true for inelastic demand, not elastic demand.
III. Positive marginal revenue – Correct. For elastic demand, marginal revenue is positive, as a price decrease increases total revenue.
IV. Negative marginal revenue – Incorrect. Negative marginal revenue occurs when demand is inelastic, not elastic.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
I. A proportionately larger increase in quantity demanded – Correct. When demand is price elastic, a price decrease leads to a larger percentage increase in quantity demanded.
II. A proportionately smaller increase in quantity demanded – Incorrect. This is true for inelastic demand, not elastic demand.
III. Positive marginal revenue – Correct. For elastic demand, marginal revenue is positive, as a price decrease increases total revenue.
IV. Negative marginal revenue – Incorrect. Negative marginal revenue occurs when demand is inelastic, not elastic. -
Question 255 of 999CB2025691
Question 255
FlagA change in output causes:
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. An upward shift in the revenue curve – Incorrect. A change in output does not necessarily shift the revenue curve; it causes movement along the curve.
B. A downward shift in the revenue curve – Incorrect. A change in output does not cause a shift; it causes movement along the curve.
C. A movement along the revenue curve – Correct. A change in output leads to a movement along the revenue curve as total revenue changes with the level of output.
D. No movement along the revenue curve – Incorrect. A change in output always leads to movement along the revenue curve.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. An upward shift in the revenue curve – Incorrect. A change in output does not necessarily shift the revenue curve; it causes movement along the curve.
B. A downward shift in the revenue curve – Incorrect. A change in output does not cause a shift; it causes movement along the curve.
C. A movement along the revenue curve – Correct. A change in output leads to a movement along the revenue curve as total revenue changes with the level of output.
D. No movement along the revenue curve – Incorrect. A change in output always leads to movement along the revenue curve. -
Question 256 of 999CB2025692
Question 256
FlagWhich of the following statements are true?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. In the short run, a firm will shut down if it cannot cover its variable costs – Correct. In the short run, if a firm cannot cover its variable costs, it will shut down to minimize losses.
B. In the long run, a firm will shut down if it cannot make normal profits – Correct. In the long run, if a firm is unable to earn normal profit (zero economic profit), it will exit the market.
C. A firm’s profits will be maximized at the point where there is the greatest gap between total revenue and total cost – Correct. Profit is maximized where the difference between total revenue and total cost is the largest.
D. All of the above – Correct, as all the statements are true.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. In the short run, a firm will shut down if it cannot cover its variable costs – Correct. In the short run, if a firm cannot cover its variable costs, it will shut down to minimize losses.
B. In the long run, a firm will shut down if it cannot make normal profits – Correct. In the long run, if a firm is unable to earn normal profit (zero economic profit), it will exit the market.
C. A firm’s profits will be maximized at the point where there is the greatest gap between total revenue and total cost – Correct. Profit is maximized where the difference between total revenue and total cost is the largest.
D. All of the above – Correct, as all the statements are true. -
Question 257 of 999CB2025693
Question 257
FlagUnder perfect competition, in the short run:
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Firm’s marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost – Incorrect. In perfect competition, a firm will produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost to maximize profit or minimize losses.
B. Firm’s supply curve is upward sloping – Correct. The firm’s supply curve is upward sloping in the short run, as it increases production to maximize profit where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
C. The firm’s supply curve is not dependent on the costs of production – Incorrect. The firm’s supply curve in the short run is influenced by its costs of production, particularly the marginal cost.
D. The firm’s supply curve is horizontal – Incorrect. The firm’s supply curve in perfect competition is horizontal only in the long run under constant cost conditions, not in the short run.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Firm’s marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost – Incorrect. In perfect competition, a firm will produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost to maximize profit or minimize losses.
B. Firm’s supply curve is upward sloping – Correct. The firm’s supply curve is upward sloping in the short run, as it increases production to maximize profit where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
C. The firm’s supply curve is not dependent on the costs of production – Incorrect. The firm’s supply curve in the short run is influenced by its costs of production, particularly the marginal cost.
D. The firm’s supply curve is horizontal – Incorrect. The firm’s supply curve in perfect competition is horizontal only in the long run under constant cost conditions, not in the short run. -
Question 258 of 999CB2025694
Question 258
FlagWhich of the following statements about Perfect Competition is true?
I. The long run equilibrium is where the price is equal to the long run average cost
II. Perfect competition leads to a fair distribution of income
III. Perfect competition will lead to economies of scale in the long run
IV. Perfect competition could lead to consumer sovereigntyCorrect
The correct answer is D
I. The long run equilibrium is where the price is equal to the long run average cost – Correct. In the long run, firms in perfect competition make zero economic profit, where price equals long-run average cost.
II. Perfect competition leads to a fair distribution of income – Incorrect. While it may lead to allocative efficiency, perfect competition does not necessarily ensure a fair distribution of income.
III. Perfect competition will lead to economies of scale in the long run – Incorrect. Perfect competition does not necessarily lead to economies of scale; firms may operate at constant or decreasing costs, but economies of scale are not guaranteed.
IV. Perfect competition could lead to consumer sovereignty – Correct. In perfect competition, consumers have full control over the types and quantities of goods produced, which reflects consumer sovereignty.So, the correct combination is I and IV.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D
I. The long run equilibrium is where the price is equal to the long run average cost – Correct. In the long run, firms in perfect competition make zero economic profit, where price equals long-run average cost.
II. Perfect competition leads to a fair distribution of income – Incorrect. While it may lead to allocative efficiency, perfect competition does not necessarily ensure a fair distribution of income.
III. Perfect competition will lead to economies of scale in the long run – Incorrect. Perfect competition does not necessarily lead to economies of scale; firms may operate at constant or decreasing costs, but economies of scale are not guaranteed.
IV. Perfect competition could lead to consumer sovereignty – Correct. In perfect competition, consumers have full control over the types and quantities of goods produced, which reflects consumer sovereignty.So, the correct combination is I and IV.
-
Question 259 of 999CB2025695
Question 259
FlagWhich of the following is not an example Switching cost for a consumer under Monopoly?
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Sunk costs – Correct. Sunk costs are costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered. They are not considered switching costs because they do not affect the decision to switch suppliers.
B. Searching costs – Incorrect. Searching costs are the costs a consumer incurs to find information about alternatives, making it a switching cost.
C. Contractual costs – Incorrect. Contractual costs are associated with breaking or changing a contract, which is a type of switching cost.
D. Learning costs – Incorrect. Learning costs refer to the time and effort needed to learn to use a new product or service, which is a switching cost.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Sunk costs – Correct. Sunk costs are costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered. They are not considered switching costs because they do not affect the decision to switch suppliers.
B. Searching costs – Incorrect. Searching costs are the costs a consumer incurs to find information about alternatives, making it a switching cost.
C. Contractual costs – Incorrect. Contractual costs are associated with breaking or changing a contract, which is a type of switching cost.
D. Learning costs – Incorrect. Learning costs refer to the time and effort needed to learn to use a new product or service, which is a switching cost. -
Question 260 of 999CB2025696
Question 260
FlagWhich of the following statements is false?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Monopolist can use advertising to create barriers of entry – Correct. Heavy advertising can build brand loyalty, making it harder for new firms to compete.
B. Policy makers focus on sunk costs when considering anti-monopoly policy – Correct. High sunk costs discourage entry and are a key concern in assessing market contestability.
C. Lower the exit costs more the market is contestable – Correct. Easy exit reduces risk for new entrants, increasing contestability.
D. All markets are perfectly contestable – Incorrect. Most real-world markets have barriers like sunk costs, regulations, or brand loyalty, making them imperfectly contestable.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Monopolist can use advertising to create barriers of entry – Correct. Heavy advertising can build brand loyalty, making it harder for new firms to compete.
B. Policy makers focus on sunk costs when considering anti-monopoly policy – Correct. High sunk costs discourage entry and are a key concern in assessing market contestability.
C. Lower the exit costs more the market is contestable – Correct. Easy exit reduces risk for new entrants, increasing contestability.
D. All markets are perfectly contestable – Incorrect. Most real-world markets have barriers like sunk costs, regulations, or brand loyalty, making them imperfectly contestable. -
Question 261 of 999CB2025697
Question 261
FlagIn a monopolistic competition:
I. There are many firms in the market
II. There is independence of firms in a market
III. There is some product differentiation
IV. The firms are interdependent on each otherWhich of the above statements are true?
Correct
The correct answer is B
I. There are many firms in the market – Correct. Monopolistic competition involves a large number of small firms.
II. There is independence of firms in a market – Correct. Each firm makes decisions independently, assuming rivals’ reactions are not significant.
III. There is some product differentiation – Correct. Firms sell similar but not identical products, leading to brand preference.
IV. The firms are interdependent on each other – Incorrect. Interdependence is a feature of oligopoly, not monopolistic competition.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
I. There are many firms in the market – Correct. Monopolistic competition involves a large number of small firms.
II. There is independence of firms in a market – Correct. Each firm makes decisions independently, assuming rivals’ reactions are not significant.
III. There is some product differentiation – Correct. Firms sell similar but not identical products, leading to brand preference.
IV. The firms are interdependent on each other – Incorrect. Interdependence is a feature of oligopoly, not monopolistic competition. -
Question 262 of 999CB2025698
Question 262
FlagWhich of the following is not a reason for Plant economies of scale :
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Container Principle – Incorrect. This is a valid plant-level economy of scale where larger containers or equipment are more efficient in volume relative to their cost.
B. Multi Stage production – Incorrect. Integrating multiple stages of production within a single plant reduces handling and processing costs, contributing to plant economies.
C. By-Products – Incorrect. Efficient use of by-products within a plant reduces waste and lowers unit cost, qualifying as a plant economy.
D. Lower rate of interest for large firms – Correct. This is a financial economy of scale, not a plant economy, as it relates to external financing advantages, not production efficiency within the plant.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Container Principle – Incorrect. This is a valid plant-level economy of scale where larger containers or equipment are more efficient in volume relative to their cost.
B. Multi Stage production – Incorrect. Integrating multiple stages of production within a single plant reduces handling and processing costs, contributing to plant economies.
C. By-Products – Incorrect. Efficient use of by-products within a plant reduces waste and lowers unit cost, qualifying as a plant economy.
D. Lower rate of interest for large firms – Correct. This is a financial economy of scale, not a plant economy, as it relates to external financing advantages, not production efficiency within the plant. -
Question 263 of 999CB2025699
Question 263
FlagWhich of the following is not an assumption for constructing the long run average cost curve?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Factor prices are given – Incorrect. This is a standard assumption in constructing the LRAC curve.
B. The state of technology and factor quality change only in the very long run – Incorrect. This is an assumption for the typical LRAC curve, which assumes constant technology and factor quality in the long run.
C. Firms choose the least cost combination of factors for each output – Incorrect. The LRAC curve reflects cost minimization at each output level.
D. Factor prices are same at different level of output – Correct. It is assumed that factor prices are given in general, it is not with respect to the output level. It is because that Option A is given to us that we differ between the two statements, else we would have used them interchangeably.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Factor prices are given – Incorrect. This is a standard assumption in constructing the LRAC curve.
B. The state of technology and factor quality change only in the very long run – Incorrect. This is an assumption for the typical LRAC curve, which assumes constant technology and factor quality in the long run.
C. Firms choose the least cost combination of factors for each output – Incorrect. The LRAC curve reflects cost minimization at each output level.
D. Factor prices are same at different level of output – Correct. It is assumed that factor prices are given in general, it is not with respect to the output level. It is because that Option A is given to us that we differ between the two statements, else we would have used them interchangeably. -
Question 264 of 999CB2025700
Question 264
FlagUnder a Monopolistic Competition:
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Firms have higher costs than perfectly competitive firms due to excess capacity – Correct. In monopolistic competition, firms don’t produce at the minimum point of their average cost curve, leading to higher costs from excess capacity.
B. Firms have higher economies of scale than monopolies – Incorrect. Monopolies are typically larger and benefit more from economies of scale than the smaller firms in monopolistic competition.
C. Firms conduct more research and development than monopolies – Incorrect. Monopolies often have more resources and incentive to invest in R&D to maintain barriers to entry.
D. There is less choice of products than perfect competition – Incorrect. Monopolistic competition features more product variety due to differentiation, whereas perfect competition has identical products.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Firms have higher costs than perfectly competitive firms due to excess capacity – Correct. In monopolistic competition, firms don’t produce at the minimum point of their average cost curve, leading to higher costs from excess capacity.
B. Firms have higher economies of scale than monopolies – Incorrect. Monopolies are typically larger and benefit more from economies of scale than the smaller firms in monopolistic competition.
C. Firms conduct more research and development than monopolies – Incorrect. Monopolies often have more resources and incentive to invest in R&D to maintain barriers to entry.
D. There is less choice of products than perfect competition – Incorrect. Monopolistic competition features more product variety due to differentiation, whereas perfect competition has identical products. -
Question 265 of 999CB2025701
Question 265
FlagWhich of the following statements about Oligopoly is false:
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. There is interdependence of firms – Correct. In an oligopoly, firms are few and closely watch each other, leading to strategic interdependence.
B. Each firm is affected by its rival’s actions – Correct. Pricing, output, and marketing decisions by one firm directly influence others.
C. Cartel is an informal collusive agreement – False. A cartel is a formal collusive agreement where firms agree on prices, output, or market sharing to reduce competition.
D. Members of a cartel compete against each other using non-price competition – Correct. Even within cartels, firms may use advertising, branding, or other non-price tactics to gain advantage without breaking price agreements.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. There is interdependence of firms – Correct. In an oligopoly, firms are few and closely watch each other, leading to strategic interdependence.
B. Each firm is affected by its rival’s actions – Correct. Pricing, output, and marketing decisions by one firm directly influence others.
C. Cartel is an informal collusive agreement – False. A cartel is a formal collusive agreement where firms agree on prices, output, or market sharing to reduce competition.
D. Members of a cartel compete against each other using non-price competition – Correct. Even within cartels, firms may use advertising, branding, or other non-price tactics to gain advantage without breaking price agreements. -
Question 266 of 999CB2025702
Question 266
FlagTacit Collusion under an oligopoly does not include:
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. A formal arrangement between firms – Correct. Tacit collusion is implicit and unspoken, without any formal agreement, so this is not part of tacit collusion.
B. Average cost pricing – Incorrect. Firms may follow similar pricing strategies like average cost pricing as a form of implicit coordination.
C. Benchmark pricing – Incorrect. Using a common reference price (benchmark) is a common feature of tacit collusion.
D. Price leadership – Incorrect. One firm setting a price that others follow, without a formal agreement, is a classic example of tacit collusioIncorrect
The correct answer is A
A. A formal arrangement between firms – Correct. Tacit collusion is implicit and unspoken, without any formal agreement, so this is not part of tacit collusion.
B. Average cost pricing – Incorrect. Firms may follow similar pricing strategies like average cost pricing as a form of implicit coordination.
C. Benchmark pricing – Incorrect. Using a common reference price (benchmark) is a common feature of tacit collusion.
D. Price leadership – Incorrect. One firm setting a price that others follow, without a formal agreement, is a classic example of tacit collusio -
Question 267 of 999CB2025703
Question 267
FlagCournot Model:
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Is a model of monopolistic competition – Incorrect. The Cournot model is a model of oligopoly, not monopolistic competition.
B. Assumes that all the firms in the market sell their output for the same price – Correct. In the Cournot model, firms compete by choosing quantities, and the market determines a single price based on total output.
C. Assumes that all the firms in the market sell their output at different prices – Incorrect. The model assumes a uniform market price for a homogeneous product.
D. Assumes that production has short lead times and is relatively flexible – Incorrect. This is not a core assumption of the Cournot model, which focuses on quantity-setting behavior.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Is a model of monopolistic competition – Incorrect. The Cournot model is a model of oligopoly, not monopolistic competition.
B. Assumes that all the firms in the market sell their output for the same price – Correct. In the Cournot model, firms compete by choosing quantities, and the market determines a single price based on total output.
C. Assumes that all the firms in the market sell their output at different prices – Incorrect. The model assumes a uniform market price for a homogeneous product.
D. Assumes that production has short lead times and is relatively flexible – Incorrect. This is not a core assumption of the Cournot model, which focuses on quantity-setting behavior. -
Question 268 of 999CB2025704
Question 268
FlagWhich of the following markets in India is contestable?
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. Defence Manufacturing – Incorrect. This market has high entry barriers due to regulation, licensing, and capital intensity, making it non-contestable.
B. Natural Gas Distribution – Incorrect. It involves heavy infrastructure investment and regulatory hurdles, limiting contestability.
C. Selling Groceries in a neighbourhood – Correct. This market is relatively easy to enter and exit with low sunk costs, making it highly contestable.
D. Railways – Incorrect. Railways require massive infrastructure and government permissions, making entry difficult and the market non-contestable.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. Defence Manufacturing – Incorrect. This market has high entry barriers due to regulation, licensing, and capital intensity, making it non-contestable.
B. Natural Gas Distribution – Incorrect. It involves heavy infrastructure investment and regulatory hurdles, limiting contestability.
C. Selling Groceries in a neighbourhood – Correct. This market is relatively easy to enter and exit with low sunk costs, making it highly contestable.
D. Railways – Incorrect. Railways require massive infrastructure and government permissions, making entry difficult and the market non-contestable. -
Question 269 of 999CB2025705
Question 269
FlagA firm that produces a main product and a by-product will maximize profits if it:
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect. The decision to produce the by-product should be considered as part of the overall production decision, not just after deciding on the main product.
B. To maximize profits, the firm should produce at a level where the marginal cost of producing both the main product and the by-product equals the combined marginal revenue from both products.
C. Incorrect. The firm’s total profit maximization requires considering both the main product and the by-product together, not separately.
D. Incorrect. Cost-based pricing may not necessarily maximize profits; profit maximization requires considering marginal costs and revenues, not just costs.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect. The decision to produce the by-product should be considered as part of the overall production decision, not just after deciding on the main product.
B. To maximize profits, the firm should produce at a level where the marginal cost of producing both the main product and the by-product equals the combined marginal revenue from both products.
C. Incorrect. The firm’s total profit maximization requires considering both the main product and the by-product together, not separately.
D. Incorrect. Cost-based pricing may not necessarily maximize profits; profit maximization requires considering marginal costs and revenues, not just costs. -
Question 270 of 999CB2025706
Question 270
FlagHeuristics might include:
I. Copying the strategy of the most profitable business in the market
II. Focussing on relative rather than absolute profits
III. Focussing on absolute rather than relative profits
IV. Making a satisfactory / target level of profitWhich of the above statements are true?
Correct
The correct answer is D
I. Copying the strategy of the most profitable business in the market – Correct. This is a heuristic, where businesses may imitate successful competitors’ strategies to simplify decision-making.
II. Focussing on relative rather than absolute profits – Correct. Heuristics often involve focusing on relative performance compared to competitors, rather than focusing solely on absolute profits.
III. Focussing on absolute rather than relative profits – Incorrect. Heuristics are more likely to focus on relative rather than absolute measures to simplify decision-making in complex environments.
IV. Making a satisfactory/target level of profit – Correct. Many firms use heuristics to achieve a target level of profit, often referred to as “satisficing” rather than maximizing.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Copying the strategy of the most profitable business in the market – Correct. This is a heuristic, where businesses may imitate successful competitors’ strategies to simplify decision-making.
II. Focussing on relative rather than absolute profits – Correct. Heuristics often involve focusing on relative performance compared to competitors, rather than focusing solely on absolute profits.
III. Focussing on absolute rather than relative profits – Incorrect. Heuristics are more likely to focus on relative rather than absolute measures to simplify decision-making in complex environments.
IV. Making a satisfactory/target level of profit – Correct. Many firms use heuristics to achieve a target level of profit, often referred to as “satisficing” rather than maximizing. -
Question 271 of 999CB2025707
Question 271
FlagWhich of the following factors not affect the mark up used in cost-based pricing?
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Elasticity of demand for the product – Incorrect. A product with inelastic demand allows a higher mark-up, while elastic demand limits pricing power.
B. Corporate social spending – Correct. This is not typically considered in setting the mark-up for cost-based pricing, as it is unrelated to the product’s market performance or cost structure.
C. Competitor’s prices – Incorrect. Firms may adjust their mark-up to remain competitive, so rival pricing affects mark-up decisions.
D. Average cost – Incorrect. Cost-based pricing directly uses average cost as the base to which the mark-up is added.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Elasticity of demand for the product – Incorrect. A product with inelastic demand allows a higher mark-up, while elastic demand limits pricing power.
B. Corporate social spending – Correct. This is not typically considered in setting the mark-up for cost-based pricing, as it is unrelated to the product’s market performance or cost structure.
C. Competitor’s prices – Incorrect. Firms may adjust their mark-up to remain competitive, so rival pricing affects mark-up decisions.
D. Average cost – Incorrect. Cost-based pricing directly uses average cost as the base to which the mark-up is added. -
Question 272 of 999CB2025708
Question 272
FlagWhich of the following statements are false?
I. The substitution effect of a price change is always positive
II. The income effect for a Normal good is positive
III. The income effect for a Giffen good is positive
IV. The income effect of inferior good is positiveCorrect
The correct answer is A
Increase in price of the good will cause a fall in the quantity of goods and hence there would be negative subsititution effect – option A is incorrect.
Income effect would be negative in the case of normal good, when fall in income will cause a fall in demand and hence there would be negative income effect – option B is incorrect.
Income effect will be positive in case of inferior goods, as fall in income would cause a rise in demand and hence there would be positive income effect – option C and D are correct.
All Giffen goods are inferior goods but not all inferior goods are Giffen goods.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
Increase in price of the good will cause a fall in the quantity of goods and hence there would be negative subsititution effect – option A is incorrect.
Income effect would be negative in the case of normal good, when fall in income will cause a fall in demand and hence there would be negative income effect – option B is incorrect.
Income effect will be positive in case of inferior goods, as fall in income would cause a rise in demand and hence there would be positive income effect – option C and D are correct.
All Giffen goods are inferior goods but not all inferior goods are Giffen goods. -
Question 273 of 999CB2025709
Question 273
FlagGovernment intervention in the market:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Government intervention like price ceilings or floors can lead to shortages or surpluses.
B. Incorrect – Government decisions are rarely based on perfect information; they often operate with limited or asymmetric data.
C. Incorrect – Government interventions usually involve administrative costs, making them more expensive.
D. Correct – Interventions such as subsidies or welfare can reduce motivation to work or innovate, thus stifling incentives.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Government intervention like price ceilings or floors can lead to shortages or surpluses.
B. Incorrect – Government decisions are rarely based on perfect information; they often operate with limited or asymmetric data.
C. Incorrect – Government interventions usually involve administrative costs, making them more expensive.
D. Correct – Interventions such as subsidies or welfare can reduce motivation to work or innovate, thus stifling incentives. -
Question 274 of 999CB2025710
Question 274
FlagWhich of the following is a public good?
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Correct – The army is non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning its protection benefits all and one person’s benefit doesn’t reduce another’s.
B. Incorrect – Museums can charge entry fees, making them excludable; also, crowding can reduce enjoyment, making them rivalrous.
C. Incorrect – Healthcare is excludable and rivalrous to some extent, as services are limited and often accessed individually.
D. Incorrect – Education is excludable (schools can charge fees) and rivalrous when resources are limited, like class size.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Correct – The army is non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning its protection benefits all and one person’s benefit doesn’t reduce another’s.
B. Incorrect – Museums can charge entry fees, making them excludable; also, crowding can reduce enjoyment, making them rivalrous.
C. Incorrect – Healthcare is excludable and rivalrous to some extent, as services are limited and often accessed individually.
D. Incorrect – Education is excludable (schools can charge fees) and rivalrous when resources are limited, like class size. -
Question 275 of 999CB2025711
Question 275
FlagWhich of the following is not an example of collusion between firms?
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. Incorrect – Horizontal price fixing is a clear form of collusion where firms agree to set prices at a certain level.
B. Incorrect – Agreements to limit production reduce supply and manipulate market conditions, a typical collusive behavior.
C. Correct – Price discrimination is a pricing strategy based on consumer segments, done individually by firms without collusion.
D. Incorrect – Bid rigging involves firms coordinating bids to manipulate outcomes, which is a form of collusion.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. Incorrect – Horizontal price fixing is a clear form of collusion where firms agree to set prices at a certain level.
B. Incorrect – Agreements to limit production reduce supply and manipulate market conditions, a typical collusive behavior.
C. Correct – Price discrimination is a pricing strategy based on consumer segments, done individually by firms without collusion.
D. Incorrect – Bid rigging involves firms coordinating bids to manipulate outcomes, which is a form of collusion. -
Question 276 of 999CB2025712
Question 276
FlagWhich of the following is not an approach to the environment and sustainability?
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Social Efficiency approach – This approach emphasizes achieving an optimal allocation of resources where marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit. It accounts for externalities like pollution and aims to internalize them using tools like taxes or subsidies to protect the environment.
B. The Green approach – This is not a formally defined or widely accepted economic or philosophical framework. While “green” may colloquially refer to environmentally friendly actions or policies, it does not constitute a structured approach like the others listed.
C. The Gaia approach – Based on the Gaia hypothesis by James Lovelock, this approach conceptualizes Earth as a self-regulating living system. It supports deep ecological thinking and encourages sustainable living aligned with the natural balance of the planet.
D. The free market approach – This approach argues that environmental problems can be best addressed through market mechanisms, such as tradable pollution permits or assigning property rights. It assumes minimal government intervention and relies on incentives and competition.
Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Social Efficiency approach – This approach emphasizes achieving an optimal allocation of resources where marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit. It accounts for externalities like pollution and aims to internalize them using tools like taxes or subsidies to protect the environment.
B. The Green approach – This is not a formally defined or widely accepted economic or philosophical framework. While “green” may colloquially refer to environmentally friendly actions or policies, it does not constitute a structured approach like the others listed.
C. The Gaia approach – Based on the Gaia hypothesis by James Lovelock, this approach conceptualizes Earth as a self-regulating living system. It supports deep ecological thinking and encourages sustainable living aligned with the natural balance of the planet.
D. The free market approach – This approach argues that environmental problems can be best addressed through market mechanisms, such as tradable pollution permits or assigning property rights. It assumes minimal government intervention and relies on incentives and competition.
-
Question 277 of 999CB2025760
Question 277
FlagThe following GDP data is given:
$\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text { Data } & 2014 & 2024 \\
\hline \text { GDP in Millions } & 300 & 600 \\
\hline \text { GDP Deflator }(2000=100) & 160 & 250 \\
\hline
\end{array}$GDP for 2024 in 2014 prices is:
Correct
The correct answer is B
GDP of 2024 as per 2014 prices would be:
$\text {Real GDP} = 600 \times \frac {160}{250} = 384 \, \text {millions}$Incorrect
The correct answer is B
GDP of 2024 as per 2014 prices would be:
$\text {Real GDP} = 600 \times \frac {160}{250} = 384 \, \text {millions}$ -
Question 278 of 999CB2025761
Question 278
FlagWhich of the following is not a reason for the government making direct provision of goods and services?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Governments often provide goods directly to promote social justice by ensuring equitable access regardless of income.
B. Incorrect – Goods with large positive externalities, like education, are directly provided to ensure they are consumed at socially optimal levels.
C. Incorrect – When markets fail due to imperfect information, the government may intervene directly to ensure efficient and safe provision.
D. Correct – Public ownership is a method or outcome, not a reason; it results from the decision to provide goods, not a justification for it.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Governments often provide goods directly to promote social justice by ensuring equitable access regardless of income.
B. Incorrect – Goods with large positive externalities, like education, are directly provided to ensure they are consumed at socially optimal levels.
C. Incorrect – When markets fail due to imperfect information, the government may intervene directly to ensure efficient and safe provision.
D. Correct – Public ownership is a method or outcome, not a reason; it results from the decision to provide goods, not a justification for it. -
Question 279 of 999CB2025762
Question 279
FlagReducing the power of labour may lead to:
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. Incorrect – Reducing labour power usually doesn’t increase disequilibrium unemployment; it may reduce wage rigidity instead.
B. Incorrect – While it might reduce wage pressures, the effect on equilibrium unemployment is uncertain and depends on broader market conditions.
C. Correct – Lower labour power can reduce wage demands and industrial action, encouraging businesses to invest more, potentially boosting growth.
D. Incorrect – Reduced labour power typically lowers wage pressure, making cost push inflation less likely, not more.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. Incorrect – Reducing labour power usually doesn’t increase disequilibrium unemployment; it may reduce wage rigidity instead.
B. Incorrect – While it might reduce wage pressures, the effect on equilibrium unemployment is uncertain and depends on broader market conditions.
C. Correct – Lower labour power can reduce wage demands and industrial action, encouraging businesses to invest more, potentially boosting growth.
D. Incorrect – Reduced labour power typically lowers wage pressure, making cost push inflation less likely, not more. -
Question 280 of 999CB2025763
Question 280
FlagOne of the arguments in favour of interventionist supply side policies is that:
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Correct – The free rider problem discourages private firms from investing adequately in R&D and training, justifying government intervention to boost long-term productivity.
B. Incorrect – This supports free market arguments, not interventionist policies.
C. Incorrect – Deregulation is a market-based (non-interventionist) supply side policy aimed at increasing efficiency through competition.
D. Incorrect – This is a core argument for free market economics, not interventionist approaches.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Correct – The free rider problem discourages private firms from investing adequately in R&D and training, justifying government intervention to boost long-term productivity.
B. Incorrect – This supports free market arguments, not interventionist policies.
C. Incorrect – Deregulation is a market-based (non-interventionist) supply side policy aimed at increasing efficiency through competition.
D. Incorrect – This is a core argument for free market economics, not interventionist approaches. -
Question 281 of 999CB2025764
Question 281
FlagWhich of the following statements is false about socially efficient perfect markets:
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. Correct – Socially efficient perfect markets achieve Pareto efficiency, where no one can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
B. Correct – Perfect competition is a key characteristic of socially efficient markets, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
C. False – Externalities distort market outcomes and prevent social efficiency, so their presence contradicts the conditions of a perfect market.
D. Correct – In perfect markets, no single buyer or seller has market power, which ensures competitive pricing and efficiency.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. Correct – Socially efficient perfect markets achieve Pareto efficiency, where no one can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
B. Correct – Perfect competition is a key characteristic of socially efficient markets, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
C. False – Externalities distort market outcomes and prevent social efficiency, so their presence contradicts the conditions of a perfect market.
D. Correct – In perfect markets, no single buyer or seller has market power, which ensures competitive pricing and efficiency. -
Question 282 of 999CB2025765
Question 282
FlagSuppose Country A and country B are trading partners. Which of the following statements is/are true if country A raises interest rates to tackle inflation.
I. It will drive up the interest rates in country B
II. If aggregate demand in country A falls, aggregate demand in country B also falls
III. Exports of country B fall
IV. Imports of country B riseCorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Correct – Country A raising interest rates does increases the supply of loanable funds in country A and reduce the supply of loanable funds in country B, this will drive up the interest rate in country B.
II. Correct – If aggregate demand in country A falls, it may import less from country B, reducing country B’s aggregate demand.
III and IV. Incorrect – Increase in interest in country A will increase the demand for assets in country A – as people (both residents of country A and country B) would want to hold assets in currency of country A. This will reduce the exports of country B and increase imports for country B.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Correct – Country A raising interest rates does increases the supply of loanable funds in country A and reduce the supply of loanable funds in country B, this will drive up the interest rate in country B.
II. Correct – If aggregate demand in country A falls, it may import less from country B, reducing country B’s aggregate demand.
III and IV. Incorrect – Increase in interest in country A will increase the demand for assets in country A – as people (both residents of country A and country B) would want to hold assets in currency of country A. This will reduce the exports of country B and increase imports for country B. -
Question 283 of 999CB2025766
Question 283
FlagIf injections exceed withdrawals:
I. National income will rise
II. National income will fall
III. The resulting rise in national income will lead to a fall in withdrawals
IV. The resulting fall in national income will lead to a rise in withdrawals
Which of the above statements are true?Correct
The correct answer is A
If injections exceeds withdrawal there would be a rise in national income.
There may or may not be a corresponding increase in withdrawal – as it would depend on lot of other factors as well.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
If injections exceeds withdrawal there would be a rise in national income.
There may or may not be a corresponding increase in withdrawal – as it would depend on lot of other factors as well. -
Question 284 of 999CB2025767
Question 284
FlagWhich of the following is not a reason for fall in demand for products as prices rise?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – The international substitution effect occurs when higher domestic prices lead consumers to substitute with cheaper foreign goods, reducing demand.
B. Incorrect – The inter-temporal substitution effect refers to consumers shifting their consumption to the future when prices rise today, reducing current demand.
C. Incorrect – The real balance effect means that as prices rise, the real value of money holdings falls, leading to lower consumer spending and reduced demand.
D. Correct – The equilibrium effect is not a standard economic concept related to changes in demand due to price changes.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – The international substitution effect occurs when higher domestic prices lead consumers to substitute with cheaper foreign goods, reducing demand.
B. Incorrect – The inter-temporal substitution effect refers to consumers shifting their consumption to the future when prices rise today, reducing current demand.
C. Incorrect – The real balance effect means that as prices rise, the real value of money holdings falls, leading to lower consumer spending and reduced demand.
D. Correct – The equilibrium effect is not a standard economic concept related to changes in demand due to price changes. -
Question 285 of 999CB2025768
Question 285
FlagWhich of the following is false?
According to the Classical theory-Correct
The correct answer is C
Option A is incorrect – Classical economists, like Monetarists, believed that increase in quantity of money in the economy will lead to increase in general prices in the commodity.
Option B is incorrect – Classical economists believed there would no demand-deficient unemployment and there is no friction or lag in the market.
Option C is correct – Classical economists believed that Government spending should be equal to taxation to avoid budget deficits.
Option D is incorrect – Same reason as option C.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
Option A is incorrect – Classical economists, like Monetarists, believed that increase in quantity of money in the economy will lead to increase in general prices in the commodity.
Option B is incorrect – Classical economists believed there would no demand-deficient unemployment and there is no friction or lag in the market.
Option C is correct – Classical economists believed that Government spending should be equal to taxation to avoid budget deficits.
Option D is incorrect – Same reason as option C. -
Question 286 of 999CB2025769
Question 286
FlagKeynesian argued that:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Keynesians argue that labour markets are not perfect and can experience rigidity, especially in wages.
B. Incorrect – Keynesians believe that wages are often inflexible downward, especially during recessions, leading to unemployment.
C. Incorrect – During a recession, Keynesians argue that real wages tend to fall or remain stagnant, not rise, due to weak demand.
D. Correct – Keynesians believe that in times of economic downturns, government intervention, through fiscal policies like increased spending, can help stimulate aggregate demand and reduce unemployment.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Keynesians argue that labour markets are not perfect and can experience rigidity, especially in wages.
B. Incorrect – Keynesians believe that wages are often inflexible downward, especially during recessions, leading to unemployment.
C. Incorrect – During a recession, Keynesians argue that real wages tend to fall or remain stagnant, not rise, due to weak demand.
D. Correct – Keynesians believe that in times of economic downturns, government intervention, through fiscal policies like increased spending, can help stimulate aggregate demand and reduce unemployment. -
Question 287 of 999CB2025770
Question 287
FlagWhich of the following statements are true?
I. Actual growth is the percentage increase in national output produced
II. When actual output exceeds potential output, the output gap is negative
III. When actual output is less than the potential output, the output gap is negative
IV. When actual output is less than the potential output, the output gap is positiveCorrect
The correct answer is A
I. Correct – Actual growth refers to the percentage increase in the national output produced, reflecting how much the economy has grown.
II. Incorrect – If actual output exceeds potential output, the output gap is positive, not negative.
III. Correct – When actual output is less than potential output, the output gap is negative, indicating underutilized resources.
IV. Incorrect – When actual output is less than potential output, the output gap is negative, not positive.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
I. Correct – Actual growth refers to the percentage increase in the national output produced, reflecting how much the economy has grown.
II. Incorrect – If actual output exceeds potential output, the output gap is positive, not negative.
III. Correct – When actual output is less than potential output, the output gap is negative, indicating underutilized resources.
IV. Incorrect – When actual output is less than potential output, the output gap is negative, not positive. -
Question 288 of 999CB2025771
Question 288
FlagWhich of the following statements about aggregate demand of country X is false?
Aggregate demand consists of spending by:Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Aggregate demand includes consumer spending on goods and services and firm investments.
B. Incorrect – Government spending on goods, services, and investments is part of aggregate demand.
C. Incorrect – Spending by foreigners on country X’s exports contributes to aggregate demand.
D. Correct – Spending on imports is not part of aggregate demand because imports are subtracted from the total demand (they represent spending on foreign-produced goods).Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Aggregate demand includes consumer spending on goods and services and firm investments.
B. Incorrect – Government spending on goods, services, and investments is part of aggregate demand.
C. Incorrect – Spending by foreigners on country X’s exports contributes to aggregate demand.
D. Correct – Spending on imports is not part of aggregate demand because imports are subtracted from the total demand (they represent spending on foreign-produced goods). -
Question 289 of 999CB2025772
Question 289
FlagWhich of the following is not a form of equilibrium unemployment?
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – Frictional unemployment is the short-term unemployment that occurs when people are transitioning between jobs, and it is considered a form of equilibrium unemployment.
B. Correct – Cyclical unemployment is caused by fluctuations in the business cycle (e.g., recessions), which is not considered equilibrium unemployment since it occurs due to insufficient aggregate demand.
C. Incorrect – Structural unemployment arises from mismatches between workers’ skills and job requirements, and it can be part of equilibrium unemployment.
D. Incorrect – Regional unemployment, which occurs due to regional economic imbalances, can also be part of equilibrium unemployment, as it reflects labor market adjustments.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – Frictional unemployment is the short-term unemployment that occurs when people are transitioning between jobs, and it is considered a form of equilibrium unemployment.
B. Correct – Cyclical unemployment is caused by fluctuations in the business cycle (e.g., recessions), which is not considered equilibrium unemployment since it occurs due to insufficient aggregate demand.
C. Incorrect – Structural unemployment arises from mismatches between workers’ skills and job requirements, and it can be part of equilibrium unemployment.
D. Incorrect – Regional unemployment, which occurs due to regional economic imbalances, can also be part of equilibrium unemployment, as it reflects labor market adjustments. -
Question 290 of 999CB2025773
Question 290
FlagWhich of the following is not a source of cost push inflation?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Trade unions pushing up wages can lead to higher production costs, causing cost-push inflation.
B. Incorrect – Firms with monopoly power can raise prices above competitive levels, contributing to cost-push inflation.
C. Incorrect – An increase in international commodity prices, like oil or raw materials, raises costs for producers and can lead to cost-push inflation.
D. Correct – Globalization and increased international competition generally lead to lower prices, as competition drives firms to reduce costs, rather than causing cost-push inflation.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Trade unions pushing up wages can lead to higher production costs, causing cost-push inflation.
B. Incorrect – Firms with monopoly power can raise prices above competitive levels, contributing to cost-push inflation.
C. Incorrect – An increase in international commodity prices, like oil or raw materials, raises costs for producers and can lead to cost-push inflation.
D. Correct – Globalization and increased international competition generally lead to lower prices, as competition drives firms to reduce costs, rather than causing cost-push inflation. -
Question 291 of 999CB2025774
Question 291
FlagBalance of payments account consists of:
I. Current account
II. Capital account
III. Financial account
IV. Transfer account
Which of the above statements are true?Correct
The correct answer is B
I. Correct – The current account includes trade in goods and services, income from abroad, and current transfers.
II. Correct – The capital account records capital transfers and the acquisition/disposal of non-financial assets.
III. Correct – The financial account records transactions involving financial assets and liabilities, like foreign direct investment and portfolio investment.
IV. Incorrect – There is no separate “transfer account” in the balance of payments; transfers are typically included within the current account.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
I. Correct – The current account includes trade in goods and services, income from abroad, and current transfers.
II. Correct – The capital account records capital transfers and the acquisition/disposal of non-financial assets.
III. Correct – The financial account records transactions involving financial assets and liabilities, like foreign direct investment and portfolio investment.
IV. Incorrect – There is no separate “transfer account” in the balance of payments; transfers are typically included within the current account. -
Question 292 of 999CB2025775
Question 292
FlagWhich of the following factors can have a positive impact on exchange rates?
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – High inflation tends to reduce the value of a currency as it erodes purchasing power and reduces demand for the currency.
B. Correct – High interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency, which can lead to an appreciation of the exchange rate.
C. Incorrect – Capital outflows tend to decrease demand for the domestic currency as investors exchange it for foreign currencies, leading to a depreciation.
D. Incorrect – A rise in domestic incomes relative to incomes abroad can increase demand for imports, which would lead to a higher demand for foreign currencies and put downward pressure on the domestic currency.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – High inflation tends to reduce the value of a currency as it erodes purchasing power and reduces demand for the currency.
B. Correct – High interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency, which can lead to an appreciation of the exchange rate.
C. Incorrect – Capital outflows tend to decrease demand for the domestic currency as investors exchange it for foreign currencies, leading to a depreciation.
D. Incorrect – A rise in domestic incomes relative to incomes abroad can increase demand for imports, which would lead to a higher demand for foreign currencies and put downward pressure on the domestic currency. -
Question 293 of 999CB2025776
Question 293
FlagWhich of the following statements about free floating exchange rates is true?
I. There is a lot of official intervention in foreign exchange market
II. Little or no speculation
III. Increase in interest rates in a particular country will raise the value of country’s currency
IV. If investment prospects increase in a country the value of its currency increasesCorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Incorrect – In a free-floating exchange rate system, there is minimal or no official intervention in the foreign exchange market; exchange rates are determined by market forces.
II. Incorrect – Free-floating exchange rates are subject to speculation as traders and investors react to market expectations, news, and economic indicators.
III. Correct – An increase in interest rates in a country tends to attract foreign capital, increasing demand for the country’s currency, thus raising its value.
IV. Correct – If investment prospects improve in a country, foreign investors will likely increase their investments, raising demand for that country’s currency and causing its value to rise.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Incorrect – In a free-floating exchange rate system, there is minimal or no official intervention in the foreign exchange market; exchange rates are determined by market forces.
II. Incorrect – Free-floating exchange rates are subject to speculation as traders and investors react to market expectations, news, and economic indicators.
III. Correct – An increase in interest rates in a country tends to attract foreign capital, increasing demand for the country’s currency, thus raising its value.
IV. Correct – If investment prospects improve in a country, foreign investors will likely increase their investments, raising demand for that country’s currency and causing its value to rise. -
Question 294 of 999CB2025777
Question 294
FlagRecapitalization of a bank:
I. Involves re-structuring existing capital
II. Does not involve significant changes in the funding structure of a bank
III. Involves new capital
IV. Is aimed at reducing systemic risk
Which of the above statements are true?Correct
The correct answer is B
I. Incorrect – Recapitalization typically involves raising new capital, not just restructuring existing capital.
II. Incorrect – Recapitalization often involves significant changes in a bank’s funding structure, such as raising new equity or issuing new debt.
III. Correct – Recapitalization usually involves introducing new capital to strengthen a bank’s balance sheet and improve its financial stability.
IV. Correct – One of the goals of recapitalization is to reduce systemic risk by ensuring that banks have adequate capital to withstand financial shocks.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
I. Incorrect – Recapitalization typically involves raising new capital, not just restructuring existing capital.
II. Incorrect – Recapitalization often involves significant changes in a bank’s funding structure, such as raising new equity or issuing new debt.
III. Correct – Recapitalization usually involves introducing new capital to strengthen a bank’s balance sheet and improve its financial stability.
IV. Correct – One of the goals of recapitalization is to reduce systemic risk by ensuring that banks have adequate capital to withstand financial shocks. -
Question 295 of 999CB2025778
Question 295
FlagWhich of the following statements about money is false?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Correct – Money functions as a store of value, allowing individuals to preserve wealth over time.
B. Correct – Money acts as a standard of deferred payment, helping establish the value of future claims and obligations.
C. Correct – Money serves as a unit of account, allowing for the valuation and comparison of goods and services.
D. False – An increase in money supply does not always lead to an equal increase in national income; the actual impact depends on factors like velocity of money and economic conditions (e.g., liquidity trap, inflation).Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Correct – Money functions as a store of value, allowing individuals to preserve wealth over time.
B. Correct – Money acts as a standard of deferred payment, helping establish the value of future claims and obligations.
C. Correct – Money serves as a unit of account, allowing for the valuation and comparison of goods and services.
D. False – An increase in money supply does not always lead to an equal increase in national income; the actual impact depends on factors like velocity of money and economic conditions (e.g., liquidity trap, inflation). -
Question 296 of 999CB2025779
Question 296
FlagWhich of the following is included in Equity tier 1 capital for calculation of Capital Adequacy Ratio?
I. Bank reserves from retained profits
II. Ordinary share capital
III. Preference shares
IV. Subordinated debtCorrect
The correct answer is A
I. Correct – Retained earnings and bank reserves are part of core capital and are included in Equity Tier 1 capital.
II. Correct – Ordinary share capital is a primary component of Equity Tier 1 capital.
III. Incorrect – Preference shares are typically included in Tier 2 capital, not Equity Tier 1.
IV. Incorrect – Subordinated debt is also classified under Tier 2 capital, not Equity Tier 1.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
I. Correct – Retained earnings and bank reserves are part of core capital and are included in Equity Tier 1 capital.
II. Correct – Ordinary share capital is a primary component of Equity Tier 1 capital.
III. Incorrect – Preference shares are typically included in Tier 2 capital, not Equity Tier 1.
IV. Incorrect – Subordinated debt is also classified under Tier 2 capital, not Equity Tier 1. -
Question 297 of 999CB2025780
Question 297
FlagWhich of the following statements is true?
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. True – Borrowing from the non-bank private sector simply reallocates existing funds within the economy and does not directly affect the overall money supply.
B. False – Such borrowing does not reduce the money supply; it maintains it, as money is merely transferred from the private sector to the government.
C. False – An increase in liquidity ratios means banks hold more reserves and lend less, which reduces the money supply.
D. False – The sale of exports paid for in domestic currency generally increases demand for the currency but doesn’t directly reduce the money supply.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. True – Borrowing from the non-bank private sector simply reallocates existing funds within the economy and does not directly affect the overall money supply.
B. False – Such borrowing does not reduce the money supply; it maintains it, as money is merely transferred from the private sector to the government.
C. False – An increase in liquidity ratios means banks hold more reserves and lend less, which reduces the money supply.
D. False – The sale of exports paid for in domestic currency generally increases demand for the currency but doesn’t directly reduce the money supply. -
Question 298 of 999CB2025781
Question 298
FlagWhich of the following statements is false?
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. Correct – Reducing the money supply can help restrict aggregate demand by limiting available credit and spending.
B. Correct – Raising interest rates increases the cost of borrowing, which can reduce consumption and investment, thereby restricting aggregate demand.
C. False – Monetary policy can influence aggregate demand, but it is not a precise tool in the short term due to time lags, uncertain transmission mechanisms, and external influences.
D. Correct – Changing how the national debt is funded (e.g., borrowing from banks vs. non-banks) can influence the money supply and hence aggregate demand.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. Correct – Reducing the money supply can help restrict aggregate demand by limiting available credit and spending.
B. Correct – Raising interest rates increases the cost of borrowing, which can reduce consumption and investment, thereby restricting aggregate demand.
C. False – Monetary policy can influence aggregate demand, but it is not a precise tool in the short term due to time lags, uncertain transmission mechanisms, and external influences.
D. Correct – Changing how the national debt is funded (e.g., borrowing from banks vs. non-banks) can influence the money supply and hence aggregate demand. -
Question 299 of 999CB2025782
Question 299
FlagBank deposit multiplier is:
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – The deposit multiplier decreases as the liquidity ratio increases, so they are not directly proportional.
B. Correct – The deposit multiplier is the inverse of the liquidity ratio (or reserve ratio); a lower ratio allows more lending and deposit creation.
C. Incorrect – The deposit multiplier relates to expansion, not contraction, of the bank’s base.
D. Incorrect – The deposit multiplier is not defined as a ratio of deposit increase to liability expansion, but rather to reserves or liquidity held.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – The deposit multiplier decreases as the liquidity ratio increases, so they are not directly proportional.
B. Correct – The deposit multiplier is the inverse of the liquidity ratio (or reserve ratio); a lower ratio allows more lending and deposit creation.
C. Incorrect – The deposit multiplier relates to expansion, not contraction, of the bank’s base.
D. Incorrect – The deposit multiplier is not defined as a ratio of deposit increase to liability expansion, but rather to reserves or liquidity held. -
Question 300 of 999CB2025783
Question 300
FlagWhich of the following equation is correct?
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – This is the inverse of the correct relationship.
B. Incorrect – The multiplier and base are not multiplied by the broad money supply but rather to get it.
C. Incorrect – This rearrangement is incorrect; dividing the monetary base by the multiplier gives a smaller value, not the broad money supply.
D. Correct – The broad money supply is calculated by multiplying the money multiplier with the monetary base.The difference between monetary base and broad money supply is due to the fact that some money is hoarded by the public and banks keep more than excess reserves with them.
Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – This is the inverse of the correct relationship.
B. Incorrect – The multiplier and base are not multiplied by the broad money supply but rather to get it.
C. Incorrect – This rearrangement is incorrect; dividing the monetary base by the multiplier gives a smaller value, not the broad money supply.
D. Correct – The broad money supply is calculated by multiplying the money multiplier with the monetary base.The difference between monetary base and broad money supply is due to the fact that some money is hoarded by the public and banks keep more than excess reserves with them.
-
Question 301 of 999CB2025784
Question 301
FlagIf an increase in aggregate demand causes:
Correct
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – A vertical aggregate supply curve implies only prices change, not output.
B. Correct – A horizontal aggregate supply curve means firms can increase output without raising prices, typically in the short run when there is spare capacity.
C. Incorrect – A horizontal curve implies constant prices, so only output would change, not prices.
D. Incorrect – A vertical supply curve results in only price changes, not changes in output.Incorrect
The correct answer is B
A. Incorrect – A vertical aggregate supply curve implies only prices change, not output.
B. Correct – A horizontal aggregate supply curve means firms can increase output without raising prices, typically in the short run when there is spare capacity.
C. Incorrect – A horizontal curve implies constant prices, so only output would change, not prices.
D. Incorrect – A vertical supply curve results in only price changes, not changes in output. -
Question 302 of 999CB2025785
Question 302
FlagWhich of the following statements are false?
I. Increased expectations of inflation will move the Phillips curve upwards
II. Increased expectations of inflation will move the Phillips curve downwards
III. If the economy suffers from Hysteresis, then the Phillips curve shifts to the right
IV. If the economy suffers from Hysteresis, then the Phillips curve shifts to the leftCorrect
The correct answer is A
Incorrect
The correct answer is A
-
Question 303 of 999CB2025786
Question 303
FlagWhich of the following will enhance the effectiveness of a pure fiscal expansion?
I. Crowding out
II. Injections Multiplier
III. Confidence on behalf of businesses and banksCorrect
The correct answer is C
I. Incorrect – Crowding out reduces the effectiveness of fiscal expansion by decreasing private sector spending due to higher interest rates.
II. Correct – A strong injections multiplier means that government spending leads to a larger overall increase in national income, enhancing fiscal expansion.
III. Correct – High confidence among businesses and banks encourages investment and lending, amplifying the impact of fiscal policy.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
I. Incorrect – Crowding out reduces the effectiveness of fiscal expansion by decreasing private sector spending due to higher interest rates.
II. Correct – A strong injections multiplier means that government spending leads to a larger overall increase in national income, enhancing fiscal expansion.
III. Correct – High confidence among businesses and banks encourages investment and lending, amplifying the impact of fiscal policy. -
Question 304 of 999CB2025787
Question 304
FlagMarket oriented supply side policies does not include:
Correct
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Reducing the tax burden is a market-oriented supply side policy that aims to increase incentives to work and invest.
B. Incorrect – Reducing welfare payments can reduce the poverty trap and improve work incentives, aligning with market-oriented policies.
C. Incorrect – Encouraging competition is a key feature of market-oriented supply side policies to improve efficiency and productivity.
D. Correct – Nationalization involves increased government control and ownership, which is the opposite of market-oriented policies.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
A. Incorrect – Reducing the tax burden is a market-oriented supply side policy that aims to increase incentives to work and invest.
B. Incorrect – Reducing welfare payments can reduce the poverty trap and improve work incentives, aligning with market-oriented policies.
C. Incorrect – Encouraging competition is a key feature of market-oriented supply side policies to improve efficiency and productivity.
D. Correct – Nationalization involves increased government control and ownership, which is the opposite of market-oriented policies. -
Question 305 of 999CB2025788
Question 305
FlagThe economic functions of the financial system include:
I. Maturity transformation
II. Risk reduction through diversification
III. The transfer of consumption across timeCorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Correct – Maturity transformation involves converting short-term liabilities (like deposits) into long-term assets (like loans), a key function of the financial system.
II. Correct – Financial systems reduce risk by pooling resources and offering diversification opportunities to investors.
III. Correct – The financial system enables individuals to transfer consumption across time through saving and borrowing mechanisms.Incorrect
The correct answer is D
I. Correct – Maturity transformation involves converting short-term liabilities (like deposits) into long-term assets (like loans), a key function of the financial system.
II. Correct – Financial systems reduce risk by pooling resources and offering diversification opportunities to investors.
III. Correct – The financial system enables individuals to transfer consumption across time through saving and borrowing mechanisms. -
Question 306 of 999CB2025789
Question 306
FlagWhich of the following statement is not true?
Correct
The correct answer is C
A. True – Discount markets are part of the broader money market, dealing in short-term financial instruments.
B. True – Treasury bills and commercial bills are sold at a discount and redeemed at face value, generating a return.
C. False – Both new and existing Treasury or Commercial bills can be sold in the discount market; it’s not limited to existing ones.
D. True – Certificates of Deposit are negotiable time deposits often used in interbank lending.Incorrect
The correct answer is C
A. True – Discount markets are part of the broader money market, dealing in short-term financial instruments.
B. True – Treasury bills and commercial bills are sold at a discount and redeemed at face value, generating a return.
C. False – Both new and existing Treasury or Commercial bills can be sold in the discount market; it’s not limited to existing ones.
D. True – Certificates of Deposit are negotiable time deposits often used in interbank lending. -
Question 307 of 999CB2025790
Question 307
FlagStagflation is a combination of:
Correct
The correct answer is A
A. Correct – Stagflation is characterized by stagnant economic growth, rising unemployment, and high inflation, making it difficult to address with standard policies.
B. Incorrect – High growth and low unemployment are not features of stagflation.
C. Incorrect – High growth contradicts the “stag” (stagnation) aspect of stagflation.
D. Incorrect – This represents a healthy economy, not stagflation.Incorrect
The correct answer is A
A. Correct – Stagflation is characterized by stagnant economic growth, rising unemployment, and high inflation, making it difficult to address with standard policies.
B. Incorrect – High growth and low unemployment are not features of stagflation.
C. Incorrect – High growth contradicts the “stag” (stagnation) aspect of stagflation.
D. Incorrect – This represents a healthy economy, not stagflation. -
Question 308 of 999CB2031197
Question 308
FlagIf an economy moves from producing 10 units of Good $X$ and 5 units of Good $Y$ to producing 8 units of Good $X$ and 6 units of Good $Y$, the opportunity cost of the 6th unit of Good $Y$ is:
Correct
Answer: C
This question is testing the concept of opportunity cost introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes.Recall that the opportunity cost is the cost of something (here the sixth unit of Good Y) in terms of the best alternative foregone to obtain it (here in terms of units of Good X).
In order to free up the resources to increase output of Good $Y$ by one unit (from five to six), output of Good X has to be reduced by two units (from ten to eight). Consequently, the opportunity cost of the sixth unit of Good $Y$ must two units of Good X.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
Answer: C
This question is testing the concept of opportunity cost introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes.Recall that the opportunity cost is the cost of something (here the sixth unit of Good Y) in terms of the best alternative foregone to obtain it (here in terms of units of Good X).
In order to free up the resources to increase output of Good $Y$ by one unit (from five to six), output of Good X has to be reduced by two units (from ten to eight). Consequently, the opportunity cost of the sixth unit of Good $Y$ must two units of Good X.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 309 of 999CB2031198
Question 309
FlagThe main categories of economic resources are:
Correct
This is a straightforward question to start the paper. It is testing the main categories of economic resources.
The three main categories of resources are:
1. labour – all forms of human input
2. land and raw materials – all naturally occurring resources
3. capital – manufactured resources.Therefore the answer is Option D.
Note that factories are a type of capital (along with machinery, computers etc). Money is not a resource in the economic sense because it is not actually an input that is used to produce goods and services.Answer: D
Incorrect
This is a straightforward question to start the paper. It is testing the main categories of economic resources.
The three main categories of resources are:
1. labour – all forms of human input
2. land and raw materials – all naturally occurring resources
3. capital – manufactured resources.Therefore the answer is Option D.
Note that factories are a type of capital (along with machinery, computers etc). Money is not a resource in the economic sense because it is not actually an input that is used to produce goods and services.Answer: D
-
Question 310 of 999CB2031199
Question 310
FlagThe problem of scarcity in economics:
Correct
This is another straightforward question.
The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants’.Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
Answer: D
Incorrect
This is another straightforward question.
The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants’.Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
Answer: D
-
Question 311 of 999CB2031200
Question 311
FlagA company makes economic profits of $10 \%$. The risk premium for the company’s line of business is $5 \%$. If the banks offer a rate of interest on savings accounts of $3 \%$, the opportunity cost to the owners of the company is:
Correct
The concept of opportunity cost is introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes.
The question states that a company is making economic profits of 10\%, ie profits of 10\% over and above normal profit, which represents the opportunity cost of being in business. Recall that the opportunity cost arises because by investing their time and money in this business, the owners of the business forego the opportunity to invest their time and money to make profits elsewhere. However, the 10\% itself tells us nothing about the size of this opportunity cost.Recall that opportunity cost (or normal profit) can be expressed in terms of the rate of return foregone by investing capital in the particular business, which can in turn be broken down into the risk-free rate plus a suitable risk premium, reflecting the riskiness of the business.
The question tells us that the risk premium for the company’s line of business is 5\% (presumably per annum) and that banks offer a rate of interest on savings accounts of 3\%, which here represents the risk-free rate of return. Consequently the opportunity cost to the owners of the company is:
$$
3 \%+5 \%=8 \%
$$
and so Option C is the correct answer.Answer: C
Incorrect
The concept of opportunity cost is introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes.
The question states that a company is making economic profits of 10\%, ie profits of 10\% over and above normal profit, which represents the opportunity cost of being in business. Recall that the opportunity cost arises because by investing their time and money in this business, the owners of the business forego the opportunity to invest their time and money to make profits elsewhere. However, the 10\% itself tells us nothing about the size of this opportunity cost.Recall that opportunity cost (or normal profit) can be expressed in terms of the rate of return foregone by investing capital in the particular business, which can in turn be broken down into the risk-free rate plus a suitable risk premium, reflecting the riskiness of the business.
The question tells us that the risk premium for the company’s line of business is 5\% (presumably per annum) and that banks offer a rate of interest on savings accounts of 3\%, which here represents the risk-free rate of return. Consequently the opportunity cost to the owners of the company is:
$$
3 \%+5 \%=8 \%
$$
and so Option C is the correct answer.Answer: C
-
Question 312 of 999CB2031201
Question 312
FlagScarcity exists if:
Correct
This is a straightforward question to start the paper. It is testing one of the key definitions from Module 1 of the Course Notes.
Recall that scarcity is defined as the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants. It therefore exists if human wants cannot be satisfied (from the available resources). Consequently, Option B is the correct answer.
Economics is the study how scarce resources are allocated in practice. In a free market, the allocation decisions are solved by the price mechanism, whereby prices increase / decrease in response to shortages or surpluses.
Note that a good or service will normally be scarce regardless of the structure of the market in which it is produced and sold.
Answer: B
Incorrect
This is a straightforward question to start the paper. It is testing one of the key definitions from Module 1 of the Course Notes.
Recall that scarcity is defined as the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants. It therefore exists if human wants cannot be satisfied (from the available resources). Consequently, Option B is the correct answer.
Economics is the study how scarce resources are allocated in practice. In a free market, the allocation decisions are solved by the price mechanism, whereby prices increase / decrease in response to shortages or surpluses.
Note that a good or service will normally be scarce regardless of the structure of the market in which it is produced and sold.
Answer: B
-
Question 313 of 999CB2031202
Question 313
FlagWhich of the following statements is always TRUE?
Correct
Opportunity cost is another of the economic concepts introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes. It arises from the need to make choices between alternatives courses of action due to scarcity. This question is a straightforward test of the definition.
The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone, so Option D is the correct answer.
Note that although the opportunity cost of an activity may be constant, this need not be the case. For example, for a firm producing under diminishing marginal returns, the opportunity cost of successive units of Good X will be an increasing number of units of Good Y.
Also, total revenue less total variable cost is equal to the producer surplus of a firm in the short run.
Finally, the opportunity cost of being in business is sometimes referred to as normal profit.
Answer: D
Incorrect
Opportunity cost is another of the economic concepts introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes. It arises from the need to make choices between alternatives courses of action due to scarcity. This question is a straightforward test of the definition.
The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone, so Option D is the correct answer.
Note that although the opportunity cost of an activity may be constant, this need not be the case. For example, for a firm producing under diminishing marginal returns, the opportunity cost of successive units of Good X will be an increasing number of units of Good Y.
Also, total revenue less total variable cost is equal to the producer surplus of a firm in the short run.
Finally, the opportunity cost of being in business is sometimes referred to as normal profit.
Answer: D
-
Question 314 of 999CB2031203
Question 314
FlagThe solution to the economic problem of deciding which goods to produce requires:
Correct
Three main allocation decisions have to be made by any economic system:
1. Which goods are going to be produced?
2. How are those goods going to be produced?
3. Who will receive the goods?In the decision of which goods will be produced, a choice has to be made between consumer goods (eg clothes) and capital goods (eg machinery). When making this choice, the alternatives must be considered. For example, more clothes can be produced only if fewer machines are produced, so machines would have to be sacrificed for clothes. This idea is clearly demonstrated in Option C.
An economy might operate as a free market economy without any government intervention. In this case, resources would be allocated according to the market forces of supply and demand and the market prices resulting from their interaction (Option B). To be competitive, there would have to be freedom of entry and exit (Option A). However, a free market economy is not the only option. In practice, in most economies, governments intervene in the allocation of resources. For example, public goods are usually provided by the state. So Options A and B are not correct.
Option D relates to the second decision, ie it is concerned with how goods will be produced, the choice being between capital-intensive and labour-intensive methods.
Answer: C
Incorrect
Three main allocation decisions have to be made by any economic system:
1. Which goods are going to be produced?
2. How are those goods going to be produced?
3. Who will receive the goods?In the decision of which goods will be produced, a choice has to be made between consumer goods (eg clothes) and capital goods (eg machinery). When making this choice, the alternatives must be considered. For example, more clothes can be produced only if fewer machines are produced, so machines would have to be sacrificed for clothes. This idea is clearly demonstrated in Option C.
An economy might operate as a free market economy without any government intervention. In this case, resources would be allocated according to the market forces of supply and demand and the market prices resulting from their interaction (Option B). To be competitive, there would have to be freedom of entry and exit (Option A). However, a free market economy is not the only option. In practice, in most economies, governments intervene in the allocation of resources. For example, public goods are usually provided by the state. So Options A and B are not correct.
Option D relates to the second decision, ie it is concerned with how goods will be produced, the choice being between capital-intensive and labour-intensive methods.
Answer: C
-
Question 315 of 999CB2031204
Question 315
FlagOpportunity cost is always:
Correct
Opportunity cost is another of the economic concepts introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes. It arises from the need to make choices between alternatives courses of action due to scarcity. This question is a straightforward test of the definition.
The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone, so Option D is the correct answer.
Note that although the opportunity cost of an activity may be constant, this need not be the case. For example, for a firm producing Good $X$ under diminishing marginal returns, the opportunity cost of successive units of Good X will be an increasing number of units of Good Y.
Also, total revenue less total variable cost is equal to the producer surplus of a firm in the short run.
Finally, the opportunity cost of being in business is sometimes referred to as normal profit, whereas the supernormal profit earned by a firm is equal to the excess of total revenue over total cost, including the opportunity cost of being in business.
Answer: D
Incorrect
Opportunity cost is another of the economic concepts introduced in Module 1 of the Course Notes. It arises from the need to make choices between alternatives courses of action due to scarcity. This question is a straightforward test of the definition.
The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone, so Option D is the correct answer.
Note that although the opportunity cost of an activity may be constant, this need not be the case. For example, for a firm producing Good $X$ under diminishing marginal returns, the opportunity cost of successive units of Good X will be an increasing number of units of Good Y.
Also, total revenue less total variable cost is equal to the producer surplus of a firm in the short run.
Finally, the opportunity cost of being in business is sometimes referred to as normal profit, whereas the supernormal profit earned by a firm is equal to the excess of total revenue over total cost, including the opportunity cost of being in business.
Answer: D
-
Question 316 of 999CB2031205
Question 316
FlagTo prevent the value of the euro from depreciating against the US dollar, the European Central Bank might:
Correct
Answer: B
The value of a currency will tend to depreciate, ie reduce in value in terms of other currencies, if there is an excess supply of it on the foreign currency markets. So here, as the euro is depreciating, it must be the case that more people are wanting to sell euros than are wanting to buy euros. This might be the case if, for example, the eurozone countries are a net importer of goods and services.
So, in order to stop the depreciation of the euro, the European Central Bank (ECB) will need to buy up the excess supply of euros, which rules out Options C and D as correct answers. The ECB will buy euros by selling some of its reserves of other currencies in return for euros. Consequently, its foreign exchange reserves will fall, meaning that Option B must be the correct answer.
Under a fixed exchange rate regime, central banks will intervene directly into the foreign exchange markets, continually buying and selling currencies, in order to maintain exchange rates within a narrow range of values against each other. Even with the floating exchange rate system which currently prevails, they may intervene occasionally in order to stop exchange rates becoming more volatile than is deemed to be desirable.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The value of a currency will tend to depreciate, ie reduce in value in terms of other currencies, if there is an excess supply of it on the foreign currency markets. So here, as the euro is depreciating, it must be the case that more people are wanting to sell euros than are wanting to buy euros. This might be the case if, for example, the eurozone countries are a net importer of goods and services.
So, in order to stop the depreciation of the euro, the European Central Bank (ECB) will need to buy up the excess supply of euros, which rules out Options C and D as correct answers. The ECB will buy euros by selling some of its reserves of other currencies in return for euros. Consequently, its foreign exchange reserves will fall, meaning that Option B must be the correct answer.
Under a fixed exchange rate regime, central banks will intervene directly into the foreign exchange markets, continually buying and selling currencies, in order to maintain exchange rates within a narrow range of values against each other. Even with the floating exchange rate system which currently prevails, they may intervene occasionally in order to stop exchange rates becoming more volatile than is deemed to be desirable.
-
Question 317 of 999CB2031206
Question 317
FlagThe problem of scarcity in economics:
Correct
This question tests knowledge of the material in Module 1.
The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants’. Therefore the correct answer is Option D.Answer: D
Incorrect
This question tests knowledge of the material in Module 1.
The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants’. Therefore the correct answer is Option D.Answer: D
-
Question 318 of 999CB2031207
Question 318
FlagIf the government chooses to use resources to build a hospital instead of a school, this illustrates the concept of:
Correct
This is another question testing knowledge of the material in Module 1.
Opportunity cost is defined as ‘the cost of an activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone’. This concept illustrates that, as resources are limited, it is necessary to choose between alternatives. So, one way of measuring the cost of building a new hospital is to determine what the nation has to give up in order to achieve this. In this case, it appears that the opportunity cost of the hospital is a new school.Answer: D
Incorrect
This is another question testing knowledge of the material in Module 1.
Opportunity cost is defined as ‘the cost of an activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone’. This concept illustrates that, as resources are limited, it is necessary to choose between alternatives. So, one way of measuring the cost of building a new hospital is to determine what the nation has to give up in order to achieve this. In this case, it appears that the opportunity cost of the hospital is a new school.Answer: D
-
Question 319 of 999CB2031208
Question 319
FlagIf the government chooses to use resources to build a hospital instead of a school, this illustrates the concept of:
Correct
If the government chooses to use some of its finite resources to build a hospital, then it gives up the chance to use those same resources to instead build a school. This clearly illustrates the concept of opportunity cost, which is defined as the cost of an activity in terms of the next best alternative foregone.
Answer: D
Incorrect
If the government chooses to use some of its finite resources to build a hospital, then it gives up the chance to use those same resources to instead build a school. This clearly illustrates the concept of opportunity cost, which is defined as the cost of an activity in terms of the next best alternative foregone.
Answer: D
-
Question 320 of 999CB2031209
Question 320
FlagWhich of the following statements about real variables in the economy is FALSE?
Correct
CORRECT ANSWER- D
This question is testing the relationship between real and nominal variables, which is discussed in a number of modules. Questions on real and nominal variables have appeared a number of times in the Subject CT7 exam, so it’s important to have a good understanding of the relationship.
When asked to identify whether a statement is true or false, it is good practice to go through all four options thoroughly. This should help reduce the risk of making a silly mistake.
Basically, a real quantity has had inflation stripped out of it, ie it is equal to the nominal quantity less inflation. Equivalently, a real quantity plus inflation is equal to the nominal quantity.
Option A – If there is no inflation, then a rise in nominal GDP of 5\% corresponds to a rise in real GDP of 5\%. Therefore Option A is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option B – Recall that:
The nominal exchange rate is the actual rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
The real exchange rate is the nominal exchange rate adjusted for inflation in export and import prices.For example:
the real \$/£ exchange rate
$$
=\text { nominal } \$ / £ \text { exchange rate } \times \frac{\text { index of prices of UK exports to US }}{\text { index of prices of UK imports from US }}
$$The ratio of the prices of exports and imports is a measure of the relative inflation rates in the UK and the US.
This means that the real \$/£ exchange rate will decrease, ie depreciate, if:
– the nominal $\$ / £$ exchange rate decreases and/or
– the prices of UK exports to the US fall relative to the prices of UK imports from the US, perhaps because the UK inflation rate is lower than the US inflation rate.This suggests that Option B is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option C – In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transaction purposes. Therefore Option C is true, and so is not the correct answer. (Note that the textbook considers the nominal demand for money (rather than the real demand for money), and this will be affected by both nominal income and inflation.)Option D-Recall that the exante (before the event) real interest rate is equal to nominal interest rates less the expected rate of inflation. Therefore, the ex ante real interest rate will be positive if the expected rate of inflation is less than the nominal interest rate. For example, if the nominal interest rate is $5 \%$ pa and inflation is expected to be $3 \%$ pa, then the ex ante real interest rate is 2\% pa. Therefore Option D is false, and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
CORRECT ANSWER- D
This question is testing the relationship between real and nominal variables, which is discussed in a number of modules. Questions on real and nominal variables have appeared a number of times in the Subject CT7 exam, so it’s important to have a good understanding of the relationship.
When asked to identify whether a statement is true or false, it is good practice to go through all four options thoroughly. This should help reduce the risk of making a silly mistake.
Basically, a real quantity has had inflation stripped out of it, ie it is equal to the nominal quantity less inflation. Equivalently, a real quantity plus inflation is equal to the nominal quantity.
Option A – If there is no inflation, then a rise in nominal GDP of 5\% corresponds to a rise in real GDP of 5\%. Therefore Option A is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option B – Recall that:
The nominal exchange rate is the actual rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
The real exchange rate is the nominal exchange rate adjusted for inflation in export and import prices.For example:
the real \$/£ exchange rate
$$
=\text { nominal } \$ / £ \text { exchange rate } \times \frac{\text { index of prices of UK exports to US }}{\text { index of prices of UK imports from US }}
$$The ratio of the prices of exports and imports is a measure of the relative inflation rates in the UK and the US.
This means that the real \$/£ exchange rate will decrease, ie depreciate, if:
– the nominal $\$ / £$ exchange rate decreases and/or
– the prices of UK exports to the US fall relative to the prices of UK imports from the US, perhaps because the UK inflation rate is lower than the US inflation rate.This suggests that Option B is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option C – In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transaction purposes. Therefore Option C is true, and so is not the correct answer. (Note that the textbook considers the nominal demand for money (rather than the real demand for money), and this will be affected by both nominal income and inflation.)Option D-Recall that the exante (before the event) real interest rate is equal to nominal interest rates less the expected rate of inflation. Therefore, the ex ante real interest rate will be positive if the expected rate of inflation is less than the nominal interest rate. For example, if the nominal interest rate is $5 \%$ pa and inflation is expected to be $3 \%$ pa, then the ex ante real interest rate is 2\% pa. Therefore Option D is false, and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 321 of 999CB2031210
Question 321
FlagIf an economy moves from producing 10 units of Good $X$ and 5 units of Good $Y$ to producing 8 units of Good $X$ and 6 units of Good $Y$, the opportunity cost of the 6th unit of Good $Y$ is:
Correct
B Recall that the opportunity cost is the cost of something (here the sixth unit of Good Y ) in terms of the best alternative foregone to obtain it (here in terms of units of Good X).
In order to free up the resources to increase output of Good $Y$ by one unit (from five to six), output of Good $X$ has to be reduced by two units (from ten to eight). Consequently, the opportunity cost of the sixth unit of Good Y must be two units of Good X .
Hence the correct answer is Option B.
Incorrect
B Recall that the opportunity cost is the cost of something (here the sixth unit of Good Y ) in terms of the best alternative foregone to obtain it (here in terms of units of Good X).
In order to free up the resources to increase output of Good $Y$ by one unit (from five to six), output of Good $X$ has to be reduced by two units (from ten to eight). Consequently, the opportunity cost of the sixth unit of Good Y must be two units of Good X .
Hence the correct answer is Option B.
-
Question 322 of 999CB2031211
Question 322
FlagUnder a floating exchange rate system:
Correct
This is a tricky question that tackles a floating exchange rate system.
Under a fixed exchange rate system, countries must maintain similar inflation rates. This is because if one country has persistently higher inflation than the others against which its currency is fixed, then its exports will become increasingly uncompetitive, resulting in a balance of payments deficit. In order to alleviate the consequent downward pressure on its currency and so maintain the fixed exchange rate, the country will need to deflate its economy, so as to reduce inflation back down to the common level.Under a floating exchange rate system, however, inflation rates need not be closely linked. This is because any differences in inflation, which lead to a balance of payments deficit, might result in a depreciation of the currency of the high-inflation country. This will make its exports cheaper for the importing country, thus helping to counteract the effect of the high inflation.
Option A is therefore not the correct answer.
Next let’s consider Option B. This seems similar to Option A, but whereas Option A suggests that inflation rates are definitely linked under floating rates, Option B is suggesting that there could be a link. For example, higher inflation in a country that produces a commodity with highly inelastic demand, such as oil, could lead to higher production costs of that good and hence a higher market price. This in turn could lead to higher cost-push inflation when it is imported into another country. In this case, the currency of the high-inflation exporting country might not fall because the demand for its exports is inelastic and therefore the demand for the currency might be unchanged. This would means that its inflation is passed on to the importing country. So, Option B could be the correct answer.As mentioned previously, there is much more freedom for inflation to vary within a country that operates under a floating exchange rate system than under a fixed exchange rate system. So, if this is taken to mean that ‘domestic inflation is dictated outside of the bounds that would have constrained prices in a fixed rate regime’, then Option C could also be the correct answer.
Finally, if either Option B or C is correct, then Option D cannot be the correct answer.
Although Option D was originally the intended answer, the examiners decided that Options B and C could both be true statements. So, ultimately it was decided to award $11 / 2$ marks to all students who offered any answer.Incorrect
This is a tricky question that tackles a floating exchange rate system.
Under a fixed exchange rate system, countries must maintain similar inflation rates. This is because if one country has persistently higher inflation than the others against which its currency is fixed, then its exports will become increasingly uncompetitive, resulting in a balance of payments deficit. In order to alleviate the consequent downward pressure on its currency and so maintain the fixed exchange rate, the country will need to deflate its economy, so as to reduce inflation back down to the common level.Under a floating exchange rate system, however, inflation rates need not be closely linked. This is because any differences in inflation, which lead to a balance of payments deficit, might result in a depreciation of the currency of the high-inflation country. This will make its exports cheaper for the importing country, thus helping to counteract the effect of the high inflation.
Option A is therefore not the correct answer.
Next let’s consider Option B. This seems similar to Option A, but whereas Option A suggests that inflation rates are definitely linked under floating rates, Option B is suggesting that there could be a link. For example, higher inflation in a country that produces a commodity with highly inelastic demand, such as oil, could lead to higher production costs of that good and hence a higher market price. This in turn could lead to higher cost-push inflation when it is imported into another country. In this case, the currency of the high-inflation exporting country might not fall because the demand for its exports is inelastic and therefore the demand for the currency might be unchanged. This would means that its inflation is passed on to the importing country. So, Option B could be the correct answer.As mentioned previously, there is much more freedom for inflation to vary within a country that operates under a floating exchange rate system than under a fixed exchange rate system. So, if this is taken to mean that ‘domestic inflation is dictated outside of the bounds that would have constrained prices in a fixed rate regime’, then Option C could also be the correct answer.
Finally, if either Option B or C is correct, then Option D cannot be the correct answer.
Although Option D was originally the intended answer, the examiners decided that Options B and C could both be true statements. So, ultimately it was decided to award $11 / 2$ marks to all students who offered any answer. -
Question 323 of 999CB2031212
Question 323
FlagThe problem of scarcity in economics:
Correct
Answer:D
The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants’. Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer:D
The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can be produced to fulfil those wants’. Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 324 of 999CB2031213
Question 324
FlagUnder a fixed exchange rate system, the following approaches might be considered by governments to correct a balance of payments deficit:
I discouraging imports
II support for exporters
III increasing the level of aggregate demandWhich of the following is most likely to achieve this objective?
Correct
Answer: C
this question is testing fixed exchange rates.
The balance of payments is an account of a country’s monetary transactions with the rest of the world, and, as such it balances, ie it sums to zero. However, it is common practice to use the term ‘balance of payments deficit’ when meaning ‘current account deficit’.
A balance of payments deficit arises when the value of imports is greater than the value of exports. Therefore in order to correct a balance of payments deficit, the government needs to take action to reduce the value of imports and/or increase the value of exports.
Approach I is to discourage imports, eg using tariffs and/or quotas, which should help to achieve the government’s aim.
Approach II is to support exporters, eg via subsidies, which again, should help to achieve the government’s aim.
Approach III is to increase the level of (domestic) aggregate demand. Demand for one country’s exports will depend on the level of national income in other countries, ie higher incomes abroad are more likely to mean higher exports to those countries. So, changing the level of domestic aggregate demand will not directly affect exports. However, the demand for imports will depend on aggregate demand for goods and services in the domestic country, so increased (domestic) aggregate demand will increase the demand for imports, which will actually worsen a balance of payments deficit. In addition, an increase in aggregate demand might lead to an increase in domestic inflation and hence production costs, making the country less competitive and potentially further worsening the balance of payments deficit.
Note also that while increased domestic aggregate demand will not directly affect exports, it is possible that with higher domestic demand, firms that sell to both the domestic and overseas markets will be more able to sell their goods domestically and so might fight less hard for export business. Therefore exports might actually fall, which would actually act to worsen the balance of payments deficit.
So, Approaches I and II are most likely to correct a balance of payments deficit, and hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
this question is testing fixed exchange rates.
The balance of payments is an account of a country’s monetary transactions with the rest of the world, and, as such it balances, ie it sums to zero. However, it is common practice to use the term ‘balance of payments deficit’ when meaning ‘current account deficit’.
A balance of payments deficit arises when the value of imports is greater than the value of exports. Therefore in order to correct a balance of payments deficit, the government needs to take action to reduce the value of imports and/or increase the value of exports.
Approach I is to discourage imports, eg using tariffs and/or quotas, which should help to achieve the government’s aim.
Approach II is to support exporters, eg via subsidies, which again, should help to achieve the government’s aim.
Approach III is to increase the level of (domestic) aggregate demand. Demand for one country’s exports will depend on the level of national income in other countries, ie higher incomes abroad are more likely to mean higher exports to those countries. So, changing the level of domestic aggregate demand will not directly affect exports. However, the demand for imports will depend on aggregate demand for goods and services in the domestic country, so increased (domestic) aggregate demand will increase the demand for imports, which will actually worsen a balance of payments deficit. In addition, an increase in aggregate demand might lead to an increase in domestic inflation and hence production costs, making the country less competitive and potentially further worsening the balance of payments deficit.
Note also that while increased domestic aggregate demand will not directly affect exports, it is possible that with higher domestic demand, firms that sell to both the domestic and overseas markets will be more able to sell their goods domestically and so might fight less hard for export business. Therefore exports might actually fall, which would actually act to worsen the balance of payments deficit.
So, Approaches I and II are most likely to correct a balance of payments deficit, and hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 325 of 999CB2031214
Question 325
FlagA student studying a one-year Masters degree in Actuarial Science has course fees of $£ 12,000$. Were she not studying she could have had a job paying an after-tax income of $£ 20,000$. Irrespective of whether she studies or works the cost of her accommodation is £7,000 and the food bill is $£ 3,000$. The opportunity cost of studying for the Masters degree is:
Correct
B or C The opportunity cost of an activity is the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone. In this case, the ‘activity’ in question is studying a one-year Masters degree in Actuarial Science, and the ‘best alternative foregone’ is getting a job.
In either scenario, the student would incur accommodation and food costs, and so these can be ignored.
If she does the Masters degree, she has to pay $£ 12,000$. If she gets a job, then she earns $£ 20,000$. The difference in overall earnings between these two scenarios is $£ 32,000$, and hence the correct answer is Option C.
This is the interpretation provided in the textbook, although the answer could be argued to be Option B. The argument here is that the fee she pays is in return for the Masters degree she will obtain and hence should not be taken into account. So by doing the degree, she is only foregoing the income she would have earned had she not been studying, ie $£ 20,000$.
Incorrect
B or C The opportunity cost of an activity is the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone. In this case, the ‘activity’ in question is studying a one-year Masters degree in Actuarial Science, and the ‘best alternative foregone’ is getting a job.
In either scenario, the student would incur accommodation and food costs, and so these can be ignored.
If she does the Masters degree, she has to pay $£ 12,000$. If she gets a job, then she earns $£ 20,000$. The difference in overall earnings between these two scenarios is $£ 32,000$, and hence the correct answer is Option C.
This is the interpretation provided in the textbook, although the answer could be argued to be Option B. The argument here is that the fee she pays is in return for the Masters degree she will obtain and hence should not be taken into account. So by doing the degree, she is only foregoing the income she would have earned had she not been studying, ie $£ 20,000$.
-
Question 326 of 999CB2031216
Question 326
FlagIn a free-market economy, the basic function of the price mechanism is to:
Correct
A Recall from Module 1 of the Course Notes that:
– A free market is one without government intervention, so individual producers and consumers are free to make their own economic decisions.
– The price mechanism is the system whereby changes in price in response to changes in demand and supply have the effect of making demand equal to supply.In a free market, an excess of demand over supply will lead to a price rise, which will encourage an increase in production to meet that excess demand. In other words, the price rise signals that more resources need to be allocated to the production of the good in short supply. So, Option A is correct.
The scarcity of resources means that consumers wants can never be fully satisfied, regardless of the means of allocating resources, so Option B is incorrect.
In addition, the definition of a free market as one with no government intervention means that Option C cannot be the correct answer.Finally, recall from Module 9 that a key reason for government intervention is the failure of the free market to produce the socially efficient quantities of some goods. In particular, features such as non-excludability, undervalued private benefits and external social benefits mean that a free market will typically produce smaller quantities of certain goods (including public goods and merit goods) than would be optimal, ruling out Option D.
Incorrect
A Recall from Module 1 of the Course Notes that:
– A free market is one without government intervention, so individual producers and consumers are free to make their own economic decisions.
– The price mechanism is the system whereby changes in price in response to changes in demand and supply have the effect of making demand equal to supply.In a free market, an excess of demand over supply will lead to a price rise, which will encourage an increase in production to meet that excess demand. In other words, the price rise signals that more resources need to be allocated to the production of the good in short supply. So, Option A is correct.
The scarcity of resources means that consumers wants can never be fully satisfied, regardless of the means of allocating resources, so Option B is incorrect.
In addition, the definition of a free market as one with no government intervention means that Option C cannot be the correct answer.Finally, recall from Module 9 that a key reason for government intervention is the failure of the free market to produce the socially efficient quantities of some goods. In particular, features such as non-excludability, undervalued private benefits and external social benefits mean that a free market will typically produce smaller quantities of certain goods (including public goods and merit goods) than would be optimal, ruling out Option D.
-
Question 327 of 999CB2031217
Question 327
FlagWhich of the following best describes the opportunity cost of producing Good X?
Correct
B The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone, so Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
B The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone, so Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 328 of 999CB2031218
Question 328
FlagA production possibility frontier illustrates the limits on output of finished goods, as imposed by a limited supply of productive inputs. On the axes of the production possibility frontier, we place the:
Correct
C :A production possibility frontier, also known as a production possibility curve, is a curve showing all the possible combinations of two goods that a country can produce within a specified time period with all its resources fully and efficiently employed. It is the quantities of each good placed on each axis and so Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
C :A production possibility frontier, also known as a production possibility curve, is a curve showing all the possible combinations of two goods that a country can produce within a specified time period with all its resources fully and efficiently employed. It is the quantities of each good placed on each axis and so Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 329 of 999CB2031219
Question 329
FlagIf the government chooses to use resources to build a hospital instead of a school, this illustrates the concept of:
Correct
D: Opportunity cost is defined as ‘the cost of an activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone’. This concept illustrates that, as resources are limited, it is necessary to choose between alternatives. So, one way of measuring the cost of building a new hospital is to determine what the nation has to give up in order to achieve it. In this case, it appears that the opportunity cost of the hospital is a new school
Incorrect
D: Opportunity cost is defined as ‘the cost of an activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone’. This concept illustrates that, as resources are limited, it is necessary to choose between alternatives. So, one way of measuring the cost of building a new hospital is to determine what the nation has to give up in order to achieve it. In this case, it appears that the opportunity cost of the hospital is a new school
-
Question 330 of 999CB2031220
Question 330
FlagThe maximum an economy can produce is either 20 units of Good $X$ or 80 units of Good $Y$, and its production possibility curve is a straight line. The opportunity cost of producing 5 units of Good X is:
Correct
D: If the production possibility curve is a straight line, then the opportunity cost of producing 5 units of Good $X$ will be the same at all levels of production of Good $X$.
Given all its resources, the economy can produce either:
– 20 units of Good X, or
– 80 units of Good Y.Therefore given a quarter of its resources, the economy can produce either:
– 5 units of Good X, or
– 20 units of Good Y.Hence, the opportunity cost of producing 5 units of Good $X$ is 20 units of Good $Y$, so the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
D: If the production possibility curve is a straight line, then the opportunity cost of producing 5 units of Good $X$ will be the same at all levels of production of Good $X$.
Given all its resources, the economy can produce either:
– 20 units of Good X, or
– 80 units of Good Y.Therefore given a quarter of its resources, the economy can produce either:
– 5 units of Good X, or
– 20 units of Good Y.Hence, the opportunity cost of producing 5 units of Good $X$ is 20 units of Good $Y$, so the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 331 of 999CB2031221
Question 331
FlagWhich one of the following most accurately describes microeconomic topics?
Correct
A Microeconomics looks at individual units in the economy, such as consumers and firms. It considers:
– the demand for individual goods and services (such as electricity, housing, healthcare and newspapers)
– the price of individual goods and services (such as newspapers, private education, healthcare, electricity and housing).Macroeconomics is concerned with the economy as a whole, including:
– the overall price level, which is included in Option B
– the rate of economic growth, which is included in Option C
– the rate of inflation, which is included in Option D.Since Options B, C and D all include macroeconomic topics / variables, the correct answer must be Option A.
Incorrect
A Microeconomics looks at individual units in the economy, such as consumers and firms. It considers:
– the demand for individual goods and services (such as electricity, housing, healthcare and newspapers)
– the price of individual goods and services (such as newspapers, private education, healthcare, electricity and housing).Macroeconomics is concerned with the economy as a whole, including:
– the overall price level, which is included in Option B
– the rate of economic growth, which is included in Option C
– the rate of inflation, which is included in Option D.Since Options B, C and D all include macroeconomic topics / variables, the correct answer must be Option A.
-
Question 332 of 999CB2031222
Question 332
FlagIn economics, the problem of scarcity:
Correct
D: The definition of scarcity is:
‘The excess of human wants over what can actually be produced to fulfil these wants.’
Hence Option D is the correct answer.
The definition is not related to the level of employment, and so Option A is not true. The definition applies in all types of market structure, whether perfect or imperfect and it does not relate to prices, just to what will potentially be demanded and what can potentially be produced, so Option B is not true.Shortages exist where actual demand for a good or service exceeds what is actually produced at a certain price. Scarcity exists where actual demand for a good or service exceeds what can be produced. Since shortages relate to actual demand and supply at a specific price, Option C is not true.
Incorrect
D: The definition of scarcity is:
‘The excess of human wants over what can actually be produced to fulfil these wants.’
Hence Option D is the correct answer.
The definition is not related to the level of employment, and so Option A is not true. The definition applies in all types of market structure, whether perfect or imperfect and it does not relate to prices, just to what will potentially be demanded and what can potentially be produced, so Option B is not true.Shortages exist where actual demand for a good or service exceeds what is actually produced at a certain price. Scarcity exists where actual demand for a good or service exceeds what can be produced. Since shortages relate to actual demand and supply at a specific price, Option C is not true.
-
Question 333 of 999CB2031223
Question 333
FlagAn economy moves from producing 15 units of Good $X$ and six units of Good $Y$ to instead producing 16 units of Good $X$ and three units of Good $Y$. How many units of Good $Y$ is the opportunity cost of the 16th unit of Good X?
Correct
C: The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone.
In this case, the ‘activity’ in question is producing the sixteenth unit of Good X , and the ‘best alternative foregone’ is stated in terms of units of Good Y.
In order to free up the resources to increase output of Good X by one unit (from fifteen to sixteen), output of Good X has to be reduced by three units (from six to three).
Consequently, the opportunity cost of the sixteenth unit of Good X must be three units of Good YIncorrect
C: The opportunity cost of an activity is defined as the cost of the activity measured in terms of the best alternative foregone.
In this case, the ‘activity’ in question is producing the sixteenth unit of Good X , and the ‘best alternative foregone’ is stated in terms of units of Good Y.
In order to free up the resources to increase output of Good X by one unit (from fifteen to sixteen), output of Good X has to be reduced by three units (from six to three).
Consequently, the opportunity cost of the sixteenth unit of Good X must be three units of Good Y -
Question 334 of 999CB2031224
Question 334
FlagWhich of the following would not be classified as a resource in economics?
Correct
C Economic resources, also known as factors of production, are of three broad types:
– human resources (or labour)
– natural resources, including land and raw materials
– manufactured resources (or capital), including factories, machines, transportation and other equipment.Option A is a manufactured resource, Option B is a human resource and Option D is a natural resource. Money in the bank is not an economic resource, so Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
C Economic resources, also known as factors of production, are of three broad types:
– human resources (or labour)
– natural resources, including land and raw materials
– manufactured resources (or capital), including factories, machines, transportation and other equipment.Option A is a manufactured resource, Option B is a human resource and Option D is a natural resource. Money in the bank is not an economic resource, so Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 335 of 999CB2031225
Question 335
FlagFree market economies are classed as those where:
Correct
B :A free market is one without government intervention, so individual producers and consumers are free to make their own economic decisions. In reality, many economies are mixed economies, ie a mix of free-market and command economies.
Option A refers to SOME government involvement, so is not the correct answer. Options C and D refer to (joint) government involvement, so these are not the correct answer.
Option B refers to NO government involvement, so must be the correct answer. It also states that individuals and firms make the decisions that determine economic outcomes, which is consistent with the definition.
Incorrect
B :A free market is one without government intervention, so individual producers and consumers are free to make their own economic decisions. In reality, many economies are mixed economies, ie a mix of free-market and command economies.
Option A refers to SOME government involvement, so is not the correct answer. Options C and D refer to (joint) government involvement, so these are not the correct answer.
Option B refers to NO government involvement, so must be the correct answer. It also states that individuals and firms make the decisions that determine economic outcomes, which is consistent with the definition.
-
Question 336 of 999CB2031226
Question 336
FlagWhich of the following does NOT limit the maximum output an economy is able to produce?
Correct
C :The output of an economy is limited by the quantity and quality of economic resources available to produce it.
Option A is a determinant in the quantity of manufactured resources available, Option B is a determinant in the quality of human resources available, and Option D is most likely to relate to raw materials (which are a type of natural resource).
Option C (the level of demand in the economy) does not affect the quantity of output that can be produced. It relates to the quantity of output that is likely to be bought. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
C :The output of an economy is limited by the quantity and quality of economic resources available to produce it.
Option A is a determinant in the quantity of manufactured resources available, Option B is a determinant in the quality of human resources available, and Option D is most likely to relate to raw materials (which are a type of natural resource).
Option C (the level of demand in the economy) does not affect the quantity of output that can be produced. It relates to the quantity of output that is likely to be bought. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 337 of 999CB2031227
Question 337
FlagIf a country’s unemployment level rises, it is likely that:
Correct
D: A production possibility frontier, also known as a production possibility curve, is a curve showing all the possible combinations of two goods that a country can produce within a specified time period with all its resources fully and efficiently employed. If a country’s unemployment level rises, then it will not be employing its resources fully, and according so it must be producing inside of its production possibility curve. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
The production possibility curve would shift outwards (Option C) if there was an increase in the country’s productive capacity, but this is not consistent with an increase in unemployment, so Option C is not the correct answer.
Options A and B are likely to occur if a country’s unemployment level falls, so these are not correct answers.
Incorrect
D: A production possibility frontier, also known as a production possibility curve, is a curve showing all the possible combinations of two goods that a country can produce within a specified time period with all its resources fully and efficiently employed. If a country’s unemployment level rises, then it will not be employing its resources fully, and according so it must be producing inside of its production possibility curve. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
The production possibility curve would shift outwards (Option C) if there was an increase in the country’s productive capacity, but this is not consistent with an increase in unemployment, so Option C is not the correct answer.
Options A and B are likely to occur if a country’s unemployment level falls, so these are not correct answers.
-
Question 338 of 999CB2031228
Question 338
FlagWhich changes are most relevant to macroeconomics?
Changes in:Correct
A :Microeconomics looks at individual units in the economy, such as consumers and firms. Options B, C and D all relate to individual aspects of the economy, in particular:
– Option B relates to the wage rate of a specific subset of workers
– Option C relates to the price of computers
– Option D relates to the quantity of ships.Macroeconomics is concerned with the economy as a whole. Option A – real gross domestic product – relates to the economy as a whole, and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
A :Microeconomics looks at individual units in the economy, such as consumers and firms. Options B, C and D all relate to individual aspects of the economy, in particular:
– Option B relates to the wage rate of a specific subset of workers
– Option C relates to the price of computers
– Option D relates to the quantity of ships.Macroeconomics is concerned with the economy as a whole. Option A – real gross domestic product – relates to the economy as a whole, and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 339 of 999CB2031229
Question 339
FlagA key principle of economics is that human wants $\_\_\_\_$ (i) $\_\_\_\_$ the availability of $\_\_\_\_$ (ii) $\_\_\_\_$ . This concept is known as $\_\_\_\_$ (iii) $\_\_\_\_$ .
Correct
B: The definition of scarcity is:
‘The excess of human wants over what can actually be produced to fulfil these wants’
This could be reworded as ‘human wants exceed the availability of resources’, since what can actually be produced depends on the availability of resources. Given this is the definition of scarcity, Option B is the correct answer.Incorrect
B: The definition of scarcity is:
‘The excess of human wants over what can actually be produced to fulfil these wants’
This could be reworded as ‘human wants exceed the availability of resources’, since what can actually be produced depends on the availability of resources. Given this is the definition of scarcity, Option B is the correct answer. -
Question 340 of 999CB2031230
Question 340
FlagWhich of the following is most likely to lead to an outward shift in the production possibility curve for a country?
Correct
C :A production possibility curve (PPC) is a curve showing all the possible combinations of two goods that a country can produce within a specified time period with all its resources fully and efficiently employed.
A reduction in unemployment benefits (Option C) is likely to encourage (some of) the unemployed back to work. This will increase the country’s productive capacity, and so shift the production possibility curve to the right (ie outwards).Options A, B and D will not directly affect the country’s productive capacity:
– a reduction in government spending on hospitals (Option A) is likely to reduce the number of jobs available in the medical industry, but will not affect the productive capacity
– an increase in import taxes and duties (Option B) is likely to reduce the amount of goods and services that are imported, but will not increase the productive capacity
– an increase in the price level (Option D) will not affect the amount of physical output that a country is able to produce.Incorrect
C :A production possibility curve (PPC) is a curve showing all the possible combinations of two goods that a country can produce within a specified time period with all its resources fully and efficiently employed.
A reduction in unemployment benefits (Option C) is likely to encourage (some of) the unemployed back to work. This will increase the country’s productive capacity, and so shift the production possibility curve to the right (ie outwards).Options A, B and D will not directly affect the country’s productive capacity:
– a reduction in government spending on hospitals (Option A) is likely to reduce the number of jobs available in the medical industry, but will not affect the productive capacity
– an increase in import taxes and duties (Option B) is likely to reduce the amount of goods and services that are imported, but will not increase the productive capacity
– an increase in the price level (Option D) will not affect the amount of physical output that a country is able to produce. -
Question 341 of 999CB2031231
Question 341
FlagThe problem of scarcity in economics:
Correct
Option D. The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can actually be produced to fulfil these wants’.
Incorrect
Option D. The definition of scarcity is ‘the excess of human wants over what can actually be produced to fulfil these wants’.
-
Question 342 of 999CB2031232
Question 342
FlagAn economy can produce either Good $X$ or Good $Y$. The opportunity cost of producing an extra unit of Good $X$ is:
Correct
Option B. The definition of opportunity cost is the cost ‘in terms of the best alternative foregone’. In this case, it is the amount of Good $Y$ that would have to be given up to produce the extra unit of Good X.
Incorrect
Option B. The definition of opportunity cost is the cost ‘in terms of the best alternative foregone’. In this case, it is the amount of Good $Y$ that would have to be given up to produce the extra unit of Good X.
-
Question 343 of 999CB2031233
Question 343
FlagIn a free-market economy, allocation decisions are made by:
Correct
Option B. A free-market economy is one in which there is no government intervention. Instead all allocation decisions are made by the interaction of supply and demand, driven by individuals (aiming to maximise their utility) and firms (aiming to maximise their profits).
Incorrect
Option B. A free-market economy is one in which there is no government intervention. Instead all allocation decisions are made by the interaction of supply and demand, driven by individuals (aiming to maximise their utility) and firms (aiming to maximise their profits).
-
Question 344 of 999CB2031234
Question 344
FlagWhich of the following statements relating to the distinction between a command economy and a free-market economy is/are true?
I ) In a free-market economy, the state is free to plan the allocation of resources based on an estimation of people’s wants and needs, the availability of resources and the state’s priorities.
II) In a command economy, resource allocation is commanded by the price mechanism, which reflects the wishes of consumers and producers through the forces of supply and demand.
III) The notion that an increase in demand for a good or service leads to an increase in the price of that good or service is most relevant to a free-market economy.
Correct
Option C.
In a command economy, the state plans the allocation of resources, the plans being based on an estimation of people’s wants and needs, the availability of resources and the state’s priorities, so Statement I is incorrect.In a free-market economy, there is no government intervention; instead resources are allocated to different uses by the price mechanism. The wishes of consumers and producers are reflected in the market forces of supply and demand, which together, determine prices and determine resource allocation, so Statement II is incorrect.
For example, if there’s an increase in the demand for cars, the price of cars will increase (Statement III), the profits from car production will increase and firms will produce more cars.
Incorrect
Option C.
In a command economy, the state plans the allocation of resources, the plans being based on an estimation of people’s wants and needs, the availability of resources and the state’s priorities, so Statement I is incorrect.In a free-market economy, there is no government intervention; instead resources are allocated to different uses by the price mechanism. The wishes of consumers and producers are reflected in the market forces of supply and demand, which together, determine prices and determine resource allocation, so Statement II is incorrect.
For example, if there’s an increase in the demand for cars, the price of cars will increase (Statement III), the profits from car production will increase and firms will produce more cars.
-
Question 345 of 999CB2031235
Question 345
FlagIf a country experiences high domestic inflation compared to its trading partners with a fixed exchange rate then the effect of the inflation will be to:
Correct
Answer: C
This is a question on the operation of a fixed exchange rate system.
Under a fixed exchange rate system, the currency is fixed against another currency or an external standard of value, eg the price of one ounce of gold. The government, through its central bank, intervenes in the currency markets to maintain the value of the currency.If the country experiences higher domestic inflation than its trading partners, it will suffer a reduction in the demand for its relatively more expensive exports and an increase in demand for the more competitively priced imports. Hence Options A and B are incorrect.
In the currency market, there will be a reduction in the demand for the domestic currency (to buy exports) and an increase in the supply of the currency (as the domestic currency is converted into foreign currency to buy the imports), ie:
– a leftward shift of the demand curve
– a rightward shift of the supply curve.The answer must therefore be Option C. To follow the argument in Option C, consider the following diagram.
Suppose the government wishes to maintain the exchange rate at $r_1$. The increase in the supply of $£ s$ causes an excess supply of $Q_2-Q_1$ at the exchange rate $r_1$. To avoid a fall in the exchange rate, the central bank will have to artificially create a demand for this excess, ie the central bank will buy quantity $Q_2-Q_1$ of $£ s$ (with its foreign currency reserves).
Incorrect
Answer: C
This is a question on the operation of a fixed exchange rate system.
Under a fixed exchange rate system, the currency is fixed against another currency or an external standard of value, eg the price of one ounce of gold. The government, through its central bank, intervenes in the currency markets to maintain the value of the currency.If the country experiences higher domestic inflation than its trading partners, it will suffer a reduction in the demand for its relatively more expensive exports and an increase in demand for the more competitively priced imports. Hence Options A and B are incorrect.
In the currency market, there will be a reduction in the demand for the domestic currency (to buy exports) and an increase in the supply of the currency (as the domestic currency is converted into foreign currency to buy the imports), ie:
– a leftward shift of the demand curve
– a rightward shift of the supply curve.The answer must therefore be Option C. To follow the argument in Option C, consider the following diagram.

Suppose the government wishes to maintain the exchange rate at $r_1$. The increase in the supply of $£ s$ causes an excess supply of $Q_2-Q_1$ at the exchange rate $r_1$. To avoid a fall in the exchange rate, the central bank will have to artificially create a demand for this excess, ie the central bank will buy quantity $Q_2-Q_1$ of $£ s$ (with its foreign currency reserves).
-
Question 346 of 999CB2031236
Question 346
FlagThe introduction of a restrictive monetary policy in an open economy operating with a flexible exchange rate would most likely lead to:
Correct
Answer: A
The effect of monetary policy in an economy that operates a flexible exchange rate system is covered in Module 22.
Recall that a restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will lead to higher domestic interest rates. To see this, we could draw a similar diagram to that in Question 21 above, but showing the money supply curve shifting to the left, resulting in a rise in interest rates rather than a fall.
Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Note that an open economy is one that is open to international trade and capital flows.Incorrect
Answer: A
The effect of monetary policy in an economy that operates a flexible exchange rate system is covered in Module 22.
Recall that a restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will lead to higher domestic interest rates. To see this, we could draw a similar diagram to that in Question 21 above, but showing the money supply curve shifting to the left, resulting in a rise in interest rates rather than a fall.
Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Note that an open economy is one that is open to international trade and capital flows. -
Question 347 of 999CB2031237
Question 347
FlagWhich one of the following will NOT happen following a devaluation of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange market?
Correct
Answer: A
This is a question on the effects of a devaluation.
A devaluation of the domestic currency is the refixing of the fixed exchange rate at a lower level.
Such a move:
– reduces the price of exports in terms of foreign currency (so Option C is true and is not the correct answer). This in turn will lead to an increase in export volumes (so Option B is true and is not the answer).
– increases the domestic currency price of imports (so Option D is true and is not the correct answer). This in turn will lead to a reduction in the volume of imports (so Option A is not true and is the correct answer).Incorrect
Answer: A
This is a question on the effects of a devaluation.
A devaluation of the domestic currency is the refixing of the fixed exchange rate at a lower level.
Such a move:
– reduces the price of exports in terms of foreign currency (so Option C is true and is not the correct answer). This in turn will lead to an increase in export volumes (so Option B is true and is not the answer).
– increases the domestic currency price of imports (so Option D is true and is not the correct answer). This in turn will lead to a reduction in the volume of imports (so Option A is not true and is the correct answer). -
Question 348 of 999CB2031238
Question 348
FlagIf the central bank has to intervene in the foreign exchange markets to prevent the home currency from appreciating, then its foreign exchange reserves will:
Correct
Answer: B
In a fixed exchange rate system, the rate of the currency is typically fixed against another currency and the central bank intervenes in the currency markets to maintain the fixed value.
In the following diagram, suppose the exchange rate is originally fixed at $r_1$.
The question states that the exchange rate is in danger of appreciating, so there must be an increase in demand for and/or a decrease in supply of the currency. Suppose that demand increases from $D_1$ to $D_2$. At $r_1$, there is excess demand of $Q_2-Q_1$, and without intervention from the central bank, the exchange rate will increase from $r_1$ to $r_2$. To prevent this happening, the central bank will have to satisfy this demand by supplying $Q_2-Q_1$ £s to the market. It will achieve this by buying foreign currency with $£ s$, which will ultimately increase the volume of £s in circulation when the £s are deposited in domestic banks. Therefore, the country’s foreign exchange reserves will increase and the domestic money supply will rise. So the answer is Option B.
Incorrect
Answer: B
In a fixed exchange rate system, the rate of the currency is typically fixed against another currency and the central bank intervenes in the currency markets to maintain the fixed value.
In the following diagram, suppose the exchange rate is originally fixed at $r_1$.

The question states that the exchange rate is in danger of appreciating, so there must be an increase in demand for and/or a decrease in supply of the currency. Suppose that demand increases from $D_1$ to $D_2$. At $r_1$, there is excess demand of $Q_2-Q_1$, and without intervention from the central bank, the exchange rate will increase from $r_1$ to $r_2$. To prevent this happening, the central bank will have to satisfy this demand by supplying $Q_2-Q_1$ £s to the market. It will achieve this by buying foreign currency with $£ s$, which will ultimately increase the volume of £s in circulation when the £s are deposited in domestic banks. Therefore, the country’s foreign exchange reserves will increase and the domestic money supply will rise. So the answer is Option B.
-
Question 349 of 999CB2031239
Question 349
FlagDevaluation of a country’s currency will lead to the greatest improvement in the current account of a country’s balance of payments when the demand for:
Correct
Answer: D
Balance of payments and exchange rates are discussed in Modules 13 and 22 of the Course Notes.
The aim of a devaluation is to increase export earnings and/or decrease import expenditure, leading to an improvement in the current account.A devaluation reduces the foreign price of each unit that a country exports but has no impact on the price or revenue per unit in domestic currency terms. The reduction in the foreign price will increase demand for exports and so increase the volume of exports. Therefore, a devaluation will increase export earnings in domestic currency terms. The greater the price elasticity of demand for exports, the greater the increase in volume of exports and export earnings.
A devaluation will increase the domestic price of imports. This will reduce demand for imports so that the volume of imports falls. If demand for imports is price-elastic, an increase in the domestic price of imports will lead to a more than proportionate decrease in the quantity of imports and so a decrease in the value of imports, measured in domestic currency terms.
Therefore, a devaluation will lead to the greatest improvement in the current account of the balance of payments when demand for both exports and imports is price-elastic and so Option D is the correct answer.
Note that the above example could be done in terms of foreign currency and the same conclusion reached.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Balance of payments and exchange rates are discussed in Modules 13 and 22 of the Course Notes.
The aim of a devaluation is to increase export earnings and/or decrease import expenditure, leading to an improvement in the current account.A devaluation reduces the foreign price of each unit that a country exports but has no impact on the price or revenue per unit in domestic currency terms. The reduction in the foreign price will increase demand for exports and so increase the volume of exports. Therefore, a devaluation will increase export earnings in domestic currency terms. The greater the price elasticity of demand for exports, the greater the increase in volume of exports and export earnings.
A devaluation will increase the domestic price of imports. This will reduce demand for imports so that the volume of imports falls. If demand for imports is price-elastic, an increase in the domestic price of imports will lead to a more than proportionate decrease in the quantity of imports and so a decrease in the value of imports, measured in domestic currency terms.
Therefore, a devaluation will lead to the greatest improvement in the current account of the balance of payments when demand for both exports and imports is price-elastic and so Option D is the correct answer.
Note that the above example could be done in terms of foreign currency and the same conclusion reached.
-
Question 350 of 999CB2031240
Question 350
FlagAll other things being equal, which one of the following statements is always TRUE?
Correct
Answer- B
Remember that an appreciation or depreciation of the exchange rate will have an effect on:
– prices, ie the foreign price of exports and the domestic price of imports
– volumes, ie the demand for exports and the demand for imports
– values, ie the effect on the value of exports (export revenue) and the value of imports (import expenditure), which are dependent upon the elasticities of demand for exports and imports.For example, a depreciation of a currency will:
– decrease the foreign price of exports and increase the domestic price of imports
– increase the demand for exports and hence export volumes
– decrease the demand for imports and hence import volumes
– lead to an increase in the value of exports (measured in domestic currency terms), but an uncertain effect on the value of imports (measured in domestic currency terms), which depends on the elasticity of demand for imports
– lead to an uncertain effect on the value of exports (measured in foreign currency terms), which depends on the elasticity of demand for exports, but a decrease in the value of imports (measured in foreign currency terms).Since the effect on the value of imports (measured in domestic currency terms) is uncertain (as is the value of exports measured in foreign currency terms), Options A and D can be ruled out. From the above, we can see that Option B is correct and Option C is incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer- B
Remember that an appreciation or depreciation of the exchange rate will have an effect on:
– prices, ie the foreign price of exports and the domestic price of imports
– volumes, ie the demand for exports and the demand for imports
– values, ie the effect on the value of exports (export revenue) and the value of imports (import expenditure), which are dependent upon the elasticities of demand for exports and imports.For example, a depreciation of a currency will:
– decrease the foreign price of exports and increase the domestic price of imports
– increase the demand for exports and hence export volumes
– decrease the demand for imports and hence import volumes
– lead to an increase in the value of exports (measured in domestic currency terms), but an uncertain effect on the value of imports (measured in domestic currency terms), which depends on the elasticity of demand for imports
– lead to an uncertain effect on the value of exports (measured in foreign currency terms), which depends on the elasticity of demand for exports, but a decrease in the value of imports (measured in foreign currency terms).Since the effect on the value of imports (measured in domestic currency terms) is uncertain (as is the value of exports measured in foreign currency terms), Options A and D can be ruled out. From the above, we can see that Option B is correct and Option C is incorrect.
-
Question 351 of 999CB2031241
Question 351
FlagAn economy with a floating exchange rate has a large deficit on the current account of its balance of payments. Which policy combination would be most likely to reduce this deficit?
Correct
Answer- D
This is a tricky question on exchange rates and macroeconomic policy.
The question has given two aspects of the policy to consider: changing interest rates and changing income tax rates.It will be necessary to work out the impact on the current account of the balance of payments essentially, this is exports less imports (or net exports, $X-M$ ). The policy is trying to cure a deficit; in other words, it is trying to increase $X-M$.
The following answer starts by looking at income tax rates and then moves on to consider interest rates.
D An increase in income tax rates will reduce the amount of disposable income consumers have available to spend. Since they would tend to spend some of their disposable income on imports, the quantity of imported goods ( M ) would fall, hence increasing $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$.
This rules out Options B and C.
There are two main ways in which net exports will be affected by a change in interest rates:
1. as a result of a change in national income – in particular, imports are usually a function of national income
2. through movements in the exchange rate, which affects the relative prices of exports and imports.An increase in interest rates will reduce consumption and investment in the economy and dampen economic growth. This will tend to reduce M , and hence increase $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$.
Hence the examiners’ intended answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer- D
This is a tricky question on exchange rates and macroeconomic policy.
The question has given two aspects of the policy to consider: changing interest rates and changing income tax rates.It will be necessary to work out the impact on the current account of the balance of payments essentially, this is exports less imports (or net exports, $X-M$ ). The policy is trying to cure a deficit; in other words, it is trying to increase $X-M$.
The following answer starts by looking at income tax rates and then moves on to consider interest rates.
D An increase in income tax rates will reduce the amount of disposable income consumers have available to spend. Since they would tend to spend some of their disposable income on imports, the quantity of imported goods ( M ) would fall, hence increasing $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$.
This rules out Options B and C.
There are two main ways in which net exports will be affected by a change in interest rates:
1. as a result of a change in national income – in particular, imports are usually a function of national income
2. through movements in the exchange rate, which affects the relative prices of exports and imports.An increase in interest rates will reduce consumption and investment in the economy and dampen economic growth. This will tend to reduce M , and hence increase $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$.
Hence the examiners’ intended answer is Option D.
-
Question 352 of 999CB2031242
Question 352
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT likely to happen following a devaluation of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange market?
Correct
Answer-B
This is a question on the effects of devaluation.
A devaluation of the domestic currency is the refixing of a fixed or adjustable peg exchange rate at a lower level. Such a move:
– decreases the foreign price of exports (so Option A is true and is not the answer)
– increases the domestic price of imports (so Option B – which states that imports become cheaper is false and so is the correct answer).As a result of the price changes, there will be:
– an increase in the demand for exports (so Option C is true and is not the answer)
– a decrease in the demand for imports (so Option D is true and is not the answer).Incorrect
Answer-B
This is a question on the effects of devaluation.
A devaluation of the domestic currency is the refixing of a fixed or adjustable peg exchange rate at a lower level. Such a move:
– decreases the foreign price of exports (so Option A is true and is not the answer)
– increases the domestic price of imports (so Option B – which states that imports become cheaper is false and so is the correct answer).As a result of the price changes, there will be:
– an increase in the demand for exports (so Option C is true and is not the answer)
– a decrease in the demand for imports (so Option D is true and is not the answer). -
Question 353 of 999CB2031243
Question 353
FlagIf Canadian dollars are cheaper in Scotland than in Toronto, to benefit from the purchase and sale of foreign exchange Canadian dollars should be:
Correct
Answer-A
This question is on exchange rates, although the logic required to identify the correct answer requires no knowledge of exchange rates. (To make money from buying and selling anything, whether it be a good, service or currency, it should be purchased for less than it is sold.)
To benefit from the exchange, dollars should be purchased where they are cheap and sold where they are expensive.
Incorrect
Answer-A
This question is on exchange rates, although the logic required to identify the correct answer requires no knowledge of exchange rates. (To make money from buying and selling anything, whether it be a good, service or currency, it should be purchased for less than it is sold.)
To benefit from the exchange, dollars should be purchased where they are cheap and sold where they are expensive.
-
Question 354 of 999CB2031244
Question 354
FlagWhich of the following are the correct responses for the missing words (i), (ii) and (iii) in the following statement? ‘An appreciation of the domestic currency will likely act to $\_\_\_\_$ (i) $\_\_\_\_$ the volume of imports and $\_\_\_\_$ (ii) $\_\_\_\_$ the volume of exports and $\_\_\_\_$ (iii) $\_\_\_\_$ the recorded inflation rate.’
Correct
the correct answer is Option B.
This question is testing the effects of a currency appreciation.
B An appreciation of the domestic currency will:
– make exports less competitive, ie exports will be relatively expensive
– tend to decrease export volumes – this rules out Option C
– make imports relatively cheap
– tend to increase import volumes – this rules out Options C and D.Relatively cheap imports might reduce cost-push inflationary pressures, and lower demand for (more expensive) exports might reduce demand-pull inflationary pressures. Therefore the recorded inflation rate might decrease. This rules out Options A and C.
Incorrect
the correct answer is Option B.
This question is testing the effects of a currency appreciation.
B An appreciation of the domestic currency will:
– make exports less competitive, ie exports will be relatively expensive
– tend to decrease export volumes – this rules out Option C
– make imports relatively cheap
– tend to increase import volumes – this rules out Options C and D.Relatively cheap imports might reduce cost-push inflationary pressures, and lower demand for (more expensive) exports might reduce demand-pull inflationary pressures. Therefore the recorded inflation rate might decrease. This rules out Options A and C.
-
Question 355 of 999CB2031245
Question 355
FlagWhich of the following are the correct responses for the missing words (i) and (ii) in the following statement?
Automatic stabilisers act to $\_\_\_\_$ (i) $\_\_\_\_$ government expenditures and $\_\_\_\_$ (ii) $\_\_\_\_$ government revenues during an expansionary period.
Correct
Answer: C
This is a question on fiscal policy, and in particular automatic stabilisers.
Recall that automatic fiscal stabilisers are those parts of government spending and taxation that adjust naturally to the state of the economy and so go some way to automatically stabilising it without any need for explicit additional government action.This question considers an expansionary period meaning that GDP is growing. Consequently, even if the government takes no action:
– Government spending on unemployment and other income-related benefits will decrease as unemployment falls. This rules out Options A and B.
– Government tax revenues will increase as household incomes rise and firms make higher profits. This rules out Options A and D.This leaves Option C as the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
This is a question on fiscal policy, and in particular automatic stabilisers.
Recall that automatic fiscal stabilisers are those parts of government spending and taxation that adjust naturally to the state of the economy and so go some way to automatically stabilising it without any need for explicit additional government action.This question considers an expansionary period meaning that GDP is growing. Consequently, even if the government takes no action:
– Government spending on unemployment and other income-related benefits will decrease as unemployment falls. This rules out Options A and B.
– Government tax revenues will increase as household incomes rise and firms make higher profits. This rules out Options A and D.This leaves Option C as the correct answer.
-
Question 356 of 999CB2031246
Question 356
FlagThe budget deficit tends to decrease when:
Correct
Answer: B
This is the third multiple-choice question on fiscal policy (in addition to Questions 16 and 19) and the second on the budget deficit. Recall that the budget deficit, which is also sometimes referred to as the fiscal deficit, is the excess of government spending $(G)$ over tax revenues $(T)$.
When national income ( $Y$ ) falls:
– Government spending on unemployment and other income-related benefits will increase as unemployment increases.
– Government tax revenues will decrease as household incomes fall and firms make lower profits.As a result, the budget deficit will increase. This means that Option A is incorrect.
Conversely, when national income rises, the opposite will occur, leading to a fall in the budget deficit. Option B is therefore the correct answer.If the government cuts the rate of income tax, then income tax receipts will most likely fall. All else being equal, the budget deficit will therefore rise and not fall.
Likewise, an increase in government spending will generally lead to an increase in the budget deficit – although it is likely that the increase in national income resulting from the increased spending will also lead to a rise in tax revenues.
Incorrect
Answer: B
This is the third multiple-choice question on fiscal policy (in addition to Questions 16 and 19) and the second on the budget deficit. Recall that the budget deficit, which is also sometimes referred to as the fiscal deficit, is the excess of government spending $(G)$ over tax revenues $(T)$.
When national income ( $Y$ ) falls:
– Government spending on unemployment and other income-related benefits will increase as unemployment increases.
– Government tax revenues will decrease as household incomes fall and firms make lower profits.As a result, the budget deficit will increase. This means that Option A is incorrect.
Conversely, when national income rises, the opposite will occur, leading to a fall in the budget deficit. Option B is therefore the correct answer.If the government cuts the rate of income tax, then income tax receipts will most likely fall. All else being equal, the budget deficit will therefore rise and not fall.
Likewise, an increase in government spending will generally lead to an increase in the budget deficit – although it is likely that the increase in national income resulting from the increased spending will also lead to a rise in tax revenues.
-
Question 357 of 999CB2031247
Question 357
FlagThe adoption of an expansionary fiscal policy will result in:
Correct
Answer: C
Fiscal policy is covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.
An expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending and/or reducing taxation. Government spending is a component of aggregate demand, so increasing government spending will increase aggregate demand. Reducing taxation could increase both consumption and investment, which are also components of aggregate demand, so a reduction in taxation will also increase aggregate demand. This rules out Option D.If aggregate demand increases, then firms will respond by increasing output, therefore there will be an increase in real output. This rules out Option A.
Real output and unemployment are inversely related: the higher the output, the more people need to be employed to produce that output, and so unemployment will fall. This rules out Option B, and so the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Fiscal policy is covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.
An expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending and/or reducing taxation. Government spending is a component of aggregate demand, so increasing government spending will increase aggregate demand. Reducing taxation could increase both consumption and investment, which are also components of aggregate demand, so a reduction in taxation will also increase aggregate demand. This rules out Option D.If aggregate demand increases, then firms will respond by increasing output, therefore there will be an increase in real output. This rules out Option A.
Real output and unemployment are inversely related: the higher the output, the more people need to be employed to produce that output, and so unemployment will fall. This rules out Option B, and so the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 358 of 999CB2031248
Question 358
FlagThe adoption of an expansionary fiscal policy will result in:
Correct
Answer: C
Fiscal policy is covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes and this particular question has appeared several times on previous exam papers.
An expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending and/or reducing taxation. Government spending is a component of aggregate demand, so increasing government spending will increase aggregate demand. Reducing taxation could increase both consumption and investment, which are also components of aggregate demand, so a reduction in taxation will also increase aggregate demand. This rules out Option D.
If aggregate demand increases, then firms will respond by increasing output and there will be an increase in real output and employment. This rules out Option A.
Real output and unemployment are inversely related: the higher is output, the more people will be employed to produce that output, and so unemployment will fall. This rules out Option B, and so the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Fiscal policy is covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes and this particular question has appeared several times on previous exam papers.
An expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending and/or reducing taxation. Government spending is a component of aggregate demand, so increasing government spending will increase aggregate demand. Reducing taxation could increase both consumption and investment, which are also components of aggregate demand, so a reduction in taxation will also increase aggregate demand. This rules out Option D.
If aggregate demand increases, then firms will respond by increasing output and there will be an increase in real output and employment. This rules out Option A.
Real output and unemployment are inversely related: the higher is output, the more people will be employed to produce that output, and so unemployment will fall. This rules out Option B, and so the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 359 of 999CB2031249
Question 359
FlagWhich of the following are the correct responses for the missing words (i) and (ii) in the following statement?
Automatic stabilisers act to (i) $\_\_\_\_$ government expenditures and (ii) $\_\_\_\_$ government revenues during a recessionary period.
Correct
Option A is the correct answer.
This is a question on fiscal policy, and in particular automatic stabilisers.
A Recall that automatic fiscal stabilisers are those parts of government spending and taxation that adjust naturally to the state of the economy and so go some way to automatically stabilising it without any need for explicit additional government action.
This question considers a recessionary period, meaning that GDP is shrinking. Consequently, even if the government takes no action:
– Government tax revenues will decrease as household incomes fall, firms make lower profits and government spending on unemployment benefits (an example of a negative tax revenue) increases. This rules out Options B and C.
– Government spending on policing and healthcare will increase as unemployment rises. This rules out Options C and D.This leaves Option A as the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option A is the correct answer.
This is a question on fiscal policy, and in particular automatic stabilisers.
A Recall that automatic fiscal stabilisers are those parts of government spending and taxation that adjust naturally to the state of the economy and so go some way to automatically stabilising it without any need for explicit additional government action.
This question considers a recessionary period, meaning that GDP is shrinking. Consequently, even if the government takes no action:
– Government tax revenues will decrease as household incomes fall, firms make lower profits and government spending on unemployment benefits (an example of a negative tax revenue) increases. This rules out Options B and C.
– Government spending on policing and healthcare will increase as unemployment rises. This rules out Options C and D.This leaves Option A as the correct answer.
-
Question 360 of 999CB2031250
Question 360
FlagWhich one of the following would NOT constitute a demand-side economic policy for reducing unemployment?
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
Demand-side macroeconomic policy is covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.
Make sure you read the question carefully. This question asks which policy is NOT a demand-side economic policy.D Demand-side macroeconomic policies aim to influence aggregate demand. A demand-side policy for reducing unemployment is one which increases aggregate demand, leading to an increase in national output and hence a reduction in unemployment.
Recall that aggregate demand is made up of consumption (from individuals), investment (from firms), government expenditure and net exports (to the foreign sector).
Increased government expenditure will directly increase aggregate demand and is therefore a demand-side policy. Thus Option A is not the correct answer.
A policy of increasing the money supply will be accompanied by lower interest rates. Lower interest rates:
– will reduce the attractiveness of saving and increase the attractiveness of borrowing, ie the demand for loans; this is likely to increase consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand
– may lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency, making exports appear cheap to other countries, and imports dear to domestic residents, and thus are likely to increase net exports and hence aggregate demand.This rules out both Options B and C.
A privatisation programme does not affect demand. Instead, it aims to increase competition, which may ultimately increase efficiency and consumer choice and lower prices. This is an example of a supply-side policy. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
Demand-side macroeconomic policy is covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.
Make sure you read the question carefully. This question asks which policy is NOT a demand-side economic policy.D Demand-side macroeconomic policies aim to influence aggregate demand. A demand-side policy for reducing unemployment is one which increases aggregate demand, leading to an increase in national output and hence a reduction in unemployment.
Recall that aggregate demand is made up of consumption (from individuals), investment (from firms), government expenditure and net exports (to the foreign sector).
Increased government expenditure will directly increase aggregate demand and is therefore a demand-side policy. Thus Option A is not the correct answer.
A policy of increasing the money supply will be accompanied by lower interest rates. Lower interest rates:
– will reduce the attractiveness of saving and increase the attractiveness of borrowing, ie the demand for loans; this is likely to increase consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand
– may lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency, making exports appear cheap to other countries, and imports dear to domestic residents, and thus are likely to increase net exports and hence aggregate demand.This rules out both Options B and C.
A privatisation programme does not affect demand. Instead, it aims to increase competition, which may ultimately increase efficiency and consumer choice and lower prices. This is an example of a supply-side policy. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 361 of 999CB2031251
Question 361
FlagIn the event of a recession in the economy, automatic fiscal stabilisers:
Correct
A is correct answer
Fiscal policy (and automatic fiscal stabilisers) are covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.Automatic fiscal stabilisers adjust naturally to the state of the economy and go some way to automatically stabilising it. In a recession, when there is too little aggregate demand in the economy, these help to stabilise it because the revenue from both direct taxes (eg income tax, corporation tax) and indirect taxes (eg taxes on products) decreases, unemployment benefit payments increase and government spending on healthcare, education, crime etc tend to increase.
Incorrect
A is correct answer
Fiscal policy (and automatic fiscal stabilisers) are covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.Automatic fiscal stabilisers adjust naturally to the state of the economy and go some way to automatically stabilising it. In a recession, when there is too little aggregate demand in the economy, these help to stabilise it because the revenue from both direct taxes (eg income tax, corporation tax) and indirect taxes (eg taxes on products) decreases, unemployment benefit payments increase and government spending on healthcare, education, crime etc tend to increase.
-
Question 362 of 999CB2031252
Question 362
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a problem associated with the active management of fiscal policy?
Correct
correct answer- D
The problems of operating fiscal policy are discussed in Module 21 of the Course Notes.
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and taxation to affect the level of aggregate demand in the economy. For example, an expansionary fiscal policy, involving increases in government spending and/or reductions in taxation, could be used to increase aggregate demand and increase output and employment.
The main problems of such a policy are:
– time lags, which could make the policy destabilising, rather than stabilising
– the uncertainty about the size of the effects of the policy because of the difficulty in predicting consumer and business reaction to tax and income changes
– the possibility of crowding out (ie increased government expenditure could ‘crowd out’ private sector spending).These points are covered by Options A, B and C.
Option D must therefore be the answer. The unknown size of the accelerator effect (which largely depends on business confidence) adds to the uncertainty, but it is not specifically a problem of fiscal policy.Incorrect
correct answer- D
The problems of operating fiscal policy are discussed in Module 21 of the Course Notes.
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and taxation to affect the level of aggregate demand in the economy. For example, an expansionary fiscal policy, involving increases in government spending and/or reductions in taxation, could be used to increase aggregate demand and increase output and employment.
The main problems of such a policy are:
– time lags, which could make the policy destabilising, rather than stabilising
– the uncertainty about the size of the effects of the policy because of the difficulty in predicting consumer and business reaction to tax and income changes
– the possibility of crowding out (ie increased government expenditure could ‘crowd out’ private sector spending).These points are covered by Options A, B and C.
Option D must therefore be the answer. The unknown size of the accelerator effect (which largely depends on business confidence) adds to the uncertainty, but it is not specifically a problem of fiscal policy. -
Question 363 of 999CB2031253
Question 363
FlagIn the event of a recession in the economy, automatic fiscal stabilisers:
Correct
Option A is the correct answer.
Fiscal policy (and automatic fiscal stabilisers) are covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.Automatic fiscal stabilisers adjust naturally to the state of the economy and go some way to automatically stabilising it. In a recession, when there is too little aggregate demand in the economy, these help to stabilise it because:
– the revenue from both direct taxes (eg income tax, corporation tax) and indirect taxes (eg taxes on products) decreases, and benefit payments (eg unemployment benefits), which are classed as a negative tax, increase – this rules out Options B and $C$
– government spending on healthcare, education, crime etc tend to increase – this rules out Options C and D.Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option A is the correct answer.
Fiscal policy (and automatic fiscal stabilisers) are covered in Module 21 of the Course Notes.Automatic fiscal stabilisers adjust naturally to the state of the economy and go some way to automatically stabilising it. In a recession, when there is too little aggregate demand in the economy, these help to stabilise it because:
– the revenue from both direct taxes (eg income tax, corporation tax) and indirect taxes (eg taxes on products) decreases, and benefit payments (eg unemployment benefits), which are classed as a negative tax, increase – this rules out Options B and $C$
– government spending on healthcare, education, crime etc tend to increase – this rules out Options C and D.Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 364 of 999CB2031254
Question 364
FlagAssuming no crowding out effects, the adoption of a policy to reduce the government’s budget deficit will involve:
Correct
the correct answer is Option C.
This question is about the effect of fiscal policy on aggregate demand and real output. The question states the assumption that there are no crowding out effects. In fact, this question still holds even if there is a degree of crowding out; there would only be an issue if the crowding out was complete.
A budget deficit arises when government spending exceeds its tax receipts. A policy to reduce the budget deficit will involve reducing government spending and/or increasing tax receipts.
Since government spending is a component of aggregate demand, a reduction in government spending will reduce aggregate demand. In addition, an increase in taxation is likely to reduce consumption and investment, which are also components of aggregate demand, so aggregate demand is likely to fall. This rules out Options A and B.
If aggregate demand falls, then real output will fall in response to this reduced demand. This rules out Options B and D.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
the correct answer is Option C.
This question is about the effect of fiscal policy on aggregate demand and real output. The question states the assumption that there are no crowding out effects. In fact, this question still holds even if there is a degree of crowding out; there would only be an issue if the crowding out was complete.
A budget deficit arises when government spending exceeds its tax receipts. A policy to reduce the budget deficit will involve reducing government spending and/or increasing tax receipts.
Since government spending is a component of aggregate demand, a reduction in government spending will reduce aggregate demand. In addition, an increase in taxation is likely to reduce consumption and investment, which are also components of aggregate demand, so aggregate demand is likely to fall. This rules out Options A and B.
If aggregate demand falls, then real output will fall in response to this reduced demand. This rules out Options B and D.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 365 of 999CB2031255
Question 365
FlagWhich one of the following would NOT constitute a demand-side economic policy for reducing unemployment?
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
This question is testing demand-side macroeconomic policy.
It is important to read the question carefully. This question asks which policy is NOT a demandside economic policy for reducing unemployment.Demand-side macroeconomic policies aim to influence aggregate demand. A demand-side policy for reducing unemployment is one which increases aggregate demand, leading to an increase in national output and hence a reduction in unemployment.
Recall that aggregate demand is made up of consumption (from individuals), investment (from firms), government expenditure and net exports (to the foreign sector).
Increased government expenditure will directly increase aggregate demand and is therefore a demand-side policy. Thus Option A is not the correct answer.
A policy of increasing the money supply will be accompanied by lower interest rates and:
– will reduce the attractiveness of saving and increase the attractiveness of borrowing, which is likely to increase both consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand
– may lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency, making exports appear cheap to other countries, and imports dear to domestic residents, and thus are likely to increase net exports and hence aggregate demand.This rules out Option B.
A policy of reducing corporate and personal taxation is often categorised as a supply-side policy because of the increased level of aggregate supply it causes. However, this type of policy will also increase consumer’s incomes and increase firms’ profits, both of which will increase aggregate demand. As Option C could therefore be viewed as a demand-side policy, it is not the best answer here.
A privatisation programme does not affect demand. Instead, it aims to increase competition, which may ultimately increase efficiency and consumer choice and lower prices. This is an example of a supply-side policy. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
This question is testing demand-side macroeconomic policy.
It is important to read the question carefully. This question asks which policy is NOT a demandside economic policy for reducing unemployment.Demand-side macroeconomic policies aim to influence aggregate demand. A demand-side policy for reducing unemployment is one which increases aggregate demand, leading to an increase in national output and hence a reduction in unemployment.
Recall that aggregate demand is made up of consumption (from individuals), investment (from firms), government expenditure and net exports (to the foreign sector).
Increased government expenditure will directly increase aggregate demand and is therefore a demand-side policy. Thus Option A is not the correct answer.
A policy of increasing the money supply will be accompanied by lower interest rates and:
– will reduce the attractiveness of saving and increase the attractiveness of borrowing, which is likely to increase both consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand
– may lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency, making exports appear cheap to other countries, and imports dear to domestic residents, and thus are likely to increase net exports and hence aggregate demand.This rules out Option B.
A policy of reducing corporate and personal taxation is often categorised as a supply-side policy because of the increased level of aggregate supply it causes. However, this type of policy will also increase consumer’s incomes and increase firms’ profits, both of which will increase aggregate demand. As Option C could therefore be viewed as a demand-side policy, it is not the best answer here.
A privatisation programme does not affect demand. Instead, it aims to increase competition, which may ultimately increase efficiency and consumer choice and lower prices. This is an example of a supply-side policy. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 366 of 999CB2031256
Question 366
FlagWhich of the following is an example of a government policy conflict?
Correct
correct answer- C
This question covers the idea of policy conflict – where a policy designed to address a particular government objective may harm another government objective.
An increase in public expenditure increases aggregate demand, which puts downward pressure on unemployment but at the risk of demand-pull inflation. Since governments and populations will generally prefer low unemployment and low price inflation, this is an example of a conflict. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Options A and B both involve pairs of outcomes that are both favourable, ie an increase in both economic growth and employment. So these are not examples of policy conflicts.
Incorrect
correct answer- C
This question covers the idea of policy conflict – where a policy designed to address a particular government objective may harm another government objective.
An increase in public expenditure increases aggregate demand, which puts downward pressure on unemployment but at the risk of demand-pull inflation. Since governments and populations will generally prefer low unemployment and low price inflation, this is an example of a conflict. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Options A and B both involve pairs of outcomes that are both favourable, ie an increase in both economic growth and employment. So these are not examples of policy conflicts.
-
Question 367 of 999CB2031257
Question 367
FlagDuring an economic boom, the government fiscal position is likely to:
Correct
Option D is correct.
This question is on the government fiscal position at different periods in the business cycle, in other words the state of government tax collection and spending.
During an economic boom, aggregate demand, output and employment all tend to be high (and unemployment low). Furthermore:
– government spending tends to be low – for example, people tend to be in better health, leading to lower spending on healthcare, and since employment prospects are likely to be good, school leavers may be more likely to get a job (rather than continuing in further education), leading to lower spending on education.
– tax revenues tend to be high (ruling out Option C) – for example, high incomes and profits lead to high personal (income) and corporation tax revenue, high levels of expenditure lead to high tax revenues from taxes on goods and services, etc
– benefit payments tend to be low – for example, due to low unemployment – so Option D is correct.All of these will improve the government fiscal position, which rules out Options A and B.
Incorrect
Option D is correct.
This question is on the government fiscal position at different periods in the business cycle, in other words the state of government tax collection and spending.
During an economic boom, aggregate demand, output and employment all tend to be high (and unemployment low). Furthermore:
– government spending tends to be low – for example, people tend to be in better health, leading to lower spending on healthcare, and since employment prospects are likely to be good, school leavers may be more likely to get a job (rather than continuing in further education), leading to lower spending on education.
– tax revenues tend to be high (ruling out Option C) – for example, high incomes and profits lead to high personal (income) and corporation tax revenue, high levels of expenditure lead to high tax revenues from taxes on goods and services, etc
– benefit payments tend to be low – for example, due to low unemployment – so Option D is correct.All of these will improve the government fiscal position, which rules out Options A and B.
-
Question 368 of 999CB2031258
Question 368
FlagIn order to avoid the problem of fiscal drag, the government should:
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
This question is on fiscal drag, which is related to the idea of an automatic fiscal stabilisers.
Fiscal drag occurs when automatic fiscal stabilisers slow the recovery of an economy or dampen down the effect of fiscal policy.
For example, when an economy is in recession, income is reduced, and people pay less income tax. This helps to turn the economy around, but once income starts to grow, individuals’ marginal rates of income tax will increase if they move into a higher tax band, slowing the growth by reducing the size of the multiplier. This can be avoided by increasing income tax bands as wages grow, so Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
This question is on fiscal drag, which is related to the idea of an automatic fiscal stabilisers.
Fiscal drag occurs when automatic fiscal stabilisers slow the recovery of an economy or dampen down the effect of fiscal policy.
For example, when an economy is in recession, income is reduced, and people pay less income tax. This helps to turn the economy around, but once income starts to grow, individuals’ marginal rates of income tax will increase if they move into a higher tax band, slowing the growth by reducing the size of the multiplier. This can be avoided by increasing income tax bands as wages grow, so Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 369 of 999CB2031259
Question 369
FlagIn an economy operating significantly below the full employment level of output, the adoption of an expansionary fiscal policy combined with a contractionary monetary policy will result in:
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
This question is on the effects of fiscal and monetary policy.
An expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government expenditure and/or reducing taxation. This would be used to boost aggregate demand and, since there is excess capacity, output and employment.
A contractionary monetary policy involves reducing the money supply and/or increasing interest rates. This would be used to reduce demand, and hence output and employment.
Therefore, the overall effect on aggregate demand and employment is indeterminate, so Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
This question is on the effects of fiscal and monetary policy.
An expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government expenditure and/or reducing taxation. This would be used to boost aggregate demand and, since there is excess capacity, output and employment.
A contractionary monetary policy involves reducing the money supply and/or increasing interest rates. This would be used to reduce demand, and hence output and employment.
Therefore, the overall effect on aggregate demand and employment is indeterminate, so Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 370 of 999CB2031260
Question 370
FlagWhich of the following is the correct response for the missing words, (i) and (ii), in the statement below?
Automatic stabilisers act to $\_\_\_\_$ (i) $\_\_\_\_$ government expenditures and $\_\_\_\_$ (ii) $\_\_\_\_$ government revenues during a recession.
Correct
the correct answer is Option A.
This question is on automatic fiscal stabilisers.
Automatic fiscal stabilisers are those parts of government spending and taxation that adjust naturally to the state of the economy and so help to stabilise it without any need for additional government action.
For example, when national income is shrinking, even if the government takes no action, tax revenues will decrease as household incomes fall, firms make lower profits and government spending on unemployment benefits increases. In addition, government spending on policing and healthcare are likely to increase as unemployment rises.
So, during a recessionary period, automatic fiscal stabilisers raise government spending and reduce tax revenue, so the correct answer is Option A.
Incorrect
the correct answer is Option A.
This question is on automatic fiscal stabilisers.
Automatic fiscal stabilisers are those parts of government spending and taxation that adjust naturally to the state of the economy and so help to stabilise it without any need for additional government action.
For example, when national income is shrinking, even if the government takes no action, tax revenues will decrease as household incomes fall, firms make lower profits and government spending on unemployment benefits increases. In addition, government spending on policing and healthcare are likely to increase as unemployment rises.
So, during a recessionary period, automatic fiscal stabilisers raise government spending and reduce tax revenue, so the correct answer is Option A.
-
Question 371 of 999CB2031261
Question 371
FlagWhich of the following will always result in an increase in the national debt?
Correct
Option C is the correct answer.
This question is testing understanding of the difference between a fiscal deficit and national debt. This concept has been the subject of a number of questions in recent years.
By definition, the national debt is the accumulated (fiscal) deficits of central government. Therefore a fiscal deficit will always increase the national debt, so Option C is the correct answer.
A fall in the rate of interest payable on government bonds (Option A) will reduce the government’s expenditure (on interest payments), which will act to reduce its fiscal deficit (or increase its fiscal surplus). As either a fiscal deficit or surplus could result, national debt could rise (in the case of a deficit) or fall (in the case of a surplus), and so Option A is not the answer.
A rise in borrowing from the rest of the world (Option B) will not affect the national debt of the domestic government.
A trade account deficit (Option D) means that exports exceed imports. This relates to the private sector, rather than the government cashflows.
Incorrect
Option C is the correct answer.
This question is testing understanding of the difference between a fiscal deficit and national debt. This concept has been the subject of a number of questions in recent years.
By definition, the national debt is the accumulated (fiscal) deficits of central government. Therefore a fiscal deficit will always increase the national debt, so Option C is the correct answer.
A fall in the rate of interest payable on government bonds (Option A) will reduce the government’s expenditure (on interest payments), which will act to reduce its fiscal deficit (or increase its fiscal surplus). As either a fiscal deficit or surplus could result, national debt could rise (in the case of a deficit) or fall (in the case of a surplus), and so Option A is not the answer.
A rise in borrowing from the rest of the world (Option B) will not affect the national debt of the domestic government.
A trade account deficit (Option D) means that exports exceed imports. This relates to the private sector, rather than the government cashflows.
-
Question 372 of 999CB2031262
Question 372
FlagA cut in the overall rate of income tax in a country will tend to lead to:
Correct
correct answer-c
This question tests understanding of demand-side policies, and in particular the effects of a cut in the rate of income tax.
A cut in the rate of income tax will increase households’ disposable income, which will increase the funds individuals have available for consumption. An increase in consumption will increase aggregate demand (also known as aggregate planned expenditure). This corresponds to Option C.
Incorrect
correct answer-c
This question tests understanding of demand-side policies, and in particular the effects of a cut in the rate of income tax.
A cut in the rate of income tax will increase households’ disposable income, which will increase the funds individuals have available for consumption. An increase in consumption will increase aggregate demand (also known as aggregate planned expenditure). This corresponds to Option C.
-
Question 373 of 999CB2031263
Question 373
FlagWhich of the following would NOT increase the government budget deficit?
Correct
Option C is the correct answer.
This question is on budget deficits and understanding what may impact them.
The budget deficit, which is also sometimes referred to as the fiscal deficit, is the excess of government spending over tax revenues.Government spending includes:
– expenditure on goods and services (Option B)
– interest on its debt (Option A).An increase in either of these items will therefore act to increase the budget deficit, hence these are not the correct answers.
In the circular flow of income model, tax revenue is calculated net of transfer payments. Therefore an increase in government transfer payments (Option D) will reduce net tax revenues, and so increase the budget deficit. Hence this is not the correct answer.
An increase in the labour participation rate (Option C) is likely to:
– increase incomes, so increasing income tax revenue
– decrease transfer payments, eg unemployment / social security / other benefits, so increasing (net) tax revenue.Higher tax revenues will reduce the budget deficit, so Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option C is the correct answer.
This question is on budget deficits and understanding what may impact them.
The budget deficit, which is also sometimes referred to as the fiscal deficit, is the excess of government spending over tax revenues.Government spending includes:
– expenditure on goods and services (Option B)
– interest on its debt (Option A).An increase in either of these items will therefore act to increase the budget deficit, hence these are not the correct answers.
In the circular flow of income model, tax revenue is calculated net of transfer payments. Therefore an increase in government transfer payments (Option D) will reduce net tax revenues, and so increase the budget deficit. Hence this is not the correct answer.
An increase in the labour participation rate (Option C) is likely to:
– increase incomes, so increasing income tax revenue
– decrease transfer payments, eg unemployment / social security / other benefits, so increasing (net) tax revenue.Higher tax revenues will reduce the budget deficit, so Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 374 of 999CB2031264
Question 374
FlagWhich of the following would constitute a supply-side economic policy for reducing unemployment?
Correct
Answer: C
Supply-side policy is covered in Module 20 of the Course Notes. Some of the options relate to demand-side policies, which are covered in Module 21.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work.
Reducing social security benefits is another supply-side policy, which aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work. Conversely, increasing social security benefits will make it more attractive to be unemployed and so is likely to increase unemployment.
The other two options given are both demand-side policies, ie they aim to increase output and/or reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand.
There is an overlap here. It could be argued that reducing corporate and personal taxation is a demand-side policy in that it increases investment and consumer spending and hence increases aggregate demand. This would be true. It depends on the government’s intention. Are they introducing this policy to increase aggregate demand or are they introducing it to increase incentives and hence improve the supply side of the economy? The other options given either cannot be interpreted as supply-side policies, or are more likely to increase unemployment. Consequently, Option C must be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Supply-side policy is covered in Module 20 of the Course Notes. Some of the options relate to demand-side policies, which are covered in Module 21.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work.
Reducing social security benefits is another supply-side policy, which aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work. Conversely, increasing social security benefits will make it more attractive to be unemployed and so is likely to increase unemployment.
The other two options given are both demand-side policies, ie they aim to increase output and/or reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand.
There is an overlap here. It could be argued that reducing corporate and personal taxation is a demand-side policy in that it increases investment and consumer spending and hence increases aggregate demand. This would be true. It depends on the government’s intention. Are they introducing this policy to increase aggregate demand or are they introducing it to increase incentives and hence improve the supply side of the economy? The other options given either cannot be interpreted as supply-side policies, or are more likely to increase unemployment. Consequently, Option C must be the correct answer.
-
Question 375 of 999CB2031265
Question 375
FlagWhich of the following would constitute a supply-side economic policy for raising employment?
Correct
Answer: A
This is the only question about supply-side policies on this paper. However, some of the options relate to demand-side policies.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Option A involves reducing social security benefits. This is a supply-side policy that aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work, thereby increasing employment. It is therefore likely to be the correct option, though it is sensible to check the others just to be sure.
Option B, which involves decreasing the money supply, is an example of a demand-side policy. This is because it aims to influence aggregate demand in order to meet the government’s economic objective. For example, decreasing the money supply would likely increase interest rates, leading to a fall in consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand, and hence output and employment.
Reducing corporate and personal taxation is another example of a supply-side policy, as it aims to increase aggregate supply, ie output. Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work. However, Option C actually says increasing corporate and personal taxation, which is likely to have the opposite effects and so is likely to reduce, rather than increase, aggregate supply and employment.
Finally, Option D, which is increasing government spending, is a further example of a demand-side policy that might be used to directly increase aggregate demand in order to increase output and employment.
Note that it could also be argued that increasing corporate and personal taxation is a demand-side policy in that it is likely to decrease investment and consumer spending and so reduce aggregate demand. However, this doesn’t affect the answer here, as whether or not it is interpreted as a demand-side or a supply-side policy, it is likely to reduce output and thereby reduce, rather than increase, employment. Consequently, Option C cannot be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
This is the only question about supply-side policies on this paper. However, some of the options relate to demand-side policies.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Option A involves reducing social security benefits. This is a supply-side policy that aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work, thereby increasing employment. It is therefore likely to be the correct option, though it is sensible to check the others just to be sure.
Option B, which involves decreasing the money supply, is an example of a demand-side policy. This is because it aims to influence aggregate demand in order to meet the government’s economic objective. For example, decreasing the money supply would likely increase interest rates, leading to a fall in consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand, and hence output and employment.
Reducing corporate and personal taxation is another example of a supply-side policy, as it aims to increase aggregate supply, ie output. Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work. However, Option C actually says increasing corporate and personal taxation, which is likely to have the opposite effects and so is likely to reduce, rather than increase, aggregate supply and employment.
Finally, Option D, which is increasing government spending, is a further example of a demand-side policy that might be used to directly increase aggregate demand in order to increase output and employment.
Note that it could also be argued that increasing corporate and personal taxation is a demand-side policy in that it is likely to decrease investment and consumer spending and so reduce aggregate demand. However, this doesn’t affect the answer here, as whether or not it is interpreted as a demand-side or a supply-side policy, it is likely to reduce output and thereby reduce, rather than increase, employment. Consequently, Option C cannot be the correct answer.
-
Question 376 of 999CB2031266
Question 376
FlagWhich of the following would constitute a supply-side economic policy for reducing unemployment?
Correct
Answer: C
Supply-side policy is covered in Module 20 of the Course Notes. Some of the options relate to demand-side policies, which are covered in Module 21.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work. This corresponds to Option C, which is therefore the correct answer.
Reducing social security benefits is another supply-side policy, which aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work. Conversely, increasing social security benefits will make it more attractive to be unemployed and so is likely increase unemployment. This rules out Option A.
The other two options given are both demand-side policies, ie they aim to increase output and/or reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand.
There is an overlap here. It could be argued that reducing corporate and personal taxation is a demand-side policy in that it increases investment and consumer spending and hence increases aggregate demand. This would be true. It depends on the government’s intention. Are they introducing this policy to increase aggregate demand or are they introducing it to increase incentives and hence improve the supply side of the economy? The other options given either cannot be interpreted as supply-side policies, or are more likely to increase unemployment. Consequently, Option C must be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Supply-side policy is covered in Module 20 of the Course Notes. Some of the options relate to demand-side policies, which are covered in Module 21.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work. This corresponds to Option C, which is therefore the correct answer.
Reducing social security benefits is another supply-side policy, which aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work. Conversely, increasing social security benefits will make it more attractive to be unemployed and so is likely increase unemployment. This rules out Option A.
The other two options given are both demand-side policies, ie they aim to increase output and/or reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand.
There is an overlap here. It could be argued that reducing corporate and personal taxation is a demand-side policy in that it increases investment and consumer spending and hence increases aggregate demand. This would be true. It depends on the government’s intention. Are they introducing this policy to increase aggregate demand or are they introducing it to increase incentives and hence improve the supply side of the economy? The other options given either cannot be interpreted as supply-side policies, or are more likely to increase unemployment. Consequently, Option C must be the correct answer.
-
Question 377 of 999CB2031267
Question 377
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a supply side economic policy aimed at promoting economic growth?
Correct
correct answer :Option D
This question is testing the material in Module 20 of the Course Notes. While supply-side policies have not historically been tested as much as demand-management policies, it is still important to know the basics. In fact, supply-side policies are also tested through one of the long-answer questions on this paper.
Supply-side policies are designed to increase aggregate supply directly, (ie independently of aggregate demand), by increasing the quantity of factors of production and/or improving their productivity. Note that the main factors of production are labour, capital, land and raw materials.
Option A – cuts in social security benefits designed to encourage more workers to take work – should increase the quantity of labour.
Option B – measures designed to reduce trade union powers – should increase the flexibility of the labour market and hence increase competition and efficiency in the labour market, leading to higher employment.
Option C – deregulation – involves the removal of monopoly rights, which should promote increased competition and hence increase efficiency / productivity and output.
Hence Options A, B and C all fit with the definition of supply-side policies and so the correct answer must be Option D.
Option D – tariffs designed to increase production of domestic goods – should increase aggregate demand, and so this is a demand-side (rather than a supply-side) policy.
Incorrect
correct answer :Option D
This question is testing the material in Module 20 of the Course Notes. While supply-side policies have not historically been tested as much as demand-management policies, it is still important to know the basics. In fact, supply-side policies are also tested through one of the long-answer questions on this paper.
Supply-side policies are designed to increase aggregate supply directly, (ie independently of aggregate demand), by increasing the quantity of factors of production and/or improving their productivity. Note that the main factors of production are labour, capital, land and raw materials.
Option A – cuts in social security benefits designed to encourage more workers to take work – should increase the quantity of labour.
Option B – measures designed to reduce trade union powers – should increase the flexibility of the labour market and hence increase competition and efficiency in the labour market, leading to higher employment.
Option C – deregulation – involves the removal of monopoly rights, which should promote increased competition and hence increase efficiency / productivity and output.
Hence Options A, B and C all fit with the definition of supply-side policies and so the correct answer must be Option D.
Option D – tariffs designed to increase production of domestic goods – should increase aggregate demand, and so this is a demand-side (rather than a supply-side) policy.
-
Question 378 of 999CB2031268
Question 378
FlagWhich of the following is least likely to lead to an increase in long-run economic growth?
Correct
correct answer- A
Economic growth is covered in Module 11 of the Course Notes. Macroeconomic policies are covered in Modules 20, 21 and 22 of the Course Notes.
Note that the question asks which of the four policies is least likely to lead to an increase in longrun economic growth.
Supply-side policies aim to increase the quantity and/or productivity of the nation’s resources and so increase potential output and long-run economic growth. Options B, C and D are all examples of supply-side policies.
Demand-side policies are designed to smooth out the fluctuations in the business cycle, which is more of a short-term aim. Option A is typically used as a demand-side policy, so seems the least likely to lead to long-run economic growth.
Note that demand-side policies might help to attain potential output in the short run, eg an increase in the money supply (Option A) will decrease interest rates, which will:
– make it cheaper and easier to borrow, therefore increasing consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand
– lead to a depreciation of the currency (if it is floating), increasing net exports and hence aggregate demand.This expansion of aggregate demand might increase business confidence and therefore further encourage investment. This investment, especially if it incorporates new technology, may increase potential output (by increasing the quantity and/or productivity of resources).
Incorrect
correct answer- A
Economic growth is covered in Module 11 of the Course Notes. Macroeconomic policies are covered in Modules 20, 21 and 22 of the Course Notes.
Note that the question asks which of the four policies is least likely to lead to an increase in longrun economic growth.
Supply-side policies aim to increase the quantity and/or productivity of the nation’s resources and so increase potential output and long-run economic growth. Options B, C and D are all examples of supply-side policies.
Demand-side policies are designed to smooth out the fluctuations in the business cycle, which is more of a short-term aim. Option A is typically used as a demand-side policy, so seems the least likely to lead to long-run economic growth.
Note that demand-side policies might help to attain potential output in the short run, eg an increase in the money supply (Option A) will decrease interest rates, which will:
– make it cheaper and easier to borrow, therefore increasing consumption and investment and hence aggregate demand
– lead to a depreciation of the currency (if it is floating), increasing net exports and hence aggregate demand.This expansion of aggregate demand might increase business confidence and therefore further encourage investment. This investment, especially if it incorporates new technology, may increase potential output (by increasing the quantity and/or productivity of resources).
-
Question 379 of 999CB2031269
Question 379
FlagWhich of the following would constitute a supply-side economic policy for reducing unemployment?
Correct
answer: C
This is a standard question on supply-side policy. Some of the options relate to demand-side policies.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work. This corresponds to Option C, which is therefore the correct answer.
Reducing social security benefits is another supply-side policy, which aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work. Conversely, increasing social security benefits will make it more attractive to be unemployed and so is likely to increase unemployment. This rules out Option A.
The other two options can be ruled out as they are both demand-side policies, ie they aim to increase output and/or reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand.
Incorrect
answer: C
This is a standard question on supply-side policy. Some of the options relate to demand-side policies.
Supply-side policies aim to increase aggregate supply, ie the total output of the domestic economy, directly rather than through aggregate demand.
Reducing corporate taxation increases the net-of-tax return on investment and so should increase the incentive to invest in new capital equipment and projects. In addition, it leaves firms with higher net-of-tax profits with which to fund investment. Likewise, reducing personal taxation increases net-of-tax earnings, ie the reward to work, and so aims to increase the incentive to work. This corresponds to Option C, which is therefore the correct answer.
Reducing social security benefits is another supply-side policy, which aims to decrease the opportunity cost of being employed and hence increase the incentive to work. Conversely, increasing social security benefits will make it more attractive to be unemployed and so is likely to increase unemployment. This rules out Option A.
The other two options can be ruled out as they are both demand-side policies, ie they aim to increase output and/or reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand.
-
Question 380 of 999CB2031270
Question 380
FlagPolicies that are designed to support the supply side of the economy do not include:
Correct
Answer: C
This is a question on supply side policy.
Government spending is a component of aggregate demand, so increasing government spending is usually considered to be a demand-side policy. The other options are likely to increase or improve at least one factor of production, in particular:
– reductions in benefits (Option A) will make not working less appealing – this might encourage more people into work, thus increasing the quantity of labour
– research and development subsidies (Option B) should lead to technological progress – this should ultimately improve the productivity of capital
– training more of the population (Option D) should directly improve the productivity of labour.Incorrect
Answer: C
This is a question on supply side policy.
Government spending is a component of aggregate demand, so increasing government spending is usually considered to be a demand-side policy. The other options are likely to increase or improve at least one factor of production, in particular:
– reductions in benefits (Option A) will make not working less appealing – this might encourage more people into work, thus increasing the quantity of labour
– research and development subsidies (Option B) should lead to technological progress – this should ultimately improve the productivity of capital
– training more of the population (Option D) should directly improve the productivity of labour. -
Question 381 of 999CB2031271
Question 381
FlagWhich one of the following would NOT constitute a supply-side economic policy for reducing unemployment?
Correct
Answer: B
This question is on supply-side policies to reduce unemployment.
Supply-side policies are typically used to shift the $\mathrm{AS}_{\mathrm{L}}$ curve to the right (effectively closing the gap between the $\mathrm{AS}_{\mathrm{L}}$ and N curves). This reduces the equilibrium (natural) level of unemployment (ie frictional, structural and seasonal unemployment).
Supply-side policies for reducing unemployment might include:
– a reduction in social security benefits (in order to encourage more people to work), so Option A is true and is not the correct answer
– a reduction in personal taxation (in order to encourage more people to work) and a reduction in corporate taxation (in order to increase the ability and incentive of firms to invest), so Option C is true and is not the correct answer
– increased government spending on education and training (which might encourage individuals back to work as well as improving the quality of the labour force), so Option D is true and is not the correct answer.Increasing the money supply is more likely to be part of a demand-side policy, so Option B is false, and is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
This question is on supply-side policies to reduce unemployment.
Supply-side policies are typically used to shift the $\mathrm{AS}_{\mathrm{L}}$ curve to the right (effectively closing the gap between the $\mathrm{AS}_{\mathrm{L}}$ and N curves). This reduces the equilibrium (natural) level of unemployment (ie frictional, structural and seasonal unemployment).
Supply-side policies for reducing unemployment might include:
– a reduction in social security benefits (in order to encourage more people to work), so Option A is true and is not the correct answer
– a reduction in personal taxation (in order to encourage more people to work) and a reduction in corporate taxation (in order to increase the ability and incentive of firms to invest), so Option C is true and is not the correct answer
– increased government spending on education and training (which might encourage individuals back to work as well as improving the quality of the labour force), so Option D is true and is not the correct answer.Increasing the money supply is more likely to be part of a demand-side policy, so Option B is false, and is the correct answer.
-
Question 382 of 999CB2031272
Question 382
FlagWhich of the following would NOT be considered a supply-side policy?
Correct
the correct answer is Option A.
Supply-side policies are designed to increase aggregate supply directly, (ie independently of aggregate demand), by increasing the quantity of factors of production and/or improving their productivity.
The main factors of production are labour, capital, land, and raw materials.
Transfer payments are money transferred from one person / group to another without production taking place, for example, an unemployment benefit being paid by the government to an individual. Such transfer payments will more directly affect aggregate demand, for example, the unemployment benefit might be used by individuals to spend on consumption.Furthermore, certain transfer payments (such as unemployment benefits) might actually disincentivise individuals from working and so contributing to the supply side of the economy.
So the correct answer is Option A.
The other options are likely to increase or improve at least one factor of production, in particular:
– increased investment in human and physical capital (Option C) should increase the quantity of labour / capital and/or improve their productivity– improvements in infrastructure (Option B) and business support for new emerging firms (Option D) should help firms to grow / thrive by increasing / improving the productivity of any of the factors of production.
Incorrect
the correct answer is Option A.
Supply-side policies are designed to increase aggregate supply directly, (ie independently of aggregate demand), by increasing the quantity of factors of production and/or improving their productivity.
The main factors of production are labour, capital, land, and raw materials.
Transfer payments are money transferred from one person / group to another without production taking place, for example, an unemployment benefit being paid by the government to an individual. Such transfer payments will more directly affect aggregate demand, for example, the unemployment benefit might be used by individuals to spend on consumption.Furthermore, certain transfer payments (such as unemployment benefits) might actually disincentivise individuals from working and so contributing to the supply side of the economy.
So the correct answer is Option A.
The other options are likely to increase or improve at least one factor of production, in particular:
– increased investment in human and physical capital (Option C) should increase the quantity of labour / capital and/or improve their productivity– improvements in infrastructure (Option B) and business support for new emerging firms (Option D) should help firms to grow / thrive by increasing / improving the productivity of any of the factors of production.
-
Question 383 of 999CB2031273
Question 383
FlagAssume that the actual rate of unemployment is above the natural rate of unemployment because the expected rate of inflation is above the actual rate of inflation. If the expected rate of inflation falls to equal the actual rate of inflation then real wage growth will:
Correct
Answer: A
This question is testing the Phillips curve. As is often the case, the diagram may help you visualise what is happening here.
According to the monetarist model, the economy is expected to operate at the natural rate of employment ( $U^*$ on the diagram below) in the long run, consistent with the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC).
Suppose, as the question states, the economy is currently operating with unemployment above the natural rate, say at Point B on the diagram, with expected inflation of $p^e=10 \%$, actual inflation lower than $10 \%$ and unemployment at $U^{\prime}>U^*$. This will be the case, for example, if the economy is in a recession. However, according to the theory, unemployment will eventually fall back to its long-run natural level as the economy recovers from recession. In other words, real output will eventually rise, which rules out Options B and D.
Now consider what would happen to wages. If the economy is suffering from higher than natural levels of unemployment, it is likely that the excess supply of labour will reduce real wages. This rules out Option C, leaving Option A as the correct answer.
In terms of the diagram, as workers eventually revise downwards their expectations of inflation, so the economy will move downwards from B towards C. Consequently wage demands will moderate. In addition, the downward pressure on real wages from the high unemployment will also reduce real wage growth. Consequently, demand for labour will increase and the economy will eventually move back to the LRPC, at Point D say, with expected inflation, actual inflation and wage inflation all equal to $5 \%$.
Incorrect
Answer: A
This question is testing the Phillips curve. As is often the case, the diagram may help you visualise what is happening here.
According to the monetarist model, the economy is expected to operate at the natural rate of employment ( $U^*$ on the diagram below) in the long run, consistent with the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC).
Suppose, as the question states, the economy is currently operating with unemployment above the natural rate, say at Point B on the diagram, with expected inflation of $p^e=10 \%$, actual inflation lower than $10 \%$ and unemployment at $U^{\prime}>U^*$. This will be the case, for example, if the economy is in a recession. However, according to the theory, unemployment will eventually fall back to its long-run natural level as the economy recovers from recession. In other words, real output will eventually rise, which rules out Options B and D.
Now consider what would happen to wages. If the economy is suffering from higher than natural levels of unemployment, it is likely that the excess supply of labour will reduce real wages. This rules out Option C, leaving Option A as the correct answer.

In terms of the diagram, as workers eventually revise downwards their expectations of inflation, so the economy will move downwards from B towards C. Consequently wage demands will moderate. In addition, the downward pressure on real wages from the high unemployment will also reduce real wage growth. Consequently, demand for labour will increase and the economy will eventually move back to the LRPC, at Point D say, with expected inflation, actual inflation and wage inflation all equal to $5 \%$.
-
Question 384 of 999CB2031274
Question 384
FlagThe demand curve for Good X, which is a normal good, will shift to the right if:
Correct
Recall from there that:
– Normal goods are goods for which demand increases as consumer incomes rise.
– Substitute goods are goods that consumers consider to be alternatives to each other-for example, two different brands of butter.
– Complementary goods are goods that are consumed together – for example, bread and butter.Remember that a demand curve shows how the quantity demanded varies with the price of the good, assuming that all the other factors that affect the demand for the good are constant. So, a change in the price of the good (Option A) will lead to a movement along the demand curve, whereas a change in any of the other factors that affect demand (such as with Options B, C and D), will lead to a shift of the demand curve.
A fall in the price of Good X (Option A) will lead to an increase in the quantity demanded and a downward movement along the existing demand curve. Consequently, Option A is not the correct answer.
A rise in the price of a substitute for Good X (Option B) will lead some consumers to switch from the substitute good to consuming Good X instead. The demand for Good X will therefore increase, corresponding to a rightward shift of its demand curve. Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
A rise in the price of a complementary good for Good $X$ (Option $C$ ) will lead to a fall in demand for both the complementary good and for Good X itself. So, the demand curve for Good X will shift to the left. Hence, Option C is incorrect.
Finally, a fall in consumers’ incomes (Option D) will, by definition, lead to a fall in demand for a normal good such as Good X, ie its demand curve will again shift to the left. Hence, Option D is also incorrect.
Answer: B
Incorrect
Recall from there that:
– Normal goods are goods for which demand increases as consumer incomes rise.
– Substitute goods are goods that consumers consider to be alternatives to each other-for example, two different brands of butter.
– Complementary goods are goods that are consumed together – for example, bread and butter.Remember that a demand curve shows how the quantity demanded varies with the price of the good, assuming that all the other factors that affect the demand for the good are constant. So, a change in the price of the good (Option A) will lead to a movement along the demand curve, whereas a change in any of the other factors that affect demand (such as with Options B, C and D), will lead to a shift of the demand curve.
A fall in the price of Good X (Option A) will lead to an increase in the quantity demanded and a downward movement along the existing demand curve. Consequently, Option A is not the correct answer.
A rise in the price of a substitute for Good X (Option B) will lead some consumers to switch from the substitute good to consuming Good X instead. The demand for Good X will therefore increase, corresponding to a rightward shift of its demand curve. Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
A rise in the price of a complementary good for Good $X$ (Option $C$ ) will lead to a fall in demand for both the complementary good and for Good X itself. So, the demand curve for Good X will shift to the left. Hence, Option C is incorrect.
Finally, a fall in consumers’ incomes (Option D) will, by definition, lead to a fall in demand for a normal good such as Good X, ie its demand curve will again shift to the left. Hence, Option D is also incorrect.
Answer: B
-
Question 385 of 999CB2031275
Question 385
FlagIf unemployment is above the natural level, the long-run Phillips curve would suggest that, other things remaining the same, real wages would:
Correct
Answer : B
First, let’s consider the simple way of looking at this question.
According to the monetarist model, in the long run, the economy is expected to operate at the natural level of unemployment. If, in the short run, the economy is operating above the natural level, then in the long run, unemployment must fall back to its long-run natural level. This rules out Options A and D.Now consider what would happen to wages. If the economy is suffering from higher than natural levels of unemployment, it is likely that the excess supply of labour will reduce wages. Hence the answer is Option B.
Now let’s consider the detailed version, using the long-run and expectations-augmented (sometimes called short-run) Phillips curves.
Suppose unemployment is above the natural level, $U^*$, at $U^{\prime}$. Why would this occur? There must have been fall in aggregate demand, perhaps due to a contractionary economic policy designed to reduce inflation. If the economy were originally at Point A, the contractionary policy would take the economy to Point B, which is the starting point in this question.
At Point B, workers still expect inflation of $\pi_1 \%$ and therefore nominal wage negotiations are based on this. Since actual inflation is lower than this, real wages rise. Unfortunately, the contractionary policies cause a decrease in demand for labour and hence an excess supply of labour at the prevailing real wage rate.
Gradually, expectations of inflation catch up with the new, lower reality and the expectationsaugmented Phillips curve moves downwards towards EAPC ${ }_2$. Workers accept lower nominal wage increases, which helps to bring the real wage back down to its equilibrium level.
The reduction in inflation leads to higher aggregate demand in real terms than would otherwise have been the case. Consequently, unemployment falls back to its natural rate.
Graphically, the economy arrives at a new long-run equilibrium at Point $C$.
Incorrect
Answer : B
First, let’s consider the simple way of looking at this question.
According to the monetarist model, in the long run, the economy is expected to operate at the natural level of unemployment. If, in the short run, the economy is operating above the natural level, then in the long run, unemployment must fall back to its long-run natural level. This rules out Options A and D.Now consider what would happen to wages. If the economy is suffering from higher than natural levels of unemployment, it is likely that the excess supply of labour will reduce wages. Hence the answer is Option B.
Now let’s consider the detailed version, using the long-run and expectations-augmented (sometimes called short-run) Phillips curves.
Suppose unemployment is above the natural level, $U^*$, at $U^{\prime}$. Why would this occur? There must have been fall in aggregate demand, perhaps due to a contractionary economic policy designed to reduce inflation. If the economy were originally at Point A, the contractionary policy would take the economy to Point B, which is the starting point in this question.

At Point B, workers still expect inflation of $\pi_1 \%$ and therefore nominal wage negotiations are based on this. Since actual inflation is lower than this, real wages rise. Unfortunately, the contractionary policies cause a decrease in demand for labour and hence an excess supply of labour at the prevailing real wage rate.
Gradually, expectations of inflation catch up with the new, lower reality and the expectationsaugmented Phillips curve moves downwards towards EAPC ${ }_2$. Workers accept lower nominal wage increases, which helps to bring the real wage back down to its equilibrium level.
The reduction in inflation leads to higher aggregate demand in real terms than would otherwise have been the case. Consequently, unemployment falls back to its natural rate.
Graphically, the economy arrives at a new long-run equilibrium at Point $C$.
-
Question 386 of 999CB2031276
Question 386
FlagWhich of the following best describes an annual supply curve?
Correct
A supply curve shows how the quantity that firms are both willing and able to supply per time period varies with the price of the good, assuming all other factors affecting supply remain constant. So, although it isn’t specifically mentioned in the Core Reading, an annual supply curve presumably refers to the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply each year at each price.
Note that ‘willing and able’ means that not only do firms want to supply the quantity indicated by the supply curve at each price (as they can presumably make profits from doing so), but they are also able to do so, ie they have the resources available with which to do so. Note also that Option A omits any reference to the price of the good, which is normally a key influence on the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply.
Answer: D
Incorrect
A supply curve shows how the quantity that firms are both willing and able to supply per time period varies with the price of the good, assuming all other factors affecting supply remain constant. So, although it isn’t specifically mentioned in the Core Reading, an annual supply curve presumably refers to the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply each year at each price.
Note that ‘willing and able’ means that not only do firms want to supply the quantity indicated by the supply curve at each price (as they can presumably make profits from doing so), but they are also able to do so, ie they have the resources available with which to do so. Note also that Option A omits any reference to the price of the good, which is normally a key influence on the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply.
Answer: D
-
Question 387 of 999CB2031277
Question 387
FlagWhich of the following will NOT cause a shift in the demand curve for Good X?
Correct
A demand curve shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good demanded over a given time period all other things being equal. Consequently, a change in the price of a good will lead to a movement along the demand curve. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Conversely, a change in any of the other factors that affect the demand for a good will cause the demand curve for the good to shift. These include changes in:
– consumer tastes (Option D)
– the number and price of substitute and complementary goods (Option B)
– consumer incomes (Option C)
– the distribution of income
– expectations of future price changes.Answer: A
Incorrect
A demand curve shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good demanded over a given time period all other things being equal. Consequently, a change in the price of a good will lead to a movement along the demand curve. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Conversely, a change in any of the other factors that affect the demand for a good will cause the demand curve for the good to shift. These include changes in:
– consumer tastes (Option D)
– the number and price of substitute and complementary goods (Option B)
– consumer incomes (Option C)
– the distribution of income
– expectations of future price changes.Answer: A
-
Question 388 of 999CB2031278
Question 388
FlagWhat is the combined effect of an increase in the cost of production and a rise in consumer income on the equilibrium price and quantity of an inferior good?
Correct
For inferior goods, the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases with income, eg an own-brand product. An increase in the cost of production will shift the supply curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and increase price.
For an inferior good, a rise in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and reduce price. Consequently, as the supply and demand curves both shift to the left, the equilibrium quantity must fall. However, the effect on the equilibrium price depends on which curve shifts the furthest, and also the slopes of the curves. So, the effect on price is indeterminate.
Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
Answer: A
Incorrect
For inferior goods, the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases with income, eg an own-brand product. An increase in the cost of production will shift the supply curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and increase price.
For an inferior good, a rise in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and reduce price. Consequently, as the supply and demand curves both shift to the left, the equilibrium quantity must fall. However, the effect on the equilibrium price depends on which curve shifts the furthest, and also the slopes of the curves. So, the effect on price is indeterminate.
Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
Answer: A
-
Question 389 of 999CB2031279
Question 389
FlagGood X is an inferior good. A rise in consumer income when the supply curve for Good X is positively sloped will cause which one of the following?
Correct
For inferior goods, the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases with income. This might be the case for an own-brand product.
So, in this question, a rise in consumer income will result in a fall in the demand for Good X, ie a shift of the demand curve to the left (or downwards). This will result in a surplus of supply at the existing price and so the price of Good X will need to fall to clear the surplus and restore equilibrium.
Consequently, Option A is the correct answer.
Answer: A
Incorrect
For inferior goods, the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases with income. This might be the case for an own-brand product.
So, in this question, a rise in consumer income will result in a fall in the demand for Good X, ie a shift of the demand curve to the left (or downwards). This will result in a surplus of supply at the existing price and so the price of Good X will need to fall to clear the surplus and restore equilibrium.
Consequently, Option A is the correct answer.
Answer: A
-
Question 390 of 999CB2031280
Question 390
FlagIf an increase in the level of the money supply results in no change in either the nominal or real value of national income, then which of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer-B
This question is testing the concept of the equation of exchange.
The equation of exchange states that:
$$
M V=P Y
$$
where: $M$ is the money supply
$V$ is the velocity of circulation (the number of times the money supply changes hands in a period of time)
$P$ is the price level
$Y$ is the level of real income or output.If an increase in the money supply results in no change in the real value of national income, then $Y$ remains unchanged. If an increase in the money supply results in no change in the nominal value of national income, then $P Y$ remains unchanged, and given that $Y$ is unchanged, this must mean that $P$ is also unchanged. This rules out Option C.
Since $P Y$ is unchanged, any increase in $M$ must be offset by a fall in $V$, so Option $B$ is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer-B
This question is testing the concept of the equation of exchange.
The equation of exchange states that:
$$
M V=P Y
$$
where: $M$ is the money supply
$V$ is the velocity of circulation (the number of times the money supply changes hands in a period of time)
$P$ is the price level
$Y$ is the level of real income or output.If an increase in the money supply results in no change in the real value of national income, then $Y$ remains unchanged. If an increase in the money supply results in no change in the nominal value of national income, then $P Y$ remains unchanged, and given that $Y$ is unchanged, this must mean that $P$ is also unchanged. This rules out Option C.
Since $P Y$ is unchanged, any increase in $M$ must be offset by a fall in $V$, so Option $B$ is the correct answer.
-
Question 391 of 999CB2031281
Question 391
FlagWhat is the combined effect of a decrease in the cost of production and a rise in consumer income on the equilibrium price and quantity of a normal good?
Correct
Recall that a normal good is one for which demand increases as income increases, ie a good that has a positive income elasticity of demand. An increase in income will therefore cause a rightward (or upward) shift of the demand curve. In addition, a decrease in the cost of production will cause a rightward (or downward) shift of the supply curve.
As both curves move to the right, there must be a resulting increase in the equilibrium quantity traded. However, it is not possible to predict the overall effect on the equilibrium price. This is because whilst an increase in demand alone would cause an increase in price, an increase in supply alone would cause price to decrease. So in the situation described here, the overall effect on price will depend on the relative sizes of the shifts.
So, there will be an increase in the equilibrium quantity but the effect on price is indeterminate. Hence the correct answer is Option B.
Answer: B
Incorrect
Recall that a normal good is one for which demand increases as income increases, ie a good that has a positive income elasticity of demand. An increase in income will therefore cause a rightward (or upward) shift of the demand curve. In addition, a decrease in the cost of production will cause a rightward (or downward) shift of the supply curve.
As both curves move to the right, there must be a resulting increase in the equilibrium quantity traded. However, it is not possible to predict the overall effect on the equilibrium price. This is because whilst an increase in demand alone would cause an increase in price, an increase in supply alone would cause price to decrease. So in the situation described here, the overall effect on price will depend on the relative sizes of the shifts.
So, there will be an increase in the equilibrium quantity but the effect on price is indeterminate. Hence the correct answer is Option B.
Answer: B
-
Question 392 of 999CB2031282
Question 392
FlagAn increase in the natural rate of unemployment will cause the long-run Phillips curve to:
Correct
Answer- A
The Phillips curve shows the relationship between inflation and unemployment. Monetarists believe that the long-run Phillips curve is vertical at the equilibrium (or natural) rate of unemployment. Therefore, an increase in the natural rate of unemployment will shift the Phillips curve to the right.
Incorrect
Answer- A
The Phillips curve shows the relationship between inflation and unemployment. Monetarists believe that the long-run Phillips curve is vertical at the equilibrium (or natural) rate of unemployment. Therefore, an increase in the natural rate of unemployment will shift the Phillips curve to the right.
-
Question 393 of 999CB2031283
Question 393
FlagWhich of the following will NOT cause a shift in the demand curve for Good X?
Correct
Recall that a demand curve is a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good demanded over a given time period all other things being equal.
Consequently, a change in the price of a good will lead to a movement along the demand curve.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.Conversely, a change in any of the other factors that affect the demand for a good will cause the demand curve for the good to shift. These include changes in:
– consumer tastes (Option A)
– the prices of other goods, eg substitutes and complements (Option D)
– consumer incomes (Option B)
– the distribution of income
– expectations of future price changes.Answer: C
Incorrect
Recall that a demand curve is a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good demanded over a given time period all other things being equal.
Consequently, a change in the price of a good will lead to a movement along the demand curve.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.Conversely, a change in any of the other factors that affect the demand for a good will cause the demand curve for the good to shift. These include changes in:
– consumer tastes (Option A)
– the prices of other goods, eg substitutes and complements (Option D)
– consumer incomes (Option B)
– the distribution of income
– expectations of future price changes.Answer: C
-
Question 394 of 999CB2031284
Question 394
FlagIf public transport is an inferior good, which of the following will cause its demand curve to shift to the left?
Correct
Recall that inferior goods are goods for which demand falls as incomes rise. In other words, they have a negative income elasticity of demand.
Public transport could be an inferior good because as incomes rise, some people will switch from travelling by public transport, to owning and travelling by their own car. Consequently, an increase in consumer incomes will cause a decrease in the demand for public transport and cause the demand curve for public transport to shift to the left. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Note that as public transport and travelling by private car are to some extent substitutes, so an increase in the price of cars is likely to result in a decrease in car ownership and an increase in the demand for public transport, ie its demand curve will shift to the right. So, Option A is not the correct answer.
Likewise, as cars and petrol are complementary goods, a rise in the price of petrol is likely to lead to a fall in the demand for both cars and petrol, again leading to an increase in the demand for public transport. So, Option B is incorrect.
Finally, an increase in the price charged to use public transport will lead to a decrease in the quantity of public transport demanded, which corresponds to an upward movement along the (unchanged) demand curve for public transport. So, Option D is incorrect.
Answer: C
Incorrect
Recall that inferior goods are goods for which demand falls as incomes rise. In other words, they have a negative income elasticity of demand.
Public transport could be an inferior good because as incomes rise, some people will switch from travelling by public transport, to owning and travelling by their own car. Consequently, an increase in consumer incomes will cause a decrease in the demand for public transport and cause the demand curve for public transport to shift to the left. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Note that as public transport and travelling by private car are to some extent substitutes, so an increase in the price of cars is likely to result in a decrease in car ownership and an increase in the demand for public transport, ie its demand curve will shift to the right. So, Option A is not the correct answer.
Likewise, as cars and petrol are complementary goods, a rise in the price of petrol is likely to lead to a fall in the demand for both cars and petrol, again leading to an increase in the demand for public transport. So, Option B is incorrect.
Finally, an increase in the price charged to use public transport will lead to a decrease in the quantity of public transport demanded, which corresponds to an upward movement along the (unchanged) demand curve for public transport. So, Option D is incorrect.
Answer: C
-
Question 395 of 999CB2031285
Question 395
FlagOther things being equal, if there is an unexpected fall in money supply, there is no change in the expected rate of inflation and the unemployment rate is above the natural rate of unemployment, then the long-run Phillips curve would suggest that the inflation rate will eventually:
Correct
Answer: B
If the unemployment rate is above the natural rate of unemployment, the economy must be to the right of its long-run Phillips curve (which is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment). This is illustrated at point A on the diagram below:
If the government or central bank decreases the money supply, perhaps in an attempt to decrease the rate of inflation, it is likely to result in decreased aggregate demand, prices and wages in the short run. However, workers may not believe that the government’s actions will reduce inflation, in which case they will continue to ask for pay rises in line with their previous expectations. This is stated as a condition of the question and is represented in the diagram by a movement along one of the expectations-augmented Phillips curves. At all points on the $\pi^e=\pi_1$ curve, expectations of inflation remain at $\pi_1$.
These pay rises will represent an increase in real costs for firms, who will respond by cutting output and laying off workers, increasing unemployment in the short run.
This is shown on the diagram by the movement from point A to point B .
In the long run, however, workers will accept that inflation is falling and eventually, they will be prepared to settle for (lower) wage increases at the government’s desired rate of inflation. This corresponds to a move on to a different expectations-augmented Phillips curve ( $\pi^e=\pi_2$ ).The economy will eventually settle at Point C, which is on the long-run Phillips curve at the desired rate of inflation. This corresponds to a fall in both unemployment and inflation, and so Option B is the correct answer.
Although not stated, the condition given in the question that ‘there is no change in the expected rate of inflation’ is assumed to apply in the short run only.
Incorrect
Answer: B
If the unemployment rate is above the natural rate of unemployment, the economy must be to the right of its long-run Phillips curve (which is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment). This is illustrated at point A on the diagram below:

If the government or central bank decreases the money supply, perhaps in an attempt to decrease the rate of inflation, it is likely to result in decreased aggregate demand, prices and wages in the short run. However, workers may not believe that the government’s actions will reduce inflation, in which case they will continue to ask for pay rises in line with their previous expectations. This is stated as a condition of the question and is represented in the diagram by a movement along one of the expectations-augmented Phillips curves. At all points on the $\pi^e=\pi_1$ curve, expectations of inflation remain at $\pi_1$.
These pay rises will represent an increase in real costs for firms, who will respond by cutting output and laying off workers, increasing unemployment in the short run.
This is shown on the diagram by the movement from point A to point B .
In the long run, however, workers will accept that inflation is falling and eventually, they will be prepared to settle for (lower) wage increases at the government’s desired rate of inflation. This corresponds to a move on to a different expectations-augmented Phillips curve ( $\pi^e=\pi_2$ ).The economy will eventually settle at Point C, which is on the long-run Phillips curve at the desired rate of inflation. This corresponds to a fall in both unemployment and inflation, and so Option B is the correct answer.
Although not stated, the condition given in the question that ‘there is no change in the expected rate of inflation’ is assumed to apply in the short run only.
-
Question 396 of 999CB2031286
Question 396
FlagWhich of the following statements explains how price, demand and supply for a good respond to an increase in the price of a substitute good?
Correct
Recall that substitute goods are alternatives, such as two different brands of the same good. Consumers typically buy one or the other but not both.
So, if, as here, the price of a substitute good increases, demand for that good will decrease and demand for the good in question will increase as some consumers switch to the now relatively cheaper alternative. Consequently, the demand curve for the good in question shifts to the right, resulting in a rise in its price, an increase in the quantity demanded and an increase in the quantity supplied. So, Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Recall that substitute goods are alternatives, such as two different brands of the same good. Consumers typically buy one or the other but not both.
So, if, as here, the price of a substitute good increases, demand for that good will decrease and demand for the good in question will increase as some consumers switch to the now relatively cheaper alternative. Consequently, the demand curve for the good in question shifts to the right, resulting in a rise in its price, an increase in the quantity demanded and an increase in the quantity supplied. So, Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 397 of 999CB2031287
Question 397
FlagIf the demand for Good X increases (due to a rise in income of consumers) and the supply of Good X increases (due to increased worker productivity) then the equilibrium price of Good X :
Correct
The question states that:
– the demand for Good X increases, ie the demand curve shifts to the right
– the supply of Good X increases, ie the supply curve shifts to the right.If both curves shift to the right, then the equilibrium must also shift to the right, meaning that the quantity traded must increase. This rules out Options A and C.
However, it is not possible to say with certainty what will happen to the equilibrium price, as this will depend on the extent to which each shifts. For example, if the supply curve shifts further to the right than the demand curve, then the price is likely to fall; whereas if the demand curve shifts further, the price is likely to rise. So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note that the causes of the shifts in the curves do not affect the answer.
Answer: D
Incorrect
The question states that:
– the demand for Good X increases, ie the demand curve shifts to the right
– the supply of Good X increases, ie the supply curve shifts to the right.If both curves shift to the right, then the equilibrium must also shift to the right, meaning that the quantity traded must increase. This rules out Options A and C.
However, it is not possible to say with certainty what will happen to the equilibrium price, as this will depend on the extent to which each shifts. For example, if the supply curve shifts further to the right than the demand curve, then the price is likely to fall; whereas if the demand curve shifts further, the price is likely to rise. So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note that the causes of the shifts in the curves do not affect the answer.
Answer: D
-
Question 398 of 999CB2031288
Question 398
FlagWhich of the following statements explains how price, demand and supply respond to a surplus?
Correct
With excess supply, prices have to fall to clear the surplus of supply over demand. As price falls, the quantity demanded increases (corresponding to a movement down the demand curve), while suppliers are prepared to supply less (corresponding to a movement down the supply curve). The surplus is eliminated as equilibrium is restored.
Answer: C
Incorrect
With excess supply, prices have to fall to clear the surplus of supply over demand. As price falls, the quantity demanded increases (corresponding to a movement down the demand curve), while suppliers are prepared to supply less (corresponding to a movement down the supply curve). The surplus is eliminated as equilibrium is restored.
Answer: C
-
Question 399 of 999CB2031289
Question 399
FlagDespite an increase in the price of admission from $£ 15.00$ to $£ 18.00$, a football club finds that attendance at matches increased by $20 \%$. Which of the following could most effectively explain this situation?
Correct
In the scenario outlined in the question, attendance at football matches has increased despite an increase in admission prices. The likeliest explanation for this is that demand for football matches has increased, presumably due to a change in consumer preferences in favour of football (and at the expense of some other activities). This suggests that Option D is the likely answer.
In the unlikely event that the change in attendance was due solely to the change in price, then the price elasticity of demand could be estimated as:
$$
P \varepsilon_D=\frac{\% \text { change in quantity demanded }}{\% \text { change in price }}=\frac{+20}{(+3 / 15)}=+1
$$This estimated value is:
– positive, as a price increase has resulted in an increase in demand, which is very unusual
– neither ‘high’ nor ‘low’, ruling out Options B and C as possible answers
– an estimate only, as it is calculated assuming that all attendees are charged the same admission price and nothing has changed except for the admission price, which may not be true.Finally, note that if the price of alternative attractions has fallen, then (all else being equal) this would make football less attractive, leading to a fall in the demand for football and hence a fall in attendance. So, Option A is also incorrect.
Answer: D
Incorrect
In the scenario outlined in the question, attendance at football matches has increased despite an increase in admission prices. The likeliest explanation for this is that demand for football matches has increased, presumably due to a change in consumer preferences in favour of football (and at the expense of some other activities). This suggests that Option D is the likely answer.
In the unlikely event that the change in attendance was due solely to the change in price, then the price elasticity of demand could be estimated as:
$$
P \varepsilon_D=\frac{\% \text { change in quantity demanded }}{\% \text { change in price }}=\frac{+20}{(+3 / 15)}=+1
$$This estimated value is:
– positive, as a price increase has resulted in an increase in demand, which is very unusual
– neither ‘high’ nor ‘low’, ruling out Options B and C as possible answers
– an estimate only, as it is calculated assuming that all attendees are charged the same admission price and nothing has changed except for the admission price, which may not be true.Finally, note that if the price of alternative attractions has fallen, then (all else being equal) this would make football less attractive, leading to a fall in the demand for football and hence a fall in attendance. So, Option A is also incorrect.
Answer: D
-
Question 400 of 999CB2031290
Question 400
FlagAssume that the actual rate of unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment because the expected rate of inflation is below the actual rate of inflation. If the expected rate of inflation rises to equal the actual rate of inflation, then real wage growth will start to:
Correct
Answer -D
According to the monetarist model, in the long run, the economy is expected to operate at the natural level of unemployment. If, in the short run, the economy is operating below the natural level, then in the long run, unemployment must rise back to its long-run natural level. A rise in unemployment is consistent with a fall in output, ruling out Options A and C.
Now consider what would happen to wages. If the economy is experiencing lower than natural levels of unemployment, it is likely that the excess demand for labour will increase wages, ruling out Options A and B. Option D is therefore the correct answer.
Now consider the detailed version, using the long-run and expectations-augmented (sometimes called short-run) Phillips curves.
Suppose unemployment is below the natural level, $U^*$, at $U^{\prime}$. Why would this occur? There might have been a rise in aggregate demand, perhaps due to an expansionary economic policy. If the economy were originally at Point $A$, the expansionary policy would take the economy to Point B, which is the starting point in this question.
At Point B, workers still expect inflation of $\pi_1 \%$ (even though actual inflation has risen) and therefore nominal wage negotiations are based on this and so firms hire more workers resulting in unemployment below the natural rate.
Gradually, expectations of inflation catch up with the new, higher reality and the expectations-augmented Phillips curve moves upwards towards EAPC ${ }_2$. Workers demand higher nominal wage increases, causing unemployment to rise back to its natural rate. The economy arrives at a new long-run equilibrium at Point $C$.
Incorrect
Answer -D
According to the monetarist model, in the long run, the economy is expected to operate at the natural level of unemployment. If, in the short run, the economy is operating below the natural level, then in the long run, unemployment must rise back to its long-run natural level. A rise in unemployment is consistent with a fall in output, ruling out Options A and C.
Now consider what would happen to wages. If the economy is experiencing lower than natural levels of unemployment, it is likely that the excess demand for labour will increase wages, ruling out Options A and B. Option D is therefore the correct answer.
Now consider the detailed version, using the long-run and expectations-augmented (sometimes called short-run) Phillips curves.
Suppose unemployment is below the natural level, $U^*$, at $U^{\prime}$. Why would this occur? There might have been a rise in aggregate demand, perhaps due to an expansionary economic policy. If the economy were originally at Point $A$, the expansionary policy would take the economy to Point B, which is the starting point in this question.

At Point B, workers still expect inflation of $\pi_1 \%$ (even though actual inflation has risen) and therefore nominal wage negotiations are based on this and so firms hire more workers resulting in unemployment below the natural rate.
Gradually, expectations of inflation catch up with the new, higher reality and the expectations-augmented Phillips curve moves upwards towards EAPC ${ }_2$. Workers demand higher nominal wage increases, causing unemployment to rise back to its natural rate. The economy arrives at a new long-run equilibrium at Point $C$.
-
Question 401 of 999CB2031291
Question 401
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a characteristic of an inferior good?
Correct
An inferior good is one for which demand falls as income rises, ie a good for which the income elasticity of demand is negative.
Options A and C are clearly true. Since Option A is true, Option B cannot be true, so Option B is false and is therefore the correct answer.
Option D is simply saying that inferior goods have downward-sloping demand curves, which is usually (though not always) true.
Answer: B
Incorrect
An inferior good is one for which demand falls as income rises, ie a good for which the income elasticity of demand is negative.
Options A and C are clearly true. Since Option A is true, Option B cannot be true, so Option B is false and is therefore the correct answer.
Option D is simply saying that inferior goods have downward-sloping demand curves, which is usually (though not always) true.
Answer: B
-
Question 402 of 999CB2031292
Question 402
FlagWhich one of the following will NOT shift the supply curve for Good X to the right?
Correct
C The supply curve will shift to the right, (ie supply will increase) if the cost of production decreases (Options A, B and D).
An increase in wages in the industry (Option C) would increase costs and cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
Incorrect
C The supply curve will shift to the right, (ie supply will increase) if the cost of production decreases (Options A, B and D).
An increase in wages in the industry (Option C) would increase costs and cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
-
Question 403 of 999CB2031293
Question 403
FlagOther things being equal in an economy with zero economic growth, if the expected rate of inflation on which wage settlements are based is $3 \% p q$ and the money supply is increasing at $4 \% p a$, then there will be a short-run:
Correct
Answer-B
In an economy with no economic growth and all else being equal, according to the equation of exchange, an increase in the money supply of $4 \% p a$ will increase prices by $4 \% p a$. Expectations of inflation are only $3 \% p a$, which suggests that inflation up to now has been only $3 \% p a$, hence inflation will increase, and this rules out Options A and C .
Since prices are increasing faster than wages, firms are incentivised to produce more, and unemployment will reduce, suggesting that Option B is the correct answer.
This is represented on the diagram below by a shift from point $A$ to point $B$ along the Phillips curve based on expected inflation of 3\%.
In the long run, expectations would change, and a new expectations-adjusted Phillips curve would prevail. The economy would move to a new equilibrium where inflation is $4 \%$ and unemployment is back at its natural rate, ie point $C$.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer-B
In an economy with no economic growth and all else being equal, according to the equation of exchange, an increase in the money supply of $4 \% p a$ will increase prices by $4 \% p a$. Expectations of inflation are only $3 \% p a$, which suggests that inflation up to now has been only $3 \% p a$, hence inflation will increase, and this rules out Options A and C .
Since prices are increasing faster than wages, firms are incentivised to produce more, and unemployment will reduce, suggesting that Option B is the correct answer.
This is represented on the diagram below by a shift from point $A$ to point $B$ along the Phillips curve based on expected inflation of 3\%.
In the long run, expectations would change, and a new expectations-adjusted Phillips curve would prevail. The economy would move to a new equilibrium where inflation is $4 \%$ and unemployment is back at its natural rate, ie point $C$.

-
Question 404 of 999CB2031294
Question 404
FlagWhich one of the following is likely to be the most effective method of reducing the natural rate of unemployment?
Correct
Answer:D
The natural level of unemployment is the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work.
In the diagram, $A B$ is the equilibrium or natural level of unemployment. It arises because some people who are in the labour force (shown by $N$ ) are not immediately willing or able to accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $A S_L$ ). These might be, for example, the structurally unemployed who may not be perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or they might be frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
The disequilibrium level of unemployment is the excess supply of labour resulting from the wage rate being above the equilibrium, ie CD above. This type of unemployment is usually caused by a reduction in the level of aggregate demand (demand-deficient unemployment) and by a reluctance of real wages to fall (real-wage unemployment).
Policies to reduce equilibrium unemployment need to address the particular type of unemployment that exists. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option D is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option A) could increase equilibrium unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in taxes (Option B) would be likely to decrease aggregate demand, and hence the aggregate demand for labour. A shift in the demand for labour curve to the left would both increase the gap between $A S_L$ and $N$, ie increase the natural rate of unemployment, and potentially increase the gap between $A D_l$ and $A S_l$, ie increase demand-deficient unemployment.
An increase in the money supply (Option C) would increase aggregate demand and be an appropriate policy to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
Incorrect
Answer:D
The natural level of unemployment is the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work.

In the diagram, $A B$ is the equilibrium or natural level of unemployment. It arises because some people who are in the labour force (shown by $N$ ) are not immediately willing or able to accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $A S_L$ ). These might be, for example, the structurally unemployed who may not be perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or they might be frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
The disequilibrium level of unemployment is the excess supply of labour resulting from the wage rate being above the equilibrium, ie CD above. This type of unemployment is usually caused by a reduction in the level of aggregate demand (demand-deficient unemployment) and by a reluctance of real wages to fall (real-wage unemployment).
Policies to reduce equilibrium unemployment need to address the particular type of unemployment that exists. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option D is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option A) could increase equilibrium unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in taxes (Option B) would be likely to decrease aggregate demand, and hence the aggregate demand for labour. A shift in the demand for labour curve to the left would both increase the gap between $A S_L$ and $N$, ie increase the natural rate of unemployment, and potentially increase the gap between $A D_l$ and $A S_l$, ie increase demand-deficient unemployment.
An increase in the money supply (Option C) would increase aggregate demand and be an appropriate policy to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
-
Question 405 of 999CB2031295
Question 405
FlagIf the price of Good X has risen and the quantity sold has increased, then there must have been a:
Correct
C: In order for the price to increase, the demand curve could shift to the right or the supply curve could shift to the left. A shift of the demand curve to the right would also increase output, whereas a shift of the supply curve to the left would decrease output. So, there must be a rightward shift of the demand curve.
This is illustrated in the following diagram:
Incorrect
C: In order for the price to increase, the demand curve could shift to the right or the supply curve could shift to the left. A shift of the demand curve to the right would also increase output, whereas a shift of the supply curve to the left would decrease output. So, there must be a rightward shift of the demand curve.
This is illustrated in the following diagram:
-
Question 406 of 999CB2031296
Question 406
FlagIf the cost of production increases and consumer income rises, the combined effect on the equilibrium price and quantity of an inferior good is:
Correct
A For inferior goods, the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases with income, eg an own-brand product.
An increase in the cost of production will shift the supply curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and increase price.
For an inferior good, a rise in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and reduce price.
Consequently, as the supply and demand curves both shift to the left, the equilibrium quantity must fall. However, the effect on the equilibrium price depends on which curve shifts the furthest, and also the slopes of the curves. So, the effect on price is indeterminate. Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
A For inferior goods, the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases with income, eg an own-brand product.
An increase in the cost of production will shift the supply curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and increase price.
For an inferior good, a rise in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and reduce price.
Consequently, as the supply and demand curves both shift to the left, the equilibrium quantity must fall. However, the effect on the equilibrium price depends on which curve shifts the furthest, and also the slopes of the curves. So, the effect on price is indeterminate. Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 407 of 999CB2031297
Question 407
FlagThe minimum wage is currently above the equilibrium wage. Which one of the following policies will increase voluntary unemployment?
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
Voluntary unemployment refers to the difference between the $N$ curve (the registered labour force) and the $A S_l$ curve (the aggregate supply of labour), ie the excess of people looking for work over those willing to accept a job at each wage rate.
A reduction in unemployment benefit (Option A), better dissemination of information about job vacancies (Option B) and an extension of job retraining programmes (Option C) would all be expected to shift the $A S_l$ curve to the right, reducing the distance between $B$ and $E$ in the diagram above, hence reducing voluntary unemployment. These options can therefore be ruled out.
A reduction in the minimum wage (Option D) should allow the average real wage rate to fall from $w_2$. At lower wage rates, disequilibrium unemployment (ie the distance between $A D_L$ and $A S_L$ ) will be smaller, however voluntary unemployment (ie the distance between $A S_l$ and $N$ ) will be greater. The reason that voluntary unemployment increases as wages decrease is that the lower the wages that are offered to the unemployed, the less willing they will be to accept jobs. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
Voluntary unemployment refers to the difference between the $N$ curve (the registered labour force) and the $A S_l$ curve (the aggregate supply of labour), ie the excess of people looking for work over those willing to accept a job at each wage rate.

A reduction in unemployment benefit (Option A), better dissemination of information about job vacancies (Option B) and an extension of job retraining programmes (Option C) would all be expected to shift the $A S_l$ curve to the right, reducing the distance between $B$ and $E$ in the diagram above, hence reducing voluntary unemployment. These options can therefore be ruled out.
A reduction in the minimum wage (Option D) should allow the average real wage rate to fall from $w_2$. At lower wage rates, disequilibrium unemployment (ie the distance between $A D_L$ and $A S_L$ ) will be smaller, however voluntary unemployment (ie the distance between $A S_l$ and $N$ ) will be greater. The reason that voluntary unemployment increases as wages decrease is that the lower the wages that are offered to the unemployed, the less willing they will be to accept jobs. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 408 of 999CB2031298
Question 408
FlagWheat is an essential input in the production of pasta. An increase in the price of wheat would have an impact on the demand and supply of pasta by shifting the:
Correct
B: The supply of pasta will reflect the cost of producing pasta, which will in turn depend upon:
– the cost of the resources used to produce it, including wheat
– the technology used to produce it
– the organisaational structure of the producer
– government policy, eg taxes and subsidies on pasta production.An increase in the costs of production will mean that firms will require a higher price to cover those costs and maintain supply. The supply curve will therefore shift vertically upwards, which corresponds to a shift to the left.
The demand curve will be unaffected by the rise in the cost of wheat, which consumers may be unaware of in any case. However, the shift in the supply curve will lead to a movement along the demand curve, resulting in a reduction in the quantity demanded.
Incorrect
B: The supply of pasta will reflect the cost of producing pasta, which will in turn depend upon:
– the cost of the resources used to produce it, including wheat
– the technology used to produce it
– the organisaational structure of the producer
– government policy, eg taxes and subsidies on pasta production.An increase in the costs of production will mean that firms will require a higher price to cover those costs and maintain supply. The supply curve will therefore shift vertically upwards, which corresponds to a shift to the left.
The demand curve will be unaffected by the rise in the cost of wheat, which consumers may be unaware of in any case. However, the shift in the supply curve will lead to a movement along the demand curve, resulting in a reduction in the quantity demanded.
-
Question 409 of 999CB2031299
Question 409
FlagWhat is the combined effect of an increase in the cost of production and a rise in consumer income on the equilibrium price and quantity of an inferior good?
Correct
A: It is important to bear in mind that the good under consideration is an inferior good. For inferior goods (eg own-brand products), the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases as income increases.
Let’s consider the two impacts in isolation:
– An increase in the cost of production will shift the supply curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and increase price.
– For an inferior good, a rise in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and reduce price.Consequently, as the supply and demand curves both shift to the left, the equilibrium quantity must fall. However, the effect on the equilibrium price depends on which curve shifts the furthest, and also the slopes of the curves. So, the effect on price is indeterminate.
Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
A: It is important to bear in mind that the good under consideration is an inferior good. For inferior goods (eg own-brand products), the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie the quantity demanded decreases as income increases.
Let’s consider the two impacts in isolation:
– An increase in the cost of production will shift the supply curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and increase price.
– For an inferior good, a rise in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the left. This will act to reduce quantity and reduce price.Consequently, as the supply and demand curves both shift to the left, the equilibrium quantity must fall. However, the effect on the equilibrium price depends on which curve shifts the furthest, and also the slopes of the curves. So, the effect on price is indeterminate.
Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 410 of 999CB2031300
Question 410
FlagA consumer’s demand curve for Good X is represented by the equation:
$$
Q_{d x}=50-0.2 P_x
$$
where $Q_{d x}$ is the quantity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ demanded and $P_x$ is the price of Good X .
A producer’s supply curve for Good X is represented by the equation:
$$
Q_{s x}=10+0.6 P_x
$$
where $Q_{5 X}$ is the quantity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ supplied and $P_x$ is the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$.
Demand and supply are in equilibrium when:Correct
D, Equilibrium can be found where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Q_{d x} & =Q_{5 x} \\
50-0.2 P_x & =10+0.6 P_x \\
0.8 P_x & =40
\end{aligned}
$$Thus:
$$
P_x=50 \text { and } Q_x=40
$$Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
D, Equilibrium can be found where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Q_{d x} & =Q_{5 x} \\
50-0.2 P_x & =10+0.6 P_x \\
0.8 P_x & =40
\end{aligned}
$$Thus:
$$
P_x=50 \text { and } Q_x=40
$$Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 411 of 999CB2031301
Question 411
FlagIf the central bank has to intervene in the foreign exchange markets to prevent the domestic currency from appreciating, then its foreign exchange reserves will:
Correct
the answer is Option C.
This is a question about central bank intervention in a fixed exchange rate system.
A diagram might be helpful to answer this question.
In a fixed exchange rate system, the rate of the currency is typically fixed against another currency and the central bank intervenes in the currency markets to maintain the fixed value.In the following diagram, suppose the exchange rate is originally fixed at $r_1$ and the currency is $£ s$.
The question states that the exchange rate is in danger of appreciating, so there must be an increase in demand for and/or a decrease in supply of the currency. Suppose demand increases from $D_1$ to $D_2$. The diagram shows that at $r_1$, there is excess demand of $Q_2-Q_1$, and without intervention from the central bank, the exchange rate will increase from $r_1$ to $r_2$. To prevent this happening, the central bank will have to satisfy this demand by supplying $Q_2-Q_1$ fs to the market. It will achieve this by buying foreign currency with $£ s$, which will ultimately increase the volume of £s in circulation as they are spent by people abroad on UK exports etc and are consequently deposited in domestic banks. Therefore, the country’s foreign exchange reserves will increase and the domestic money supply will rise. So the answer is Option C.
Note that this assumes there is no sterilisation, ie the central bank does not use open market operations to neutralise the effect on the money supply.
Incorrect
the answer is Option C.
This is a question about central bank intervention in a fixed exchange rate system.
A diagram might be helpful to answer this question.
In a fixed exchange rate system, the rate of the currency is typically fixed against another currency and the central bank intervenes in the currency markets to maintain the fixed value.In the following diagram, suppose the exchange rate is originally fixed at $r_1$ and the currency is $£ s$.

The question states that the exchange rate is in danger of appreciating, so there must be an increase in demand for and/or a decrease in supply of the currency. Suppose demand increases from $D_1$ to $D_2$. The diagram shows that at $r_1$, there is excess demand of $Q_2-Q_1$, and without intervention from the central bank, the exchange rate will increase from $r_1$ to $r_2$. To prevent this happening, the central bank will have to satisfy this demand by supplying $Q_2-Q_1$ fs to the market. It will achieve this by buying foreign currency with $£ s$, which will ultimately increase the volume of £s in circulation as they are spent by people abroad on UK exports etc and are consequently deposited in domestic banks. Therefore, the country’s foreign exchange reserves will increase and the domestic money supply will rise. So the answer is Option C.
Note that this assumes there is no sterilisation, ie the central bank does not use open market operations to neutralise the effect on the money supply.
-
Question 412 of 999CB2031302
Question 412
FlagIf the central bank has to intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent the home currency from depreciating, then its foreign exchange reserves will:
Correct
Answer: D
In the following diagram, suppose the exchange rate is originally $r_1$ and the currency is $£$ s.
The question states that the exchange rate is in danger of depreciating, so there must be a decrease in demand for and/or an increase in supply of the currency. Suppose demand decreases from $D_1$ to $D_2$. The diagram shows that at $r_1$, there is excess supply of $Q_2-Q_1$ pounds, and without intervention from the central bank, the exchange rate will decrease from $r_1$ to $r_2$.
To prevent this happening, the central bank will have to withdraw $Q_2-Q_1 £ s$ from the market. It will achieve this by buying $£ s$ with its reserves of foreign currency, which will ultimately decrease the volume of $£ s$ in circulation. Therefore, the country’s foreign exchange reserves will decrease and the domestic money supply will fall. So the answer is Option D.
Note that this assumes there is no sterilisation, ie the central bank does not use open market operations to neutralise the effect on the money supply.
Incorrect
Answer: D
In the following diagram, suppose the exchange rate is originally $r_1$ and the currency is $£$ s.

The question states that the exchange rate is in danger of depreciating, so there must be a decrease in demand for and/or an increase in supply of the currency. Suppose demand decreases from $D_1$ to $D_2$. The diagram shows that at $r_1$, there is excess supply of $Q_2-Q_1$ pounds, and without intervention from the central bank, the exchange rate will decrease from $r_1$ to $r_2$.
To prevent this happening, the central bank will have to withdraw $Q_2-Q_1 £ s$ from the market. It will achieve this by buying $£ s$ with its reserves of foreign currency, which will ultimately decrease the volume of $£ s$ in circulation. Therefore, the country’s foreign exchange reserves will decrease and the domestic money supply will fall. So the answer is Option D.
Note that this assumes there is no sterilisation, ie the central bank does not use open market operations to neutralise the effect on the money supply.
-
Question 413 of 999CB2031303
Question 413
FlagWhich of the following will NOT shift the supply curve for Good X to the right?
Correct
C :The supply curve will shift to the right, (ie supply will increase) if the cost of production decreases (Options A, B and D).
An increase in wages in the industry (Option C) would increase costs and cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
Incorrect
C :The supply curve will shift to the right, (ie supply will increase) if the cost of production decreases (Options A, B and D).
An increase in wages in the industry (Option C) would increase costs and cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
-
Question 414 of 999CB2031304
Question 414
FlagAn ‘inferior good’ is defined as a good:
Correct
B :An inferior good is one for which demand falls as people’s incomes rise. Option B is therefore correct.
Incorrect
B :An inferior good is one for which demand falls as people’s incomes rise. Option B is therefore correct.
-
Question 415 of 999CB2031305
Question 415
FlagThe substitution effect of a price decrease causes an individual to purchase more units of a normal good because:
Correct
A: The substitution effect of a reduction in price is the increase in quantity demanded resulting from the fall in the price of the product relative to other products. The consumer will substitute from the relatively more expensive good to the relatively cheaper good. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Option D describes the income effect of a reduction in price, ie the effect on quantity demanded of a rise in real income (or an increase in purchasing power) resulting from the fall in price.
Incorrect
A: The substitution effect of a reduction in price is the increase in quantity demanded resulting from the fall in the price of the product relative to other products. The consumer will substitute from the relatively more expensive good to the relatively cheaper good. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Option D describes the income effect of a reduction in price, ie the effect on quantity demanded of a rise in real income (or an increase in purchasing power) resulting from the fall in price.
-
Question 416 of 999CB2031306
Question 416
FlagWhich of the following would NOT explain why, when the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise?
Correct
A : If a firm expects the price of the good to rise in the future, then it may reduce supply now in order to sell more at the higher future price. So, expectations of future price rises do not explain why, when the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise. This appears to rule out Option D and suggests that Option A may well be the intended answer. However, it is probably sensible to check the other options just to be sure.
At higher levels of output, firms will generally incur higher costs, eg due to the higher demand for factors, diminishing marginal returns, capacity constraints, or the need to pay overtime. However, higher prices enable them to cover these higher costs and so this is one reason why quantity supplied tends to increase with price. Therefore, Option B is not the correct answer.
Likewise, if the price of a good rises, then it becomes more profitable to produce that good (relative to other goods), and so the quantity of that good supplied will typically rise. Consequently, Option C is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
A : If a firm expects the price of the good to rise in the future, then it may reduce supply now in order to sell more at the higher future price. So, expectations of future price rises do not explain why, when the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise. This appears to rule out Option D and suggests that Option A may well be the intended answer. However, it is probably sensible to check the other options just to be sure.
At higher levels of output, firms will generally incur higher costs, eg due to the higher demand for factors, diminishing marginal returns, capacity constraints, or the need to pay overtime. However, higher prices enable them to cover these higher costs and so this is one reason why quantity supplied tends to increase with price. Therefore, Option B is not the correct answer.
Likewise, if the price of a good rises, then it becomes more profitable to produce that good (relative to other goods), and so the quantity of that good supplied will typically rise. Consequently, Option C is not the correct answer.
-
Question 417 of 999CB2031307
Question 417
FlagWhich of the following will lead to a leftward shift in the demand for cars?
Correct
Answer B: A rise in the price of cars (Option A) will lead to a leftward movement along the demand curve.
Public transport may be considered to be a substitute for using a private car. Therefore a fall in the price of public transport (Option B) will make public transport relatively cheap compared to driving, which will shift the demand curve for cars to the left. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Car insurance is a complementary good to a car. Therefore a fall in car insurance premiums (Option C) will make car insurance – and hence driving – relatively cheap compared to alternatives, which will shift the demand curve for cars to the right.
Assuming cars are a normal good, a rise in consumers’ incomes (Option D) will make driving more affordable, which will shift the demand curve for cars to the right.
Incorrect
Answer B: A rise in the price of cars (Option A) will lead to a leftward movement along the demand curve.
Public transport may be considered to be a substitute for using a private car. Therefore a fall in the price of public transport (Option B) will make public transport relatively cheap compared to driving, which will shift the demand curve for cars to the left. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Car insurance is a complementary good to a car. Therefore a fall in car insurance premiums (Option C) will make car insurance – and hence driving – relatively cheap compared to alternatives, which will shift the demand curve for cars to the right.
Assuming cars are a normal good, a rise in consumers’ incomes (Option D) will make driving more affordable, which will shift the demand curve for cars to the right.
-
Question 418 of 999CB2031308
Question 418
FlagOther things remaining the same, the effect of an increase in the budget deficit is to:
Correct
ANSWER:D
Budget deficits are first discussed briefly in Module 10. The money market is discussed in Module 15 and the effect of changes in the goods market on the money market in Module 18.
Recall that a budget deficit refers to the excess of government spending ( $G$ ) over and above the government’s revenues from taxation (T). An increase in the budget deficit will therefore arise from an increase in $G$ and/or a decrease in $T$.
An increase in $G$ will directly increase total spending on domestically produced goods and services, ie it will increase aggregate demand (AD). Likewise, a reduction in $T$, eg via income and corporation tax cuts, will increase consumer spending and investment by firms, again increasing $A D$. Consequently, the $A D$ curve will shift to the right, ruling out Options $A$ and $B$.
In addition, the increase in AD will lead to an increase in GDP and a consequent rise in money demand, due to the transactions motive, as consumers and firms buy more goods. Assuming no change in the money supply, the extra money demand will lead to an increase in short-term interest rates (from $r_1$ to $r_1$ ). This is shown in the following diagram.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
ANSWER:D
Budget deficits are first discussed briefly in Module 10. The money market is discussed in Module 15 and the effect of changes in the goods market on the money market in Module 18.
Recall that a budget deficit refers to the excess of government spending ( $G$ ) over and above the government’s revenues from taxation (T). An increase in the budget deficit will therefore arise from an increase in $G$ and/or a decrease in $T$.
An increase in $G$ will directly increase total spending on domestically produced goods and services, ie it will increase aggregate demand (AD). Likewise, a reduction in $T$, eg via income and corporation tax cuts, will increase consumer spending and investment by firms, again increasing $A D$. Consequently, the $A D$ curve will shift to the right, ruling out Options $A$ and $B$.
In addition, the increase in AD will lead to an increase in GDP and a consequent rise in money demand, due to the transactions motive, as consumers and firms buy more goods. Assuming no change in the money supply, the extra money demand will lead to an increase in short-term interest rates (from $r_1$ to $r_1$ ). This is shown in the following diagram.

-
Question 419 of 999CB2031309
Question 419
FlagGood X is a normal good. Which of the following will NOT shift the demand curve for Good X to the left?
Correct
Answer B :Normal goods are goods for which demand increases as consumer incomes rise. For a normal good, a fall in consumers’ incomes (Option A) will shift the demand curve to the left.
Substitute goods are goods that consumers consider to be alternatives to each other, eg two different brands of butter. A fall in the price of a substitute Good Y (Option C ) will result in some consumers switching from Good $Y$ to Good $X$, which will shift the demand curve for Good X to the left.
Incorrect
Answer B :Normal goods are goods for which demand increases as consumer incomes rise. For a normal good, a fall in consumers’ incomes (Option A) will shift the demand curve to the left.
Substitute goods are goods that consumers consider to be alternatives to each other, eg two different brands of butter. A fall in the price of a substitute Good Y (Option C ) will result in some consumers switching from Good $Y$ to Good $X$, which will shift the demand curve for Good X to the left.
-
Question 420 of 999CB2031310
Question 420
FlagAs a result of an economic policy change, interest rates and consumption rise but investment falls. The new policy was:
Correct
Answer: A
Fiscal and monetary policy are both discussed at length in Modules 21 and 15, respectively. The effect of each on interest rates and national income are discussed in Module 18.
Recall that:
– an expansionary fiscal policy is one that involves an increase in government spending and/or a reduction in taxation
– an expansionary monetary policy involves cutting interest rates and/or increasing the money supply.In both cases, the policy is aimed at increasing aggregate demand in order to achieve economic growth. Conversely, contractionary policies involve the opposite measures being taken in order to contract economic activity, usually in order to reduce inflation or to correct a balance of payments deficit. Let’s consider the likely effects of each of the policy options in turn.
An expansionary fiscal policy will increase aggregate demand, including consumption and investment. However the resulting increase in money demand will, if the money supply is unchanged, lead to an rise in interest rates, which will in turn lead to a fall in investment. So, as it can result in the scenario outlined in the question, Option A may be the correct answer.
Conversely, a contractionary fiscal pollcy will lead to falls in both consumption and investment, the resulting fall in money demand leading to a fall in interest rates too. So, Option C is not the correct answer.
An expansionary monetary policy will increase the money supply and/or reduce interest rates, both of which will lead to increased consumption and investment by households and firms. So, Option B is not the correct answer.
Finally, a contractionary monetary policy will decrease the money supply and/or increase interest rates. Consequently, consumption and investment by households and firms respectively will both fall. So, Option D is not the correct answer.
As the other three options are all incorrect, Option A must be the correct answer.
Note that a reduction in investment due to the rise in interest rates following an increase in government spending is often referred to as crowding out. In practice, both consumption and investment could be crowded out by the rise in interest rates. However, in the scenario described in this question, there is an overall increase in consumption, as it is assumed that the multiplier effect of increased aggregate demand exceeds the impact of crowding out, whereas the opposite is true for investment by firms.Incorrect
Answer: A
Fiscal and monetary policy are both discussed at length in Modules 21 and 15, respectively. The effect of each on interest rates and national income are discussed in Module 18.
Recall that:
– an expansionary fiscal policy is one that involves an increase in government spending and/or a reduction in taxation
– an expansionary monetary policy involves cutting interest rates and/or increasing the money supply.In both cases, the policy is aimed at increasing aggregate demand in order to achieve economic growth. Conversely, contractionary policies involve the opposite measures being taken in order to contract economic activity, usually in order to reduce inflation or to correct a balance of payments deficit. Let’s consider the likely effects of each of the policy options in turn.
An expansionary fiscal policy will increase aggregate demand, including consumption and investment. However the resulting increase in money demand will, if the money supply is unchanged, lead to an rise in interest rates, which will in turn lead to a fall in investment. So, as it can result in the scenario outlined in the question, Option A may be the correct answer.
Conversely, a contractionary fiscal pollcy will lead to falls in both consumption and investment, the resulting fall in money demand leading to a fall in interest rates too. So, Option C is not the correct answer.
An expansionary monetary policy will increase the money supply and/or reduce interest rates, both of which will lead to increased consumption and investment by households and firms. So, Option B is not the correct answer.
Finally, a contractionary monetary policy will decrease the money supply and/or increase interest rates. Consequently, consumption and investment by households and firms respectively will both fall. So, Option D is not the correct answer.
As the other three options are all incorrect, Option A must be the correct answer.
Note that a reduction in investment due to the rise in interest rates following an increase in government spending is often referred to as crowding out. In practice, both consumption and investment could be crowded out by the rise in interest rates. However, in the scenario described in this question, there is an overall increase in consumption, as it is assumed that the multiplier effect of increased aggregate demand exceeds the impact of crowding out, whereas the opposite is true for investment by firms. -
Question 421 of 999CB2031311
Question 421
FlagWhich one of the following will shift the supply curve for Good $X$ to the left?
Correct
Answer C: An increase in real wages in the industry producing Good $X$ (Option $C$ ) will increase costs, which will shift the supply curve for Good X to the left. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
A fall in the costs of production will shift the supply curve for the good to the right. The fall in the costs of production may be due to:
– an increase in labour productivity in the industry producing Good X (Option A)
– a fall in the price of raw materials used to produce Good X (Option B)
– a government subsidy on the production of Good X (Option D).Incorrect
Answer C: An increase in real wages in the industry producing Good $X$ (Option $C$ ) will increase costs, which will shift the supply curve for Good X to the left. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
A fall in the costs of production will shift the supply curve for the good to the right. The fall in the costs of production may be due to:
– an increase in labour productivity in the industry producing Good X (Option A)
– a fall in the price of raw materials used to produce Good X (Option B)
– a government subsidy on the production of Good X (Option D). -
Question 422 of 999CB2031312
Question 422
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for real money balances is interest-elastic and the demand for investment is interest-inelastic. A change in the money supply will result in a relatively:
Correct
Answer: A
This question is about the effect of a change in the money supply on both the rate of interest and the level of investment.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a reduction in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium.
The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If the curve is steep, ie money demand is insensitive to, and thus inelastic with respect to, interest rates, then a large fall in interest rates will be required to increase demand sufficiently to result in the new equilibrium. Conversely, if as in this question, money demand is elastic, ie the demand curve is flat, then only a small fall in interest rates is required. This means that one of Options A and C must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if investment is interest-inelastic, ie insensitive to interest rates, then it will not change much even in response to a large reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Note that real money balances refers to the purchasing power of the nominal amount of money, just as real wages refers to the purchasing power of money wages.
Incorrect
Answer: A
This question is about the effect of a change in the money supply on both the rate of interest and the level of investment.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a reduction in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium.

The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If the curve is steep, ie money demand is insensitive to, and thus inelastic with respect to, interest rates, then a large fall in interest rates will be required to increase demand sufficiently to result in the new equilibrium. Conversely, if as in this question, money demand is elastic, ie the demand curve is flat, then only a small fall in interest rates is required. This means that one of Options A and C must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if investment is interest-inelastic, ie insensitive to interest rates, then it will not change much even in response to a large reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Note that real money balances refers to the purchasing power of the nominal amount of money, just as real wages refers to the purchasing power of money wages.
-
Question 423 of 999CB2031313
Question 423
FlagAn increase in the price of frozen yoghurt would lead to:
Correct
Answer C: Frozen yoghurt and ice cream may be considered to be (to some extent) substitutes.
If the price of frozen yoghurt goes up, then the demand for it will go down, ie the quantity demanded of frozen yoghurt will fall (and there will be a leftward movement along the demand curve). Consumers will replace frozen yoghurt for (the now relatively cheap) ice cream, and so the demand curve for ice cream will shift to the right.Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: Frozen yoghurt and ice cream may be considered to be (to some extent) substitutes.
If the price of frozen yoghurt goes up, then the demand for it will go down, ie the quantity demanded of frozen yoghurt will fall (and there will be a leftward movement along the demand curve). Consumers will replace frozen yoghurt for (the now relatively cheap) ice cream, and so the demand curve for ice cream will shift to the right.Hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 424 of 999CB2031314
Question 424
FlagThe introduction of a restrictive monetary policy in an open economy operating with a flexible exchange rate would most likely lead to:
Correct
Answer: C
The monetary transmission mechanisms are discussed in Module 18 of the Course Notes.
A restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.Incorrect
Answer: C
The monetary transmission mechanisms are discussed in Module 18 of the Course Notes.
A restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation. -
Question 425 of 999CB2031315
Question 425
FlagThe supply curve will shift to the left when:
Correct
Answer D: A fall in production costs (Option A) will make it cheaper to produce each unit of the good, which will shift the supply curve for the good to the right.
A fall in the market price of the good (Option B) will lead to a leftward movement along the supply curve.
Technological progress (Option C) is also likely to make it cheaper to produce each unit of the good, which will shift the supply curve for the good to the right.
A decrease in the number of firms producing the good (Option D) will result in a decrease in the supply of the good, which will shift the supply curve to the left. Hence Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D: A fall in production costs (Option A) will make it cheaper to produce each unit of the good, which will shift the supply curve for the good to the right.
A fall in the market price of the good (Option B) will lead to a leftward movement along the supply curve.
Technological progress (Option C) is also likely to make it cheaper to produce each unit of the good, which will shift the supply curve for the good to the right.
A decrease in the number of firms producing the good (Option D) will result in a decrease in the supply of the good, which will shift the supply curve to the left. Hence Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 426 of 999CB2031316
Question 426
FlagWhat is the combined effect of a fall in the cost of production and a fall in consumer income on the equilibrium price and quantity of a normal good?
Correct
Answer C:For normal goods, a fall in income will result in a fall in the demand for the good, ie a shift of the demand curve to the left. In addition, a decrease in the cost of production will cause the supply curve to shift to the right.
As the demand curve moves to the left but the supply curve to the right, the effect on equilibrium quantity traded will depend on the distance that each shifts, ie it is indeterminate based on the information given. However, given that a fall in demand in isolation will result in a fall in the equilibrium price level, and an increase in supply in isolation will result in a fall in the equilibrium price level, a fall in demand combined with an increase in supply will also result in a fall in the equilibrium price level.
So, there will be a fall in the equilibrium price but the effect on quantity is indeterminate. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C:For normal goods, a fall in income will result in a fall in the demand for the good, ie a shift of the demand curve to the left. In addition, a decrease in the cost of production will cause the supply curve to shift to the right.
As the demand curve moves to the left but the supply curve to the right, the effect on equilibrium quantity traded will depend on the distance that each shifts, ie it is indeterminate based on the information given. However, given that a fall in demand in isolation will result in a fall in the equilibrium price level, and an increase in supply in isolation will result in a fall in the equilibrium price level, a fall in demand combined with an increase in supply will also result in a fall in the equilibrium price level.
So, there will be a fall in the equilibrium price but the effect on quantity is indeterminate. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 427 of 999CB2031317
Question 427
Flag‘Crowding out’ describes the:
Correct
Answer: C
The final multiple-choice question is also on Module 18.
Crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector. (For example, an increase in government spending on health services might lead to a reduction in spending on private healthcare.) Financial crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government borrowing (and spending) diverts money away from the private sector. It is argued that this occurs because the consequent rise in Interest rates decreases consumption and investment, and might also reduce net exports if the rise in interest rates causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.The effect of crowding out will therefore be to reduce the size of the multiplier effect resulting from an increase in government spending. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Note that the above analysis assumes a fixed money supply, ie the government borrows from the non-bank private sector. In these circumstances, an increase in the demand for money (as a result of the increase in national income resulting from the increase in government spending) causes a rise in interest rates. Financial crowding out will not occur if the money supply is allowed to rise in line with the increase in the demand for money, eg if the government borrows in the form of Treasury bills from the banking sector.
Incorrect
Answer: C
The final multiple-choice question is also on Module 18.
Crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector. (For example, an increase in government spending on health services might lead to a reduction in spending on private healthcare.) Financial crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government borrowing (and spending) diverts money away from the private sector. It is argued that this occurs because the consequent rise in Interest rates decreases consumption and investment, and might also reduce net exports if the rise in interest rates causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.The effect of crowding out will therefore be to reduce the size of the multiplier effect resulting from an increase in government spending. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Note that the above analysis assumes a fixed money supply, ie the government borrows from the non-bank private sector. In these circumstances, an increase in the demand for money (as a result of the increase in national income resulting from the increase in government spending) causes a rise in interest rates. Financial crowding out will not occur if the money supply is allowed to rise in line with the increase in the demand for money, eg if the government borrows in the form of Treasury bills from the banking sector.
-
Question 428 of 999CB2031318
Question 428
FlagWhich of the following best describes an annual demand curve?
Correct
Answer C: A demand curve is a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good demanded over a given time period, all other things being equal.
The demand curve:
– relates the price of a good to the quantity demanded of that good – this rules out Option B, which relates quantity to income (rather than price), and suggests that Option C looks like a good description
– reflects the quantity demanded, and in order to demand a good, the consumer must be both willing and able to purchase it – this rules out Option A, which describes what consumers might like, but not what they are able to afford.Option D seems like a reasonable description of the demand curve, but with no mention of price, it is not as good a description as Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C: A demand curve is a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good demanded over a given time period, all other things being equal.
The demand curve:
– relates the price of a good to the quantity demanded of that good – this rules out Option B, which relates quantity to income (rather than price), and suggests that Option C looks like a good description
– reflects the quantity demanded, and in order to demand a good, the consumer must be both willing and able to purchase it – this rules out Option A, which describes what consumers might like, but not what they are able to afford.Option D seems like a reasonable description of the demand curve, but with no mention of price, it is not as good a description as Option C.
-
Question 429 of 999CB2031319
Question 429
FlagThe majority of breakfast cereals contain rice as a key ingredient. If the price of rice falls, what is the likely impact on the equilibrium price and quantity traded of breakfast cereals?
Correct
Answer B: The supply of breakfast cereals will reflect the cost of producing breakfast cereals, which will in turn depend upon the cost of the resources used to produce it, including rice.
A decrease in these costs of production will mean that firms will require a lower price to cover those costs and maintain supply. The supply curve will therefore shift vertically downwards, which corresponds to a shift to the right.
The demand curve will be unaffected by the rise in the cost of rice. However, the shift in the supply curve will lead to a movement down and along the demand curve, resulting in a fall in price and an increase in the quantity demanded. Option B is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B: The supply of breakfast cereals will reflect the cost of producing breakfast cereals, which will in turn depend upon the cost of the resources used to produce it, including rice.
A decrease in these costs of production will mean that firms will require a lower price to cover those costs and maintain supply. The supply curve will therefore shift vertically downwards, which corresponds to a shift to the right.
The demand curve will be unaffected by the rise in the cost of rice. However, the shift in the supply curve will lead to a movement down and along the demand curve, resulting in a fall in price and an increase in the quantity demanded. Option B is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 430 of 999CB2031320
Question 430
FlagIf the money supply rises as a result of central bank policy, this will normally result in:
Correct
Option A as the correct answer.
This question is about the monetary transmission mechanisms.
Recall that an increase in the money supply will cause short-term interest rates to fall. This is shown on the diagram below and rules out Options B and C.
A reduction in short-term interest rates will reduce the attractiveness of the domestic currency to investors. As a consequence, some investors will sell the domestic currency in exchange for foreign currency in order to obtain the relatively higher return offered on deposits in banks abroad. The resulting increased supply of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange markets will cause its value to depreciate, giving Option A as the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option A as the correct answer.
This question is about the monetary transmission mechanisms.
Recall that an increase in the money supply will cause short-term interest rates to fall. This is shown on the diagram below and rules out Options B and C.
A reduction in short-term interest rates will reduce the attractiveness of the domestic currency to investors. As a consequence, some investors will sell the domestic currency in exchange for foreign currency in order to obtain the relatively higher return offered on deposits in banks abroad. The resulting increased supply of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange markets will cause its value to depreciate, giving Option A as the correct answer.
-
Question 431 of 999CB2031321
Question 431
FlagA consumer’s demand curve for Good X is represented by the equation:
$$
Q_{d x}=100 Q_{d x}-0.2 P_x
$$Where $Q_{d x}$ is the quantity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ demanded and $P_x$ is the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$.
A producer’s supply curve for Good X is represented by the equation:
$$
Q_{5 x}=20+0.6 P_x
$$
where $Q_{s x}$ is the quantity of Good X supplied and $P_x$ is the price of Good X .
Demand and supply are in equilibrium when:Correct
Answer C: Equilibrium can be found where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Q_{d x} & =Q_{5 x} \\
100-0.2 P_x & =20+0.6 P_x \\
0.8 P_x & =80
\end{aligned}
$$Thus:
$$
P_x=100 \text { and } Q_x=80
$$Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: Equilibrium can be found where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Q_{d x} & =Q_{5 x} \\
100-0.2 P_x & =20+0.6 P_x \\
0.8 P_x & =80
\end{aligned}
$$Thus:
$$
P_x=100 \text { and } Q_x=80
$$Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 432 of 999CB2031322
Question 432
FlagGood $X$ is a normal good. Assuming no other changes to the factors that affect the supply and demand for Good X, which statement is true if there is a general fall in income?
Correct
Answer D: For a normal good, a fall in consumers’ incomes will shift the demand curve to the left. Assuming that the supply curve is unchanged (as is stated in the question), this will lead to a fall in the equilibrium price and quantity of Good X. Hence the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer D: For a normal good, a fall in consumers’ incomes will shift the demand curve to the left. Assuming that the supply curve is unchanged (as is stated in the question), this will lead to a fall in the equilibrium price and quantity of Good X. Hence the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 433 of 999CB2031323
Question 433
FlagWhich one of the following changes will cause the supply curve for a good to shift to the right?
Correct
Answer C :A movement along the supply curve occurs when the price of the good changes, which impacts the quantity supplied. The supply curve will shift if another factor that impacts quantity supplied, other than price, changes.
A fall in the cost of producing the good (Option C) will shift the supply curve for the good to the right. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
A rise in the profitability of producing substitute goods (Option A) will make producing the substitute good more attractive and producing the original good relatively less attractive. This is likely to lead to a shift in the supply curve for the good to the left.
A fall in the price of the good (Option B) will lead to a leftward movement along the supply curve.
The introduction of a new tax on the production of the good (Option D) will increase the cost of producing the good, so shifting the supply curve for the good upwards.
Incorrect
Answer C :A movement along the supply curve occurs when the price of the good changes, which impacts the quantity supplied. The supply curve will shift if another factor that impacts quantity supplied, other than price, changes.
A fall in the cost of producing the good (Option C) will shift the supply curve for the good to the right. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
A rise in the profitability of producing substitute goods (Option A) will make producing the substitute good more attractive and producing the original good relatively less attractive. This is likely to lead to a shift in the supply curve for the good to the left.
A fall in the price of the good (Option B) will lead to a leftward movement along the supply curve.
The introduction of a new tax on the production of the good (Option D) will increase the cost of producing the good, so shifting the supply curve for the good upwards.
-
Question 434 of 999CB2031324
Question 434
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for real money balances and the demand for investment are both highly interest-elastic. A change in the money supply will give:
Correct
Answer: D
This question is about the effect of a change in the money supply on both the rate of interest and the level of investment.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a reduction in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium.
The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If the curve is steep, ie money demand is insensitive to, and thus inelastic with respect to, interest rates, then a large fall in interest rates will be required to increase quantity demanded sufficiently to result in the new equilibrium. Conversely, if as in this question, money demand is elastic, ie the demand curve is flat, then only a small fall in interest rates is required. This means that one of Options A and D must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if the demand for investment is highly interest-elastic, ie very sensitive to interest rates, then it will change considerably in response to even a small reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Note that real money balances refers to the purchasing power of the nominal amount of money, just as real wages refers to the purchasing power of money wages.
Incorrect
Answer: D
This question is about the effect of a change in the money supply on both the rate of interest and the level of investment.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a reduction in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium.

The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If the curve is steep, ie money demand is insensitive to, and thus inelastic with respect to, interest rates, then a large fall in interest rates will be required to increase quantity demanded sufficiently to result in the new equilibrium. Conversely, if as in this question, money demand is elastic, ie the demand curve is flat, then only a small fall in interest rates is required. This means that one of Options A and D must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if the demand for investment is highly interest-elastic, ie very sensitive to interest rates, then it will change considerably in response to even a small reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Note that real money balances refers to the purchasing power of the nominal amount of money, just as real wages refers to the purchasing power of money wages.
-
Question 435 of 999CB2031325
Question 435
FlagAn increase in government expenditure financed by government borrowing from the non-bank private sector is most likely to:
Correct
Answer: D
The final multiple-choice question considers the effects of fiscal policy on money demand, interest rates and investment. It therefore overlaps somewhat with the ideas considered in Questions 23 and 24. This question is particularly concerned with the monetary effects of fiscal policy.
Recall that the demand for money:
– increases with money national income (due to the transactions and precautionary demands)
– is inversely related to the rate of interest (due to the asset or speculative demand), which means that on the money market equilibrium diagram, the money demand curve slopes downwards.The consequence of the first point above is that an increase in government spending increases national income and hence increases the demand for money. This causes the money demand curve to shift to the right (from $M_{d 1}$ to $M_{d 2}$ in the following diagram). This means that Options $A$ and $C$ can be ruled out.
Also, the question states that the extra spending is financed by borrowing from the non-bank private sector. This means that the money supply curve is unchanged. So, at the initial interest rate $r_1$ money demand now exceeds the money supply (by AB in the diagram).
The sale of government securities leads to a decrease in their price and an increase in interest rates. As the price of bonds falls and the interest rate rises, people are attracted to buying bonds and therefore decide to hold less cash (as an asset) and more bonds, ie there is movement along the $M_{d 2}$ curve.
Notice that we have drawn the diagram with an upward-sloping (endogenous) money supply curve, which assumes that the money supply will rise in response to higher interest rates and thus help to choke off the excess money demand. A new equilibrium in the money market is reached at the higher interest rate of $r_2$. (A vertical or exogenous money supply curve would mean that interest rates would have to rise further to reach a new equilibrium.)
Since interest rates rise, this rules out Option B. So Option D must be the correct answer. Let’s check that this is correct.
Option D says that investment will fall. This makes sense because the rise in interest rates increases the cost of borrowing to funds new projects and so investment by firms will fall.
This is an example of financial crowding out, ie the increase in government spending leads to an increase in interest rates and this ‘crowds out’ (ie reduces) private sector spending. Notice that crowding out would not occur if the government borrowed in a way that increased the money supply (eg by selling Treasury bills to the banking sector) because then interest rates would not have to rise.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The final multiple-choice question considers the effects of fiscal policy on money demand, interest rates and investment. It therefore overlaps somewhat with the ideas considered in Questions 23 and 24. This question is particularly concerned with the monetary effects of fiscal policy.
Recall that the demand for money:
– increases with money national income (due to the transactions and precautionary demands)
– is inversely related to the rate of interest (due to the asset or speculative demand), which means that on the money market equilibrium diagram, the money demand curve slopes downwards.The consequence of the first point above is that an increase in government spending increases national income and hence increases the demand for money. This causes the money demand curve to shift to the right (from $M_{d 1}$ to $M_{d 2}$ in the following diagram). This means that Options $A$ and $C$ can be ruled out.
Also, the question states that the extra spending is financed by borrowing from the non-bank private sector. This means that the money supply curve is unchanged. So, at the initial interest rate $r_1$ money demand now exceeds the money supply (by AB in the diagram).

The sale of government securities leads to a decrease in their price and an increase in interest rates. As the price of bonds falls and the interest rate rises, people are attracted to buying bonds and therefore decide to hold less cash (as an asset) and more bonds, ie there is movement along the $M_{d 2}$ curve.
Notice that we have drawn the diagram with an upward-sloping (endogenous) money supply curve, which assumes that the money supply will rise in response to higher interest rates and thus help to choke off the excess money demand. A new equilibrium in the money market is reached at the higher interest rate of $r_2$. (A vertical or exogenous money supply curve would mean that interest rates would have to rise further to reach a new equilibrium.)
Since interest rates rise, this rules out Option B. So Option D must be the correct answer. Let’s check that this is correct.
Option D says that investment will fall. This makes sense because the rise in interest rates increases the cost of borrowing to funds new projects and so investment by firms will fall.
This is an example of financial crowding out, ie the increase in government spending leads to an increase in interest rates and this ‘crowds out’ (ie reduces) private sector spending. Notice that crowding out would not occur if the government borrowed in a way that increased the money supply (eg by selling Treasury bills to the banking sector) because then interest rates would not have to rise.
-
Question 436 of 999CB2031326
Question 436
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for real money balances is interest-inelastic and the demand for investment is interest-elastic. A change in the money supply will result in a relatively:
Correct
Answer: B
This question is about the effect of a change in the money supply on both the rate of interest and the level of investment.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a reduction in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium. Note that real money balances refers to the purchasing power of the nominal amount of money, just as real wages refers to the purchasing power of money wages.
The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If the curve is steep, ie money demand is insensitive to, and thus inelastic with respect to, interest rates, then a large fall in interest rates will be required to increase demand sufficiently to result in the new equilibrium. This means that one of Options B and D must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if the demand for investment is highly interest-elastic, ie very sensitive to interest rates, then it will change considerably in response to a large change in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Incorrect
Answer: B
This question is about the effect of a change in the money supply on both the rate of interest and the level of investment.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a reduction in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium. Note that real money balances refers to the purchasing power of the nominal amount of money, just as real wages refers to the purchasing power of money wages.

The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If the curve is steep, ie money demand is insensitive to, and thus inelastic with respect to, interest rates, then a large fall in interest rates will be required to increase demand sufficiently to result in the new equilibrium. This means that one of Options B and D must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if the demand for investment is highly interest-elastic, ie very sensitive to interest rates, then it will change considerably in response to a large change in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option B.
-
Question 437 of 999CB2031327
Question 437
FlagThe introduction of a restrictive monetary policy in an open economy operating with a flexible exchange rate would most likely lead to:
Correct
Answer: A
The effect of monetary policy on interest rates and exchange rates is discussed in Module 18 of the Course Notes.
A restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. (See the diagram in Solution 23, which illustrates the impact of an increase in the money supply). Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for the domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The effect of monetary policy on interest rates and exchange rates is discussed in Module 18 of the Course Notes.
A restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. (See the diagram in Solution 23, which illustrates the impact of an increase in the money supply). Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for the domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
-
Question 438 of 999CB2031328
Question 438
FlagWhich one of the following will occur, assuming spare capacity within the economy, if both government spending and the money supply are increased?
Correct
Answer: D
Fiscal policy (including the use of government spending) and monetary policy are both discussed at length in Module 21 of the Course Notes, and this, along with knowledge of the money market model, covered in Module 15, and the goods market (Keynesian model) of Module 17, will enable us to answer this question. However, since the question asks for the effects on national income and interest rates, the easiest way to answer this question is by using the IS-LM model.
The IS curve shows the combinations of real national income and real interest rates that give equilibrium in the goods market (ie where injections = withdrawals). The IS curve slopes downwards because a lower interest rate increases aggregate demand and hence increases national income.
The LM curve shows the combinations of real national income and real interest rates that give equilibrium in the money market (ie where money demand = money supply). The LM curve slopes upwards because as national income increases, the demand for money increases and therefore interest rates increase.
The intersection of the two curves shows the equilibrium level of real national income and the real interest rate that give equilibrium in the goods and money markets.
An increase in government spending is an increase in injections, so this shifts the IS curve to the right, since at any interest rate there would be a higher level of national income. An increase in the money supply would shift the LM curve to the right, since at a given level of national income, there would be a lower interest rate.
Therefore if both curves shift, there would definitely be an increase in national income, but the effect on interest rates is uncertain. (In the diagram above, the shift in the IS curve has been greater than the shift in the LM curve and so the real interest rate has risen.) Therefore, the answer is Option D.
Without using the IS-LM model, we could argue that, all else being equal, and assuming there is spare capacity in the economy, increased government spending will lead to a multiplied increased in national income. Likewise, an increase in the money supply will tend to lead to more borrowing by households and firms to fund increased consumption and investment spending, which will also result in an increase in national income. Hence, as both policies will lead to an increase in national income, we can rule out Options B and C.
Turning to the effect on interest rates, the increased demand for money resulting from a higher level of national income will tend to lead to a rise interest rates. However, an increase in the money supply will tend to result in a fall in interest rates. Consequently, the overall effect on interest rates will be uncertain, which means that Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Fiscal policy (including the use of government spending) and monetary policy are both discussed at length in Module 21 of the Course Notes, and this, along with knowledge of the money market model, covered in Module 15, and the goods market (Keynesian model) of Module 17, will enable us to answer this question. However, since the question asks for the effects on national income and interest rates, the easiest way to answer this question is by using the IS-LM model.
The IS curve shows the combinations of real national income and real interest rates that give equilibrium in the goods market (ie where injections = withdrawals). The IS curve slopes downwards because a lower interest rate increases aggregate demand and hence increases national income.
The LM curve shows the combinations of real national income and real interest rates that give equilibrium in the money market (ie where money demand = money supply). The LM curve slopes upwards because as national income increases, the demand for money increases and therefore interest rates increase.
The intersection of the two curves shows the equilibrium level of real national income and the real interest rate that give equilibrium in the goods and money markets.

An increase in government spending is an increase in injections, so this shifts the IS curve to the right, since at any interest rate there would be a higher level of national income. An increase in the money supply would shift the LM curve to the right, since at a given level of national income, there would be a lower interest rate.
Therefore if both curves shift, there would definitely be an increase in national income, but the effect on interest rates is uncertain. (In the diagram above, the shift in the IS curve has been greater than the shift in the LM curve and so the real interest rate has risen.) Therefore, the answer is Option D.
Without using the IS-LM model, we could argue that, all else being equal, and assuming there is spare capacity in the economy, increased government spending will lead to a multiplied increased in national income. Likewise, an increase in the money supply will tend to lead to more borrowing by households and firms to fund increased consumption and investment spending, which will also result in an increase in national income. Hence, as both policies will lead to an increase in national income, we can rule out Options B and C.
Turning to the effect on interest rates, the increased demand for money resulting from a higher level of national income will tend to lead to a rise interest rates. However, an increase in the money supply will tend to result in a fall in interest rates. Consequently, the overall effect on interest rates will be uncertain, which means that Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 439 of 999CB2031329
Question 439
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a ‘crowding out’ effect resulting from a fiscal expansion?
Correct
Answer: C
Crowding out is defined in Module 17 of the Course Notes and financial crowding out is defined in Module 18.
Recall that crowding out occurs when increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector, leading to a consequent reduction in private sector spending, such as consumption or investment. Crowding out therefore reduces the multiplier effect of increased government spending.
Financial crowding out occurs when an increase in government borrowing diverts money away from the private sector. Let’s see why this might happen.
An increase in government spending increases aggregate demand and hence increases national income. This increases the demand for money. Whether or not financial crowding out occurs is determined by the effect of this on interest rates. This depends on what happens to the supply of money, which itself depends on how the government borrows. If the government borrows from the banking sector, especially if it borrows through short-term Treasury bills, the money supply wi rise; if, on the other hand, it borrows from the non-bank private sector, the money supply will not increase.
In the former case, the increase in demand for money will be counteracted by the increase in the supply of money so there will be no increase in interest rates. However, if there is no increase in the money supply (ie a pure fiscal expansion), then the increase in the demand for money will cause a rise in interest rates.
Higher interest rates could decrease borrowing (and spending) by firms on investment. This corresponds to Option A, so this cannot be the correct answer.
An increase in interest rates may also lead to an appreciation of the domestic currency, making exports more expensive in terms of foreign currency, leading to a fall in the demand for exports. This corresponds to Option D, which consequently cannot be the correct answer.
Interestingly, instead of explicitly referring to an increase in government spending, this question uses the phrase ‘fiscal expansion’, by which it means the use of fiscal policy, ie government spending and/or taxation, to expand the economy, ie increase national income. In practice, this could mean an increase in government spending with no change in the level of taxation or an increase in government spending partly funded by a smaller increase in taxation.
Suppose, it is the former case, so that although taxes haven’t increased at the moment, it could be that consumers expect taxes to be increased at some point in the near future to fund the increased spending. If this is the case, then the expectation of future higher taxes could lead them to reduce their spending now. Although not strictly in accordance with the definition of crowding out stated above, this effect on expectations is sometimes construed as being an indirect crowding out effect and so Option B is unlikely to be the correct answer.
This is confirmed by considering Option C. If part of the fiscal expansion involves the government deliberately choosing to buy domestically produced goods instead of imported ones, then this will help boost domestic demand and national income and will not have any crowding out impact. This is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Crowding out is defined in Module 17 of the Course Notes and financial crowding out is defined in Module 18.
Recall that crowding out occurs when increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector, leading to a consequent reduction in private sector spending, such as consumption or investment. Crowding out therefore reduces the multiplier effect of increased government spending.
Financial crowding out occurs when an increase in government borrowing diverts money away from the private sector. Let’s see why this might happen.
An increase in government spending increases aggregate demand and hence increases national income. This increases the demand for money. Whether or not financial crowding out occurs is determined by the effect of this on interest rates. This depends on what happens to the supply of money, which itself depends on how the government borrows. If the government borrows from the banking sector, especially if it borrows through short-term Treasury bills, the money supply wi rise; if, on the other hand, it borrows from the non-bank private sector, the money supply will not increase.
In the former case, the increase in demand for money will be counteracted by the increase in the supply of money so there will be no increase in interest rates. However, if there is no increase in the money supply (ie a pure fiscal expansion), then the increase in the demand for money will cause a rise in interest rates.
Higher interest rates could decrease borrowing (and spending) by firms on investment. This corresponds to Option A, so this cannot be the correct answer.
An increase in interest rates may also lead to an appreciation of the domestic currency, making exports more expensive in terms of foreign currency, leading to a fall in the demand for exports. This corresponds to Option D, which consequently cannot be the correct answer.
Interestingly, instead of explicitly referring to an increase in government spending, this question uses the phrase ‘fiscal expansion’, by which it means the use of fiscal policy, ie government spending and/or taxation, to expand the economy, ie increase national income. In practice, this could mean an increase in government spending with no change in the level of taxation or an increase in government spending partly funded by a smaller increase in taxation.
Suppose, it is the former case, so that although taxes haven’t increased at the moment, it could be that consumers expect taxes to be increased at some point in the near future to fund the increased spending. If this is the case, then the expectation of future higher taxes could lead them to reduce their spending now. Although not strictly in accordance with the definition of crowding out stated above, this effect on expectations is sometimes construed as being an indirect crowding out effect and so Option B is unlikely to be the correct answer.
This is confirmed by considering Option C. If part of the fiscal expansion involves the government deliberately choosing to buy domestically produced goods instead of imported ones, then this will help boost domestic demand and national income and will not have any crowding out impact. This is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 440 of 999CB2031330
Question 440
FlagWhich one of the following statements about real variables in the economy is FALSE?
Correct
ANSWER-D
A real quantity has had inflation stripped out of it, ie it is equal to the nominal quantity less inflation. Equivalently, a real quantity plus inflation is equal to the nominal quantity.
Option A – It is impossible to say what will happen to real GDP without having information relating to inflation. Real GDP may rise (if inflation is below 5\%), fall (if inflation is above $5 \%$ ) or remain unchanged (if inflation is equal to $5 \%$ ). Therefore Option A is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option B – If the nominal value of the money supply falls by a greater amount than prices, then the real value of the money supply also decreases. Option B is therefore true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option C – In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transaction purposes. Therefore Option C is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option D – If the expected rate of inflation is greater than the nominal rate of interest, then savings will be losing value, ie the real rate of interest will be negative. For example, if the nominal interest rate is $5 \%$ pa and inflation is expected to be $7 \%$ pa, then the real interest rate is minus $2 \%$ pa. Therefore Option D is not true and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
ANSWER-D
A real quantity has had inflation stripped out of it, ie it is equal to the nominal quantity less inflation. Equivalently, a real quantity plus inflation is equal to the nominal quantity.
Option A – It is impossible to say what will happen to real GDP without having information relating to inflation. Real GDP may rise (if inflation is below 5\%), fall (if inflation is above $5 \%$ ) or remain unchanged (if inflation is equal to $5 \%$ ). Therefore Option A is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option B – If the nominal value of the money supply falls by a greater amount than prices, then the real value of the money supply also decreases. Option B is therefore true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option C – In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transaction purposes. Therefore Option C is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option D – If the expected rate of inflation is greater than the nominal rate of interest, then savings will be losing value, ie the real rate of interest will be negative. For example, if the nominal interest rate is $5 \%$ pa and inflation is expected to be $7 \%$ pa, then the real interest rate is minus $2 \%$ pa. Therefore Option D is not true and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 441 of 999CB2031331
Question 441
FlagIf a fall in the price of Good $X$ causes the demand curve for Good $Y$ to shift to the right, then:
Correct
Option A. We have a fall in the price of Good X leading to an increase in the demand for Good Y . The goods are therefore likely to be complements, ie goods that are consumed together. For example, a fall in the price of cars is likely to lead to an increase in demand for cars and hence an increase in demand for petrol.
Incorrect
Option A. We have a fall in the price of Good X leading to an increase in the demand for Good Y . The goods are therefore likely to be complements, ie goods that are consumed together. For example, a fall in the price of cars is likely to lead to an increase in demand for cars and hence an increase in demand for petrol.
-
Question 442 of 999CB2031332
Question 442
FlagIf Good $X$ is an inferior good, then an increase in income will cause $a$ :
Correct
Option B. By definition, inferior goods are goods for which demand falls as income rises. This is shown as a leftward shift of the demand curve. Remember that a movement along a demand curve is caused by a change in price.
Incorrect
Option B. By definition, inferior goods are goods for which demand falls as income rises. This is shown as a leftward shift of the demand curve. Remember that a movement along a demand curve is caused by a change in price.
-
Question 443 of 999CB2031333
Question 443
FlagWhich of the following occurs when technological improvements occur, making a good easier to produce?
I a movement along a demand curve
II a shift of the supply curve
III a movement along a supply curveCorrect
Option A. Improvements in technology reduce production costs, which causes the supply curve to shift to the right, leading to a movement along the demand curve.
-
Question 444 of 999CB2031334
Question 444
FlagIf at all positive quantities, the upward-sloping supply curve lies above the downward-sloping demand curve, then:
-
Question 445 of 999CB2031335
Question 445
FlagA movement along a demand curve is best described as:
Correct
Option D. A movement along the demand curve occurs as a result of a change in price, and is referred to as a change in quantity demanded. An increase in price would lead to a lower quantity demanded, and a decrease in price would lead to a higher quantity demanded. A shift of the demand curve occurs as a result of a change in one of the other factors that determine demand (eg income) and is referred to as an increase or decrease in demand. For example, an increase in income would lead to an increase in demand for a normal good (a shift to the right) and a decrease in demand for an inferior good (a shift to the left).
Incorrect
Option D. A movement along the demand curve occurs as a result of a change in price, and is referred to as a change in quantity demanded. An increase in price would lead to a lower quantity demanded, and a decrease in price would lead to a higher quantity demanded. A shift of the demand curve occurs as a result of a change in one of the other factors that determine demand (eg income) and is referred to as an increase or decrease in demand. For example, an increase in income would lead to an increase in demand for a normal good (a shift to the right) and a decrease in demand for an inferior good (a shift to the left).
-
Question 446 of 999CB2031336
Question 446
FlagWhich one of the following events would shift the demand curve for Good X to the left?
Correct
Option B. The decrease in the price of a substitute good would lead to an increase in quantity demanded of the substitute good and therefore a decrease in demand for Good X (ie a leftward shift of the demand curve). For example, a decrease in the price of Pepsi would lead to a decrease in demand for Coca-Cola, assuming Pepsi is a substitute for Coca-Cola.
Incorrect
Option B. The decrease in the price of a substitute good would lead to an increase in quantity demanded of the substitute good and therefore a decrease in demand for Good X (ie a leftward shift of the demand curve). For example, a decrease in the price of Pepsi would lead to a decrease in demand for Coca-Cola, assuming Pepsi is a substitute for Coca-Cola.
-
Question 447 of 999CB2031337
Question 447
FlagWhich one of the following will shift the supply curve for Good X to the right?
Correct
Option B. A fall in the price of raw materials used to produce Good X will reduce the costs of producing Good X, so the producer will produce the same quantity for a lower price (or a higher quantity for the same price), and the supply curve will shift to the right. The other three options will add to the cost of supplying the good and so will cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
Incorrect
Option B. A fall in the price of raw materials used to produce Good X will reduce the costs of producing Good X, so the producer will produce the same quantity for a lower price (or a higher quantity for the same price), and the supply curve will shift to the right. The other three options will add to the cost of supplying the good and so will cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
-
Question 448 of 999CB2031338
Question 448
FlagA consumer’s demand curve for $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ is represented by the equation:
$$
Q d=50-0.2 p
$$
where $Q d$ is the quantity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ demanded and $p$ is the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$.
A producer’s supply curve for $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ is represented by the equation:
$$
Q s=10+0.6 p
$$
where $Q s$ is the quantity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ supplied and $p$ is the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$.
Demand and supply are in equilibrium when:Correct
Option D.
Equilibrium can be found where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Q_{\mathrm{d}} & =Q_{\mathrm{s}} \\
50-0.2 p & =10+0.6 p \\
0.8 p & =40 \\
p & =50
\end{aligned}
$$Substituting back into either equation then gives:
$$
Q=40
$$Incorrect
Option D.
Equilibrium can be found where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Q_{\mathrm{d}} & =Q_{\mathrm{s}} \\
50-0.2 p & =10+0.6 p \\
0.8 p & =40 \\
p & =50
\end{aligned}
$$Substituting back into either equation then gives:
$$
Q=40
$$ -
Question 449 of 999CB2031339
Question 449
FlagIf the price of a substitute good decreases and the cost of production decreases the price:
Correct
Option A. If the price of a substitute good falls, the substitute becomes more attractive, so the demand curve for this good will shift to the left. If the cost of production decreases, the supply curve will shift to the right. Therefore, the price will fall (because both events cause the price to fall). However, the effect on output is uncertain (because the decrease in demand would cause output to fall but the increase in supply would cause output to rise).
Incorrect
Option A. If the price of a substitute good falls, the substitute becomes more attractive, so the demand curve for this good will shift to the left. If the cost of production decreases, the supply curve will shift to the right. Therefore, the price will fall (because both events cause the price to fall). However, the effect on output is uncertain (because the decrease in demand would cause output to fall but the increase in supply would cause output to rise).
-
Question 450 of 999CB2031340
Question 450
FlagIn the diagram below, points X and Y represent the equilibrium price and quantity traded of a good in two successive time periods. $X$ corresponds to the first of the two time periods.
Which of the following is NOT a possible explanation?
Correct
Option B.
A movement from X to Y represents an increase in price and a fall in quantity.
An input in the production process becoming more expensive will shift the supply curve to the left. This will increase price and reduce quantity. Therefore this, in conjunction with any other factor, could be a possible explanation. (This rules out Options A, C and D.)An increase in the price of a close substitute will shift the demand curve to the right. This will increase both price and quantity. Therefore the answer is Option B.
Incorrect
Option B.
A movement from X to Y represents an increase in price and a fall in quantity.
An input in the production process becoming more expensive will shift the supply curve to the left. This will increase price and reduce quantity. Therefore this, in conjunction with any other factor, could be a possible explanation. (This rules out Options A, C and D.)An increase in the price of a close substitute will shift the demand curve to the right. This will increase both price and quantity. Therefore the answer is Option B.
-
Question 451 of 999CB2031341
Question 451
FlagIf a maximum price for Good X is fixed above the market equilibrium price there will be:
Correct
In this instance, the maximum price has been fixed above the equilibrium price, so it will have no effect upon either the equilibrium price or quantity. Consequently, Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 452 of 999CB2031342
Question 452
FlagA maximum price is set for Good X at $£ 30$ which happens to coincide with the free market price. A downward shift in the supply of Good $X$ keeping the maximum price fixed at $£ 30$ will lead to:
Correct
Answer: B or D
The intention was for this phrase to be interpreted as a downward, or rightward shift of the supply curve. As you can see from the diagram below, this will reduce the equilibrium price to P2 below the maximum price of $£ 30$, whilst the equilibrium quantity will increase, from Q1 to Q2. This corresponds to Option D.
Alternatively, a ‘downward shift in supply’ could be interpreted as meaning a reduction in supply Itself, which corresponds to a leftward shift of the supply curve. As you can see from the diagram below, in the absence of a maximum price, the equilibrium price would rise to P2 and the quantity sold would fall to Q2. Here, however, the maximum price prevents this happening. Instead, there is an excess demand over supply of Q1 – Q3 at the maximum price, ie there is a shortage. This corresponds to Option B.
Incorrect
Answer: B or D
The intention was for this phrase to be interpreted as a downward, or rightward shift of the supply curve. As you can see from the diagram below, this will reduce the equilibrium price to P2 below the maximum price of $£ 30$, whilst the equilibrium quantity will increase, from Q1 to Q2. This corresponds to Option D.
Alternatively, a ‘downward shift in supply’ could be interpreted as meaning a reduction in supply Itself, which corresponds to a leftward shift of the supply curve. As you can see from the diagram below, in the absence of a maximum price, the equilibrium price would rise to P2 and the quantity sold would fall to Q2. Here, however, the maximum price prevents this happening. Instead, there is an excess demand over supply of Q1 – Q3 at the maximum price, ie there is a shortage. This corresponds to Option B.
-
Question 453 of 999CB2031343
Question 453
FlagIf the own price elasticity of demand for $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ is -0.8 and the income elasticity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ is -0.3 , which of the following is correct?
Correct
Answer: D
A price of elasticity of demand of -0.8 , ie less than one in absolute terms, means that the percentage change in quantity demanded will be less than the percentage change in price that caused it. Demand is therefore said to be inelastic. This rules out Option A.
If price is inelastic, then a cut in price will lead to a smaller percentage rise in quantity sold and hence to a fall in total revenue (ie price $\times$ quantity). So, Option B is also incorrect.
A negative income elasticity of demand implies that demand falls in response to a rise in consumer incomes, which is often true of own-brand goods. An inferior good, such as own-brand goods, is defined as one for which this is the case. Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Finally, the economic definition of a luxury good is one with an income elasticity of demand greater than plus one, ie the quantity demanded increases more than proportionately with income. Although luxury goods are not defined explicitly in the textbook, the types of goods that are referred to as luxury goods in an everyday sense (eg yachts, sports cars and expensive jewellery) are also luxury goods in the economic sense.
Incorrect
Answer: D
A price of elasticity of demand of -0.8 , ie less than one in absolute terms, means that the percentage change in quantity demanded will be less than the percentage change in price that caused it. Demand is therefore said to be inelastic. This rules out Option A.
If price is inelastic, then a cut in price will lead to a smaller percentage rise in quantity sold and hence to a fall in total revenue (ie price $\times$ quantity). So, Option B is also incorrect.
A negative income elasticity of demand implies that demand falls in response to a rise in consumer incomes, which is often true of own-brand goods. An inferior good, such as own-brand goods, is defined as one for which this is the case. Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Finally, the economic definition of a luxury good is one with an income elasticity of demand greater than plus one, ie the quantity demanded increases more than proportionately with income. Although luxury goods are not defined explicitly in the textbook, the types of goods that are referred to as luxury goods in an everyday sense (eg yachts, sports cars and expensive jewellery) are also luxury goods in the economic sense.
-
Question 454 of 999CB2031344
Question 454
FlagThe demand for Good $X$ has a price elasticity of -1 . If the government decided to impose a sales tax of $£ 3$ per unit on Good X this would:
Correct
Answer: D
If the demand curve slopes downwards and the supply curve slopes upwards, then the imposition of a sales tax will increase the price paid by the consumer and decrease the price received by the producer, in both cases by an amount less than the sales tax.
In this case, the sales tax of $£ 3$ will cause the price to rise by less than $£ 3$.
The imposition of the sales tax of $£ 3$ per unit causes the supply curve to shift vertically upwards by the amount of the tax. This causes the price paid by the consumer to increase from $p_1$ to $p_c$ (ie less than $£ 3$ ) and the price received by the producer to decrease from $p_1$ to $p_p$. The distance AB represents the total amount of the tax, £3 per unit.
Incorrect
Answer: D
If the demand curve slopes downwards and the supply curve slopes upwards, then the imposition of a sales tax will increase the price paid by the consumer and decrease the price received by the producer, in both cases by an amount less than the sales tax.
In this case, the sales tax of $£ 3$ will cause the price to rise by less than $£ 3$.
The imposition of the sales tax of $£ 3$ per unit causes the supply curve to shift vertically upwards by the amount of the tax. This causes the price paid by the consumer to increase from $p_1$ to $p_c$ (ie less than $£ 3$ ) and the price received by the producer to decrease from $p_1$ to $p_p$. The distance AB represents the total amount of the tax, £3 per unit.
-
Question 455 of 999CB2031345
Question 455
FlagIf the income elasticity of demand for $\operatorname{Good} X$ is 2 , a rise in all consumers’ disposable incomes from $£ 50$ million to $£ 52$ million will increase the quantity demanded of Good $X$ by:
Correct
Answer D:
Recall that the income elasticity of demand is defined as:
$$
Y \varepsilon_D=\frac{\% \Delta Q_d}{\% \Delta Y}
$$Since $Y \varepsilon_D=2$, the percentage change in quantity demanded must be twice the percentage change in income. Here the percentage increase in income is $4 \%$ and so the quantity demanded must increase by 8\%.
Incorrect
Answer D:
Recall that the income elasticity of demand is defined as:
$$
Y \varepsilon_D=\frac{\% \Delta Q_d}{\% \Delta Y}
$$Since $Y \varepsilon_D=2$, the percentage change in quantity demanded must be twice the percentage change in income. Here the percentage increase in income is $4 \%$ and so the quantity demanded must increase by 8\%.
-
Question 456 of 999CB2031346
Question 456
FlagIf an $8 \%$ rise in the price of Good $X$ results in a $4 \%$ fall in the quantity of Good $X$ demanded then the approximate price elasticity of demand for $\operatorname{Good} X$ is:
Correct
Answer: B
Recall that the price of elasticity of demand is defined and calculated as:
$$
P_{E_D}=\frac{\text { % change in quantity demanded }}{\text { % change in price }}
$$So, if an $8 \%$ rise in price results in a $4 \%$ fall in quantity demanded, then:
$$
P \varepsilon_D=\frac{-4 \%}{+8 \%}=-0.5
$$
which means that Option B is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer: B
Recall that the price of elasticity of demand is defined and calculated as:
$$
P_{E_D}=\frac{\text { % change in quantity demanded }}{\text { % change in price }}
$$So, if an $8 \%$ rise in price results in a $4 \%$ fall in quantity demanded, then:
$$
P \varepsilon_D=\frac{-4 \%}{+8 \%}=-0.5
$$
which means that Option B is the correct answer. -
Question 457 of 999CB2031347
Question 457
FlagWhich one of the following statements concerning advertising is FALSE?
Correct
Answer: B
Advertising of a product is intended to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right, by bringing the product to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of consuming the product. This means that Option A is a true statement and hence not the correct answer.
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (more price inelastic), by creating brand loyalty, and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand. This means that the statement in Option B is false and so is the correct answer.Note that advertising aims to increase a firm’s profits and so in order to be successful it must increase total revenue by more than it increases total costs. In other words, Option C is a true statement. (Note that costs will increase due to both the cost of the advertising and the cost of producing the additional units sold as a consequence of the advertising.)
The fact that advertising may enable the firm to increase sales and output and thereby increase its ability to exploit economies of scale is one of the possible benefits of advertising. So, Option D is also a true statement.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Advertising of a product is intended to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right, by bringing the product to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of consuming the product. This means that Option A is a true statement and hence not the correct answer.
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (more price inelastic), by creating brand loyalty, and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand. This means that the statement in Option B is false and so is the correct answer.Note that advertising aims to increase a firm’s profits and so in order to be successful it must increase total revenue by more than it increases total costs. In other words, Option C is a true statement. (Note that costs will increase due to both the cost of the advertising and the cost of producing the additional units sold as a consequence of the advertising.)
The fact that advertising may enable the firm to increase sales and output and thereby increase its ability to exploit economies of scale is one of the possible benefits of advertising. So, Option D is also a true statement.
-
Question 458 of 999CB2031348
Question 458
FlagDespite an increase in the price of admission from $£ 15.00$ to $£ 18.00$, a football club finds that attendance at matches increased by $20 \%$. Which of the following could most effectively explain this situation?
Correct
Answer D:
This is an interesting question relating to both demand and supply and price elasticity.
In the scenario outlined in the question, attendance at football matches has increased despite an increase in admission prices. The likeliest explanation for this is that demand for football matches has increased, presumably due to a change in consumer preferences in favour of football (and at the expense of some other activities). This suggests that Option D is the likely answer.In the unlikely event that the change in attendance was due solely to the change in price, then the price elasticity of demand could be estimated as:
$$
P_{E_D}=\frac{\% \text { change in quantity demanded }}{\% \text { change in price }}=\frac{+20}{(+3 / 15)}=+1
$$This estimated value is:
– positive, as a price increase has resulted in an increase in demand, which is very unusual
– neither ‘high’ nor ‘low’, ruling out Options B and C as possible answers
– an estimate only, as it is calculated assuming that all attendees are charged the same admission price and nothing has changed except for the admission price, which may not be true.Finally, note that if the price of alternative attractions has fallen, then (all else being equal) this would make football less attractive, leading to a fall in the demand for football and hence a fall in attendance. So, Option A is also incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer D:
This is an interesting question relating to both demand and supply and price elasticity.
In the scenario outlined in the question, attendance at football matches has increased despite an increase in admission prices. The likeliest explanation for this is that demand for football matches has increased, presumably due to a change in consumer preferences in favour of football (and at the expense of some other activities). This suggests that Option D is the likely answer.In the unlikely event that the change in attendance was due solely to the change in price, then the price elasticity of demand could be estimated as:
$$
P_{E_D}=\frac{\% \text { change in quantity demanded }}{\% \text { change in price }}=\frac{+20}{(+3 / 15)}=+1
$$This estimated value is:
– positive, as a price increase has resulted in an increase in demand, which is very unusual
– neither ‘high’ nor ‘low’, ruling out Options B and C as possible answers
– an estimate only, as it is calculated assuming that all attendees are charged the same admission price and nothing has changed except for the admission price, which may not be true.Finally, note that if the price of alternative attractions has fallen, then (all else being equal) this would make football less attractive, leading to a fall in the demand for football and hence a fall in attendance. So, Option A is also incorrect.
-
Question 459 of 999CB2031349
Question 459
FlagA firm’s decision to reduce its expenditure on advertising is most likely to have the following impact on its demand curve:
Correct
Answer C:
Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction on expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
Incorrect
Answer C:
Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction on expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
-
Question 460 of 999CB2031350
Question 460
FlagGood X has a cross elasticity of demand with respect to Good Y which is equal to minus unity (ie -1 ). Good $X$ is which of the following with respect to Good $Y$ ?
Correct
Answer: C or D
A cross (price) elasticity of demand for Good $X$ with respect to Good $Y$ of -1 means that a $10 \%$ increase in the price of Good $Y$ will cause a $10 \%$ reduction in demand for Good $X$. The negative relationship tells us that these goods are complements, for example, cars and car insurance.
It is then necessary to consider whether the goods are perfect or imperfect complements. Is it significant that the cross elasticity is equal to minus one?
A perfect complement is a good that has to be consumed with another good. Perfect complements are rare, for example, a right shoe and a left shoe. Supposing that shoes were sold separately, what would be the cross elasticity of demand for a right shoe with respect to the price of a left shoe? If the price of left shoes increased by $10 \%$, what would happen to the demand for left shoes, and hence the demand for right shoes? The answer depends on the price elasticity of demand for left shoes. If, for example, the demand for left shoes fell by $20 \%$, ie the price elasticity of demand is -2 , then, since the goods are perfect complements the demand for right shoes would decline by $20 \%$. Thus the cross elasticity of demand for right shoes with respect to the price of left shoes would, in this case, be -2.
Hence, a cross elasticity of demand of -1 is not significant. It could be a perfect complement or an imperfect complement. Since perfect complements are rare, it is more likely to be an imperfect complement. However, the textbook does not define or distinguish between perfect and imperfect complements and so the examiners accepted both possibilities as being correct.
Note that two identical right shoes would be an example of perfect substitutes.
Incorrect
Answer: C or D
A cross (price) elasticity of demand for Good $X$ with respect to Good $Y$ of -1 means that a $10 \%$ increase in the price of Good $Y$ will cause a $10 \%$ reduction in demand for Good $X$. The negative relationship tells us that these goods are complements, for example, cars and car insurance.
It is then necessary to consider whether the goods are perfect or imperfect complements. Is it significant that the cross elasticity is equal to minus one?
A perfect complement is a good that has to be consumed with another good. Perfect complements are rare, for example, a right shoe and a left shoe. Supposing that shoes were sold separately, what would be the cross elasticity of demand for a right shoe with respect to the price of a left shoe? If the price of left shoes increased by $10 \%$, what would happen to the demand for left shoes, and hence the demand for right shoes? The answer depends on the price elasticity of demand for left shoes. If, for example, the demand for left shoes fell by $20 \%$, ie the price elasticity of demand is -2 , then, since the goods are perfect complements the demand for right shoes would decline by $20 \%$. Thus the cross elasticity of demand for right shoes with respect to the price of left shoes would, in this case, be -2.
Hence, a cross elasticity of demand of -1 is not significant. It could be a perfect complement or an imperfect complement. Since perfect complements are rare, it is more likely to be an imperfect complement. However, the textbook does not define or distinguish between perfect and imperfect complements and so the examiners accepted both possibilities as being correct.
Note that two identical right shoes would be an example of perfect substitutes.
-
Question 461 of 999CB2031351
Question 461
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a ‘crowding out’ effect resulting from a fiscal expansion?
Correct
Answer- D
Crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector. (For example, an increase in government spending on health services might lead to a reduction in spending on private healthcare.)
Financial crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government borrowing (and spending) diverts money away from the private sector. It is argued that this occurs because the consequent rise in interest rates decreases consumption and investment, and might also reduce net exports if the rise in interest rates causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.
A fiscal expansion involves the government increasing its spending and/or decreasing taxation. A fiscal expansion increases aggregate demand and hence increases national income. This increases the demand for money. If there is no increase in the money supply (ie a pure fiscal expansion), then the increase in the demand for money will cause a rise in interest rates.
Whether the money supply increases depends on how the government funds its extra spending:
– if it borrows from the banking sector by issuing short-term treasury bills, the money supply will rise
– if it borrows from the non-bank private sector, the money supply will not increase.Higher interest rates could decrease borrowing (and spending) by firms for investment. This corresponds to Option A, so this cannot be the correct answer.
An increase in interest rates may also result in an appreciation of the domestic currency, making exports more expensive in terms of foreign currency, leading to a fall in the demand for exports. This corresponds to Option C, which consequently cannot be the correct answer.
Interestingly, instead of explicitly referring to an increase in government spending, this question uses the phrase ‘fiscal expansion’, by which it means the use of fiscal policy, eg government spending and/or taxation, to expand the economy. In practice, this could mean an increase in government spending with no change in the level of taxation or an increase in government spending partly funded by a smaller increase in taxation.
Suppose it is the former case, so that although taxes haven’t increased at the moment, it could be that consumers expect taxes to be increased at some point in the near future to fund the increased spending. If this is the case, then the expectation of future higher taxes could lead them to reduce their spending now. Although not strictly in accordance with the definition of crowding out stated above, this effect on expectations is sometimes construed as being an indirect crowding out effect and so Option B is unlikely to be the correct answer.
This is confirmed by considering Option D. If part of the fiscal expansion involves the government deliberately choosing to buy domestically produced goods instead of imported ones, then this will help boost domestic demand and national income and will not have any crowding out impact. This is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer- D
Crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector. (For example, an increase in government spending on health services might lead to a reduction in spending on private healthcare.)
Financial crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government borrowing (and spending) diverts money away from the private sector. It is argued that this occurs because the consequent rise in interest rates decreases consumption and investment, and might also reduce net exports if the rise in interest rates causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.
A fiscal expansion involves the government increasing its spending and/or decreasing taxation. A fiscal expansion increases aggregate demand and hence increases national income. This increases the demand for money. If there is no increase in the money supply (ie a pure fiscal expansion), then the increase in the demand for money will cause a rise in interest rates.
Whether the money supply increases depends on how the government funds its extra spending:
– if it borrows from the banking sector by issuing short-term treasury bills, the money supply will rise
– if it borrows from the non-bank private sector, the money supply will not increase.Higher interest rates could decrease borrowing (and spending) by firms for investment. This corresponds to Option A, so this cannot be the correct answer.
An increase in interest rates may also result in an appreciation of the domestic currency, making exports more expensive in terms of foreign currency, leading to a fall in the demand for exports. This corresponds to Option C, which consequently cannot be the correct answer.
Interestingly, instead of explicitly referring to an increase in government spending, this question uses the phrase ‘fiscal expansion’, by which it means the use of fiscal policy, eg government spending and/or taxation, to expand the economy. In practice, this could mean an increase in government spending with no change in the level of taxation or an increase in government spending partly funded by a smaller increase in taxation.
Suppose it is the former case, so that although taxes haven’t increased at the moment, it could be that consumers expect taxes to be increased at some point in the near future to fund the increased spending. If this is the case, then the expectation of future higher taxes could lead them to reduce their spending now. Although not strictly in accordance with the definition of crowding out stated above, this effect on expectations is sometimes construed as being an indirect crowding out effect and so Option B is unlikely to be the correct answer.
This is confirmed by considering Option D. If part of the fiscal expansion involves the government deliberately choosing to buy domestically produced goods instead of imported ones, then this will help boost domestic demand and national income and will not have any crowding out impact. This is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 462 of 999CB2031352
Question 462
FlagAn increase in the money supply will have a stronger impact on real output the more:
Correct
the correct answer is Option D.
The mechanism is as follows:
1. An increase in the money supply decreases interest rates.
2. A decrease in interest rates increases investment (and consumption and possibly net exports (See Question 22)) and hence aggregate demand and therefore real output (as long as there is excess capacity).The greater the strengths of these links, the greater the impact of an increase in the money supply on real output.
The more inelastic the demand for money curve (ie the steeper that curve), the greater the drop in interest rate for a given increase in money supply. This is illustrated in the diagrams below:
The diagram on the left shows that when the money demand curve is relatively elastic (ie flat), a shift in the money supply curve has little effect on the equilibrium interest rate. The diagram on the right shows that when the money demand curve is relatively inelastic (ie steep), a shift in the money supply curve will have a large effect on the equilibrium interest rate. This rules out Options A and C.
How much investment increases in response to the fall in interest rates depends on the elasticity of demand for investment with respect to interest rates. The more interestelastic the demand for investment, the greater the increase in investment in response to the fall in interest rates. This rules out Options B and C and so the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
the correct answer is Option D.
The mechanism is as follows:
1. An increase in the money supply decreases interest rates.
2. A decrease in interest rates increases investment (and consumption and possibly net exports (See Question 22)) and hence aggregate demand and therefore real output (as long as there is excess capacity).The greater the strengths of these links, the greater the impact of an increase in the money supply on real output.
The more inelastic the demand for money curve (ie the steeper that curve), the greater the drop in interest rate for a given increase in money supply. This is illustrated in the diagrams below:

The diagram on the left shows that when the money demand curve is relatively elastic (ie flat), a shift in the money supply curve has little effect on the equilibrium interest rate. The diagram on the right shows that when the money demand curve is relatively inelastic (ie steep), a shift in the money supply curve will have a large effect on the equilibrium interest rate. This rules out Options A and C.
How much investment increases in response to the fall in interest rates depends on the elasticity of demand for investment with respect to interest rates. The more interestelastic the demand for investment, the greater the increase in investment in response to the fall in interest rates. This rules out Options B and C and so the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 463 of 999CB2031353
Question 463
FlagIf both government spending and the money supply are increased, and the economy has a high degree of unemployment, then:
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
All else being equal, and assuming there is spare capacity in the economy, increased government spending will lead to a multiplied increase in national income. Likewise, an increase in the money supply will tend to lead to more borrowing by households and firms to fund increased consumption and investment spending, which will also result in an increase in national income. Hence, as both policies will lead to an increase in national income, this rules out Options B and C.
Turning to the effect on interest rates, the increased demand for money resulting from a higher level of national income will tend to lead to a rise in interest rates. However, an increase in the money supply will tend to result in a fall in interest rates. Consequently, the overall effect on interest rates will be uncertain, which means that Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
All else being equal, and assuming there is spare capacity in the economy, increased government spending will lead to a multiplied increase in national income. Likewise, an increase in the money supply will tend to lead to more borrowing by households and firms to fund increased consumption and investment spending, which will also result in an increase in national income. Hence, as both policies will lead to an increase in national income, this rules out Options B and C.
Turning to the effect on interest rates, the increased demand for money resulting from a higher level of national income will tend to lead to a rise in interest rates. However, an increase in the money supply will tend to result in a fall in interest rates. Consequently, the overall effect on interest rates will be uncertain, which means that Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 464 of 999CB2031354
Question 464
FlagThe ‘crowding out’ effect associated with an increase in government borrowing could be reduced or eliminated by an accommodating increase in:
Correct
Option C is the correct answer
The scenario described in the question is consistent with the definition of financial crowding out, as provided in the solution to Question 14.
The way to avoid financial crowding out is to offset the increase in interest rates by increasing the money supply, and so Option C is the correct answer.
An increase in government expenditure (Option A) will lead to further crowding out, as described in the solution to Question 14. An increase in taxation (Option B) will reduce consumers’ disposable income, which will lead them to cut back their consumption. Again, this is likely to reinforce (rather than reduce) any crowding out.
Incorrect
Option C is the correct answer
The scenario described in the question is consistent with the definition of financial crowding out, as provided in the solution to Question 14.
The way to avoid financial crowding out is to offset the increase in interest rates by increasing the money supply, and so Option C is the correct answer.
An increase in government expenditure (Option A) will lead to further crowding out, as described in the solution to Question 14. An increase in taxation (Option B) will reduce consumers’ disposable income, which will lead them to cut back their consumption. Again, this is likely to reinforce (rather than reduce) any crowding out.
-
Question 465 of 999CB2031355
Question 465
FlagIf a household’s income increases from $£ 20,000$ to $£ 25,000$ and, as a result, consumption increases from $£ 17,000$ to $£ 21,000$, what is the household’s marginal propensity to save?
Correct
Answer : C or D
C or D Using the relationship $Y=T+C+S$, when household income goes up it is either saved, taxed or spent on consumption. If income goes up by $£ 5,000$ and consumption goes up by $£ 4,000$ then the amount saved or taxed must go up by $£ 1,000$. The marginal propensity to save plus the marginal rate of tax is then:
$$
m p s+m p t=1000 / 5000=0.2
$$If marginal income tax is zero then $m p s$ equals 0.2 . If marginal income tax is non-zero then $m p s$ is less than 0.2 .
Incorrect
Answer : C or D
C or D Using the relationship $Y=T+C+S$, when household income goes up it is either saved, taxed or spent on consumption. If income goes up by $£ 5,000$ and consumption goes up by $£ 4,000$ then the amount saved or taxed must go up by $£ 1,000$. The marginal propensity to save plus the marginal rate of tax is then:
$$
m p s+m p t=1000 / 5000=0.2
$$If marginal income tax is zero then $m p s$ equals 0.2 . If marginal income tax is non-zero then $m p s$ is less than 0.2 .
-
Question 466 of 999CB2031356
Question 466
FlagOther things remaining the same, in a closed economy, the effect of a cut in government expenditure is to:
Correct
Answer : A
Government expenditure is a component of aggregate demand. A cut will therefore reduce aggregate demand (ie shift the aggregate demand curve to the left in the AD-AS model).
When output falls, so does the demand for money due to the transactions and precautionary motives, pushing the money demand curve inwards. This pushes down the short-term rate of interest.
Incorrect
Answer : A
Government expenditure is a component of aggregate demand. A cut will therefore reduce aggregate demand (ie shift the aggregate demand curve to the left in the AD-AS model).
When output falls, so does the demand for money due to the transactions and precautionary motives, pushing the money demand curve inwards. This pushes down the short-term rate of interest.
-
Question 467 of 999CB2031357
Question 467
FlagThe government of Country A announces two new macroeconomic plans:
1. The central bank will increase its purchases of Country A’s government securities.
2. It is going to increase taxes for every income bracket in Country A.Which macroeconomic policies relate to these two new plans?
Correct
Option C is the correct answer.
The purchase of Country A’s government securities by the central bank will lead to an increase in the money supply (as the central bank pays money in return for the securities). This is part of an expansionary monetary policy, which rules out Options A and D.
Increasing taxes is part of a contractionary fiscal policy, which rules out Options A and B. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option C is the correct answer.
The purchase of Country A’s government securities by the central bank will lead to an increase in the money supply (as the central bank pays money in return for the securities). This is part of an expansionary monetary policy, which rules out Options A and D.
Increasing taxes is part of a contractionary fiscal policy, which rules out Options A and B. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 468 of 999CB2031358
Question 468
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a crowding out effect after an increase in government expenditure financed by increased government borrowing?
Correct
Answer-C
Crowding out in general occurs when government spending diverts resources away from the private sector. Financial crowding out is an important example of this when increased government borrowing pushes up interest rates, reducing private sector investment. This is the opposite of Option C, which must therefore be the correct answer.
An increase in interest rates will also lead to an exchange rate appreciation through the exchange rate transmission mechanism, making exports uncompetitive. So in an open economy with floating exchange rates, an expansionary fiscal policy will be crowded out not only by higher interest rates, but also by a higher exchange rate. Thus Options A and D are true.
Option B is an indirect crowding out effect. Consumers might anticipate tax rises to fund the increased government spending or borrowing, which will further divert financial resources away from the private sector.
Incorrect
Answer-C
Crowding out in general occurs when government spending diverts resources away from the private sector. Financial crowding out is an important example of this when increased government borrowing pushes up interest rates, reducing private sector investment. This is the opposite of Option C, which must therefore be the correct answer.
An increase in interest rates will also lead to an exchange rate appreciation through the exchange rate transmission mechanism, making exports uncompetitive. So in an open economy with floating exchange rates, an expansionary fiscal policy will be crowded out not only by higher interest rates, but also by a higher exchange rate. Thus Options A and D are true.
Option B is an indirect crowding out effect. Consumers might anticipate tax rises to fund the increased government spending or borrowing, which will further divert financial resources away from the private sector.
-
Question 469 of 999CB2031359
Question 469
FlagA tightening of monetary policy with a flexible exchange rate and an open economy for a country will tend to lead to:
Correct
Answer- C
A tightening of monetary policy (also known as a restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy) involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. This is shown on the diagram below:
Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for the domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
Incorrect
Answer- C
A tightening of monetary policy (also known as a restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy) involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. This is shown on the diagram below:

Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for the domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
-
Question 470 of 999CB2031360
Question 470
FlagThe US has been running a large current account deficit, and China has a large current account surplus. If their exchange rates were both flexible, how would such imbalances be eliminated?
Correct
the correct answer is Option D.
A large current account deficit means that the US has been buying more imports than it has been selling exports to other countries. This means that US firms and households have been selling more US dollars to obtain overseas currency to buy imports, than their counterparts in other countries have been selling their currencies in order to obtain US dollars to buy US exports. The excess supply of US dollars means that the US dollar is likely to depreciate in value.
For example, on the diagram below, the excess supply of dollars when each dollar is worth 60p, would result in a fall in the value of the dollar to a new and lower equilibrium value of 50p.
Likewise, a large current account surplus means that China has been buying fewer imports than it has been selling exports to other countries. This means that it has been selling fewer Chinese renminbi to obtain overseas currency to buy imports, than other countries have been selling their currencies in order to obtain Chinese renminbi to buy Chinese exports. The excess demand for Chinese renminbi means that the Chinese renminbi is likely to appreciate in value.
Answer: D
Incorrect
the correct answer is Option D.
A large current account deficit means that the US has been buying more imports than it has been selling exports to other countries. This means that US firms and households have been selling more US dollars to obtain overseas currency to buy imports, than their counterparts in other countries have been selling their currencies in order to obtain US dollars to buy US exports. The excess supply of US dollars means that the US dollar is likely to depreciate in value.
For example, on the diagram below, the excess supply of dollars when each dollar is worth 60p, would result in a fall in the value of the dollar to a new and lower equilibrium value of 50p.

Likewise, a large current account surplus means that China has been buying fewer imports than it has been selling exports to other countries. This means that it has been selling fewer Chinese renminbi to obtain overseas currency to buy imports, than other countries have been selling their currencies in order to obtain Chinese renminbi to buy Chinese exports. The excess demand for Chinese renminbi means that the Chinese renminbi is likely to appreciate in value.
Answer: D
-
Question 471 of 999CB2031361
Question 471
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a characteristic of an inferior good?
Correct
Answer: B
An inferior good is one for which demand falls as income rises, ie a good for which the income elasticity of demand is negative.
Options A and C are clearly true. Since Option A is true, Option B cannot be true, so Option B is false and is therefore the correct answer.
Option D is simply saying that inferior goods have downward-sloping demand curves, which is usually (though not always) true.
Incorrect
Answer: B
An inferior good is one for which demand falls as income rises, ie a good for which the income elasticity of demand is negative.
Options A and C are clearly true. Since Option A is true, Option B cannot be true, so Option B is false and is therefore the correct answer.
Option D is simply saying that inferior goods have downward-sloping demand curves, which is usually (though not always) true.
-
Question 472 of 999CB2031362
Question 472
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a motive for advertising by an existing firm in an industry?
Correct
Answer: A
Advertising of a product is intended to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right, by bringing the product to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of consuming the product. This means that Option B is a true statement and hence not the correct answer.
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (more price inelastic), by creating brand loyalty, and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand. This means that the statement in Option A is false and so is the correct answer.Note that advertising can act as a barrier to entry since it can increase brand loyalty and therefore make it more difficult for new firms to compete. So Option C is a true statement.
The fact that advertising may enable the firm to increase sales and output and thereby increase its ability to exploit economies of scale is one of the possible benefits of advertising. So, Option D is also a true statement.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Advertising of a product is intended to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right, by bringing the product to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of consuming the product. This means that Option B is a true statement and hence not the correct answer.
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (more price inelastic), by creating brand loyalty, and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand. This means that the statement in Option A is false and so is the correct answer.Note that advertising can act as a barrier to entry since it can increase brand loyalty and therefore make it more difficult for new firms to compete. So Option C is a true statement.
The fact that advertising may enable the firm to increase sales and output and thereby increase its ability to exploit economies of scale is one of the possible benefits of advertising. So, Option D is also a true statement.
-
Question 473 of 999CB2031363
Question 473
FlagWhich one of the following results in a decrease in total consumer expenditure?
Correct
Answer C :Total revenue is the product of price (or average revenue) and quantity.
Price elasticity of demand describes the effect on quantity of a change in price. Demand is said to be price-elastic if a change in price leads to a more-than-proportionate change in quantity. Conversely, demand is said to be price-inelastic if a change in price leads to a less-than proportionate change in quantity.Total revenue will fall if there is a fall in price and this results in a less-than-proportionate rise in quantity (or if there is a rise in price and a more-than-proportionate fall in quantity). In other words, total revenue will fall if demand is price-inelastic and price falls (or if demand is price-elastic and price rises). This corresponds to Option C, which is therefore the correct answer.
Alternatively, the question can be answered by drawing two diagrams as follows:
– the top diagram shows the average revenue (AR) and marginal revenue (MR) curves and indicates where demand is elastic, inelastic and has unit elasticity ( -1 )
– the bottom diagram, which also has quantity on the $x$-axis, shows how total revenue varies with quantity.Where demand is elastic (in the left half of the diagram), a fall in price will lead to a rightward movement along the curves, and hence a rise in total revenue, so Option B is incorrect. Where demand is inelastic (in the right half of the diagram), a fall in price will lead to a rightward movement along the curves, and hence a fall in total revenue.
Total revenue is maximised where price elasticity of demand is equal to minus one, which occurs where MR is zero, ie exactly halfway along the demand curve. Note that when demand has unit elasticity, a fall in price will lead to a proportionate increase in quantity and so no change in total revenue, so Option A is incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer C :Total revenue is the product of price (or average revenue) and quantity.
Price elasticity of demand describes the effect on quantity of a change in price. Demand is said to be price-elastic if a change in price leads to a more-than-proportionate change in quantity. Conversely, demand is said to be price-inelastic if a change in price leads to a less-than proportionate change in quantity.Total revenue will fall if there is a fall in price and this results in a less-than-proportionate rise in quantity (or if there is a rise in price and a more-than-proportionate fall in quantity). In other words, total revenue will fall if demand is price-inelastic and price falls (or if demand is price-elastic and price rises). This corresponds to Option C, which is therefore the correct answer.
Alternatively, the question can be answered by drawing two diagrams as follows:
– the top diagram shows the average revenue (AR) and marginal revenue (MR) curves and indicates where demand is elastic, inelastic and has unit elasticity ( -1 )
– the bottom diagram, which also has quantity on the $x$-axis, shows how total revenue varies with quantity.Where demand is elastic (in the left half of the diagram), a fall in price will lead to a rightward movement along the curves, and hence a rise in total revenue, so Option B is incorrect. Where demand is inelastic (in the right half of the diagram), a fall in price will lead to a rightward movement along the curves, and hence a fall in total revenue.
Total revenue is maximised where price elasticity of demand is equal to minus one, which occurs where MR is zero, ie exactly halfway along the demand curve. Note that when demand has unit elasticity, a fall in price will lead to a proportionate increase in quantity and so no change in total revenue, so Option A is incorrect.
-
Question 474 of 999CB2031364
Question 474
FlagGood X has a price elasticity of demand equal to -1.5 . In such circumstances, a per unit sales tax on Good X of £5 will lead to which of the following?
Correct
Answer D : A sales tax can be represented by an upward shift in the supply curve. In this case, it is a per unit sales tax of $£ 5$, so the supply curve will shift vertically upwards by $£ 5$. (It might help to think of the tax as effectively increasing the production costs of the firm, which will therefore want to charge a higher price than before the tax was imposed to cover the tax payable.)
Such a tax usually increases the price paid by consumers, decreases the net income of suppliers and decreases the equilibrium quantity traded.
If the demand curve is vertical, ie demand is perfectly inelastic, the full amount of the tax would be passed to the consumer and so the price rise would also be $£ 5$. However, in this case the demand curve is downward-sloping and so the price rise will be less than $£ 5$, hence Option D is the correct answer.
Note that the supply curve must also be assumed not to be horizontal: if a horizontal supply curve shifts upwards, this would also lead to a price increase of $£ 5$ (Option C).
Incorrect
Answer D : A sales tax can be represented by an upward shift in the supply curve. In this case, it is a per unit sales tax of $£ 5$, so the supply curve will shift vertically upwards by $£ 5$. (It might help to think of the tax as effectively increasing the production costs of the firm, which will therefore want to charge a higher price than before the tax was imposed to cover the tax payable.)
Such a tax usually increases the price paid by consumers, decreases the net income of suppliers and decreases the equilibrium quantity traded.
If the demand curve is vertical, ie demand is perfectly inelastic, the full amount of the tax would be passed to the consumer and so the price rise would also be $£ 5$. However, in this case the demand curve is downward-sloping and so the price rise will be less than $£ 5$, hence Option D is the correct answer.
Note that the supply curve must also be assumed not to be horizontal: if a horizontal supply curve shifts upwards, this would also lead to a price increase of $£ 5$ (Option C).
-
Question 475 of 999CB2031365
Question 475
FlagGood $Y$ has a cross elasticity of demand with respect to Good $X$ calculated using the average method of -1 . Initially 100 units of Good $Y$ are demanded when Good $X$ costs 20 pence. A rise in the price of Good $X$ to 25 pence will result in a new level of demand for Good $Y$ of:
Correct
Answer C: Cross-price elasticity of demand calculated using the average method is given by:
$$
C \varepsilon_{D_{Y X}}=\frac{\% \Delta \text { in quantity demanded of Good } \mathrm{Y}}{\% \Delta \text { in price of Good } \mathrm{X}}=\frac{\Delta Q_Y / \text { average } \mathrm{Q}_Y}{\Delta P_X / \text { average } \mathrm{P}_X}
$$
and the question states that the value of this is -1 .
Using the other figures gives:
$$
c_{\delta_{D_{1 x}}}=\frac{\left(\text { New } Q_y-100\right) /\left(100+\text { New } Q_y\right) / 2}{(25-20) /(20+25) / 2}=-1
$$So:
$$
\frac{\left(\text { New } Q_\gamma-100\right)}{\left(100+\text { New } Q_\gamma\right) / 2}=-\frac{2}{9}
$$Substituting in the different options gives Option C as the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: Cross-price elasticity of demand calculated using the average method is given by:
$$
C \varepsilon_{D_{Y X}}=\frac{\% \Delta \text { in quantity demanded of Good } \mathrm{Y}}{\% \Delta \text { in price of Good } \mathrm{X}}=\frac{\Delta Q_Y / \text { average } \mathrm{Q}_Y}{\Delta P_X / \text { average } \mathrm{P}_X}
$$
and the question states that the value of this is -1 .
Using the other figures gives:
$$
c_{\delta_{D_{1 x}}}=\frac{\left(\text { New } Q_y-100\right) /\left(100+\text { New } Q_y\right) / 2}{(25-20) /(20+25) / 2}=-1
$$So:
$$
\frac{\left(\text { New } Q_\gamma-100\right)}{\left(100+\text { New } Q_\gamma\right) / 2}=-\frac{2}{9}
$$Substituting in the different options gives Option C as the correct answer.
-
Question 476 of 999CB2031366
Question 476
FlagA firm’s decision to reduce its expenditure on advertising is most likely to have the following impact on its demand curve:
Correct
Answer C:
Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction in expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C:
Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction in expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.
-
Question 477 of 999CB2031367
Question 477
FlagThe total revenue from the sale of a good will fall if:
Correct
Answer A :Total revenue (TR) is the total amount received from the sale of products. If the firm sells its product at a constant price $(\mathrm{P})$, then $T R=P \times Q$, where $Q$ is quantity sold.
The following diagrams show the effect of a price rise on quantity demanded when demand is price-elastic and price-inelastic:
The left-hand diagram shows that if demand is relatively elastic, an increase in price causes a more than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will fall. The right-hand diagram shows that if demand is relatively inelastic, an increase in price causes a less than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will rise. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
For an inferior good, a decrease in income would cause an increase in demand and hence an increase in total revenue. Similarly, for a normal good, an increase in income would cause an increase in demand and hence an increase in total revenue. Options C and D and therefore both incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer A :Total revenue (TR) is the total amount received from the sale of products. If the firm sells its product at a constant price $(\mathrm{P})$, then $T R=P \times Q$, where $Q$ is quantity sold.
The following diagrams show the effect of a price rise on quantity demanded when demand is price-elastic and price-inelastic:
The left-hand diagram shows that if demand is relatively elastic, an increase in price causes a more than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will fall. The right-hand diagram shows that if demand is relatively inelastic, an increase in price causes a less than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will rise. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
For an inferior good, a decrease in income would cause an increase in demand and hence an increase in total revenue. Similarly, for a normal good, an increase in income would cause an increase in demand and hence an increase in total revenue. Options C and D and therefore both incorrect.
-
Question 478 of 999CB2031368
Question 478
FlagA firm’s decision to reduce its expenditure on advertising is most likely to have the following impact on its demand curve:
Correct
Answer C :Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).This is illustrated in the diagram below:
The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction in expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C :Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).This is illustrated in the diagram below:
The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction in expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.
-
Question 479 of 999CB2031369
Question 479
FlagFollowing an increase in the price of fuel, there is a 20% increase in the price of air travel tickets that results in a 20% decrease in total revenue. Which of the following statements is TRUE about the demand for air travel?
Correct
Answer B:
There has been a 20% increase in the price of air travel and a 20% decrease in total revenue. Total revenue is the product of price and quantity, so since total revenue has fallen (irrespective of the extent of the fall), this means that the increase in price has led to a more than proportionate fall in quantity demanded. This means that demand is elastic, and hence rules out Options A and D.
Infinite price elasticity means that quantity demanded will decrease to zero when price increases. At zero quantity, revenue would also be zero, and hence the decrease in revenue would be $100 \%$. This rules out Option C, and so Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B:
There has been a 20% increase in the price of air travel and a 20% decrease in total revenue. Total revenue is the product of price and quantity, so since total revenue has fallen (irrespective of the extent of the fall), this means that the increase in price has led to a more than proportionate fall in quantity demanded. This means that demand is elastic, and hence rules out Options A and D.
Infinite price elasticity means that quantity demanded will decrease to zero when price increases. At zero quantity, revenue would also be zero, and hence the decrease in revenue would be $100 \%$. This rules out Option C, and so Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 480 of 999CB2031370
Question 480
FlagThe demand for Good $X$ has a price elasticity of -3 while the supply curve has a positive slope. If the government decided to impose a tax of $£ 10$ per unit on Good $X$, this would shift the supply curve for Good X up by:
Correct
Answer D :A demand curve with a negative price elasticity is downward-sloping.
A tax of $£ 10$ per unit on Good $X$ would shift the supply curve upwards by $£ 10$, thus ruling out Options A and B. This is illustrated on the diagram below, which shows that the price would increase from P1 to P2.The diagram shows that this increase in price is less than $£ 10$, thus ruling out Option B and
C. Hence the correct answer is Option D.Incorrect
Answer D :A demand curve with a negative price elasticity is downward-sloping.
A tax of $£ 10$ per unit on Good $X$ would shift the supply curve upwards by $£ 10$, thus ruling out Options A and B. This is illustrated on the diagram below, which shows that the price would increase from P1 to P2.The diagram shows that this increase in price is less than $£ 10$, thus ruling out Option B and
C. Hence the correct answer is Option D. -
Question 481 of 999CB2031371
Question 481
FlagIf an $8 \%$ rise in the price of Good $X$ results in a $4 \%$ fall in the quantity demanded of Good $Y$, then the cross elasticity of demand for Good Y is approximately:
Correct
Answer B: Cross-price elasticity of demand is calculated as:
$$
C \varepsilon_{D_{x y}}=\frac{\% \Delta Q_{D_y}}{\% \Delta P_x}
$$
where $\% \Delta Q_{D_y}$, is the percentage change in the quantity demanded of Good Y and $\% \Delta P_X$ is the percentage change in the price of Good X.In this case, $\% \Delta Q_{D_\gamma}=-4 \%$ and $\% \Delta P_x=8 \%$, so:
$$
{ }^{\mathrm{C}} \varepsilon_{\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{kr}}}=\frac{-4 \%}{8 \%}=-0.5
$$This rules out Options A and C.
To determine whether two goods are complements or substitutes, it is necessary to look at the sign of the cross-price elasticity of demand. Here it is negative, and this implies the goods are complements: as the price of one good increases (and hence the quantity demanded of that good decreases), the quantity demanded of the other good (also) decreases.
The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Incorrect
Answer B: Cross-price elasticity of demand is calculated as:
$$
C \varepsilon_{D_{x y}}=\frac{\% \Delta Q_{D_y}}{\% \Delta P_x}
$$
where $\% \Delta Q_{D_y}$, is the percentage change in the quantity demanded of Good Y and $\% \Delta P_X$ is the percentage change in the price of Good X.In this case, $\% \Delta Q_{D_\gamma}=-4 \%$ and $\% \Delta P_x=8 \%$, so:
$$
{ }^{\mathrm{C}} \varepsilon_{\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{kr}}}=\frac{-4 \%}{8 \%}=-0.5
$$This rules out Options A and C.
To determine whether two goods are complements or substitutes, it is necessary to look at the sign of the cross-price elasticity of demand. Here it is negative, and this implies the goods are complements: as the price of one good increases (and hence the quantity demanded of that good decreases), the quantity demanded of the other good (also) decreases.
The correct answer is therefore Option B.
-
Question 482 of 999CB2031372
Question 482
FlagA firm’s decision to reduce its expenditure on advertising is most likely to have the following impact on its demand curve:
Correct
Answer C:
Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction in expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C:
Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right (by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product)
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand).The key thing to note is that this question has asked for the impact on the demand curve following a reduction in expenditure on advertising. A reduction in expenditure on advertising is likely to have opposite effects to those described above.
The correct answer is therefore Option C.
-
Question 483 of 999CB2031373
Question 483
FlagGood X has a price elasticity of demand of -1 . Which of the following statements is TRUE, following the removal of a $£ 10$ per unit sales tax on Good $X$ ?
Correct
Answer C: A negative price elasticity of demand reveals that the demand curve slopes downwards.
The removal of a $£ 10$ per unit sales tax reduces firm’s costs by $£ 10$ per unit and so causes the supply curve to shift down by $£ 10$.The following diagram shows that the price will fall from $P_1$ to $P_2$, ie by a smaller amount than the vertical distance $A B$, which reflects the size of the sales tax ( $£ 10$ ):
Incorrect
Answer C: A negative price elasticity of demand reveals that the demand curve slopes downwards.
The removal of a $£ 10$ per unit sales tax reduces firm’s costs by $£ 10$ per unit and so causes the supply curve to shift down by $£ 10$.The following diagram shows that the price will fall from $P_1$ to $P_2$, ie by a smaller amount than the vertical distance $A B$, which reflects the size of the sales tax ( $£ 10$ ):
-
Question 484 of 999CB2031374
Question 484
FlagIf the income elasticity of demand for Good X is 2, a rise in all consumers’ disposable incomes from $£ 50$ million to $£ 52$ million will increase the quantity demanded of Good $X$ by:
Correct
Answer D: Income elasticity of demand is defined as:
$$
Y_{\varepsilon_D}=\frac{\% \Delta Q_d}{\% \Delta Y}
$$Since $Y_{\delta_D}=2$, the percentage change in quantity demanded must be twice the percentage change in income. Here, the percentage increase in income is $4 \%$ and so the quantity demanded must increase by $8 \%$. Option D is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D: Income elasticity of demand is defined as:
$$
Y_{\varepsilon_D}=\frac{\% \Delta Q_d}{\% \Delta Y}
$$Since $Y_{\delta_D}=2$, the percentage change in quantity demanded must be twice the percentage change in income. Here, the percentage increase in income is $4 \%$ and so the quantity demanded must increase by $8 \%$. Option D is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 485 of 999CB2031375
Question 485
FlagIf a resident of a country purchases a foreign company’s shares, the value of the transaction is entered in which of the domestic country’s balance of payments accounts?
Correct
Answer: D
Recall that:
– The trade account records cashflows in respect of trade in goods and services, which rules out Option A.
– The current account includes the trade account, plus net income flows from abroad and net current transfers, which rules out Option B.
– The capital account records net capital transfers (such as the transfer of ownership of long-term assets and money brought into the country by migrants) and also cashflows in respect of the trade in non-produced, non-financial assets such as patents, copyrights, trademarks and franchises. Neither of these include purchases of financial assets such as shares. So, Option C is also incorrect.– The financial account records cashflows associated with investments, both direct investment (eg the purchase of a factory abroad) and portfolio investment (eg the purchase of government bonds or shares by an overseas investor); other financial flows (mainly short-term movements in bank and other deposits); and flows to and from the reserves (ie the central bank’s purchase of sale of foreign currency). So, the purchase of a foreign company’s shares by a domestic resident would be recorded in that country’s financial account. So, Option D is correct.
Note that as the money to pay for the shares leaves the domestic economy, the monetary value of the transaction is recorded as a negative entry in the financial account.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Recall that:
– The trade account records cashflows in respect of trade in goods and services, which rules out Option A.
– The current account includes the trade account, plus net income flows from abroad and net current transfers, which rules out Option B.
– The capital account records net capital transfers (such as the transfer of ownership of long-term assets and money brought into the country by migrants) and also cashflows in respect of the trade in non-produced, non-financial assets such as patents, copyrights, trademarks and franchises. Neither of these include purchases of financial assets such as shares. So, Option C is also incorrect.– The financial account records cashflows associated with investments, both direct investment (eg the purchase of a factory abroad) and portfolio investment (eg the purchase of government bonds or shares by an overseas investor); other financial flows (mainly short-term movements in bank and other deposits); and flows to and from the reserves (ie the central bank’s purchase of sale of foreign currency). So, the purchase of a foreign company’s shares by a domestic resident would be recorded in that country’s financial account. So, Option D is correct.
Note that as the money to pay for the shares leaves the domestic economy, the monetary value of the transaction is recorded as a negative entry in the financial account.
-
Question 486 of 999CB2031376
Question 486
FlagAll other things being equal, which of the following events would cause the value of Country A’s currency to appreciate against the value of Country B’s currency?
Correct
Answer: A
One factor that might cause this to be the case is a change in the relative interest rates of the two countries. More specifically, if A’s interest increases relative to B’s, it will now be more attractive to hold cash in Country A than County B, in order to obtain the now higher relative interest rate. This will lead to an increase in the supply of B’s currency on the foreign exchange markets and a corresponding increase in the demand for A’s currency, which will in turn lead A’s currency to appreciate against the value of B’s currency.
This would be the case, for example, if:
– the interest rate in $A$ increases more than the interest rate in $B$.
– the interest rate in $A$ increases, whilst the interest rate in $B$ remains the same.
– the interest rate in $A$ falls by less than the interest rate in $B$.This latter scenario corresponds to Option A, which is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
One factor that might cause this to be the case is a change in the relative interest rates of the two countries. More specifically, if A’s interest increases relative to B’s, it will now be more attractive to hold cash in Country A than County B, in order to obtain the now higher relative interest rate. This will lead to an increase in the supply of B’s currency on the foreign exchange markets and a corresponding increase in the demand for A’s currency, which will in turn lead A’s currency to appreciate against the value of B’s currency.
This would be the case, for example, if:
– the interest rate in $A$ increases more than the interest rate in $B$.
– the interest rate in $A$ increases, whilst the interest rate in $B$ remains the same.
– the interest rate in $A$ falls by less than the interest rate in $B$.This latter scenario corresponds to Option A, which is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 487 of 999CB2031377
Question 487
FlagWhich of the following items will be recorded as a plus in the balance of payments accounts?
Correct
Answer – B
Inflows of the domestic currency are recorded as positive flows (or ‘pluses’) and outflows of the domestic currency are recorded as negative flows (or ‘minuses’) in the balance of payments accounts.
Lending by domestic banks to foreign citizens (Option A) involves the domestic currency flowing out of the country, so will be recorded as a minus.
A fall in the country’s holding of foreign exchange reserves (Option B) will involve the central bank exchanging its foreign exchange reserves for the domestic currency, ie foreign exchange reserves will flow out of the country and the domestic currency will flow into the country, so this will be recorded as a plus.
Outward foreign direct investment (Option C) involves domestic citizens investing their funds in businesses overseas, ie domestic currency will flow out of the country, so this will be recorded as minuses.
Import expenditure (Option D) involves domestic citizens and firms paying money to firms overseas (in return for goods and services), so domestic currency will flow out of the country, and this will be recorded as a minus.
Incorrect
Answer – B
Inflows of the domestic currency are recorded as positive flows (or ‘pluses’) and outflows of the domestic currency are recorded as negative flows (or ‘minuses’) in the balance of payments accounts.
Lending by domestic banks to foreign citizens (Option A) involves the domestic currency flowing out of the country, so will be recorded as a minus.
A fall in the country’s holding of foreign exchange reserves (Option B) will involve the central bank exchanging its foreign exchange reserves for the domestic currency, ie foreign exchange reserves will flow out of the country and the domestic currency will flow into the country, so this will be recorded as a plus.
Outward foreign direct investment (Option C) involves domestic citizens investing their funds in businesses overseas, ie domestic currency will flow out of the country, so this will be recorded as minuses.
Import expenditure (Option D) involves domestic citizens and firms paying money to firms overseas (in return for goods and services), so domestic currency will flow out of the country, and this will be recorded as a minus.
-
Question 488 of 999CB2031378
Question 488
FlagCapital adequacy for banks is a measure of a bank’s:
Correct
The capital adequacy ratio is the ratio of a bank’s capital (reserves and shares) to its risk-weighted assets.
Option D is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
The capital adequacy ratio is the ratio of a bank’s capital (reserves and shares) to its risk-weighted assets.
Option D is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 489 of 999CB2031379
Question 489
FlagWhich of the following is NOT considered to be a function of money?
Correct
Option B is the correct answer
The functions of money are:
– a medium of exchange
– a means of storing wealth
– a means of evaluation
– a means of establishing the value of future claims and payments.Therefore, the functions of money include a unit of account, ie a means of evaluation (Option A), a store of value, ie wealth (Option C) and a medium of exchange (Option D).
Money is a liquid asset, however this is a feature of it, rather than a function. Furthermore, it is not a measure of liquidity. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option B is the correct answer
The functions of money are:
– a medium of exchange
– a means of storing wealth
– a means of evaluation
– a means of establishing the value of future claims and payments.Therefore, the functions of money include a unit of account, ie a means of evaluation (Option A), a store of value, ie wealth (Option C) and a medium of exchange (Option D).
Money is a liquid asset, however this is a feature of it, rather than a function. Furthermore, it is not a measure of liquidity. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 490 of 999CB2031380
Question 490
FlagGood Y has a cross elasticity of demand with respect to Good X of 0.8 , and 200 units of Good $Y$ are demanded when Good X costs £1. A rise in the price of Good X to £ 1.10 will change the demand for Good Y to approximately:
Correct
Here, $P_X=£ 1, Q D_Y=200$ and $C \varepsilon_{D_{Y x}}=0.8$, and the question has asked what will happen to $Q D_Y$ if $P_X$ increases to $£ 1.10$.
Using the average method:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& C \varepsilon_{D_{r X}}=\frac{\% \Delta Q D_Y}{\% \Delta P_X}=\frac{\Delta Q D_Y / \text { Average } Q D_Y}{\Delta P_X / \text { Average } P_X} \\
& \Rightarrow \frac{\left(\text { New } Q D_Y-200\right) / 0.5\left(200+\text { New } Q D_Y\right)}{(1.10-1.00) / 1.05}=0.8 \\
& \Rightarrow\left(\text { New } Q D_Y-200\right) / 0.5\left(200+\text { New } Q D_Y\right)=0.0762 \\
& \Rightarrow\left(\text { New } Q D_Y-200\right)=7.62+0.0381 \times \text { New } Q D_Y \\
& \Rightarrow 0.9619 \times \text { New } Q D_Y=207.62 \\
& \Rightarrow \text { New } Q D_Y=215.84
\end{aligned}
$$So New $Q D_Y$ is approximately equal to 216 , hence Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Here, $P_X=£ 1, Q D_Y=200$ and $C \varepsilon_{D_{Y x}}=0.8$, and the question has asked what will happen to $Q D_Y$ if $P_X$ increases to $£ 1.10$.
Using the average method:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& C \varepsilon_{D_{r X}}=\frac{\% \Delta Q D_Y}{\% \Delta P_X}=\frac{\Delta Q D_Y / \text { Average } Q D_Y}{\Delta P_X / \text { Average } P_X} \\
& \Rightarrow \frac{\left(\text { New } Q D_Y-200\right) / 0.5\left(200+\text { New } Q D_Y\right)}{(1.10-1.00) / 1.05}=0.8 \\
& \Rightarrow\left(\text { New } Q D_Y-200\right) / 0.5\left(200+\text { New } Q D_Y\right)=0.0762 \\
& \Rightarrow\left(\text { New } Q D_Y-200\right)=7.62+0.0381 \times \text { New } Q D_Y \\
& \Rightarrow 0.9619 \times \text { New } Q D_Y=207.62 \\
& \Rightarrow \text { New } Q D_Y=215.84
\end{aligned}
$$So New $Q D_Y$ is approximately equal to 216 , hence Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 491 of 999CB2031381
Question 491
FlagA significant increase in income is least likely to increase the demand for which of the following?
Correct
Answer A :An increase in income (significant or otherwise) is least likely to increase demand for goods that are income-inelastic, ie a change in income has a small effect on quantity demanded.
Demand for luxury goods increases more than proportionately with income, so the more luxurious a good, the less likely it is to be the correct answer here.
Out of the options, fizzy drinks are likely to be the least luxurious, so Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A :An increase in income (significant or otherwise) is least likely to increase demand for goods that are income-inelastic, ie a change in income has a small effect on quantity demanded.
Demand for luxury goods increases more than proportionately with income, so the more luxurious a good, the less likely it is to be the correct answer here.
Out of the options, fizzy drinks are likely to be the least luxurious, so Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 492 of 999CB2031382
Question 492
FlagThe monetary base is increased when:
Correct
Answer: B
Notice that the question asks for the effect on the monetary base. The monetary base consists solely of cash, ie notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank, whereas broader measures of the money supply include current and deposit accounts. The best method to use here is to take each option in turn and consider whether or not extra cash would be made available in the economy.
If the government (or anyone else) spends more money (Option A), eg on schools, then this money must have come from somewhere. The government will either raise the funds from taxation or it will borrow by issuing government securities (bills and bonds).
If the government securities are bought by the non-bank private sector, then the money has come from the general public. There is no new cash and therefore no change in monetary base.
If the government securities are sold to financial institutions, then, as before, the cash spent by the government has come from the cash in the financial institutions, so there is no new cash, therefore there is no change in monetary base. (However, in this case, if the commercial banks are now holding more Treasury bills, they are holding more liquid assets and these can be used as a basis for credit creation and hence an increase in broad money. This effect on broad money can be mitigated if the government sells bonds rather than Treasury bills, since these are less liquid.)
So, Option A is not the correct answer.
If the government buys Treasury bills from the public (Option B), then it will pay for these Treasury bills with cash, and hence there will be more cash in the economy. So this is the correct answer.It is worth checking the other options.
If a citizen buys a newly issued corporate bond (Option C), this is just a particular use of the available supply of cash, no different to the purchase of a new car. The money paid will simply be transferred from the citizen to the company issuing the bond, with no net effect on the monetary base.If a firm obtains an overdraft from the bank (Option D), the amount this firm can spend increases but cash does not increase. Hence deposits (and broader measures of the money supply) increase but the monetary base is unchanged.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Notice that the question asks for the effect on the monetary base. The monetary base consists solely of cash, ie notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank, whereas broader measures of the money supply include current and deposit accounts. The best method to use here is to take each option in turn and consider whether or not extra cash would be made available in the economy.
If the government (or anyone else) spends more money (Option A), eg on schools, then this money must have come from somewhere. The government will either raise the funds from taxation or it will borrow by issuing government securities (bills and bonds).
If the government securities are bought by the non-bank private sector, then the money has come from the general public. There is no new cash and therefore no change in monetary base.
If the government securities are sold to financial institutions, then, as before, the cash spent by the government has come from the cash in the financial institutions, so there is no new cash, therefore there is no change in monetary base. (However, in this case, if the commercial banks are now holding more Treasury bills, they are holding more liquid assets and these can be used as a basis for credit creation and hence an increase in broad money. This effect on broad money can be mitigated if the government sells bonds rather than Treasury bills, since these are less liquid.)
So, Option A is not the correct answer.
If the government buys Treasury bills from the public (Option B), then it will pay for these Treasury bills with cash, and hence there will be more cash in the economy. So this is the correct answer.It is worth checking the other options.
If a citizen buys a newly issued corporate bond (Option C), this is just a particular use of the available supply of cash, no different to the purchase of a new car. The money paid will simply be transferred from the citizen to the company issuing the bond, with no net effect on the monetary base.If a firm obtains an overdraft from the bank (Option D), the amount this firm can spend increases but cash does not increase. Hence deposits (and broader measures of the money supply) increase but the monetary base is unchanged.
-
Question 493 of 999CB2031383
Question 493
FlagIf the demand for a good increases from 200 units to 400 units when the price falls from $£ 16$ to $£ 12$, then the price elasticity of demand using the arc method is equal to:
Correct
Answer C: Here, price has fallen from $£ 16$ to $£ 12$ and quantity demanded has risen from 200 to 400 . Therefore the average price elasticity of demand is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
P \varepsilon_D & =\frac{(400-200) /[(200+400) / 2]}{(12-16) /[(16+12) / 2]} \\
& =\frac{200 / 300}{-4 / 14} \\
& =2.33
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: Here, price has fallen from $£ 16$ to $£ 12$ and quantity demanded has risen from 200 to 400 . Therefore the average price elasticity of demand is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
P \varepsilon_D & =\frac{(400-200) /[(200+400) / 2]}{(12-16) /[(16+12) / 2]} \\
& =\frac{200 / 300}{-4 / 14} \\
& =2.33
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 494 of 999CB2031384
Question 494
FlagThe central bank conducts an open market sale of bonds equivalent to $£ 20$ million. The commercial banks hold reserves equivalent to 5 per cent of their deposits. What is the maximum that the broad money supply may fall as a result of the open market operation?
Correct
Answer: D
If the central bank conducts an open market sale of bonds, then the purchasers of the bonds hand over cash to the central bank, and so the monetary base will decrease. The amount that the broad money supply will decrease can be calculated using the bank multiplier, which is the number of times greater the expansion of bank deposits is than the additional liquidity in banks that caused it (ie the initial change in the monetary base).
The bank multiplier is calculated as $b=\frac{1}{L}$ where $L$ is the liquidity ratio (ie the percentage of deposits that the bank must hold as reserves) – in this case 5\%.
Therefore, $b=\frac{1}{5 \%}=20$, so the broad money supply will fall by up to $£ 20 \times 20=£ 400$, so the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: D
If the central bank conducts an open market sale of bonds, then the purchasers of the bonds hand over cash to the central bank, and so the monetary base will decrease. The amount that the broad money supply will decrease can be calculated using the bank multiplier, which is the number of times greater the expansion of bank deposits is than the additional liquidity in banks that caused it (ie the initial change in the monetary base).
The bank multiplier is calculated as $b=\frac{1}{L}$ where $L$ is the liquidity ratio (ie the percentage of deposits that the bank must hold as reserves) – in this case 5\%.
Therefore, $b=\frac{1}{5 \%}=20$, so the broad money supply will fall by up to $£ 20 \times 20=£ 400$, so the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 495 of 999CB2031385
Question 495
FlagFood outlets in airport terminals are able to charge a higher price than their high street equivalent because demand for food in airport terminals is:
Correct
Answer B: Food outlets in airport terminals are able to charge higher prices than their high street equivalent because consumers at airports have fewer alternatives.
Consumers in the high street are likely to have a range of possible food outlets to choose from and may even have the option of returning home to eat. As a result, high street food outlets have to be relatively competitive.
In contrast, at airports, the choice of food outlets is likely to be much more limited, and consumers may have little choice but to eat there. Such food outlets are therefore able to charge higher prices without losing too many sales. The price elasticity of demand of these outlets is therefore relatively inelastic (a change in price leads to a relatively small change in quantity demanded). Hence Option B is the correct answer and Option D is incorrect.
Perfect price elasticity (Option C) is the same as ‘infinite price elasticity’, ie quantity demanded will decrease to zero when price increases, which is not a reason for food outlets in airport terminals charging higher prices.
Perfect price inelasticity (Option A) means that the quantity demanded will not respond to a change in price, which is also not the case for food outlets in airport terminals because consumers will only buy food there if they can afford to do so.
Incorrect
Answer B: Food outlets in airport terminals are able to charge higher prices than their high street equivalent because consumers at airports have fewer alternatives.
Consumers in the high street are likely to have a range of possible food outlets to choose from and may even have the option of returning home to eat. As a result, high street food outlets have to be relatively competitive.
In contrast, at airports, the choice of food outlets is likely to be much more limited, and consumers may have little choice but to eat there. Such food outlets are therefore able to charge higher prices without losing too many sales. The price elasticity of demand of these outlets is therefore relatively inelastic (a change in price leads to a relatively small change in quantity demanded). Hence Option B is the correct answer and Option D is incorrect.
Perfect price elasticity (Option C) is the same as ‘infinite price elasticity’, ie quantity demanded will decrease to zero when price increases, which is not a reason for food outlets in airport terminals charging higher prices.
Perfect price inelasticity (Option A) means that the quantity demanded will not respond to a change in price, which is also not the case for food outlets in airport terminals because consumers will only buy food there if they can afford to do so.
-
Question 496 of 999CB2031386
Question 496
FlagIf the demand curve is more price inelastic than the supply curve, then a subsidy will benefit:
Correct
Answer A :Indirect taxes and subsidies affect supply:
– an indirect tax shifts the supply curve vertically upwards by the amount of the tax
– a subsidy shifts the supply curve vertically downwards by the amount of the subsidy.In each case, there will be a movement along the demand curve to a new equilibrium price and quantity.
The diagram below shows the incidence of a subsidy. Without the subsidy, a quantity $Q_1$ is produced, and sold for price $P_1$. The subsidy reduces the price paid by consumers and increases the quantity produced leading to a new equilibrium $Q_2, P_2$. The price received by producers, which includes the subsidy, increases to $P_3$.
When demand is relatively inelastic (steep), the subsidy will benefit the consumer more. The reduction in the price paid by consumers, $P_1-P_2$ is more than the increase in price received by producers, $P_3-P_1$.
Incorrect
Answer A :Indirect taxes and subsidies affect supply:
– an indirect tax shifts the supply curve vertically upwards by the amount of the tax
– a subsidy shifts the supply curve vertically downwards by the amount of the subsidy.In each case, there will be a movement along the demand curve to a new equilibrium price and quantity.
The diagram below shows the incidence of a subsidy. Without the subsidy, a quantity $Q_1$ is produced, and sold for price $P_1$. The subsidy reduces the price paid by consumers and increases the quantity produced leading to a new equilibrium $Q_2, P_2$. The price received by producers, which includes the subsidy, increases to $P_3$.
When demand is relatively inelastic (steep), the subsidy will benefit the consumer more. The reduction in the price paid by consumers, $P_1-P_2$ is more than the increase in price received by producers, $P_3-P_1$.
-
Question 497 of 999CB2031387
Question 497
FlagThe overall money multiplier effect might be smaller than the full bank deposits multiplier because:
Correct
Answer: B
Remember that:
– The bank deposits multiplier ( $b=1 / L$ ) is the ratio of the ‘theoretical’ increase in total deposits or broad money in response to an initial increase in deposits.
– The money multiplier represents the ‘actual’ ratio of the increase in broad money to an increase in the monetary base.The bank deposits multiplier assumes that:
1. All extra money created by lending is re-deposited back in the banking system.
2. Banks are able to increase their lending as much they wish (based on their desired liquidity ratio, L) in response to additional liquidity.However, in practice, the actual multiplier effect might be smaller than the full bank deposits multiplier because:
1. Some of the extra money created by lending may be withdrawn from the banking system, eg kept as cash outside of the banks.
2. The actual liquidity ratio ( L ) is higher than that desired because firms and households do not want to borrow as much as the banks wish to lend.Option A bears no direct relation to either of these reasons and so is not correct.
Option B relates to the second reason above – high interest rates discourage borrowing, so that customers choose not to borrow as much as banks are prepared to lend, so this is the correct answer.Option C tells us that banks are not holding excess cash reserves, ie they do not have surplus liquidity because they are lending as much as they want to. If this is the case, then the two multipliers must be equal and so Option C is not the correct answer.
Option D relates to the first assumption above. If all cash is re-deposited with banks (and banks are able to lend as much as they wish), then the money multiplier will be the same as the bank deposits multiplier and not smaller, so this is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Remember that:
– The bank deposits multiplier ( $b=1 / L$ ) is the ratio of the ‘theoretical’ increase in total deposits or broad money in response to an initial increase in deposits.
– The money multiplier represents the ‘actual’ ratio of the increase in broad money to an increase in the monetary base.The bank deposits multiplier assumes that:
1. All extra money created by lending is re-deposited back in the banking system.
2. Banks are able to increase their lending as much they wish (based on their desired liquidity ratio, L) in response to additional liquidity.However, in practice, the actual multiplier effect might be smaller than the full bank deposits multiplier because:
1. Some of the extra money created by lending may be withdrawn from the banking system, eg kept as cash outside of the banks.
2. The actual liquidity ratio ( L ) is higher than that desired because firms and households do not want to borrow as much as the banks wish to lend.Option A bears no direct relation to either of these reasons and so is not correct.
Option B relates to the second reason above – high interest rates discourage borrowing, so that customers choose not to borrow as much as banks are prepared to lend, so this is the correct answer.Option C tells us that banks are not holding excess cash reserves, ie they do not have surplus liquidity because they are lending as much as they want to. If this is the case, then the two multipliers must be equal and so Option C is not the correct answer.
Option D relates to the first assumption above. If all cash is re-deposited with banks (and banks are able to lend as much as they wish), then the money multiplier will be the same as the bank deposits multiplier and not smaller, so this is not the correct answer.
-
Question 498 of 999CB2031388
Question 498
FlagThe demand for Good X has a price elasticity of -1 . Tax on Good X is € 10 per unit. If the government decides to reduce the tax on Good X to £ 5 per unit, this would shift the supply curve for Good X down by:
Correct
Answer D: The reduction of a $£ 10$ per unit tax to a $£ 5$ per unit tax on Good $X$ would shift the supply curve downwards by $£ 5$, thus ruling out Options A and B .
The fall in price will be smaller than the fall in the tax, ie the price will fall by less than $£ 5$. Hence Option D is the correct answer.
This can be seen in the following diagram. The supply curve must also be assumed not to be horizontal: if a horizontal supply curve shifts downwards, this would also lead to a price decrease of $£ 5$ (Option C).
Incorrect
Answer D: The reduction of a $£ 10$ per unit tax to a $£ 5$ per unit tax on Good $X$ would shift the supply curve downwards by $£ 5$, thus ruling out Options A and B .
The fall in price will be smaller than the fall in the tax, ie the price will fall by less than $£ 5$. Hence Option D is the correct answer.
This can be seen in the following diagram. The supply curve must also be assumed not to be horizontal: if a horizontal supply curve shifts downwards, this would also lead to a price decrease of $£ 5$ (Option C).
-
Question 499 of 999CB2031389
Question 499
FlagIf a maximum price for Good X is fixed above the market equilibrium price, there will be:
Correct
Answer A: A price ceiling that is set above the free-market price will have no impact on the price or quantity of the good that is traded. So, Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A: A price ceiling that is set above the free-market price will have no impact on the price or quantity of the good that is traded. So, Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 500 of 999CB2031390
Question 500
FlagFollowing a $10 \%$ rise in price of Good $A$, the quantity demanded for Good B rises by $25 \%$. What does this imply about the relationship between Goods A and B ?
Correct
Answer C :Since $\% \Delta Q_{D_B}=25 \%$ and $\% \Delta P_A=10 \%$ :
$$
C E_{D_{B A}}=\frac{\% \Delta Q D_B}{\% \Delta P_A}=\frac{25 \%}{10 \%}=2.5
$$To determine whether two goods are complements or substitutes, it is necessary to look at the sign of the cross-price elasticity of demand. Here it is positive, and this implies the goods are substitutes: as the price of one good increases (and hence the quantity demanded of that good decreases), the quantity demanded of the other good increases. This rules out Options A and B.
In addition, the relationship between the price of one good and the quantity demanded of the other is fairly strong – a $10 \%$ change in price leads to a $25 \%$ change in quantity, which would suggest a close relationship between the goods.
Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C :Since $\% \Delta Q_{D_B}=25 \%$ and $\% \Delta P_A=10 \%$ :
$$
C E_{D_{B A}}=\frac{\% \Delta Q D_B}{\% \Delta P_A}=\frac{25 \%}{10 \%}=2.5
$$To determine whether two goods are complements or substitutes, it is necessary to look at the sign of the cross-price elasticity of demand. Here it is positive, and this implies the goods are substitutes: as the price of one good increases (and hence the quantity demanded of that good decreases), the quantity demanded of the other good increases. This rules out Options A and B.
In addition, the relationship between the price of one good and the quantity demanded of the other is fairly strong – a $10 \%$ change in price leads to a $25 \%$ change in quantity, which would suggest a close relationship between the goods.
Option C is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 501 of 999CB2031392
Question 501
FlagThe direct impact of open market operations, where the central bank purchases government securities, is to:
Correct
Answer: D
This question is on open market operations.
Remember that the monetary base is defined as notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank.When the central bank buys government bonds in the market, it pays the sellers of the bonds, who deposit the cash received into their own banks. This increases the cash reserves of the commercial banks and so increases the monetary base (Option D).
Incorrect
Answer: D
This question is on open market operations.
Remember that the monetary base is defined as notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank.When the central bank buys government bonds in the market, it pays the sellers of the bonds, who deposit the cash received into their own banks. This increases the cash reserves of the commercial banks and so increases the monetary base (Option D).
-
Question 502 of 999CB2031393
Question 502
FlagYou are given the following data:
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline Price (£) & \text{Quantity demanded} \\
\hline 90 & 200 \\
\hline 80 & 300 \\
\hline 70 & 400 \\
\hline 60 & 500 \\
\hline 50 & 600 \\
\hline
\end{array}For which price change is the price elasticity of demand equal to -1.0 using the arc (average) method?
Correct
Answer D: Price elasticity of demand $\left(P \varepsilon_D\right)$ is calculated as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
P \varepsilon_D & =\frac{\% \text { change in quantity demanded }}{\% \text { change in price }} \\
& =\frac{\Delta Q_D / Q_D}{\Delta P / P}
\end{aligned}
$$According to the average of midpoint method this is:
$$
P_{E_D}=\frac{\Delta Q_D / \text { average } Q_D}{\Delta P / \text { average } P}
$$From $£ 80$ to $£ 90$ (Option A):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(300-200) / 250}{(80-90) / 85} \\
& =\frac{100 / 250}{-10 / 85} \\
& =-3.4
\end{aligned}
$$From $£ 60$ to $£ 70$ (Option C):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(500-400) / 450}{(60-70) / 65} \\
& =\frac{100 / 450}{-10 / 65} \\
& =-1.44
\end{aligned}
$$From $£ 70$ to $£ 80$ (Option B):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(400-300) / 350}{(70-80) / 75} \\
& =\frac{100 / 350}{-10 / 75} \\
& =-2.14
\end{aligned}
$$From $£ 50$ to $£ 60$ (Option D):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(600-500) / 550}{(50-60) / 55} \\
& =\frac{100 / 550}{-10 / 55} \\
& =-1
\end{aligned}
$$
Hence Option D is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer D: Price elasticity of demand $\left(P \varepsilon_D\right)$ is calculated as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
P \varepsilon_D & =\frac{\% \text { change in quantity demanded }}{\% \text { change in price }} \\
& =\frac{\Delta Q_D / Q_D}{\Delta P / P}
\end{aligned}
$$According to the average of midpoint method this is:
$$
P_{E_D}=\frac{\Delta Q_D / \text { average } Q_D}{\Delta P / \text { average } P}
$$From $£ 80$ to $£ 90$ (Option A):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(300-200) / 250}{(80-90) / 85} \\
& =\frac{100 / 250}{-10 / 85} \\
& =-3.4
\end{aligned}
$$From $£ 60$ to $£ 70$ (Option C):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(500-400) / 450}{(60-70) / 65} \\
& =\frac{100 / 450}{-10 / 65} \\
& =-1.44
\end{aligned}
$$From $£ 70$ to $£ 80$ (Option B):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(400-300) / 350}{(70-80) / 75} \\
& =\frac{100 / 350}{-10 / 75} \\
& =-2.14
\end{aligned}
$$From $£ 50$ to $£ 60$ (Option D):
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{\varepsilon_D} & =\frac{(600-500) / 550}{(50-60) / 55} \\
& =\frac{100 / 550}{-10 / 55} \\
& =-1
\end{aligned}
$$
Hence Option D is the correct answer. -
Question 503 of 999CB2031394
Question 503
FlagWhich of the following would cause the demand for money curve to shift inwards to the left?
Correct
Answer: D
A shift in the demand for money curve inwards to the left represents a fall in the demand for money.
The factors affecting the demand for money include:
1. money national income (or GDP). An increase in money national income, which may arise from an increase in real national income or an increase in prices, will lead to an increase in expenditure on goods and services, and hence an increase in the transactions demand for money. This rules out Options A and C.
2. the rate of interest. A change in the rate of interest leads to a movement along a given money demand curve, rather than a shift in the money demand curve. This rules out Option B.
3. the frequency with which people are paid. The more frequently people get paid, the less cash they need to hold on average and so the lower is the demand for money – hence Option D is correct.Incorrect
Answer: D
A shift in the demand for money curve inwards to the left represents a fall in the demand for money.
The factors affecting the demand for money include:
1. money national income (or GDP). An increase in money national income, which may arise from an increase in real national income or an increase in prices, will lead to an increase in expenditure on goods and services, and hence an increase in the transactions demand for money. This rules out Options A and C.
2. the rate of interest. A change in the rate of interest leads to a movement along a given money demand curve, rather than a shift in the money demand curve. This rules out Option B.
3. the frequency with which people are paid. The more frequently people get paid, the less cash they need to hold on average and so the lower is the demand for money – hence Option D is correct. -
Question 504 of 999CB2031395
Question 504
FlagWhich of the following scenarios leads to no change in total consumer expenditure when prices increase?
Correct
Answer C: ‘Total consumer expenditure’ in this context is the same as total revenue, ie the product of the price of the good and the quantity purchased.
When demand is relatively elastic, an increase in price causes a more than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will fall. When demand is relatively inelastic, an increase in price causes a less than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will rise. Perfectly elastic and perfectly inelastic demand would be the extreme examples of this point.
Unit elasticity of demand (Option C ) means that the price elasticity of demand is minus one. Therefore a change in price will be exactly offset by an (opposite) change in quantity demanded, and total revenue will not change.
Incorrect
Answer C: ‘Total consumer expenditure’ in this context is the same as total revenue, ie the product of the price of the good and the quantity purchased.
When demand is relatively elastic, an increase in price causes a more than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will fall. When demand is relatively inelastic, an increase in price causes a less than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded, so that total revenue will rise. Perfectly elastic and perfectly inelastic demand would be the extreme examples of this point.
Unit elasticity of demand (Option C ) means that the price elasticity of demand is minus one. Therefore a change in price will be exactly offset by an (opposite) change in quantity demanded, and total revenue will not change.
-
Question 505 of 999CB2031396
Question 505
FlagA paint manufacturer is planning to engage the services of a popular social media influencer to boost sales revenue against its main competitor.
If this initiative is successful the competitor firm’s demand curve for paint will:
Correct
Answer D: Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right, by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (more price-inelastic), by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand.In this particular question, the planned initiative is to use a social media influencer, which is a particular form of advertising. Therefore, if successful, the impact on the firm carrying out the advertising would be to shift their demand curve to the right and make it less price-elastic (ie steeper). This would correspond to Option B.
However, the question asks for the impact on the competitor firm’s demand curve. Essentially, this will be the opposite. Their demand curve will shift to the left, as fewer people will find the competitor firm attractive (relative to the firm carrying out the advertising). Similarly their demand curve will become more price-elastic (less steep), as their brand loyalty has likely been reduced, and even a relatively small rise in price will lead to customers switching to the firm who has been carrying out the advertising. Therefore, the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer D: Advertising a product aims to:
– shift the product’s demand curve to the right, by bringing the product more to consumers’ attention and increasing the attractiveness and marginal utility of the product
– make the product’s demand less price-elastic (more price-inelastic), by creating brand loyalty and so reducing the number of perceived substitute goods, enabling the firm to increase prices without a substantial decrease in demand.In this particular question, the planned initiative is to use a social media influencer, which is a particular form of advertising. Therefore, if successful, the impact on the firm carrying out the advertising would be to shift their demand curve to the right and make it less price-elastic (ie steeper). This would correspond to Option B.
However, the question asks for the impact on the competitor firm’s demand curve. Essentially, this will be the opposite. Their demand curve will shift to the left, as fewer people will find the competitor firm attractive (relative to the firm carrying out the advertising). Similarly their demand curve will become more price-elastic (less steep), as their brand loyalty has likely been reduced, and even a relatively small rise in price will lead to customers switching to the firm who has been carrying out the advertising. Therefore, the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 506 of 999CB2031397
Question 506
FlagWhich one of the following will have a negative impact upon money demand?
Correct
Answer: C
A negative impact upon money demand corresponds to a fall in the demand for money, ie a shift in the demand for money curve to the left.
The factors affecting the demand for money include:
– the rate of interest. A change in the rate of interest leads to a movement along a given money demand curve, rather than a shift in it. This rules out Option A.
– money national income or gross domestic product (GDP). An increase in the monetary value of GDP may arise from an increase in the real value of GDP (ie the quantity of goods and services produced) or an increase in the average level of prices (or both). In either case, it will lead to an increase in expenditure on goods and services, and hence an increase in the transactions demand for money. This rules out Option B.
– the frequency with which people are paid. The more frequently people get paid, the less cash they need to hold on average and so the lower is the demand for money – hence Option C is correct.
– expectations regarding stock prices. For example, if people believe that stock prices are about to fall, then they will prefer protect the value of their wealth by holding money, rather than stocks, resulting in an increase in the demand for money. Hence, Option D is an incorrect statement.Other factors that may affect the demand for money include:
– expectations regarding the value of the domestic currency. For example, if the pound is expected to depreciate against the dollar, then investors may choose to exchange their pounds for dollars, resulting in a fall in the demand for pounds.
– financial innovation, such as the more widespread use of credit cards. For example, an increase in the use of credit cards is likely to reduce the demand for money as consumers use their credit cards for transactions rather than cash.Incorrect
Answer: C
A negative impact upon money demand corresponds to a fall in the demand for money, ie a shift in the demand for money curve to the left.
The factors affecting the demand for money include:
– the rate of interest. A change in the rate of interest leads to a movement along a given money demand curve, rather than a shift in it. This rules out Option A.
– money national income or gross domestic product (GDP). An increase in the monetary value of GDP may arise from an increase in the real value of GDP (ie the quantity of goods and services produced) or an increase in the average level of prices (or both). In either case, it will lead to an increase in expenditure on goods and services, and hence an increase in the transactions demand for money. This rules out Option B.
– the frequency with which people are paid. The more frequently people get paid, the less cash they need to hold on average and so the lower is the demand for money – hence Option C is correct.
– expectations regarding stock prices. For example, if people believe that stock prices are about to fall, then they will prefer protect the value of their wealth by holding money, rather than stocks, resulting in an increase in the demand for money. Hence, Option D is an incorrect statement.Other factors that may affect the demand for money include:
– expectations regarding the value of the domestic currency. For example, if the pound is expected to depreciate against the dollar, then investors may choose to exchange their pounds for dollars, resulting in a fall in the demand for pounds.
– financial innovation, such as the more widespread use of credit cards. For example, an increase in the use of credit cards is likely to reduce the demand for money as consumers use their credit cards for transactions rather than cash. -
Question 507 of 999CB2031398
Question 507
FlagThe price of Good X increases by 5% and the quantity demanded decreases by 10%. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option D.
The PED of Good X can be calculated as P $\varepsilon_{\mathrm{D}}=\frac{\% \Delta \text { in quantity demanded of Good X }}{\% \Delta \text { in price of Good X }}=\frac{-10 \%}{5 \%}=-2$
Therefore, Option A is true.
The absolute value of the PED is greater than 1, so demand for Good X is elastic, and so Option B is true.The PED is negative, indicating that Good X has a downward sloping demand curve. Therefore Option C is true.
Demand for Good X is elastic. In other words, as the price of Good X rises, there is a more than proportionate decrease in demand. This is likely to be partly because consumers are purchasing cheaper substitutes for Good X. Therefore Option D is likely to be false, and is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D.
The PED of Good X can be calculated as P $\varepsilon_{\mathrm{D}}=\frac{\% \Delta \text { in quantity demanded of Good X }}{\% \Delta \text { in price of Good X }}=\frac{-10 \%}{5 \%}=-2$
Therefore, Option A is true.
The absolute value of the PED is greater than 1, so demand for Good X is elastic, and so Option B is true.The PED is negative, indicating that Good X has a downward sloping demand curve. Therefore Option C is true.
Demand for Good X is elastic. In other words, as the price of Good X rises, there is a more than proportionate decrease in demand. This is likely to be partly because consumers are purchasing cheaper substitutes for Good X. Therefore Option D is likely to be false, and is the correct answer.
-
Question 508 of 999CB2031399
Question 508
FlagWhich one of the following statements about the demand for money is TRUE?
Correct
Answer: D
The money demand curve slopes downwards, which demonstrates that the demand for money is negatively related to the interest rate. This is due to the asset motive: if interest rates increase, then the opportunity cost of holding cash (compared to higher yielding assets such as bonds and shares) increases. Therefore Option A is false.
If wealth increases, then the demand for money will likely increase. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives – the more wealth individuals have, the more they will want to hold as cash for everyday transactions and also for unexpected spending. Therefore the demand for money is positively related to the level of wealth, ie Option B is false.
If the general price level increases, then the demand for money will increase. This is because more money will be needed to purchase the same volume of goods and services as before. So, the demand for money is positively related to the general price level, which means Option C is false.
Finally, if real national income increases, then the demand for money will increase. A similar argument applies here as for an increase in wealth, ie the more income individuals have in real terms, the more goods and services they will wish to buy and so the more money they will want to hold as cash in order to do so. So, the demand for money is positively related to the level of national income, ie Option D is true.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The money demand curve slopes downwards, which demonstrates that the demand for money is negatively related to the interest rate. This is due to the asset motive: if interest rates increase, then the opportunity cost of holding cash (compared to higher yielding assets such as bonds and shares) increases. Therefore Option A is false.
If wealth increases, then the demand for money will likely increase. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives – the more wealth individuals have, the more they will want to hold as cash for everyday transactions and also for unexpected spending. Therefore the demand for money is positively related to the level of wealth, ie Option B is false.
If the general price level increases, then the demand for money will increase. This is because more money will be needed to purchase the same volume of goods and services as before. So, the demand for money is positively related to the general price level, which means Option C is false.
Finally, if real national income increases, then the demand for money will increase. A similar argument applies here as for an increase in wealth, ie the more income individuals have in real terms, the more goods and services they will wish to buy and so the more money they will want to hold as cash in order to do so. So, the demand for money is positively related to the level of national income, ie Option D is true.
-
Question 509 of 999CB2031400
Question 509
FlagAlong a straight-line demand curve which of the following is FALSE?
Correct
Option C.
The following diagram shows how price elasticity varies along a straight-line demand curve:When quantity demanded equals zero, price elasticity of demand is (minus) infinity, ie it is perfectly elastic-Option A.
Midway along the curve, demand is unit elastic-Option B.
Elasticity decreases as the price falls and the quantity demanded rises-Option D.
Note that since Options C and D are opposites, the correct answer has to be one of these.Incorrect
Option C.
The following diagram shows how price elasticity varies along a straight-line demand curve:When quantity demanded equals zero, price elasticity of demand is (minus) infinity, ie it is perfectly elastic-Option A.
Midway along the curve, demand is unit elastic-Option B.
Elasticity decreases as the price falls and the quantity demanded rises-Option D.
Note that since Options C and D are opposites, the correct answer has to be one of these. -
Question 510 of 999CB2031401
Question 510
FlagWhich one of the following statements about the demand for money is TRUE?
Correct
Answer: A
The demand for money comprises three main components: the transactions and precautionary demands (which are likely to be positively related to wealth (Option B), prices (Option C) and real income (Option D)) and the speculative or asset demand (which is negatively related to interest rates (Option A)). So, Option A is true and hence the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The demand for money comprises three main components: the transactions and precautionary demands (which are likely to be positively related to wealth (Option B), prices (Option C) and real income (Option D)) and the speculative or asset demand (which is negatively related to interest rates (Option A)). So, Option A is true and hence the correct answer.
-
Question 511 of 999CB2031402
Question 511
FlagWhich of the following statements is TRUE?
Correct
Answer C:
The price elasticity of demand varies along a straight-line demand curve as shown above.
Although the absolute change in quantity demanded in response to a given absolute change in price is the same at all points along a straight-line demand curve, the demand is more elastic at higher prices because it is expressed in percentage terms. For example, the higher the price and the lower the quantity demanded, the lower the percentage change in price and the higher the percentage change in quantity demanded. Hence, the higher is the elasticity. Conversely, the lower the price and the higher the quantity demanded, the higher the percentage change in price and the lower the percentage change in quantity demanded, giving a lower elasticity. Therefore Option C is TRUE.The cross-price elasticity of demand will generally be negative for complementary goods that are used together, such as cars and petrol. This is because an increase in the price of cars say will lead to a decrease in the number of cars purchased and a corresponding decrease in the use of petrol. Therefore Option A is FALSE.
Elasticity of supply is infinite along a horizontal supply curve, as an infinitesimal fall in price will (in theory at least) lead to an infinite decrease in the quantity supplied. An elasticity of zero instead corresponds to a vertical supply curve. (Remember that in general flatter/steeper curves tend to be more/less elastic). Therefore Option B is FALSE.
An inferior good is defined as a good for which the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie for which demand goes down as income goes up. Therefore Option D is FALSE.
Incorrect
Answer C:
The price elasticity of demand varies along a straight-line demand curve as shown above.
Although the absolute change in quantity demanded in response to a given absolute change in price is the same at all points along a straight-line demand curve, the demand is more elastic at higher prices because it is expressed in percentage terms. For example, the higher the price and the lower the quantity demanded, the lower the percentage change in price and the higher the percentage change in quantity demanded. Hence, the higher is the elasticity. Conversely, the lower the price and the higher the quantity demanded, the higher the percentage change in price and the lower the percentage change in quantity demanded, giving a lower elasticity. Therefore Option C is TRUE.The cross-price elasticity of demand will generally be negative for complementary goods that are used together, such as cars and petrol. This is because an increase in the price of cars say will lead to a decrease in the number of cars purchased and a corresponding decrease in the use of petrol. Therefore Option A is FALSE.
Elasticity of supply is infinite along a horizontal supply curve, as an infinitesimal fall in price will (in theory at least) lead to an infinite decrease in the quantity supplied. An elasticity of zero instead corresponds to a vertical supply curve. (Remember that in general flatter/steeper curves tend to be more/less elastic). Therefore Option B is FALSE.
An inferior good is defined as a good for which the income elasticity of demand is negative, ie for which demand goes down as income goes up. Therefore Option D is FALSE.
-
Question 512 of 999CB2031403
Question 512
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option A. Uncertainty occurs when the probability of an outcome is not known. Therefore uncertainty cannot be a measure of the variability of an outcome, so Option A is false and is the correct answer. Risk is a measure of the variability of an outcome.
Incorrect
Option A. Uncertainty occurs when the probability of an outcome is not known. Therefore uncertainty cannot be a measure of the variability of an outcome, so Option A is false and is the correct answer. Risk is a measure of the variability of an outcome.
-
Question 513 of 999CB2031404
Question 513
FlagThe direct impact of open market operations, where the central bank purchases government securities, is to:
Correct
Answer: D
This is a question on open market operations.
Remember that the monetary base is defined as notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank.When the central bank buys government bonds in the market, it pays the sellers of the bonds, who deposit the cash received into their own banks. This increases the cash reserves of the commercial banks and so increases the monetary base (Option D).
Incorrect
Answer: D
This is a question on open market operations.
Remember that the monetary base is defined as notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank.When the central bank buys government bonds in the market, it pays the sellers of the bonds, who deposit the cash received into their own banks. This increases the cash reserves of the commercial banks and so increases the monetary base (Option D).
-
Question 514 of 999CB2031405
Question 514
FlagA maximum price (ceiling) set below the free-market price results in:
Correct
Option A. In the diagram, we can see that a maximum price set below the equilibrium price results in excess demand and hence a shortage equal to $Q_d-Q_s$.
-
Question 515 of 999CB2031406
Question 515
FlagA government’s attempts to increase the monetary base (narrow money supply) through open market operations are likely to cause short-term interest rates to:
Correct
Answer: B
The question asks for the effect of open market operations on both interest rates and the demand for money.
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government bonds by the central bank in order to bring about a change in the monetary base and hence the broad money supply. If the central bank wishes to increase the money supply, it buys bonds in the open market, thus increasing liquidity and enabling the banks to create more credit.
The short-term interest rate is the rate at which supply and demand for money are in equilibrium. The increase in the money supply will decrease the equilibrium interest rate, as shown in the diagram below:
This rules out Options C and D.
Recall that there are three motives for holding money:
1. transactions motive
2. precautionary motive
3. asset motive.The reduction in interest rates reduces the opportunity cost of holding money under the asset motive and so the quantity of money demanded should increase, ie there is a movement along the demand for money curve as people sell their bonds to the central bank and hold money instead. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Note that, strictly speaking, the movement along the (unchanged) money demand curve in this diagram should be referred to as an increase in the quantity of money demanded, rather than an increase in the demand for money. However, as this phrase isn’t used in any of the options provided, Option B is the best available option.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The question asks for the effect of open market operations on both interest rates and the demand for money.
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government bonds by the central bank in order to bring about a change in the monetary base and hence the broad money supply. If the central bank wishes to increase the money supply, it buys bonds in the open market, thus increasing liquidity and enabling the banks to create more credit.
The short-term interest rate is the rate at which supply and demand for money are in equilibrium. The increase in the money supply will decrease the equilibrium interest rate, as shown in the diagram below:

This rules out Options C and D.
Recall that there are three motives for holding money:
1. transactions motive
2. precautionary motive
3. asset motive.The reduction in interest rates reduces the opportunity cost of holding money under the asset motive and so the quantity of money demanded should increase, ie there is a movement along the demand for money curve as people sell their bonds to the central bank and hold money instead. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Note that, strictly speaking, the movement along the (unchanged) money demand curve in this diagram should be referred to as an increase in the quantity of money demanded, rather than an increase in the demand for money. However, as this phrase isn’t used in any of the options provided, Option B is the best available option.
-
Question 516 of 999CB2031407
Question 516
FlagA maximum price for widgets set above the free-market price will lead to:
Correct
Option C. A maximum price has no effect on the market if it is above the equilibrium price.
Incorrect
Option C. A maximum price has no effect on the market if it is above the equilibrium price.
-
Question 517 of 999CB2031408
Question 517
FlagWhat is the intended effect of an advertising campaign on the demand curve:
Correct
Option D. Advertising campaigns generally intend to increase both demand and brand loyalty for a product. A shift of the curve to the right corresponds to an increase in demand. If the curve becomes more inelastic ie steeper, consumers are becoming less price sensitive, in this scenario probably because of an increase in brand loyalty.
Incorrect
Option D. Advertising campaigns generally intend to increase both demand and brand loyalty for a product. A shift of the curve to the right corresponds to an increase in demand. If the curve becomes more inelastic ie steeper, consumers are becoming less price sensitive, in this scenario probably because of an increase in brand loyalty.
-
Question 518 of 999CB2031409
Question 518
FlagThis question is based on the following three supply curves, where $P$ is price and $Q$ is the quantity supplied.
I $P=2 Q$
II $\quad P=Q$
III $P=0.5 Q$
Which of the following statements is TRUE?Correct
Option A.
Any straight-line supply curve passing through the origin has a supply elasticity of 1 at all points.
For example, let:
$$
P=c Q \text { (where } P \text { is price, } Q \text { is quantity supplied and } c \text { is a constant). }
$$Then the elasticity of supply is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{E_{\mathrm{S}}} & =\frac{P}{Q} \times \frac{d Q}{d P} \\
& =\frac{P}{Q} \times \frac{1}{c} \\
& =\frac{c Q}{Q} \times \frac{1}{c}=1
\end{aligned}
$$Thus, I, II and III all have a supply elasticity of 1 at all levels.
Incorrect
Option A.
Any straight-line supply curve passing through the origin has a supply elasticity of 1 at all points.
For example, let:
$$
P=c Q \text { (where } P \text { is price, } Q \text { is quantity supplied and } c \text { is a constant). }
$$Then the elasticity of supply is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
P_{E_{\mathrm{S}}} & =\frac{P}{Q} \times \frac{d Q}{d P} \\
& =\frac{P}{Q} \times \frac{1}{c} \\
& =\frac{c Q}{Q} \times \frac{1}{c}=1
\end{aligned}
$$Thus, I, II and III all have a supply elasticity of 1 at all levels.
-
Question 519 of 999CB2031410
Question 519
FlagIf the income elasticity of demand for $\operatorname{Good} X$ is 1.5 , a $4 \%$ increase in consumer income will increase the quantity demanded of Good X by:
Correct
Option D. Income elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded as a proportion of the percentage change in income. The percentage increase in demand for Good X will therefore be $1.5 \times 4 \%=6 \%$.
Incorrect
Option D. Income elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded as a proportion of the percentage change in income. The percentage increase in demand for Good X will therefore be $1.5 \times 4 \%=6 \%$.
-
Question 520 of 999CB2031411
Question 520
FlagThe total revenue from the sale of a good will fall if:
Correct
Option A.
Demand for a good is said to be ‘elastic’ when the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand is greater than one. Option A is therefore correct because the (larger) percentage fall in quantity will have a greater effect on revenue than the increase in price.Option C is wrong because when consumer income falls, the demand curve for an inferior good shifts to the right. This increases both price and quantity and hence revenue. Option D is wrong by a similar argument, as the demand for a normal good will shift to the right if consumer income rises.
Incorrect
Option A.
Demand for a good is said to be ‘elastic’ when the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand is greater than one. Option A is therefore correct because the (larger) percentage fall in quantity will have a greater effect on revenue than the increase in price.Option C is wrong because when consumer income falls, the demand curve for an inferior good shifts to the right. This increases both price and quantity and hence revenue. Option D is wrong by a similar argument, as the demand for a normal good will shift to the right if consumer income rises.
-
Question 521 of 999CB2031412
Question 521
FlagGood $Y$ has a cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to Good X of 0.5. 100 units of Good Y are demanded when Good $X$ costs $\$ 50$. Using the ‘original’ formula for cross-price elasticity of demand between two points (ie arc elasticity), a rise in the price of Good X to $\$ 75$ will lead to a change in the demand for Good Y to:
Correct
Option B.
We are given:
$$
\frac{\text { % change in quantity demanded of } Y}{\text { % change in price of } X}=0.5
$$The price of Good X rises from \$50 to \$75, a 50% increase. Substituting in our equation gives:
$$
\frac{\text { % change in quantity demanded of } \mathrm{Y}}{50 \%}=0.5
$$We therefore have a $25 \%$ increase in the quantity of Good Y demanded, taking the demand from 100 units to 125 units.
Incorrect
Option B.
We are given:
$$
\frac{\text { % change in quantity demanded of } Y}{\text { % change in price of } X}=0.5
$$The price of Good X rises from \$50 to \$75, a 50% increase. Substituting in our equation gives:
$$
\frac{\text { % change in quantity demanded of } \mathrm{Y}}{50 \%}=0.5
$$We therefore have a $25 \%$ increase in the quantity of Good Y demanded, taking the demand from 100 units to 125 units.
-
Question 522 of 999CB2031413
Question 522
FlagA government’s attempts to increase the monetary base (narrow money supply) through open market operations are likely to cause short-term interest rates to:
Correct
Answer: D
Recall that open market operations involve the central bank (on behalf of the government) buying and/or selling government bonds in the open market in order to influence the amount of cash banks hold and hence the money supply. The monetary base, or narrow money supply, refers to the notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank.
Here, in order to increase the monetary base, the central bank will buy government bonds in the market. So, the sellers hand over the bonds in return for cash, resulting in an increase in the amount of cash held in the banking system. Banks can then use this cash as a basis for additional lending. In the diagram below, the increase in the money supply is shown as a rightward shift, from $M S_1$ to $M S_2$.
In the bond market, the increase in demand for bonds causes an increase in the price of bonds and hence a decrease in their yield. This leads to a general decrease in interest rates. As bond prices rise and interest rates fall, the opportunity cost of holding money under the asset motive falls, so people are encouraged to sell their bonds and hence hold more cash instead. There is therefore a movement along the demand for money curve.
Note that, strictly speaking, the movement along the (unchanged) money demand curve in this diagram should be referred to as an increase in the quantity of money demanded, rather than an increase in the demand for money. However, as this phrase isn’t used in any of the options provided, Option D is the best available option.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Recall that open market operations involve the central bank (on behalf of the government) buying and/or selling government bonds in the open market in order to influence the amount of cash banks hold and hence the money supply. The monetary base, or narrow money supply, refers to the notes and coins in circulation outside of the central bank.
Here, in order to increase the monetary base, the central bank will buy government bonds in the market. So, the sellers hand over the bonds in return for cash, resulting in an increase in the amount of cash held in the banking system. Banks can then use this cash as a basis for additional lending. In the diagram below, the increase in the money supply is shown as a rightward shift, from $M S_1$ to $M S_2$.
In the bond market, the increase in demand for bonds causes an increase in the price of bonds and hence a decrease in their yield. This leads to a general decrease in interest rates. As bond prices rise and interest rates fall, the opportunity cost of holding money under the asset motive falls, so people are encouraged to sell their bonds and hence hold more cash instead. There is therefore a movement along the demand for money curve.
Note that, strictly speaking, the movement along the (unchanged) money demand curve in this diagram should be referred to as an increase in the quantity of money demanded, rather than an increase in the demand for money. However, as this phrase isn’t used in any of the options provided, Option D is the best available option.
-
Question 523 of 999CB2031414
Question 523
FlagThe income elasticity of demand for a normal good:
Correct
Option C. By definition, the income elasticity for a normal good is positive, but it could be either greater or less than +1 .
Incorrect
Option C. By definition, the income elasticity for a normal good is positive, but it could be either greater or less than +1 .
-
Question 524 of 999CB2031415
Question 524
FlagShadow markets are most likely to be associated with:
Correct
Option A. Shadow markets tend to develop when there is a shortage. A shortage occurs when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. This occurs if the price is below the equilibrium price and is not allowed to increase to the equilibrium price, ie if the government has set a ceiling (or maximum price) below the equilibrium.
Incorrect
Option A. Shadow markets tend to develop when there is a shortage. A shortage occurs when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. This occurs if the price is below the equilibrium price and is not allowed to increase to the equilibrium price, ie if the government has set a ceiling (or maximum price) below the equilibrium.
-
Question 525 of 999CB2031416
Question 525
FlagA price floor set above the market equilibrium price is likely to cause:
Correct
Option A. A price floor sets a minimum price for the product, so if this is set above the equilibrium price, the price has to increase from the equilibrium price to the minimum price. At this price, the quantity supplied will exceed the quantity demanded so there will be a surplus. The quantity traded will be the quantity demanded at the minimum price, which is lower than the equilibrium quantity.
Incorrect
Option A. A price floor sets a minimum price for the product, so if this is set above the equilibrium price, the price has to increase from the equilibrium price to the minimum price. At this price, the quantity supplied will exceed the quantity demanded so there will be a surplus. The quantity traded will be the quantity demanded at the minimum price, which is lower than the equilibrium quantity.
-
Question 526 of 999CB2031417
Question 526
FlagIf the demand for $\operatorname{Good} X$ is price-inelastic and the supply of Good $X$ is price-elastic, then the burden of a sales tax on Good $X$ will be borne:
Correct
Option B.
At any given market price, suppliers will be willing to supply less, and so the supply curve will shift vertically upward by the amount of the tax. If demand is inelastic (steep demand curve) and supply elastic (flat supply curve), then price will rise substantially with little effect on quantity supplied and demanded. Thus, buyers will bear most of the brunt of the new tax. This is because their demand is relatively insensitive to the price of Good X, perhaps because it has few close substitutes.On the diagram below, the (market) price paid by consumers increases from $P_1$ to $P_2$ whilst the (net of tax) price received by suppliers falls from $P_1$ to $P_5$ – the difference between $P_2$ and $P_5$ representing the amount of the tax.
Incorrect
Option B.
At any given market price, suppliers will be willing to supply less, and so the supply curve will shift vertically upward by the amount of the tax. If demand is inelastic (steep demand curve) and supply elastic (flat supply curve), then price will rise substantially with little effect on quantity supplied and demanded. Thus, buyers will bear most of the brunt of the new tax. This is because their demand is relatively insensitive to the price of Good X, perhaps because it has few close substitutes.On the diagram below, the (market) price paid by consumers increases from $P_1$ to $P_2$ whilst the (net of tax) price received by suppliers falls from $P_1$ to $P_5$ – the difference between $P_2$ and $P_5$ representing the amount of the tax.
-
Question 527 of 999CB2031419
Question 527
FlagConsumer X has a higher income than Consumer Y but they have identical preferences and pay the same prices for the goods which they consume. If they both maximise utility then:
Correct
Answer: C
According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{M U_1}{p_1}=\frac{M U_2}{p_2}=\cdots=\frac{M U_n}{p_n}
$$
where $M U$ and $p$ refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the $n$ goods.Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.
In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer $X$ has a higher income, so Consumer $X$ will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and $D$.
Let’s consider marginal utility. Since marginal utility diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer X will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer Y. Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Finally, note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
Incorrect
Answer: C
According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{M U_1}{p_1}=\frac{M U_2}{p_2}=\cdots=\frac{M U_n}{p_n}
$$
where $M U$ and $p$ refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the $n$ goods.Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.
In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer $X$ has a higher income, so Consumer $X$ will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and $D$.
Let’s consider marginal utility. Since marginal utility diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer X will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer Y. Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Finally, note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
-
Question 528 of 999CB2031420
Question 528
FlagAdverse selection refers to a situation where:
Correct
In the context of insurance, adverse selection describes the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks. Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Note that in the context of insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that a policyholder may, because they have insurance, act in a way that makes the insured event more likely. This is Option A, and the opposite of this is Option B.
Answer: C
Incorrect
In the context of insurance, adverse selection describes the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks. Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Note that in the context of insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that a policyholder may, because they have insurance, act in a way that makes the insured event more likely. This is Option A, and the opposite of this is Option B.
Answer: C
-
Question 529 of 999CB2031421
Question 529
FlagConsumer A has a higher income than Consumer B but they have identical preferences and pay the same prices for the goods which they consume. If they both maximise utility then the marginal utility from each good consumed will be:
Correct
Answer: C
According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{M U_1}{p_1}=\frac{M U_2}{p_2}=\cdots=\frac{M U_n}{p_n}
$$
where $M U$ and $p$ refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the $n$ goods.
Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer $X$ has a higher income, so will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and D.
Let’s consider marginal utility: since it diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer $X$ will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer Y. Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Finally, note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
Incorrect
Answer: C
According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{M U_1}{p_1}=\frac{M U_2}{p_2}=\cdots=\frac{M U_n}{p_n}
$$
where $M U$ and $p$ refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the $n$ goods.
Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer $X$ has a higher income, so will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and D.
Let’s consider marginal utility: since it diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer $X$ will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer Y. Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Finally, note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
-
Question 530 of 999CB2031422
Question 530
FlagAdverse selection refers to a situation where:
Correct
In the context of insurance, adverse selection describes the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Note that Option A describes the problem of moral hazard, which arises because people who are insured have less incentive to be careful as insurance protects them against the consequences of not being careful.
Answer: C
Incorrect
In the context of insurance, adverse selection describes the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Note that Option A describes the problem of moral hazard, which arises because people who are insured have less incentive to be careful as insurance protects them against the consequences of not being careful.
Answer: C
-
Question 531 of 999CB2031424
Question 531
FlagDiminishing marginal utility of income implies that individuals are:
Correct
Recall that diminishing marginal utility of income refers to the situation in which an individual gains less additional utility from each extra pound of income. It can be represented by a total utility curve, the gradient of which represents the marginal utility of income. The total utility curve is normally assumed to be:
– upward-sloping – as the marginal utility of income is positive
– concave – as the marginal utility of income decreases with income.Diminishing marginal utility of income means that an individual will gain less utility from an additional pound of income, than she would lose if she were to lose a pound of income.
Consequently, she would reject a fair gamble with expected winnings of zero. In other words, diminishing marginal utility of income means that the individual is risk-averse and so the answer is Option B.Remember that a risk-lover likes risk and will accept a fair gamble, whilst someone who is riskneutral is indifferent between accepting or rejecting a fair gamble. Although diversification (of investments) is a way of reducing exposure to risk, and hence something that would appeal to a risk-averse individual, the term ‘risk-diversifier’ does not appear in the Core Reading.
Answer: B
Incorrect
Recall that diminishing marginal utility of income refers to the situation in which an individual gains less additional utility from each extra pound of income. It can be represented by a total utility curve, the gradient of which represents the marginal utility of income. The total utility curve is normally assumed to be:
– upward-sloping – as the marginal utility of income is positive
– concave – as the marginal utility of income decreases with income.Diminishing marginal utility of income means that an individual will gain less utility from an additional pound of income, than she would lose if she were to lose a pound of income.
Consequently, she would reject a fair gamble with expected winnings of zero. In other words, diminishing marginal utility of income means that the individual is risk-averse and so the answer is Option B.Remember that a risk-lover likes risk and will accept a fair gamble, whilst someone who is riskneutral is indifferent between accepting or rejecting a fair gamble. Although diversification (of investments) is a way of reducing exposure to risk, and hence something that would appeal to a risk-averse individual, the term ‘risk-diversifier’ does not appear in the Core Reading.
Answer: B
-
Question 532 of 999CB2031425
Question 532
FlagConsumer A has a higher income than Consumer B but they have identical preferences and pay the same prices for the goods which they consume. If they both maximise utility then the marginal utility from each good consumed will be:
Correct
According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{M U_1}{p_1}=\frac{M U_2}{p_2}=\cdots=\frac{M U_n}{p_n}
$$
where $M U$ and $p$ refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the $n$ goods.
Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer A has a higher income, so Consumer A will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and D.
Let’s consider marginal utility. Since marginal utility diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer A will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer B. Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Finally, note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
Answer: C
Incorrect
According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{M U_1}{p_1}=\frac{M U_2}{p_2}=\cdots=\frac{M U_n}{p_n}
$$
where $M U$ and $p$ refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the $n$ goods.
Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer A has a higher income, so Consumer A will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and D.
Let’s consider marginal utility. Since marginal utility diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer A will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer B. Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Finally, note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
Answer: C
-
Question 533 of 999CB2031426
Question 533
FlagIn relation to insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that:
Correct
In the context of insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that policyholders may, because they have insurance, act in a way that makes the insured event more likely. Option B is therefore the correct answer.
Note that Option A describes the problem of adverse selection; the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks.
Answer: B
Incorrect
In the context of insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that policyholders may, because they have insurance, act in a way that makes the insured event more likely. Option B is therefore the correct answer.
Note that Option A describes the problem of adverse selection; the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks.
Answer: B
-
Question 534 of 999CB2031427
Question 534
FlagWhich of the following statements defines adverse selection in relation to insurance?
Correct
In the context of insurance, adverse selection describes the fact that people who know they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks.
Note that:
– Option B describes the problem of moral hazard; the fact that having bought insurance, people take less care to guard against the insured event, as they are protected against the consequences of it happening.
– An insurance company may face false claims regardless of the problems of adverse selection and moral hazard.Answer: A
Incorrect
In the context of insurance, adverse selection describes the fact that people who know they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks.
Note that:
– Option B describes the problem of moral hazard; the fact that having bought insurance, people take less care to guard against the insured event, as they are protected against the consequences of it happening.
– An insurance company may face false claims regardless of the problems of adverse selection and moral hazard.Answer: A
-
Question 535 of 999CB2031428
Question 535
FlagConsumer A has a higher income than Consumer B but they have identical preferences and pay the same prices for the goods which they consume. If both consumers maximise utility then the marginal utility from each good consumed will be:
Correct
Answer C: According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{\mathrm{MU}_1}{\mathrm{p}_1}=\frac{\mathrm{MU}_2}{\mathrm{p}_2}=\cdots=\frac{\mathrm{MU}_{\mathrm{n}}}{\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{n}}}
$$
where MU and p refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the n goods.
Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer X has a higher income, so Consumer X will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and D.
Let’s consider marginal utility. Since marginal utility diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer X will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer Y . Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
Incorrect
Answer C: According to marginal utility theory, a consumer maximises total utility from a given level of income when the marginal utility per $£$ spent is equal for all goods, ie when:
$$
\frac{\mathrm{MU}_1}{\mathrm{p}_1}=\frac{\mathrm{MU}_2}{\mathrm{p}_2}=\cdots=\frac{\mathrm{MU}_{\mathrm{n}}}{\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{n}}}
$$
where MU and p refer to the marginal utility and the price of each of the n goods.
Given a consumer’s total and marginal utility schedules, a number of combinations of goods will meet this rule, but the actual choice will depend on the consumer’s income. The higher the consumer’s income, the more goods the consumer will be able to afford to buy. Assuming positive marginal utility from additional consumption, the more goods the consumer buys, the higher the consumer’s total utility.In this case, as the two consumers have identical preferences (ie they have the same marginal utility for each unit of each good consumed) and pay the same prices for the goods, they would end up buying identical quantities of each good if their incomes were equal.
However, the question states that Consumer X has a higher income, so Consumer X will be able to afford more of all goods and will therefore have a higher total utility. This rules out Options B and D.
Let’s consider marginal utility. Since marginal utility diminishes with the quantity consumed, Consumer X will have a lower marginal utility than Consumer Y . Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Note that, by definition, demand increases with income for normal goods, whereas the opposite is true for inferior goods. The answer therefore implicitly assumes that all goods are normal goods, whereas in practice, a minority of goods will actually be inferior goods.
-
Question 536 of 999CB2031429
Question 536
FlagA consumer uses only two goods, X and Y . Currently the marginal utility of the last unit of Good X consumed is six times as great as the marginal utility of the last unit of Good $Y$ consumed. The price of Good X is three times that of Good Y. To maximise utility, the consumer should:
Correct
Answer A :Recall that consumers are maximising their utility when:
$$
\frac{\text { Marginal utility of Good } \mathrm{X}\left(\mathrm{MU}_{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\text { Marginal utility of Good } \mathrm{Y}\left(\mathrm{MU}_{\mathrm{y}}\right)}=\frac{\text { Price of Good } \mathrm{X}\left(\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\text { Price of Good } \mathrm{Y}\left(\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{y}}\right)}
$$The question states that:
$$
\frac{M U_x}{M U_y}=6 \text { and } \frac{P_x}{P_y}=3
$$In other words, the consumer current receives six times as much utility from consuming Good $X$ than from consuming Good $Y$, but at only three times the cost. Therefore, the consumer should consume more of Good $X$ and less of Good $Y$. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
As the consumption of Good $X$ increases, the marginal utility of Good $X$ will fall, and as the consumption of Good $Y$ decreases, the marginal utility of Good $Y$ will rise. The consumer will therefore continue to reallocate expenditure in favour of Good $X$ as long as the ratio of the marginal utility of Good $X$ to the marginal utility of Good $Y\left(M U_x / M U_y\right)$ exceeds the price ratio of 3 .
Incorrect
Answer A :Recall that consumers are maximising their utility when:
$$
\frac{\text { Marginal utility of Good } \mathrm{X}\left(\mathrm{MU}_{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\text { Marginal utility of Good } \mathrm{Y}\left(\mathrm{MU}_{\mathrm{y}}\right)}=\frac{\text { Price of Good } \mathrm{X}\left(\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{x}}\right)}{\text { Price of Good } \mathrm{Y}\left(\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{y}}\right)}
$$The question states that:
$$
\frac{M U_x}{M U_y}=6 \text { and } \frac{P_x}{P_y}=3
$$In other words, the consumer current receives six times as much utility from consuming Good $X$ than from consuming Good $Y$, but at only three times the cost. Therefore, the consumer should consume more of Good $X$ and less of Good $Y$. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
As the consumption of Good $X$ increases, the marginal utility of Good $X$ will fall, and as the consumption of Good $Y$ decreases, the marginal utility of Good $Y$ will rise. The consumer will therefore continue to reallocate expenditure in favour of Good $X$ as long as the ratio of the marginal utility of Good $X$ to the marginal utility of Good $Y\left(M U_x / M U_y\right)$ exceeds the price ratio of 3 .
-
Question 537 of 999CB2031430
Question 537
FlagWhen a consumer with a given income chooses between two goods with fixed prices, the slope of the budget line is equal to the:
Correct
Answer A :The budget line shows the combinations of two goods that consumers can purchase if they spend all of their incomes on the two goods. The budget line therefore reflects the relative prices of the two goods, ie its gradient is equal to the ratio of their prices and so Option A is the correct answer.
The income of the consumer divided by the price of each good (Option B) gives the number of units of each good that the consumer can afford if they buy none of the other good, ie the intersection points on each axis. Option B is therefore incorrect.
Options C and D relate to utility, which is reflected in indifference curves, but not the budget line and so are both incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer A :The budget line shows the combinations of two goods that consumers can purchase if they spend all of their incomes on the two goods. The budget line therefore reflects the relative prices of the two goods, ie its gradient is equal to the ratio of their prices and so Option A is the correct answer.
The income of the consumer divided by the price of each good (Option B) gives the number of units of each good that the consumer can afford if they buy none of the other good, ie the intersection points on each axis. Option B is therefore incorrect.
Options C and D relate to utility, which is reflected in indifference curves, but not the budget line and so are both incorrect.
-
Question 538 of 999CB2031432
Question 538
FlagWater is generally cheaper than diamonds when consumers are in equilibrium because the:
Correct
Answer C: The diamonds-water paradox explores why water, which is essential to life, is so much cheaper than diamonds, which are not essential.
Although the total utility derived from water is very high and the total utility derived from diamonds is far lower, it is marginal utility, not total utility, that determines prices. The much lower consumption of diamonds means that the marginal utility of diamonds is much higher than the marginal utility of water, and so the amount someone would be willing to pay (ie the price) for one more diamond is much greater than that for one more glass of water. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: The diamonds-water paradox explores why water, which is essential to life, is so much cheaper than diamonds, which are not essential.
Although the total utility derived from water is very high and the total utility derived from diamonds is far lower, it is marginal utility, not total utility, that determines prices. The much lower consumption of diamonds means that the marginal utility of diamonds is much higher than the marginal utility of water, and so the amount someone would be willing to pay (ie the price) for one more diamond is much greater than that for one more glass of water. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 539 of 999CB2031433
Question 539
FlagIn relation to insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that:
Correct
Answer D: In the context of insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that policyholders may, because they have insurance, act in a way that makes the insured event more likely. Option D is therefore the correct answer.
Option A describes the problem of adverse selection: the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks.
Incorrect
Answer D: In the context of insurance, moral hazard describes the fact that policyholders may, because they have insurance, act in a way that makes the insured event more likely. Option D is therefore the correct answer.
Option A describes the problem of adverse selection: the fact that people who know that they are particularly bad risks are more inclined to take out insurance than those who know that they are good risks.
-
Question 540 of 999CB2031434
Question 540
FlagA consumer has £ 200 of income, which is spent entirely on two goods, Good X and Good Y. Good X costs £ 40 per unit and Good Y costs £ 40 per unit.
The relevant marginal utilities for the consumer are:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline Good X & Good Y \\
\hline \text{Quantity (in units)} & \text{Marginal utility} & \text{Quantity (in units)} & \text{Marginal utility} \\
\hline 1 & 100 & 1 & 70 \\
\hline 2 & 80 & 2 & 50 \\
\hline 3 & 50 & 3 & 40 \\
\hline 4 & 25 & 4 & 30 \\
\hline 5 & 10 & 5 & 20 \\
\hline
\end{array}The optimum combination of units of Good X and Good Y for the consumer to purchase is:
Correct
Answer C:
Since the price of both goods is $£ 40$ and since the consumer spends the entire $£ 200$ of income on them, the consumer must purchase a total of five goods.
When choosing the optimal combination of the two goods to purchase, the consumer will aim to maximise total utility, which will always involve choosing the good with the highest marginal utility.
Hence the consumer will select:
– a unit of Good X (with marginal utility of 100) as the first unit
– a unit of Good X (with marginal utility of 80) as the second unit
– a unit of Good $Y$ (with marginal utility of 70 ) as the third unit
– a unit of Good X and a unit of Good Y (both with marginal utilities of 50) as the fourth and fifth units.In total, the consumer will therefore consume three units of Good X and two units of Good Y, which corresponds to Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C:
Since the price of both goods is $£ 40$ and since the consumer spends the entire $£ 200$ of income on them, the consumer must purchase a total of five goods.
When choosing the optimal combination of the two goods to purchase, the consumer will aim to maximise total utility, which will always involve choosing the good with the highest marginal utility.
Hence the consumer will select:
– a unit of Good X (with marginal utility of 100) as the first unit
– a unit of Good X (with marginal utility of 80) as the second unit
– a unit of Good $Y$ (with marginal utility of 70 ) as the third unit
– a unit of Good X and a unit of Good Y (both with marginal utilities of 50) as the fourth and fifth units.In total, the consumer will therefore consume three units of Good X and two units of Good Y, which corresponds to Option C.
-
Question 541 of 999CB2031435
Question 541
FlagIf the money supply increases due to an expansionary open market operation by the central bank, then the price of treasury bills will:Correct
Answer A
An expansionary open market operation to increase the money supply involves the central bank buying Treasury bills, hence the demand for Treasury bills increases. (By buying Treasury bills, the central bank is taking Treasury bills out of the markets and pumping money into the economy.)
The following diagram shows that an increase in the money supply will lead to a fall in short-term interest rates. This rules out Options B and C.
An increase in demand for Treasury bills leads to an increase in their price. Since the central bank wants to buy Treasury bills, demand for Treasury bills will increase and hence so will their price. This rules out Options C and D, hence the correct answer is Option A.
The increase in price is equivalent to a decrease in yield; this is because the more investors pay for the investment (ie the price), the lower the yield they will receive on it.
As the price increases and the yield decreases, the opportunity cost of holding money for asset purposes decreases, so holders of Treasury bills are encouraged to sell bills and hold cash instead. This causes a movement along the $\mathrm{M}_{\mathrm{d}}$ curve
Incorrect
Answer A
An expansionary open market operation to increase the money supply involves the central bank buying Treasury bills, hence the demand for Treasury bills increases. (By buying Treasury bills, the central bank is taking Treasury bills out of the markets and pumping money into the economy.)
The following diagram shows that an increase in the money supply will lead to a fall in short-term interest rates. This rules out Options B and C.
An increase in demand for Treasury bills leads to an increase in their price. Since the central bank wants to buy Treasury bills, demand for Treasury bills will increase and hence so will their price. This rules out Options C and D, hence the correct answer is Option A.
The increase in price is equivalent to a decrease in yield; this is because the more investors pay for the investment (ie the price), the lower the yield they will receive on it.
As the price increases and the yield decreases, the opportunity cost of holding money for asset purposes decreases, so holders of Treasury bills are encouraged to sell bills and hold cash instead. This causes a movement along the $\mathrm{M}_{\mathrm{d}}$ curve
-
Question 542 of 999CB2031436
Question 542
FlagA consumer has been consuming Good X , which previously had a positive marginal utility, to the point that the consumer now has a zero marginal utility and Good X is a free good. This means that the:
Correct
Answer A :Good X is a free good, so the consumer should continue to consume it while it has positive marginal utility, because doing so will increase the consumer’s total utility, so Option B is not correct.
Since Good X previously had a positive marginal utility (and there is no indication that it has ever had a negative marginal utility), the total utility derived from consuming it must be positive. So Option D is not correct. Option C is also incorrect: reducing consumption will only increase total utility if the marginal utility of consuming those units is negative.
Since the marginal utility of consuming extra units is now zero, the consumer has reached a level of maximum utility, and has no incentive to decrease or increase consumption. This can be described as a point of equilibrium, and so Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A :Good X is a free good, so the consumer should continue to consume it while it has positive marginal utility, because doing so will increase the consumer’s total utility, so Option B is not correct.
Since Good X previously had a positive marginal utility (and there is no indication that it has ever had a negative marginal utility), the total utility derived from consuming it must be positive. So Option D is not correct. Option C is also incorrect: reducing consumption will only increase total utility if the marginal utility of consuming those units is negative.
Since the marginal utility of consuming extra units is now zero, the consumer has reached a level of maximum utility, and has no incentive to decrease or increase consumption. This can be described as a point of equilibrium, and so Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 543 of 999CB2031437
Question 543
FlagGood X is an inferior good (but not a Giffen good). If a budget line is drawn with quantity of Good Y on the vertical axis and quantity of Good X on the horizontal axis, a fall in price of Good X will cause the budget line of the consumer to:
Correct
Answer B: The budget line reflects the relative prices of the two goods.
A fall in the price of Good $X$ will mean that consumers are able to afford more units of Good X . The budget line will therefore intersect the $x$-axis further to the right. Since the price of Good Y remains unchanged, the budget line will still intersect the $y$-axis in the same place. The budget line will therefore become flatter, and the correct answer must be Option B.Incorrect
Answer B: The budget line reflects the relative prices of the two goods.
A fall in the price of Good $X$ will mean that consumers are able to afford more units of Good X . The budget line will therefore intersect the $x$-axis further to the right. Since the price of Good Y remains unchanged, the budget line will still intersect the $y$-axis in the same place. The budget line will therefore become flatter, and the correct answer must be Option B. -
Question 544 of 999CB2031438
Question 544
FlagIf Good X is a Giffen good then a rise in the price of Good X will result in:
Correct
Answer D :A Giffen good is defined as an inferior good whose demand increases as its price increases. This is consistent with Option D, which is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D :A Giffen good is defined as an inferior good whose demand increases as its price increases. This is consistent with Option D, which is the correct answer.
-
Question 545 of 999CB2031439
Question 545
FlagAn indifference set is a:
Correct
Answer B: An indifference set is the alternative combinations of two goods that yield the same level of satisfaction. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B: An indifference set is the alternative combinations of two goods that yield the same level of satisfaction. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 546 of 999CB2031440
Question 546
FlagThe endowment effect is associated with people exhibiting which characteristic?
Correct
Answer C: According to the textbook, the endowment effect (or divestiture aversion) is the hypothesis that people ascribe more value to things when they own them than when they are merely considering purchasing or acquiring them – in other words, when the reference point is one of ownership rather than non-ownership.
Furthermore, it states that the theory of reference dependent preferences leads to another important result: that of reference dependent loss aversion. Outcomes coded as losses are disliked more than the pleasure received from an equivalent sized gain.
Incorrect
Answer C: According to the textbook, the endowment effect (or divestiture aversion) is the hypothesis that people ascribe more value to things when they own them than when they are merely considering purchasing or acquiring them – in other words, when the reference point is one of ownership rather than non-ownership.
Furthermore, it states that the theory of reference dependent preferences leads to another important result: that of reference dependent loss aversion. Outcomes coded as losses are disliked more than the pleasure received from an equivalent sized gain.
-
Question 547 of 999CB2031441
Question 547
FlagThe difference between what an individual is willing to pay and what they actually pay for a good is:
Correct
Answer B: Total consumer surplus is defined as the total excess of what the people would have paid over what they actually paid for the goods consumed and so represents the total utility gained less the total expenditure. This corresponds to Option B.
Incorrect
Answer B: Total consumer surplus is defined as the total excess of what the people would have paid over what they actually paid for the goods consumed and so represents the total utility gained less the total expenditure. This corresponds to Option B.
-
Question 548 of 999CB2031442
Question 548
FlagAn individual likes pears and peaches. Assume that their income doubles and the prices of pears and peaches also doubles. The individual’s budget line will:
Correct
Answer B: The budget line shows the combinations of two goods that consumers can purchase if they spend all of their incomes on the two goods. The budget line therefore reflects the relative prices of the two goods, ie its gradient is equal to the ratio of their prices.
Since the prices of pears and peaches have both doubled, the relative prices of the two goods remain unchanged, and so the slope of the budget line remains unchanged. This rules out Option D.
The income of the consumer divided by the price of each good gives the number of units of each good that the consumer can afford if they buy none of the other good, ie the intersection points on each axis. Since both income and prices have doubled, the intersection points on each axis also remain unchanged. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B: The budget line shows the combinations of two goods that consumers can purchase if they spend all of their incomes on the two goods. The budget line therefore reflects the relative prices of the two goods, ie its gradient is equal to the ratio of their prices.
Since the prices of pears and peaches have both doubled, the relative prices of the two goods remain unchanged, and so the slope of the budget line remains unchanged. This rules out Option D.
The income of the consumer divided by the price of each good gives the number of units of each good that the consumer can afford if they buy none of the other good, ie the intersection points on each axis. Since both income and prices have doubled, the intersection points on each axis also remain unchanged. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 549 of 999CB2031443
Question 549
FlagA consumer is considering buying a new car. It will cost $£ 10,000$ at the outset, it will last for 10 years, it will cost $£ 500$ per year to run and will yield $£ 1,600$ of utility each year of its life. Should the consumer buy the car?
Correct
Option D.
We need to calculate the present value of the costs and benefits. To do this we need to know the discount factor, ie the factor that we need to multiply a cost or benefit in the future by to adjust it to what it would be worth to the consumer now.For example, if the yearly discount factor is 0.9 , and if the costs and benefits are assumed to occur at the end of each year (to make the arithmetic easier):
the present value of the costs
$
\begin{aligned}
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500+0.9^2 \times £ 500+\cdots+0.9^{10} \times £ 500 \\
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500\left(1+0.9+\cdots+0.9^9\right) \\
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500 \frac{\left(1-0.9^{10}\right)}{(1-0.9)} \text { using the formula for the sum of a GP } \\
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500 \times 6.5132 \\
& =£ 12,930.95
\end{aligned}
$
the present value of the benefits
$
\begin{aligned}
& =0.9 \times £ 1,600+0.9^2 \times £ 1,600+\cdots+0.9^{10} \times £ 1,600 \\
& =0.9 \times £ 1,600\left(1+0.9+\cdots+0.9^9\right) \\
& =0.9 \times £ 1,600 \times 6.5132 \\
& =£ 9,379.03
\end{aligned}
$So, in this case, the present value of the benefits does not exceed the present value of the costs and the car would not be worth buying.
Incorrect
Option D.
We need to calculate the present value of the costs and benefits. To do this we need to know the discount factor, ie the factor that we need to multiply a cost or benefit in the future by to adjust it to what it would be worth to the consumer now.For example, if the yearly discount factor is 0.9 , and if the costs and benefits are assumed to occur at the end of each year (to make the arithmetic easier):
the present value of the costs
$
\begin{aligned}
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500+0.9^2 \times £ 500+\cdots+0.9^{10} \times £ 500 \\
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500\left(1+0.9+\cdots+0.9^9\right) \\
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500 \frac{\left(1-0.9^{10}\right)}{(1-0.9)} \text { using the formula for the sum of a GP } \\
& =£ 10,000+0.9 \times £ 500 \times 6.5132 \\
& =£ 12,930.95
\end{aligned}
$
the present value of the benefits
$
\begin{aligned}
& =0.9 \times £ 1,600+0.9^2 \times £ 1,600+\cdots+0.9^{10} \times £ 1,600 \\
& =0.9 \times £ 1,600\left(1+0.9+\cdots+0.9^9\right) \\
& =0.9 \times £ 1,600 \times 6.5132 \\
& =£ 9,379.03
\end{aligned}
$So, in this case, the present value of the benefits does not exceed the present value of the costs and the car would not be worth buying.
-
Question 550 of 999CB2031444
Question 550
FlagWhich of the following statements is TRUE?
Correct
Option B.
If the price elasticity of demand is equal to -1 , the overall effect of a price reduction is a proportionate increase in quantity demanded, whereas if the substitution and income effects are equal in magnitude and act in opposite directions, they would cancel each other out exactly, so that quantity demanded remained the same. In this case, the price elasticity of demand would be zero and not -1 .An inferior good is one for which the income and substitution effects act in the opposite direction.
For a normal good the income and substitution effects act in the same direction, so the income effect from a price increase will lead to a reduction in quantity demanded.The substitution effect always reduces the quantity demanded in response to a price increase, regardless of the type of good.
Incorrect
Option B.
If the price elasticity of demand is equal to -1 , the overall effect of a price reduction is a proportionate increase in quantity demanded, whereas if the substitution and income effects are equal in magnitude and act in opposite directions, they would cancel each other out exactly, so that quantity demanded remained the same. In this case, the price elasticity of demand would be zero and not -1 .An inferior good is one for which the income and substitution effects act in the opposite direction.
For a normal good the income and substitution effects act in the same direction, so the income effect from a price increase will lead to a reduction in quantity demanded.The substitution effect always reduces the quantity demanded in response to a price increase, regardless of the type of good.
-
Question 551 of 999CB2031445
Question 551
FlagSuppose there are two investment alternatives that an investor can afford, A and B. Investment A will generate a revenue of £ 1,000 per year for certain and B will generate a revenue of either £ 500, £ 1,000 or £ 1,500 per year with equal probability of one-third. Assuming that the acquisition cost of each investment is equal, which one of the following statements is always TRUE?
Correct
Option C. The first thing to note is that Investments A and B both offer the same expected return of £ 1,000 per year and so Option B is incorrect. A risk-loving investor is one who will always choose to accept a gamble if the odds are fair. Given that Investments A and B offer the same expected return, the risk-loving investor will choose the riskier alternative, ie Investment B. Conversely, a risk-averse investor will choose Investment A precisely because it is less risky. A risk-neutral investor will be indifferent between Investment A and Investment B , and therefore might choose Investment B, but will not always do so.
Incorrect
Option C. The first thing to note is that Investments A and B both offer the same expected return of £ 1,000 per year and so Option B is incorrect. A risk-loving investor is one who will always choose to accept a gamble if the odds are fair. Given that Investments A and B offer the same expected return, the risk-loving investor will choose the riskier alternative, ie Investment B. Conversely, a risk-averse investor will choose Investment A precisely because it is less risky. A risk-neutral investor will be indifferent between Investment A and Investment B , and therefore might choose Investment B, but will not always do so.
-
Question 552 of 999CB2031446
Question 552
FlagWhich of the following is NOT true about a risk-averse investor?
Correct
Option B. A risk-averse investor will always reject a gamble if the odds are fair (Option A). He or she will value an incremental gain in wealth less than the same incremental decrease in wealth precisely because the marginal utility of wealth decreases as wealth increases (Option C). In addition, the insurance premium that a risk-averse person is prepared to pay is greater than the long-run average value of claims in order to reduce or remove the risk that they face (Option D). However, we cannot say that a risk-averse person will avoid all risk. All we can say is that a risk-averse person might accept a gamble if the expected value of the gamble is greater than the certain payoff from not taking the gamble.
Incorrect
Option B. A risk-averse investor will always reject a gamble if the odds are fair (Option A). He or she will value an incremental gain in wealth less than the same incremental decrease in wealth precisely because the marginal utility of wealth decreases as wealth increases (Option C). In addition, the insurance premium that a risk-averse person is prepared to pay is greater than the long-run average value of claims in order to reduce or remove the risk that they face (Option D). However, we cannot say that a risk-averse person will avoid all risk. All we can say is that a risk-averse person might accept a gamble if the expected value of the gamble is greater than the certain payoff from not taking the gamble.
-
Question 553 of 999CB2031447
Question 553
FlagWhich of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Option B. The risk premium is the expected value of a gamble minus the person’s certainty equivalent of the gamble (so Option A is incorrect), where the certainty equivalent is the certain amount of money that would give the person the same amount of utility as the expected value of the gamble (so Option D is incorrect). For risk-loving people, the risk premium is negative because the expected value of the gamble is less than the certainty equivalent. (For risk-neutral people, the risk premium is zero because the expected value of the gamble is equal to the certainty equivalent. For risk-averse people, the risk premium is positive because the expected value of the gamble is greater than the certainty equivalent of the gamble (so Option C is incorrect).)
Incorrect
Option B. The risk premium is the expected value of a gamble minus the person’s certainty equivalent of the gamble (so Option A is incorrect), where the certainty equivalent is the certain amount of money that would give the person the same amount of utility as the expected value of the gamble (so Option D is incorrect). For risk-loving people, the risk premium is negative because the expected value of the gamble is less than the certainty equivalent. (For risk-neutral people, the risk premium is zero because the expected value of the gamble is equal to the certainty equivalent. For risk-averse people, the risk premium is positive because the expected value of the gamble is greater than the certainty equivalent of the gamble (so Option C is incorrect).)
-
Question 554 of 999CB2031448
Question 554
FlagBehavioural economics differs from traditional economics in all of the following ways except one. Which is the exception?
Correct
Option B. Traditional economic theory assumes that people behave rationally. Even if traditional economists recognise that people do not behave rationally all of the time, they assume that any mistakes resulting from irrational choices would balance out on average. Behavioural economists recognise that people act irrationally – they act out of habit, on impulse, are influenced by group behaviour, and have to make decisions with imperfect information. Although experiments are rarely used by traditional economists, they are often used by behavioural economists.
Incorrect
Option B. Traditional economic theory assumes that people behave rationally. Even if traditional economists recognise that people do not behave rationally all of the time, they assume that any mistakes resulting from irrational choices would balance out on average. Behavioural economists recognise that people act irrationally – they act out of habit, on impulse, are influenced by group behaviour, and have to make decisions with imperfect information. Although experiments are rarely used by traditional economists, they are often used by behavioural economists.
-
Question 555 of 999CB2031449
Question 555
FlagThe law of diminishing marginal utility applied to consumption of Good X implies that the:
Correct
Option B. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the increase in the total utility derived from the consumption of a good decreases with each additional unit consumed. In other words, utility increases, but at a decreasing rate.
Incorrect
Option B. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the increase in the total utility derived from the consumption of a good decreases with each additional unit consumed. In other words, utility increases, but at a decreasing rate.
-
Question 556 of 999CB2031450
Question 556
FlagWhich of the following is a measure of total consumer surplus?
Correct
Option C. Total consumer surplus is the excess of what the person would have paid over what the person actually paid for the goods consumed and so represents the total utility gained less the total expenditure.
Incorrect
Option C. Total consumer surplus is the excess of what the person would have paid over what the person actually paid for the goods consumed and so represents the total utility gained less the total expenditure.
-
Question 557 of 999CB2031451
Question 557
FlagA change in consumer tastes would change:
Correct
Option A.
A consumer’s indifference curve reflects the consumer’s preferences. The budget line displays what the consumer can afford, given the consumer’s income and the prices of the goods.A change in consumer tastes would therefore change the indifference curve. The absolute value of the gradient of the indifference curve is equal to the marginal rate of substitution, ie the amount of one good the consumer would be willing to give up to obtain another unit of the other good. A change in tastes would therefore change the marginal rate of substitution (and hence the slope of the indifference curve).
Incorrect
Option A.
A consumer’s indifference curve reflects the consumer’s preferences. The budget line displays what the consumer can afford, given the consumer’s income and the prices of the goods.A change in consumer tastes would therefore change the indifference curve. The absolute value of the gradient of the indifference curve is equal to the marginal rate of substitution, ie the amount of one good the consumer would be willing to give up to obtain another unit of the other good. A change in tastes would therefore change the marginal rate of substitution (and hence the slope of the indifference curve).
-
Question 558 of 999CB2031452
Question 558
FlagConsumer A purchases Good X and Good Y. If Consumer A’s income and the prices of Good X and Good $Y$ double Consumer A’s budget line will:
Correct
Option A. The budget line shows the combinations of Goods X and Y that Consumer A can purchase if all income is spent on the two goods. If both prices double and income also doubles, then exactly the same bundles of goods as before could be purchased. Consequently, the budget line should be unchanged.
Incorrect
Option A. The budget line shows the combinations of Goods X and Y that Consumer A can purchase if all income is spent on the two goods. If both prices double and income also doubles, then exactly the same bundles of goods as before could be purchased. Consequently, the budget line should be unchanged.
-
Question 559 of 999CB2031453
Question 559
FlagThe budget line for a particular consumer is given as:
$$
3 Q_x+2 Q_y=30
$$
where $Q_{\mathrm{x}}$ is the quantity of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ and $Q_{\mathrm{y}}$ is the quantity of Good Y .
Goods $X$ and $Y$ can only be consumed in whole units.
Which of the following is TRUE?Correct
Option D.
The budget line is given as:
$$
3 Q_x+2 Q_y=30
$$
so we know that the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ is 3 , the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{Y}$ is 2 and the consumer’s income is 30.We can rearrange the equation as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
2 Q_{\mathrm{y}} & =30-3 Q_{\mathrm{x}} \\
Q_{\mathrm{y}} & =15-1.5 Q_{\mathrm{x}}
\end{aligned}
$$Hence we can draw the budget line.
At equilibrium, the slope of the indifference curve (which is the marginal rate of substitution of Good $X$ for Good $Y$ ) is equal to the slope of the budget line. The slope of the budget line is -1.5 .
Incorrect
Option D.
The budget line is given as:
$$
3 Q_x+2 Q_y=30
$$
so we know that the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{X}$ is 3 , the price of $\operatorname{Good} \mathrm{Y}$ is 2 and the consumer’s income is 30.We can rearrange the equation as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
2 Q_{\mathrm{y}} & =30-3 Q_{\mathrm{x}} \\
Q_{\mathrm{y}} & =15-1.5 Q_{\mathrm{x}}
\end{aligned}
$$Hence we can draw the budget line.
At equilibrium, the slope of the indifference curve (which is the marginal rate of substitution of Good $X$ for Good $Y$ ) is equal to the slope of the budget line. The slope of the budget line is -1.5 .
-
Question 560 of 999CB2031454
Question 560
FlagA Giffen good has an income elasticity of demand that is:
Correct
Option A. Giffen goods must be inferior goods and therefore they have a negative income elasticity of demand. In the case of Giffen goods, the positive income effect of a price change outweighs the negative substitution effect of a price change, so that the price elasticity of demand is positive.
Incorrect
Option A. Giffen goods must be inferior goods and therefore they have a negative income elasticity of demand. In the case of Giffen goods, the positive income effect of a price change outweighs the negative substitution effect of a price change, so that the price elasticity of demand is positive.
-
Question 561 of 999CB2031455
Question 561
FlagWhich one of the following provides an economic explanation of risk aversion?
Correct
Option C. A risk-averse individual will reject a fair gamble because the increase in utility from an incremental increase in income is lower than the decrease in utility from an incremental decrease. This is precisely because the marginal utility of income decreases with income. Option A is simply the opposite of the truth. Option B may be true but it does not give an ‘economic explanation of risk aversion’. The meaning of Option D is unclear.
Incorrect
Option C. A risk-averse individual will reject a fair gamble because the increase in utility from an incremental increase in income is lower than the decrease in utility from an incremental decrease. This is precisely because the marginal utility of income decreases with income. Option A is simply the opposite of the truth. Option B may be true but it does not give an ‘economic explanation of risk aversion’. The meaning of Option D is unclear.
-
Question 562 of 999CB2031456
Question 562
FlagAdverse selection describes the fact that people who know that they are particularly:
Correct
Option C. The first sentence in Option C is the definition of adverse selection. This is the same as the first sentence in Option A. The second sentence in Option C is not part of the definition of adverse selection; it is the correct response of the insurance companies to the problem. This was not strictly asked for in the question, but Option C is the more sensible option to choose.
Incorrect
Option C. The first sentence in Option C is the definition of adverse selection. This is the same as the first sentence in Option A. The second sentence in Option C is not part of the definition of adverse selection; it is the correct response of the insurance companies to the problem. This was not strictly asked for in the question, but Option C is the more sensible option to choose.
-
Question 563 of 999CB2031458
Question 563
FlagA firm’s total costs are £ 150 when 10 units are produced and the marginal cost of the 10 th unit is £ 40. The marginal cost of the 11 th unit is £ 15. Which of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer: D
If the total cost (T C) of producing 10 units is £ 150, then the average cost (A C) of producing each of those 10 units is £ 15.
If the marginal cost $(\mathrm{MC})$ of the 11 th unit is £ 15, then producing the 11 th unit will add £ 15 to the TC, which will then be £ 165. However, as the MC of the 11th unit is equal to the AC of the original 10 units, producing the 11 th unit will not change the AC, which will remain at £ 15.
You can confirm this by calculating the AC of 11 units as:
$$
\frac{165}{11}=£ 15
$$Let’s now consider each of the four options presented in turn.
As you’ve just seen, the AC of 11 units is the same as that for 10 units. Consequently, Option A is incorrect.As the total cost of 11 units is $£ 165$, the existence of marginal costs, which are simply the variable cost of each additional unit, indicates that the total fixed cost must be less than $£ 165$. So, Option B is incorrect.
Following on from this, if the total fixed cost is less than $£ 165$, then the average fixed cost of each of those 11 units must be less than the average (total ) cost of $£ 15$ and hence also less than the MC of the 11 th unit, which is also $£ 15$. So, Option C must be incorrect and Option D must be correct.
Note that in this example, the MC is falling (from $£ 40$ for the 10th unit to $£ 15$ for the 11th unit) when it is equal to the AC. This is in contrast to the usual situation, where the MC curve cuts the AC curve from below and at its minimum, with MC increasing.
Incorrect
Answer: D
If the total cost (T C) of producing 10 units is £ 150, then the average cost (A C) of producing each of those 10 units is £ 15.
If the marginal cost $(\mathrm{MC})$ of the 11 th unit is £ 15, then producing the 11 th unit will add £ 15 to the TC, which will then be £ 165. However, as the MC of the 11th unit is equal to the AC of the original 10 units, producing the 11 th unit will not change the AC, which will remain at £ 15.
You can confirm this by calculating the AC of 11 units as:
$$
\frac{165}{11}=£ 15
$$Let’s now consider each of the four options presented in turn.
As you’ve just seen, the AC of 11 units is the same as that for 10 units. Consequently, Option A is incorrect.As the total cost of 11 units is $£ 165$, the existence of marginal costs, which are simply the variable cost of each additional unit, indicates that the total fixed cost must be less than $£ 165$. So, Option B is incorrect.
Following on from this, if the total fixed cost is less than $£ 165$, then the average fixed cost of each of those 11 units must be less than the average (total ) cost of $£ 15$ and hence also less than the MC of the 11 th unit, which is also $£ 15$. So, Option C must be incorrect and Option D must be correct.
Note that in this example, the MC is falling (from $£ 40$ for the 10th unit to $£ 15$ for the 11th unit) when it is equal to the AC. This is in contrast to the usual situation, where the MC curve cuts the AC curve from below and at its minimum, with MC increasing.
-
Question 564 of 999CB2031459
Question 564
FlagThe total output and the average physical product of the variable factor of production both always increase as long as the marginal physical product of the variable factor is:
Correct
Answer: B
Recall that average physical product (APP) is equal to the TPP per unit of a variable factor. So, if $Q_v$ is the quantity of the variable factor:
$$
A P P=\frac{T P P}{Q_v}
$$In addition, marginal physical product (MPP) is the extra output produced by employing one extra unit of the variable factor, when the input of other factors is held constant, ie:
$$
M P P=\frac{\Delta T P P}{\Delta Q_v}
$$Hence, so long as the MPP is above the APP, then the APP must be increasing.
To see, this suppose that the APP of the first 10 units of input is 10 and that the MPP of the 11th unit of input is 15. Employing the extra unit of input will increase output by 15, which is more than the APP, causing the APP itself to increase to:
$$
A P P=\frac{100+15}{11}=10.45
$$Note also that provided output cannot be negative, then APP must also be positive. This means that when MPP > APP, then MPP must be positive, in which case adding an extra unit of input must increase total output. So, Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Recall that average physical product (APP) is equal to the TPP per unit of a variable factor. So, if $Q_v$ is the quantity of the variable factor:
$$
A P P=\frac{T P P}{Q_v}
$$In addition, marginal physical product (MPP) is the extra output produced by employing one extra unit of the variable factor, when the input of other factors is held constant, ie:
$$
M P P=\frac{\Delta T P P}{\Delta Q_v}
$$Hence, so long as the MPP is above the APP, then the APP must be increasing.
To see, this suppose that the APP of the first 10 units of input is 10 and that the MPP of the 11th unit of input is 15. Employing the extra unit of input will increase output by 15, which is more than the APP, causing the APP itself to increase to:
$$
A P P=\frac{100+15}{11}=10.45
$$Note also that provided output cannot be negative, then APP must also be positive. This means that when MPP > APP, then MPP must be positive, in which case adding an extra unit of input must increase total output. So, Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 565 of 999CB2031460
Question 565
FlagGlobal Airways, which is a profit-maximising firm, has to decide whether or not to run an extra daily flight between London and Edinburgh. The total daily fixed costs of the airline are $£ 4,000$, the total variable costs of the extra flight are $£ 5,000$ and the expected revenue from the extra flight is $£ 5,500$. In such circumstances Global Airways will:
Correct
Answer: C
In deciding whether to run the extra flight, Global Airways will need to consider the marginal cost and the marginal revenue of the extra flight. Recall that marginal cost is the cost of supplying an additional unit, ie it tell us the variable cost of supplying that additional unit, as fixed costs are already set. So, here $£ 5,000$ represents the marginal cost of the extra flight. As this is less than the £5,500 expected revenue from the extra flight, running the extra flight would increase profit. Consequently, Global Airways will run the extra flight and in doing so will increase its profits (or reduce its losses) by:
$$
£ 5,500-£ 5,000=£ 500
$$So, the correct answer is Option C.
Remember also that according to the bygones principles, fixed and sunk costs are both irrelevant in deciding how much to produce, or here, whether to run the extra flight. So, the fact that the total daily fixed costs are $£ 4,000$ is irrelevant in making the decision here.Incorrect
Answer: C
In deciding whether to run the extra flight, Global Airways will need to consider the marginal cost and the marginal revenue of the extra flight. Recall that marginal cost is the cost of supplying an additional unit, ie it tell us the variable cost of supplying that additional unit, as fixed costs are already set. So, here $£ 5,000$ represents the marginal cost of the extra flight. As this is less than the £5,500 expected revenue from the extra flight, running the extra flight would increase profit. Consequently, Global Airways will run the extra flight and in doing so will increase its profits (or reduce its losses) by:
$$
£ 5,500-£ 5,000=£ 500
$$So, the correct answer is Option C.
Remember also that according to the bygones principles, fixed and sunk costs are both irrelevant in deciding how much to produce, or here, whether to run the extra flight. So, the fact that the total daily fixed costs are $£ 4,000$ is irrelevant in making the decision here. -
Question 566 of 999CB2031462
Question 566
FlagDiseconomies of scale means:
Correct
Economies and diseconomies of scale are a long-run concept, ie they affect production in the long run. This rules out Options A and D.
More specifically, diseconomies of scale refer to the situation where long-run average costs rise as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore the correct answer is Option C.
Note that the corresponding short-run concept is the law of diminishing (marginal) returns.
Answer: C
Incorrect
Economies and diseconomies of scale are a long-run concept, ie they affect production in the long run. This rules out Options A and D.
More specifically, diseconomies of scale refer to the situation where long-run average costs rise as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore the correct answer is Option C.
Note that the corresponding short-run concept is the law of diminishing (marginal) returns.
Answer: C
-
Question 567 of 999CB2031463
Question 567
FlagWhen a monopolist maximises profits, price exceeds marginal revenue. The difference between price and marginal revenue occurs because:
Correct
A monopoly typically faces a downward-sloping demand curve. This means that it will need to reduce its price in order to sell more units.
Suppose it drops its price a little in order to sell exactly one more unit. Then the marginal revenue of this extra unit will be equal to the additional revenue received from selling that particular unit (ie the new and reduced selling price) less the loss of revenue from all of the previous units, which are now being sold for a lower price than before. It is this loss of revenue from the previous units which means that the marginal revenue must be less than the price.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Note that Option B is the opposite to Option C, and so is not the correct answer. Option A refers to cost, whereas the question is asking about the relationship between revenues (rather than costs). Option D (diminishing returns) relates to production in the short run – and so the law of diminishing returns affects costs, and hence price in the short run. However, it is not the reason why price exceeds marginal revenue.Answer: C
Incorrect
A monopoly typically faces a downward-sloping demand curve. This means that it will need to reduce its price in order to sell more units.
Suppose it drops its price a little in order to sell exactly one more unit. Then the marginal revenue of this extra unit will be equal to the additional revenue received from selling that particular unit (ie the new and reduced selling price) less the loss of revenue from all of the previous units, which are now being sold for a lower price than before. It is this loss of revenue from the previous units which means that the marginal revenue must be less than the price.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Note that Option B is the opposite to Option C, and so is not the correct answer. Option A refers to cost, whereas the question is asking about the relationship between revenues (rather than costs). Option D (diminishing returns) relates to production in the short run – and so the law of diminishing returns affects costs, and hence price in the short run. However, it is not the reason why price exceeds marginal revenue.Answer: C
-
Question 568 of 999CB2031464
Question 568
FlagWhich of the following statements regarding the productivity of labour is correct?
Correct
Answer: A
Average physical product (APP) is total physical product (TPP) per unit of the variable factor, ie $A P P=\frac{T P P}{Q_v}$ where $Q_v$ is the quantity of the variable factor.
Marginal physical product (MPP) is the extra output produced by employing one extra unit of the variable factor, when the input of other factors is held constant, ie $M P P=\frac{\Delta T P P}{\Delta Q_v}$.
Assuming that as production increases, it does so under increasing and then diminishing marginal returns to labour, the MPP curve will rise and then fall. This will cause the APP curve to also rise and then fall and to have the following relationship with the MPP curve:
The diagram shows that MPP $=A P P$ when the APP is at its maximum. This has to be the case by simple arithmetic:
– If $M P P>A P P$, ie the additional worker adds more to the total than the average, then the average (APP) will increase.
– If $M P P=A P P$, ie the additional worker adds the same to the total as the average, then APP will remain the same.
– If $M P P<A P P$, ie the additional worker adds less to the total than the average, then APP will fall.Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Average physical product (APP) is total physical product (TPP) per unit of the variable factor, ie $A P P=\frac{T P P}{Q_v}$ where $Q_v$ is the quantity of the variable factor.
Marginal physical product (MPP) is the extra output produced by employing one extra unit of the variable factor, when the input of other factors is held constant, ie $M P P=\frac{\Delta T P P}{\Delta Q_v}$.
Assuming that as production increases, it does so under increasing and then diminishing marginal returns to labour, the MPP curve will rise and then fall. This will cause the APP curve to also rise and then fall and to have the following relationship with the MPP curve:
The diagram shows that MPP $=A P P$ when the APP is at its maximum. This has to be the case by simple arithmetic:
– If $M P P>A P P$, ie the additional worker adds more to the total than the average, then the average (APP) will increase.
– If $M P P=A P P$, ie the additional worker adds the same to the total as the average, then APP will remain the same.
– If $M P P<A P P$, ie the additional worker adds less to the total than the average, then APP will fall.Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 569 of 999CB2031465
Question 569
FlagA firm’s fixed costs are £ 1,000 per period, the average total cost of its output is £ 4 and its average variable cost is £ 3.50. Which one of the following will represent its total output per period?
Correct
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { average total cost }=\frac{\text { total cost }}{\text { units of output }} \\
& \text { average total cost }=\frac{\text { total variable cost }}{\text { units of output }}+\frac{\text { total fixed cost }}{\text { units of output }} \\
& \text { average total cost }=\text { average variable cost }+ \text { average fixed cost }
\end{aligned}
$$The question gives us the following information:
1. total fixed costs $=£ 1,000$
2. average total cost $=£ 4$
3. average variable cost $=£ 3.50$The question has asked for the total output. So, using the final equation above, you can deduce that:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { average fixed cost } & =\text { average total cost }- \text { average variable cost } \\
& =£ 4-£ 3.50 \\
& =£ 0.50
\end{aligned}
$$The second and third equations above can then be used to determine the number of units of output produced, ie:
$$
\text { units of output }=\frac{\text { total fixed cost }}{\text { average fixed cost }}=\frac{£ 1,000}{£ 0.50}=2,000
$$Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Answer: C
Incorrect
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { average total cost }=\frac{\text { total cost }}{\text { units of output }} \\
& \text { average total cost }=\frac{\text { total variable cost }}{\text { units of output }}+\frac{\text { total fixed cost }}{\text { units of output }} \\
& \text { average total cost }=\text { average variable cost }+ \text { average fixed cost }
\end{aligned}
$$The question gives us the following information:
1. total fixed costs $=£ 1,000$
2. average total cost $=£ 4$
3. average variable cost $=£ 3.50$The question has asked for the total output. So, using the final equation above, you can deduce that:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { average fixed cost } & =\text { average total cost }- \text { average variable cost } \\
& =£ 4-£ 3.50 \\
& =£ 0.50
\end{aligned}
$$The second and third equations above can then be used to determine the number of units of output produced, ie:
$$
\text { units of output }=\frac{\text { total fixed cost }}{\text { average fixed cost }}=\frac{£ 1,000}{£ 0.50}=2,000
$$Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Answer: C
-
Question 570 of 999CB2031466
Question 570
FlagIncreasing long-run average costs are associated with:
Correct
Remember that:
– The long run is the period of time when all factors of production can be varied, so the whole scale of production can change.
– Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs do not vary with output, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production.
– Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. If factor costs do not vary with output, then this will result in long-run average costs that also do not vary with the scale of production.
– Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. If factor costs do not vary with output, then this will result in long-run average costs that increase with the scale of production.The answer is therefore Option C.
Note that Option D is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns applies to the short run only. The law states that as more of a variable factor is added to the fixed factors, ultimately the marginal physical product of the variable factor will fall. Since this theory assumes that there are fixed factors, it must apply to the short run only.
Answer: C
Incorrect
Remember that:
– The long run is the period of time when all factors of production can be varied, so the whole scale of production can change.
– Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs do not vary with output, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production.
– Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. If factor costs do not vary with output, then this will result in long-run average costs that also do not vary with the scale of production.
– Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. If factor costs do not vary with output, then this will result in long-run average costs that increase with the scale of production.The answer is therefore Option C.
Note that Option D is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns applies to the short run only. The law states that as more of a variable factor is added to the fixed factors, ultimately the marginal physical product of the variable factor will fall. Since this theory assumes that there are fixed factors, it must apply to the short run only.
Answer: C
-
Question 571 of 999CB2031469
Question 571
FlagIn the short run, the range of output over which average total cost falls will be the same as the range over which:
Correct
Answer: B
Average physical product (APP) is the total physical output per unit of a variable factor, eg the number of units produced divided by the quantity of labour:
$$
\text { APP }=\frac{\text { # of units of output }}{Q_{\text {labour }}}
$$If the APP rises, then the number of units of labour needed to produce each unit of output must be falling. Consequently, and assuming that the price of labour does not vary, then the average variable cost of output must fall. This in turn means that average total cost is likely to fall and so Option B is the correct answer.
Note that it is possible that the average total cost could fall even when average physical product falls. In particular, if the average fixed cost falls by more than the average variable cost rises, then the average total cost will also fall. However, this is unlikely to be the case in practice.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Average physical product (APP) is the total physical output per unit of a variable factor, eg the number of units produced divided by the quantity of labour:
$$
\text { APP }=\frac{\text { # of units of output }}{Q_{\text {labour }}}
$$If the APP rises, then the number of units of labour needed to produce each unit of output must be falling. Consequently, and assuming that the price of labour does not vary, then the average variable cost of output must fall. This in turn means that average total cost is likely to fall and so Option B is the correct answer.
Note that it is possible that the average total cost could fall even when average physical product falls. In particular, if the average fixed cost falls by more than the average variable cost rises, then the average total cost will also fall. However, this is unlikely to be the case in practice.
-
Question 572 of 999CB2031470
Question 572
FlagWhich one of the following reveals constant returns to scale?
Correct
Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. This is the case in Option D, which is therefore the correct answer.
Note that:
– increasing/decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater/smaller percentage change in output
– returns to scale is a long-run concept, as it assumes that the scale of production can be changed, ie the volumes of all factor inputs can be changed. This is in contrast to the marginal product of labour mentioned in Option A, which is a short-run concept, as it describes the increase in output from employing one more unit of labour, assuming that all other factor inputs are held constant.Answer: D
Incorrect
Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. This is the case in Option D, which is therefore the correct answer.
Note that:
– increasing/decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater/smaller percentage change in output
– returns to scale is a long-run concept, as it assumes that the scale of production can be changed, ie the volumes of all factor inputs can be changed. This is in contrast to the marginal product of labour mentioned in Option A, which is a short-run concept, as it describes the increase in output from employing one more unit of labour, assuming that all other factor inputs are held constant.Answer: D
-
Question 573 of 999CB2031472
Question 573
FlagGo Global Airways, which is a profit-maximising firm, has to decide whether or not to run an extra daily flight between London and Berlin. The total daily fixed costs of the airline are $£ 6,000$, the total variable costs of the extra flight are $£ 3,000$ and the expected revenue from the extra flight is $£ 4,500$. In such circumstances, Go Global Airways, which is overall a profitable firm. will:
Correct
In deciding whether to run the extra flight, Go Global Airways will need to consider its marginal cost and marginal revenue. Recall that marginal cost is the cost of supplying an additional unit, ie the variable cost of supplying that additional unit (as fixed costs are already set). So, here $£ 3,000$ represents the marginal cost of the extra flight. As this is less than the $£ 4,500$ expected revenue from the extra flight, running the extra flight would increase profit.
Consequently, Go Global Airways will run the extra flight, and in doing so will increase its profits (or reduce its losses) by:
$$
£ 4,500-£ 3,000=£ 1,500
$$So, the correct answer is Option C.
Answer: C
Incorrect
In deciding whether to run the extra flight, Go Global Airways will need to consider its marginal cost and marginal revenue. Recall that marginal cost is the cost of supplying an additional unit, ie the variable cost of supplying that additional unit (as fixed costs are already set). So, here $£ 3,000$ represents the marginal cost of the extra flight. As this is less than the $£ 4,500$ expected revenue from the extra flight, running the extra flight would increase profit.
Consequently, Go Global Airways will run the extra flight, and in doing so will increase its profits (or reduce its losses) by:
$$
£ 4,500-£ 3,000=£ 1,500
$$So, the correct answer is Option C.
Answer: C
-
Question 574 of 999CB2031473
Question 574
FlagWhich of the following reveals constant returns to scale?
Correct
Answer: A
Constant returns to scale arises when a given percentage increase in all factor inputs leads to an identical percentage increase in output. Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
As all factor inputs are varied, constant returns to scale is strictly a long-run phenomenon. In contrast, the marginal product of labour is a short-run phenomenon that is relevant when more units of a variable input (usually labour) are added to a given amount of a fixed factor (usually capital).
Given constant factor prices, constant returns to scale corresponds to a situation in which there are neither economies of scale nor diseconomies of scale.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Constant returns to scale arises when a given percentage increase in all factor inputs leads to an identical percentage increase in output. Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
As all factor inputs are varied, constant returns to scale is strictly a long-run phenomenon. In contrast, the marginal product of labour is a short-run phenomenon that is relevant when more units of a variable input (usually labour) are added to a given amount of a fixed factor (usually capital).
Given constant factor prices, constant returns to scale corresponds to a situation in which there are neither economies of scale nor diseconomies of scale.
-
Question 575 of 999CB2031474
Question 575
FlagWhich of the following is an example of economies of scope?
Correct
Economies of scope arise, when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Note that Option A is an example of increasing returns to scale.Answer: C
Incorrect
Economies of scope arise, when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Note that Option A is an example of increasing returns to scale.Answer: C
-
Question 576 of 999CB2031475
Question 576
FlagIncreasing long-run average costs are associated with:
Correct
Answer: B
– The long run is the period of time when all factors of production can be varied, so the whole scale of production can change.
– Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production.
– Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that also do not vary with the scale of production.
– Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that increase with the scale of production.The answer is therefore Option B.
Note that Option D is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns applies to the short run only. The law states that as more of a variable factor is added to the fixed factors, ultimately the marginal physical product of the variable factor will fall. Since this theory assumes that there are fixed factors, it must apply to the short run only.Incorrect
Answer: B
– The long run is the period of time when all factors of production can be varied, so the whole scale of production can change.
– Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production.
– Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that also do not vary with the scale of production.
– Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that increase with the scale of production.The answer is therefore Option B.
Note that Option D is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns applies to the short run only. The law states that as more of a variable factor is added to the fixed factors, ultimately the marginal physical product of the variable factor will fall. Since this theory assumes that there are fixed factors, it must apply to the short run only. -
Question 577 of 999CB2031476
Question 577
FlagIn which situation will a firm cease production in the short run?
Correct
The firm should continue to produce in the short run provided it can cover its variable costs, ie provided that average revenue exceeds average variable cost, so it is making some contribution to its fixed costs. This is because, if it were to stop producing, although it would have no variable costs, it would still have to pay the fixed costs (in the short run) and so would make a loss equal in value to its fixed costs.
The question has asked in which situation a firm will cease production in the short run. It will cease production if it cannot cover its variable costs, ie average revenue does not exceed average variable cost. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Answer: D
Incorrect
The firm should continue to produce in the short run provided it can cover its variable costs, ie provided that average revenue exceeds average variable cost, so it is making some contribution to its fixed costs. This is because, if it were to stop producing, although it would have no variable costs, it would still have to pay the fixed costs (in the short run) and so would make a loss equal in value to its fixed costs.
The question has asked in which situation a firm will cease production in the short run. It will cease production if it cannot cover its variable costs, ie average revenue does not exceed average variable cost. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Answer: D
-
Question 578 of 999CB2031478
Question 578
FlagWhich of the following statements about short-run costs of production is FALSE?
Correct
Answer: A
Option A states that marginal cost cannot exceed average total cost. The diagram shows that this is not the case: marginal cost can exceed average total (and average variable) cost, and as soon as it does, average total (and average variable) cost starts to increase. Therefore Option A is incorrect and hence the right answer.
Option B states that marginal cost is equal to average variable cost when average variable cost is at a minimum. It is always true that the marginal cost curve intersects the average variable and average total cost curves at their minimum points, so Option B is correct, and so is not the right answer.
Option C states that average fixed cost always falls as output rises. This is true, since total fixed costs do not increase with output (by definition), so as output rises, a fixed number is being divided by an ever-increasing number. Therefore Option C is not the right answer.
Option D states that average total cost exceeds average variable cost by an amount that declines with increasing output. This is true, since the difference between average total cost and average variable cost is average fixed costs, which we know (from Option C) decrease as output increases. Therefore Option D is not the right answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Option A states that marginal cost cannot exceed average total cost. The diagram shows that this is not the case: marginal cost can exceed average total (and average variable) cost, and as soon as it does, average total (and average variable) cost starts to increase. Therefore Option A is incorrect and hence the right answer.
Option B states that marginal cost is equal to average variable cost when average variable cost is at a minimum. It is always true that the marginal cost curve intersects the average variable and average total cost curves at their minimum points, so Option B is correct, and so is not the right answer.
Option C states that average fixed cost always falls as output rises. This is true, since total fixed costs do not increase with output (by definition), so as output rises, a fixed number is being divided by an ever-increasing number. Therefore Option C is not the right answer.
Option D states that average total cost exceeds average variable cost by an amount that declines with increasing output. This is true, since the difference between average total cost and average variable cost is average fixed costs, which we know (from Option C) decrease as output increases. Therefore Option D is not the right answer.
-
Question 579 of 999CB2031480
Question 579
FlagWhen a monopolist maximises profits, price exceeds marginal revenue. The difference between price and marginal revenue occurs because:
Correct
Recall that whenever a firm faces a downward-sloping demand, or average revnue, curve, as is the case with a monopoly, the corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. This is because in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the additional unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling the additional unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price.
Thus, Option C is the correct answer.
As an example, suppose that currently the firm sells 10 units at $\$ 10$ each, so its total revenue is $\$ 100$. Suppose that it then drops the price to $\$ 9$ in order to increase sales to 11 units.The effect of this is that its average revenue, or price per unit, will now be $\$ 9$ and its total revenue will fall to $\$ 99$. So, the marginal revenue of the 11 th unit will be $-\$ 1$, which represents the revenue of $+\$ 9$ from the additional unit, which is the price of that unit, less the loss of $\$ 1$ per unit on the 10 units it sold previously.
Recall that under perfect competition, each firm is so small that its actions do not affect the market price and so it can sell as many units as it likes at that market price. Consequently, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve and the price charged and the marginal revenue are the same.
Answer: C
Incorrect
Recall that whenever a firm faces a downward-sloping demand, or average revnue, curve, as is the case with a monopoly, the corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. This is because in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the additional unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling the additional unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price.
Thus, Option C is the correct answer.
As an example, suppose that currently the firm sells 10 units at $\$ 10$ each, so its total revenue is $\$ 100$. Suppose that it then drops the price to $\$ 9$ in order to increase sales to 11 units.The effect of this is that its average revenue, or price per unit, will now be $\$ 9$ and its total revenue will fall to $\$ 99$. So, the marginal revenue of the 11 th unit will be $-\$ 1$, which represents the revenue of $+\$ 9$ from the additional unit, which is the price of that unit, less the loss of $\$ 1$ per unit on the 10 units it sold previously.
Recall that under perfect competition, each firm is so small that its actions do not affect the market price and so it can sell as many units as it likes at that market price. Consequently, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve and the price charged and the marginal revenue are the same.
Answer: C
-
Question 580 of 999CB2031481
Question 580
FlagWhich one of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D
In the long run, all factors of production are variable. This means that there are no fixed costs, so Option C must be false.
So, in the long run, the firm can alter its land and capital as well as its labour. The whole scale of operation can change. If the firm doubles all its inputs and achieves only a 50\% rise in output, then these inputs are not being used very efficiently and the firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale. So Option D is true, and so is the correct answer.
The usual shape for a long-run average cost curve is a U-shape. Firms usually experience economies of scale at first (long-run average cost falls), then constant returns to scale (long-run average costs are constant) and then diseconomies of scale (long-run average cost rises).
If an industry generally experiences economies of scale, then small firms cannot compete with large firms. Firms will have to be of a certain minimum size to be able to compete. This minimum efficient scale is the level of output where long-run average costs stop falling, ie there are no further economies of scale to be exploited. (The minimum efficient scale is shown in the diagram below.) Option B states that the minimum efficient scale is the point at which long-run average costs must begin to fall, so Option B is false.
The long-run average cost curve shows the minimum unit cost of making every feasible level of output. Since all factors are variable in the long run, they can be adjusted until they are optimal for making each level of output.A short-run cost curve is drawn up for each amount of fixed factors. The short-run average cost curve shows the unit cost of making every possible level of output given the constraint of the fixed factors. The fixed factors are optimal for making a particular level of output and at this level of output, the short-run average cost is equal to the long-run average cost. At every other level of output the short-run average cost is greater than the long-run average cost. However, this does not mean that the long-run average cost curve passes through the minimum points of all the short-run average cost curves, as the following diagram illustrates.
The diagram shows that the minimum point of the short-run average cost curve is not generally equal to the long-run average cost, so Option A is false.
Incorrect
Answer D
In the long run, all factors of production are variable. This means that there are no fixed costs, so Option C must be false.
So, in the long run, the firm can alter its land and capital as well as its labour. The whole scale of operation can change. If the firm doubles all its inputs and achieves only a 50\% rise in output, then these inputs are not being used very efficiently and the firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale. So Option D is true, and so is the correct answer.
The usual shape for a long-run average cost curve is a U-shape. Firms usually experience economies of scale at first (long-run average cost falls), then constant returns to scale (long-run average costs are constant) and then diseconomies of scale (long-run average cost rises).
If an industry generally experiences economies of scale, then small firms cannot compete with large firms. Firms will have to be of a certain minimum size to be able to compete. This minimum efficient scale is the level of output where long-run average costs stop falling, ie there are no further economies of scale to be exploited. (The minimum efficient scale is shown in the diagram below.) Option B states that the minimum efficient scale is the point at which long-run average costs must begin to fall, so Option B is false.
The long-run average cost curve shows the minimum unit cost of making every feasible level of output. Since all factors are variable in the long run, they can be adjusted until they are optimal for making each level of output.A short-run cost curve is drawn up for each amount of fixed factors. The short-run average cost curve shows the unit cost of making every possible level of output given the constraint of the fixed factors. The fixed factors are optimal for making a particular level of output and at this level of output, the short-run average cost is equal to the long-run average cost. At every other level of output the short-run average cost is greater than the long-run average cost. However, this does not mean that the long-run average cost curve passes through the minimum points of all the short-run average cost curves, as the following diagram illustrates.
The diagram shows that the minimum point of the short-run average cost curve is not generally equal to the long-run average cost, so Option A is false.
-
Question 581 of 999CB2031482
Question 581
FlagA firm with fixed costs of £ 400 per week and constant average variable costs of £ 8 per unit of output, has the following information about its weekly sales:
\begin{array}{cc}
Output & \text{Total revenue }\left(£^{\prime} \mathbf{s}\right) \\
10 & 400 \\
20 & 720 \\
30 & 960 \\
40 & 1,120 \\
50 & 1,250
\end{array}Which of the following levels of output yields the highest profit?
Correct
Answer D: Often the simplest (and safest) way of determining the output level that yields the highest profit is to calculate profit at each output level. This is probably the case here. (An alternative method involves equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.)
Profit is calculated as total revenue minus total cost. The question has given total revenue figures, so it remains to calculate total cost figures, and then to take the difference.
Total costs are made up of fixed costs (which are £ 400 per week at any level of output) and variable costs (which are $£ 8$ per unit of output). So total cost will be given by 400+8 \times output .
\begin{array}{cccc}
Output & \text{Total revenue} & \text{Total cost} & Profit \\
10 & 400 & 480 & -80 \\
20 & 720 & 560 & 160 \\
30 & 960 & 640 & 320 \\
40 & 1,120 & 720 & 400 \\
50 & 1,250 & 800 & 450
\end{array}The highest level of profit is 450 when 50 units are produced.
Incorrect
Answer D: Often the simplest (and safest) way of determining the output level that yields the highest profit is to calculate profit at each output level. This is probably the case here. (An alternative method involves equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.)
Profit is calculated as total revenue minus total cost. The question has given total revenue figures, so it remains to calculate total cost figures, and then to take the difference.
Total costs are made up of fixed costs (which are £ 400 per week at any level of output) and variable costs (which are $£ 8$ per unit of output). So total cost will be given by 400+8 \times output .
\begin{array}{cccc}
Output & \text{Total revenue} & \text{Total cost} & Profit \\
10 & 400 & 480 & -80 \\
20 & 720 & 560 & 160 \\
30 & 960 & 640 & 320 \\
40 & 1,120 & 720 & 400 \\
50 & 1,250 & 800 & 450
\end{array}The highest level of profit is 450 when 50 units are produced.
-
Question 582 of 999CB2031487
Question 582
FlagWhich of the following does NOT contribute to economies of scale?
Correct
Answer C: Indivisibilities describe inputs into the production process that are of a minimum size, eg certain types of machinery. Small-scale operations may not be able to make full (or perhaps even any) use of indivisibilities, so these do contribute to economies of scale. Hence Option A is not the correct answer.
Overheads are a type of indivisibility, although these tend to exist at firm-level rather than plant-level. Overheads might include senior management and research and development costs. Hence Option B is not the correct answer.
Dilution of ownership is a diseconomy of scale. People are likely to work less hard in a large firm. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Specialisation within large firms allows workers to become highly efficient at their particular role, and so these do contribute to economies of scale. Hence Option D is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: Indivisibilities describe inputs into the production process that are of a minimum size, eg certain types of machinery. Small-scale operations may not be able to make full (or perhaps even any) use of indivisibilities, so these do contribute to economies of scale. Hence Option A is not the correct answer.
Overheads are a type of indivisibility, although these tend to exist at firm-level rather than plant-level. Overheads might include senior management and research and development costs. Hence Option B is not the correct answer.
Dilution of ownership is a diseconomy of scale. People are likely to work less hard in a large firm. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Specialisation within large firms allows workers to become highly efficient at their particular role, and so these do contribute to economies of scale. Hence Option D is not the correct answer.
-
Question 583 of 999CB2031488
Question 583
FlagAssume that a firm has a fixed capital stock and variable units of labour as the only inputs into its production process. If increasing amounts of the variable labour input are added to the fixed factor, then according to the law of diminishing returns which of the following is FALSE?
Correct
Answer D: The following diagram shows the shapes (and relationships between) the total physical product of labour $\left(T P P_L\right)$, average physical product of labour $\left(A P P_L\right)$ and marginal physical product of labour $\left(M P P_{\mathrm{L}}\right)$.
The diagram shows that both Option A and Option B are true:
– the $M P P_L$ reaches a maximum at $Q^*$, while the $T P P_L$ reaches a maximum to the right of this (ie at a higher level of output), where $M P P_L$ is zero
– the $M P P_1$ curve intersects the $A P P_L$ curve at its maximum point, so while the $M P P_1$ curve is above the $A P P_L$ curve, the $A P P_L$ curve is rising, and while the $M P P_L$ curve is below the $A P P_{\perp}$ curve, the $A P P_L$ curve is falling.Option C is true by definition, as the marginal physical product of labour is defined as the rate of change of the total physical product. Hence, the total physical product must be maximised when the marginal physical product is equal to zero.
The diagram also shows that the $A P P_l$ is in fact maximised when it is equal to the $M P P_l$, and since $A P P_L$ is positive (and hence at this point, $M P P_L$ is positive), Option D must be false.
Incorrect
Answer D: The following diagram shows the shapes (and relationships between) the total physical product of labour $\left(T P P_L\right)$, average physical product of labour $\left(A P P_L\right)$ and marginal physical product of labour $\left(M P P_{\mathrm{L}}\right)$.
The diagram shows that both Option A and Option B are true:
– the $M P P_L$ reaches a maximum at $Q^*$, while the $T P P_L$ reaches a maximum to the right of this (ie at a higher level of output), where $M P P_L$ is zero
– the $M P P_1$ curve intersects the $A P P_L$ curve at its maximum point, so while the $M P P_1$ curve is above the $A P P_L$ curve, the $A P P_L$ curve is rising, and while the $M P P_L$ curve is below the $A P P_{\perp}$ curve, the $A P P_L$ curve is falling.Option C is true by definition, as the marginal physical product of labour is defined as the rate of change of the total physical product. Hence, the total physical product must be maximised when the marginal physical product is equal to zero.
The diagram also shows that the $A P P_l$ is in fact maximised when it is equal to the $M P P_l$, and since $A P P_L$ is positive (and hence at this point, $M P P_L$ is positive), Option D must be false.
-
Question 584 of 999CB2031489
Question 584
FlagDiseconomies of scale means:
Correct
Answer C: Economies and diseconomies of scale are a long-run concept, ie they affect production in the long run. This rules out Options A and D.
More specifically, diseconomies of scale refer to the situation where long-run average costs rise as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore the correct answer is Option C.
The corresponding short-run concept is the law of diminishing (marginal) returns.
Incorrect
Answer C: Economies and diseconomies of scale are a long-run concept, ie they affect production in the long run. This rules out Options A and D.
More specifically, diseconomies of scale refer to the situation where long-run average costs rise as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore the correct answer is Option C.
The corresponding short-run concept is the law of diminishing (marginal) returns.
-
Question 585 of 999CB2031490
Question 585
FlagWhich of the following is an example of economies of scope?
Correct
Answer C: Economies of scope arise when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Option A is an example of increasing returns (or economies) to scale.
Option B relates to the impact on budget and Option D relates to the impact on price, rather than the impact on cost.Incorrect
Answer C: Economies of scope arise when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Option A is an example of increasing returns (or economies) to scale.
Option B relates to the impact on budget and Option D relates to the impact on price, rather than the impact on cost. -
Question 586 of 999CB2031492
Question 586
FlagIn the short run, a loss-making firm that seeks to maximise profits will continue to produce if:
Correct
Answer D: The profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) condition for any firm operating in any industry is marginal revenue $(\mathrm{MR})=$ marginal cost $(\mathrm{MC})$. Option A is therefore incorrect.
In the short run, a firm should continue to produce if it can charge a price greater than its average variable cost. Option D is therefore correct.
The reason for this is that if the price does not cover the variable cost of each unit, then it should shut down production, in which case it will not have any variable costs. In this case, the loss that it makes is just the fixed costs. (Its fixed costs are not relevant in making this decision because they are incurred whatever the level of production, so Options B and C are not correct.)
Incorrect
Answer D: The profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) condition for any firm operating in any industry is marginal revenue $(\mathrm{MR})=$ marginal cost $(\mathrm{MC})$. Option A is therefore incorrect.
In the short run, a firm should continue to produce if it can charge a price greater than its average variable cost. Option D is therefore correct.
The reason for this is that if the price does not cover the variable cost of each unit, then it should shut down production, in which case it will not have any variable costs. In this case, the loss that it makes is just the fixed costs. (Its fixed costs are not relevant in making this decision because they are incurred whatever the level of production, so Options B and C are not correct.)
-
Question 587 of 999CB2031493
Question 587
FlagIn the short run, a firm’s average fixed costs of production will:
Correct
Answer B: Total fixed costs do not vary with output. So average fixed costs $=\left(\frac{\text { total fixed cost }}{\text { output }}\right)$ must decrease as output increases. Option B is therefore the correct answer.
There is no rule about the relative levels of fixed and variable costs. Which is the greater will depend on the nature of the production processes for a particular product, eg a labour-intensive process is likely to have relatively high variable costs, whereas a more automated process may have relatively high fixed costs.
Incorrect
Answer B: Total fixed costs do not vary with output. So average fixed costs $=\left(\frac{\text { total fixed cost }}{\text { output }}\right)$ must decrease as output increases. Option B is therefore the correct answer.
There is no rule about the relative levels of fixed and variable costs. Which is the greater will depend on the nature of the production processes for a particular product, eg a labour-intensive process is likely to have relatively high variable costs, whereas a more automated process may have relatively high fixed costs.
-
Question 588 of 999CB2031494
Question 588
FlagThe narrow money supply (monetary base) is increased when:
Correct
Answer: B
If the government (or anyone else) spends more money (Option A), eg on schools, then this money must have come from somewhere. The government will either raise the funds from taxation or it will borrow by issuing government securities (bills and bonds).
If the government securities are bought by the non-bank private sector, then the money has come from the general public. There is no new cash and therefore no change in narrow money supply.
If the government securities are sold to financial institutions, then, as before, the cash spent by the government has come from the cash in the financial institutions, so there is no new cash, therefore there is no change in the narrow money supply.
So, Option A is not the correct answer.
If the central bank buys Treasury bills from the public (Option B), then it will pay for these Treasury bills with cash. Cash that sits within the central bank does not form part of the monetary base, however, when this cash is paid to the public (in return for the treasury bills), new money is effectively injected into the economy and hence there will be more cash in the economy. So this is the correct answer.It is worth checking the other options.
If a citizen buys a newly issued corporate bond (Option C), this is just a particular use of the available supply of cash, no different to the purchase of a new car. The money paid will simply be transferred from the citizen to the company issuing the bond, with no net effect on the narrow money supply.If a firm obtains an overdraft from a bank (Option D), the amount this firm can spend increases but cash does not increase. Hence deposits (and broader measures of the money supply) increase but the narrow money supply is unchanged.
Incorrect
Answer: B
If the government (or anyone else) spends more money (Option A), eg on schools, then this money must have come from somewhere. The government will either raise the funds from taxation or it will borrow by issuing government securities (bills and bonds).
If the government securities are bought by the non-bank private sector, then the money has come from the general public. There is no new cash and therefore no change in narrow money supply.
If the government securities are sold to financial institutions, then, as before, the cash spent by the government has come from the cash in the financial institutions, so there is no new cash, therefore there is no change in the narrow money supply.
So, Option A is not the correct answer.
If the central bank buys Treasury bills from the public (Option B), then it will pay for these Treasury bills with cash. Cash that sits within the central bank does not form part of the monetary base, however, when this cash is paid to the public (in return for the treasury bills), new money is effectively injected into the economy and hence there will be more cash in the economy. So this is the correct answer.It is worth checking the other options.
If a citizen buys a newly issued corporate bond (Option C), this is just a particular use of the available supply of cash, no different to the purchase of a new car. The money paid will simply be transferred from the citizen to the company issuing the bond, with no net effect on the narrow money supply.If a firm obtains an overdraft from a bank (Option D), the amount this firm can spend increases but cash does not increase. Hence deposits (and broader measures of the money supply) increase but the narrow money supply is unchanged.
-
Question 589 of 999CB2031495
Question 589
FlagWhat will be the impact of an increase in a firm’s fixed costs of production on the firm’s marginal cost?
Correct
Answer D : Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with the amount of output produced. Marginal cost is the extra cost of producing one more unit of output, and so all marginal costs must be variable costs. A change in fixed costs therefore has no impact on marginal cost and so Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D : Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with the amount of output produced. Marginal cost is the extra cost of producing one more unit of output, and so all marginal costs must be variable costs. A change in fixed costs therefore has no impact on marginal cost and so Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 590 of 999CB2031496
Question 590
FlagOther things being equal, an increase in the level of real output in an economy will result in:
Correct
Answer c
The question asks for the effect of an increase in real output (or GDP or national income) on either the money supply, the demand for money or interest rates. The money supply (Option A) is mainly affected by central bank policy, eg open market operations, and is not affected directly by real output, so Option A can be ruled out.
The demand for money arises from three main motives: transactions, precautionary and speculative (or asset). Are any of these affected by income? Yes. People are likely to hold more money for transactions purposes and precautionary purposes if their incomes increase because they are likely to buy more goods and services and they will probably hold more money ‘just in case’ too. The demand for money is therefore likely to increase, Option B can be ruled out.
The speculative demand for money (ie saving in money rather than bonds or equities) is mainly affected by interest rates (rather than income) and hence Option D can be ruled out.
Option C must therefore be the correct answer. The increase in income leads to an increase in the demand for money and an increase in interest rates, as the following diagram shows.
Incorrect
Answer c
The question asks for the effect of an increase in real output (or GDP or national income) on either the money supply, the demand for money or interest rates. The money supply (Option A) is mainly affected by central bank policy, eg open market operations, and is not affected directly by real output, so Option A can be ruled out.
The demand for money arises from three main motives: transactions, precautionary and speculative (or asset). Are any of these affected by income? Yes. People are likely to hold more money for transactions purposes and precautionary purposes if their incomes increase because they are likely to buy more goods and services and they will probably hold more money ‘just in case’ too. The demand for money is therefore likely to increase, Option B can be ruled out.
The speculative demand for money (ie saving in money rather than bonds or equities) is mainly affected by interest rates (rather than income) and hence Option D can be ruled out.
Option C must therefore be the correct answer. The increase in income leads to an increase in the demand for money and an increase in interest rates, as the following diagram shows.
-
Question 591 of 999CB2031497
Question 591
FlagA perfectly competitive firm is currently producing 2,000 units of Good X per week that are sold at £ 3 per unit. The firm’s total cost is currently £ 12,000 per week of which £ 4,000 is the fixed cost per week. The marginal cost of production is £ 3 per unit. To maximise profits or minimise losses, the firm should:
Correct
Answer B :
The profit-maximising condition for any firm is to produce where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost $(\mathrm{MC})$, ie $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. Since the firm can sell each unit at $£ 3, \mathrm{MR}=£ 3$. The question states that $M C=£ 3$ per unit, so $M R=M C$, ie the firm is already maximising its profits (or minimising its losses). This means profits cannot be increased by increasing or decreasing output, and hence Options A and C are incorrect.
To decide whether the firm would be better off shutting down immediately (Option B) or continuing to produce 2,000 units in the short run (Option D), it is necessary to compare the profit under each scenario.
If the firm shuts down and ceases production (Option B):
Weekly revenue = £ 0
Weekly cost $=$ fixed cost only $=£ 4,000$
Weekly profit $=$ revenue – cost $=0-£ 4,000=-£ 4,000$
If the firm continues to produce 2,000 units per week (Option D):
Weekly revenue $=$ price $\times$ quantity $=£ 3 \times 2,000=£ 6,000$
Weekly cost $=£ 12,000$Weekly profit= revenue – cost = £ 6,000 – £ 12,000 = -£ 6,000
The firm’s losses will therefore be minimised if it shuts down and hence Option B is correct.
Incorrect
Answer B :
The profit-maximising condition for any firm is to produce where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost $(\mathrm{MC})$, ie $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. Since the firm can sell each unit at $£ 3, \mathrm{MR}=£ 3$. The question states that $M C=£ 3$ per unit, so $M R=M C$, ie the firm is already maximising its profits (or minimising its losses). This means profits cannot be increased by increasing or decreasing output, and hence Options A and C are incorrect.
To decide whether the firm would be better off shutting down immediately (Option B) or continuing to produce 2,000 units in the short run (Option D), it is necessary to compare the profit under each scenario.
If the firm shuts down and ceases production (Option B):
Weekly revenue = £ 0
Weekly cost $=$ fixed cost only $=£ 4,000$
Weekly profit $=$ revenue – cost $=0-£ 4,000=-£ 4,000$
If the firm continues to produce 2,000 units per week (Option D):
Weekly revenue $=$ price $\times$ quantity $=£ 3 \times 2,000=£ 6,000$
Weekly cost $=£ 12,000$Weekly profit= revenue – cost = £ 6,000 – £ 12,000 = -£ 6,000
The firm’s losses will therefore be minimised if it shuts down and hence Option B is correct.
-
Question 592 of 999CB2031498
Question 592
FlagMoney that is held because of possible unforeseen events is held mainly because of the:
Correct
Answer C
There are three motives for holding money:
– the transactions motive, ie to buy goods and services with
– the precautionary motive, ie to hold in case of unexpected events
– the asset or speculative motive, ie to hold as a form of savings.The correct answer is therefore Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C
There are three motives for holding money:
– the transactions motive, ie to buy goods and services with
– the precautionary motive, ie to hold in case of unexpected events
– the asset or speculative motive, ie to hold as a form of savings.The correct answer is therefore Option C.
-
Question 593 of 999CB2031499
Question 593
FlagWhich of the following is an example of economies of scope?
Correct
Answer C: Economies of scope arise when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer.
Option A is an example of increasing returns to scale.
Incorrect
Answer C: Economies of scope arise when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer.
Option A is an example of increasing returns to scale.
-
Question 594 of 999CB2031500
Question 594
FlagAn increase in the general price level with no change in the money supply will:
Correct
Answer C
An increase in the general price level increases the amount of money required to purchase a given quantity of goods and services. This will tend to increase the demand for money and hence Options B and D can be ruled out.
The following diagram shows that an increase in the demand for money increases the equilibrium interest rate. This in turn increases the incentive to save and also the cost of borrowing in the economy, which reduces spending and aggregate demand. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
An increase in the general price level increases the amount of money required to purchase a given quantity of goods and services. This will tend to increase the demand for money and hence Options B and D can be ruled out.
The following diagram shows that an increase in the demand for money increases the equilibrium interest rate. This in turn increases the incentive to save and also the cost of borrowing in the economy, which reduces spending and aggregate demand. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 595 of 999CB2031501
Question 595
FlagThe proportion of deposits held by the public as cash is 0.5 and the proportion of deposits held by the banks for reserves is 0.5 . If the broad money supply is $£ 300$ million, what is the value of the narrow money supply?
Correct
The formula for the money multiplier is:
$$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}
$$
where: $c$ is the proportion of deposits held by the public as cash
$r$ is the proportion of deposits held by the banks for reserves.
So, here:
$$
m=\frac{1+0.5}{0.5+0.5}=1.5
$$This means that the ratio of broad money to narrow money is 1.5 , so the narrow money supply must be:
$$
\frac{£ 300 \mathrm{~m}}{1.5}=£ 200 \mathrm{~m}
$$The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Incorrect
The formula for the money multiplier is:
$$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}
$$
where: $c$ is the proportion of deposits held by the public as cash
$r$ is the proportion of deposits held by the banks for reserves.
So, here:
$$
m=\frac{1+0.5}{0.5+0.5}=1.5
$$This means that the ratio of broad money to narrow money is 1.5 , so the narrow money supply must be:
$$
\frac{£ 300 \mathrm{~m}}{1.5}=£ 200 \mathrm{~m}
$$The correct answer is therefore Option B.
-
Question 596 of 999CB2031502
Question 596
FlagConsider the following table:
\begin{array}{ccc}
\text{Units of capital} & \text{Units of labour} & Output \\
3 & 1 & 100 \\
6 & 2 & 190 \\
9 & 3 & 270 \\
12 & 4 & 340 \\
15 & 5 & 400
\end{array}The table illustrates which one of the following?
Correct
Answer C: The difference between marginal productivity and returns to scale is the time period under consideration. In the short run, at least one factor of production is fixed (usually capital) and therefore the extent to which output increases as a result of increased use of the variable factor depends on the returns to the variable factor (typically labour), ie the marginal productivity of that factor. In contrast, in the long run, all factors are variable and therefore the extent to which output increases as a result of increased use of all factors depends on the returns to scale.
Looking at the information given in the question, it is apparent that both labour and capital are varying, so the scenario given must be concerned with the long run and so returns to scale. Option D can therefore be ruled out.
In this case, the increase in both inputs is causing a less than proportionate increase in output, so this scenario is demonstrating decreasing returns to scale. Consequently, Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: The difference between marginal productivity and returns to scale is the time period under consideration. In the short run, at least one factor of production is fixed (usually capital) and therefore the extent to which output increases as a result of increased use of the variable factor depends on the returns to the variable factor (typically labour), ie the marginal productivity of that factor. In contrast, in the long run, all factors are variable and therefore the extent to which output increases as a result of increased use of all factors depends on the returns to scale.
Looking at the information given in the question, it is apparent that both labour and capital are varying, so the scenario given must be concerned with the long run and so returns to scale. Option D can therefore be ruled out.
In this case, the increase in both inputs is causing a less than proportionate increase in output, so this scenario is demonstrating decreasing returns to scale. Consequently, Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 597 of 999CB2031503
Question 597
FlagIf the money supply increases due to an expansionary open market operation by the central bank, then the price of Treasury bills will:
Correct
An expansionary open market operation to increase the money supply involves the central bank buying Treasury bills, hence the supply for Treasury bills decreases. (By buying Treasury bills, the central bank is taking Treasury bills out of the markets and pumping money into the economy.)
The following diagram shows that an increase in the money supply will lead to a fall in short-term interest rates. This rules out Options A and C.
Since the central bank wants to buy back Treasury bills, supply for Treasury bills will decrease and hence their price will increase. This rules out Options C and D, hence the correct answer is Option B.
Incorrect
An expansionary open market operation to increase the money supply involves the central bank buying Treasury bills, hence the supply for Treasury bills decreases. (By buying Treasury bills, the central bank is taking Treasury bills out of the markets and pumping money into the economy.)
The following diagram shows that an increase in the money supply will lead to a fall in short-term interest rates. This rules out Options A and C.
Since the central bank wants to buy back Treasury bills, supply for Treasury bills will decrease and hence their price will increase. This rules out Options C and D, hence the correct answer is Option B.
-
Question 598 of 999CB2031504
Question 598
FlagIf the money supply decreases due to a contractionary open market operation by the central bank, then the price of Treasury bills will:
Correct
A contractionary open market operation to decrease the money supply involves the central bank selling Treasury bills, hence the supply for Treasury bills increases. (By selling Treasury bills, the central bank is putting Treasury bills into the markets and taking money out of the economy.)
The following diagram shows that a decrease in the money supply will lead to an increase in short-term interest rates. This rules out Options A and C.
Since the central bank wants to sell Treasury bills, supply for Treasury bills will increases and hence their price will in decrease. This rules out Options C and D, hence the correct answer is B
Incorrect
A contractionary open market operation to decrease the money supply involves the central bank selling Treasury bills, hence the supply for Treasury bills increases. (By selling Treasury bills, the central bank is putting Treasury bills into the markets and taking money out of the economy.)
The following diagram shows that a decrease in the money supply will lead to an increase in short-term interest rates. This rules out Options A and C.
Since the central bank wants to sell Treasury bills, supply for Treasury bills will increases and hence their price will in decrease. This rules out Options C and D, hence the correct answer is B
-
Question 599 of 999CB2031505
Question 599
FlagWhich of the following statements about the demand for money is FALSE?
Correct
Answer C
The money demand curve slopes downwards, which demonstrates that the demand for money is negatively related to the interest rate. This is due to the asset motive: if interest rates increase, then there is a greater opportunity cost of holding cash. Therefore, Option A is true and so is not the correct answer.
If nominal income increases, then the demand for money will increase. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives: the more income individuals receive, the more they will want to hold as cash for transactions and ‘just-in-case’. Therefore, the demand for money is positively related to the level of nominal income, meaning Option B is true and so is not the correct answer.
If prices increase, then individuals will want to hold more cash. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives: if goods and services cost more, then individuals will need to hold more cash to pay for them. Therefore, the demand for money is positively related to the price level, meaning Option C is false and so is the correct answer.
If real income increases, then the demand for money will increase. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives: the better off individuals are (in real terms), the more goods and services they will want to buy. Therefore, the demand for money is positively related to the level of real income, meaning Option D is true and so is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
The money demand curve slopes downwards, which demonstrates that the demand for money is negatively related to the interest rate. This is due to the asset motive: if interest rates increase, then there is a greater opportunity cost of holding cash. Therefore, Option A is true and so is not the correct answer.
If nominal income increases, then the demand for money will increase. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives: the more income individuals receive, the more they will want to hold as cash for transactions and ‘just-in-case’. Therefore, the demand for money is positively related to the level of nominal income, meaning Option B is true and so is not the correct answer.
If prices increase, then individuals will want to hold more cash. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives: if goods and services cost more, then individuals will need to hold more cash to pay for them. Therefore, the demand for money is positively related to the price level, meaning Option C is false and so is the correct answer.
If real income increases, then the demand for money will increase. This is due to the transactions and precautionary motives: the better off individuals are (in real terms), the more goods and services they will want to buy. Therefore, the demand for money is positively related to the level of real income, meaning Option D is true and so is not the correct answer.
-
Question 600 of 999CB2031506
Question 600
FlagThe introduction of a restrictive monetary policy in an open economy operating with a flexible exchange rate would most likely lead to:
Correct
Answer: A
A restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. This is shown on the diagram below:
Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for the domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
Incorrect
Answer: A
A restrictive, or contractionary, monetary policy involves reducing the money supply, which will tend to lead to higher domestic interest rates. This is shown on the diagram below:
Higher domestic interest rates will make it more attractive to place money on deposit in domestic banks than previously was the case. This will lead to a flow of hot money into the country, with investors selling their foreign currency in order to obtain domestic currency to place on deposit. This increased demand for the domestic currency will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency, ie to an exchange rate appreciation.
-
Question 601 of 999CB2031507
Question 601
FlagA government’s attempts to increase the narrow money supply through open market operations are likely to cause short-term interest rates to:
Correct
Answer D
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government bonds by the central bank in order to bring about a change in the monetary base and hence the broad money supply. If the central bank wishes to increase the money supply, it buys bonds in the open market, thus increasing the amount of money in circulation.
The short-term interest rate is the rate at which supply and demand for money are in equilibrium. The increase in the money supply will decrease the equilibrium interest rate, as shown in the diagram below:
This rules out Options A and B.
Recall that there are three motives for holding money:
1. transactions motive
2. precautionary motive
3. asset motive.The reduction in interest rates reduces the opportunity cost of holding money under the asset motive and so the quantity of money demanded should increase, $i e$ there is a movement along the demand for money curve as people sell their bonds to the central bank and hold money instead. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government bonds by the central bank in order to bring about a change in the monetary base and hence the broad money supply. If the central bank wishes to increase the money supply, it buys bonds in the open market, thus increasing the amount of money in circulation.
The short-term interest rate is the rate at which supply and demand for money are in equilibrium. The increase in the money supply will decrease the equilibrium interest rate, as shown in the diagram below:
This rules out Options A and B.
Recall that there are three motives for holding money:
1. transactions motive
2. precautionary motive
3. asset motive.The reduction in interest rates reduces the opportunity cost of holding money under the asset motive and so the quantity of money demanded should increase, $i e$ there is a movement along the demand for money curve as people sell their bonds to the central bank and hold money instead. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 602 of 999CB2031508
Question 602
FlagPeople hold cash in order to make general purchases. This is known as:
Correct
Answer B
There are three motives for holding money:
– the transactions motive (Option B) – money needed to conduct transactions
– the precautionary motive – additional money held as a precaution (for uncertain or unexpected outgo)
– the speculative or assets motive – the desire to hold assets in the form of money balances (rather than in bonds, shares, etc).Incorrect
Answer B
There are three motives for holding money:
– the transactions motive (Option B) – money needed to conduct transactions
– the precautionary motive – additional money held as a precaution (for uncertain or unexpected outgo)
– the speculative or assets motive – the desire to hold assets in the form of money balances (rather than in bonds, shares, etc). -
Question 603 of 999CB2031509
Question 603
FlagAn increase in the money supply will:
Correct
Answer: A
An increase in the money supply is represented on the money market model diagram by a rightward shift in the money supply (MS) curve. This reduces interest rates (and hence the cost of borrowing) which will in turn boost consumption and investment, which boosts aggregate demand.
Incorrect
Answer: A
An increase in the money supply is represented on the money market model diagram by a rightward shift in the money supply (MS) curve. This reduces interest rates (and hence the cost of borrowing) which will in turn boost consumption and investment, which boosts aggregate demand.
-
Question 604 of 999CB2031510
Question 604
FlagThe purchase of Treasury bills by the central bank will likely lead to:
Correct
Answer: D
The purchase of Treasury bills by the central bank in exchange for cash injects money into the economy, increasing the money supply. This puts downward pressure on the rate of interest, so Option D is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer: D
The purchase of Treasury bills by the central bank in exchange for cash injects money into the economy, increasing the money supply. This puts downward pressure on the rate of interest, so Option D is the correct answer. -
Question 605 of 999CB2031511
Question 605
FlagMoney that is held to take advantage of unforeseen events is associated with the:
Correct
Answer B
There are three motives for holding money:
– the transactions motive (Option B) – money needed to conduct transactions
– the precautionary motive – additional money held as a precaution (for uncertain or unexpected outgo)
– the speculative or assets motive – the desire to hold assets in the form of money balances (rather than in bonds, shares, etc).Incorrect
Answer B
There are three motives for holding money:
– the transactions motive (Option B) – money needed to conduct transactions
– the precautionary motive – additional money held as a precaution (for uncertain or unexpected outgo)
– the speculative or assets motive – the desire to hold assets in the form of money balances (rather than in bonds, shares, etc). -
Question 606 of 999CB2031512
Question 606
FlagIf the money supply decreases due to a contractionary open market operation by the central bank, then the short-term rate of interest will:
Correct
A decrease in the money supply due to a contractionary open market operation is shown by a shift in the money supply curve to the left. The diagram below shows this will increase the equilibrium rate of interest (ruling out Options C and D).
Treasury bills are short-term assets that do not pay a coupon and are sold at a discount to their face value. The higher the discount, the higher the return that is made at maturity. Since Treasury bills are a close substitute for putting money in a bank account, the return on the Treasury bills will reflect the interest rate, ie a higher interest rate will lead to a higher return on Treasury bills.
The return earned on an asset is inversely related to the price paid for it, ie the lower the price paid for the asset, the higher the return that will be earned on it. Therefore the higher return on Treasury bills occurs through a decrease in their price (ruling out Options B and D).
The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Incorrect
A decrease in the money supply due to a contractionary open market operation is shown by a shift in the money supply curve to the left. The diagram below shows this will increase the equilibrium rate of interest (ruling out Options C and D).
Treasury bills are short-term assets that do not pay a coupon and are sold at a discount to their face value. The higher the discount, the higher the return that is made at maturity. Since Treasury bills are a close substitute for putting money in a bank account, the return on the Treasury bills will reflect the interest rate, ie a higher interest rate will lead to a higher return on Treasury bills.
The return earned on an asset is inversely related to the price paid for it, ie the lower the price paid for the asset, the higher the return that will be earned on it. Therefore the higher return on Treasury bills occurs through a decrease in their price (ruling out Options B and D).
The correct answer is therefore Option A.
-
Question 607 of 999CB2031513
Question 607
FlagIf the central bank of Country $X$ buys Country $X$ ‘s government bonds in the open market, then the supply curve for money for Country X will:
Correct
Answer: D
Open market operations are when the central bank buys or sells government securities in the open market. Open market operations are used to manipulate the monetary base (ie cash in circulation). Buying securities puts money into circulation, so increases the monetary base, while selling securities takes money out of circulation, so reducing the monetary base.
A change in the monetary base affects broad money, both directly (as the monetary base forms part of the broad money supply) and indirectly (through the credit creation process).
The central bank buying government bonds in the open market increases the monetary base and the broad money supply, so the money supply curve shifts to the right. This rules out Options B and C.
A rightward shift of the money supply curve will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium rate of interest, ruling out Options A and C. Hence the correct answer is Option D.
This is illustrated in the following diagram:
Incorrect
Answer: D
Open market operations are when the central bank buys or sells government securities in the open market. Open market operations are used to manipulate the monetary base (ie cash in circulation). Buying securities puts money into circulation, so increases the monetary base, while selling securities takes money out of circulation, so reducing the monetary base.
A change in the monetary base affects broad money, both directly (as the monetary base forms part of the broad money supply) and indirectly (through the credit creation process).
The central bank buying government bonds in the open market increases the monetary base and the broad money supply, so the money supply curve shifts to the right. This rules out Options B and C.
A rightward shift of the money supply curve will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium rate of interest, ruling out Options A and C. Hence the correct answer is Option D.
This is illustrated in the following diagram:
-
Question 608 of 999CB2031514
Question 608
FlagIn a simple closed economy, consumption is given by the relationship
$$
C=0.75 Y
$$
where $C$ is consumption expenditure and $Y$ is gross domestic product (GDP).
If government expenditure is $£ 150$ million and investment is $£ 50$ million, what will be the equilibrium value of the gross domestic product of the economy?Correct
Answer: D
The equilibrium level of GDP can be calculated either by equating injections and withdrawals or by equating actual output ( $Y$ ) to aggregate demand (AD). Here, you do not have information on all of the three withdrawals ( $S, T$ and $M$ ) and so you need to use the second approach. Remembering that AD in general consists of total consumption (C), plus investment (I), plus government spending (G) plus net exports ( $X-M$ ), you have:
$$
Y=C+I+G+X-M
$$Here you are dealing with a closed economy, ie one that is closed to international trade. This means that $X$ and $M$ are both zero. So, substituting in the consumption function plus the values given for $I$ and $G$ you have:
$$
Y=0.75 Y+50+150
$$
$0.25 \mathrm{Y}=200$
ie $\quad Y=800$Incorrect
Answer: D
The equilibrium level of GDP can be calculated either by equating injections and withdrawals or by equating actual output ( $Y$ ) to aggregate demand (AD). Here, you do not have information on all of the three withdrawals ( $S, T$ and $M$ ) and so you need to use the second approach. Remembering that AD in general consists of total consumption (C), plus investment (I), plus government spending (G) plus net exports ( $X-M$ ), you have:
$$
Y=C+I+G+X-M
$$Here you are dealing with a closed economy, ie one that is closed to international trade. This means that $X$ and $M$ are both zero. So, substituting in the consumption function plus the values given for $I$ and $G$ you have:
$$
Y=0.75 Y+50+150
$$
$0.25 \mathrm{Y}=200$
ie $\quad Y=800$ -
Question 609 of 999CB2031515
Question 609
FlagFor a profit-maximising firm, fixed costs are $£ 20$, and the firm’s normal profit is $£ 10$. The marginal costs of production are shown in the table below. The firm faces a horizontal demand curve when the price is $£ 50$. How much supernormal profit does the firm make?
\begin{array}{cc}
\text{Quantity produced} & \text{Marginal cost} \\
1 & 20 \\
2 & 30 \\
3 & 40 \\
4 & 50 \\
5 & 60 \\
6 & 70
\end{array}Correct
Answer A :The profit-maximising level of output occurs where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. Since the firm is facing a horizontal demand curve at £ 50, the marginal revenue must equal £ 50. Hence, looking at the table of marginal costs, the profit-maximising level of output occurs at 4 units of output.
The total revenue from producing 4 units is £ 200. The total variable cost of producing 4 units can be found by adding the marginal costs up to 4 units of output. This totals £ 140. Once fixed costs and the owner’s reward (totalling £ 30 ) are deducted, the supernormal profit is £ 30. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A :The profit-maximising level of output occurs where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. Since the firm is facing a horizontal demand curve at £ 50, the marginal revenue must equal £ 50. Hence, looking at the table of marginal costs, the profit-maximising level of output occurs at 4 units of output.
The total revenue from producing 4 units is £ 200. The total variable cost of producing 4 units can be found by adding the marginal costs up to 4 units of output. This totals £ 140. Once fixed costs and the owner’s reward (totalling £ 30 ) are deducted, the supernormal profit is £ 30. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 610 of 999CB2031516
Question 610
FlagAccording to the equation of exchange, an increase in the money supply is most likely to lead to inflation if the:
Correct
Answer: D
The equation of exchange is an important element of monetary theory.
Recall that the equation of exchange shows a theoretical relationship between money and GDP:
$$
M V=P Y
$$
where:
– $M$ is the nominal money supply
– $\quad V$ is the velocity of circulation (ie the average number of times that the money is spent on goods and services in a year)
– $\quad P$ is the average price level, expressed as an index
– $Y$ is real national income (or real GDP).Both sides of the equation therefore tell us the total spending on domestic goods and services in the course of a year, ie nominal or money GDP. Hence, the two sides are identically equal. Here you need to consider what will happen if there is an increase in the money supply, $M$.
If there is a fall in V, this will tend to offset the increase in $M$ on the left-hand side of the equation. It therefore makes an increase in the right-hand side, and hence an increase in the price level $P$, less likely. Option A is therefore unlikely to be the correct answer.
If there is a rise in real national income $Y$, this increases the right-hand side of the equation, which makes it is less likely that $P$ will need to increase in order to maintain the equality. So, Option B is also unlikely to be the correct answer.
If $M$ increases, then it is not possible for both $V$ and the nominal national income ( $P \times Y$ ) to remain unchanged. So, Option C cannot be the correct answer.
Finally, if $V$ and $Y$ are both constant, then an increase in $M$ must lead to a corresponding increase in the price level P, ie inflation, in order to maintain the equality. Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The equation of exchange is an important element of monetary theory.
Recall that the equation of exchange shows a theoretical relationship between money and GDP:
$$
M V=P Y
$$
where:
– $M$ is the nominal money supply
– $\quad V$ is the velocity of circulation (ie the average number of times that the money is spent on goods and services in a year)
– $\quad P$ is the average price level, expressed as an index
– $Y$ is real national income (or real GDP).Both sides of the equation therefore tell us the total spending on domestic goods and services in the course of a year, ie nominal or money GDP. Hence, the two sides are identically equal. Here you need to consider what will happen if there is an increase in the money supply, $M$.
If there is a fall in V, this will tend to offset the increase in $M$ on the left-hand side of the equation. It therefore makes an increase in the right-hand side, and hence an increase in the price level $P$, less likely. Option A is therefore unlikely to be the correct answer.
If there is a rise in real national income $Y$, this increases the right-hand side of the equation, which makes it is less likely that $P$ will need to increase in order to maintain the equality. So, Option B is also unlikely to be the correct answer.
If $M$ increases, then it is not possible for both $V$ and the nominal national income ( $P \times Y$ ) to remain unchanged. So, Option C cannot be the correct answer.
Finally, if $V$ and $Y$ are both constant, then an increase in $M$ must lead to a corresponding increase in the price level P, ie inflation, in order to maintain the equality. Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 611 of 999CB2031517
Question 611
FlagWhich one of the following reveals decreasing returns to scale?
Correct
Answer C: Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs (including both labour and capital) by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Option B can be ruled out because the inputs are not all being increased by the same amount (the relative amounts of labour and capital are being changed).
Option A is an example of the concept of diminishing marginal returns, which states that when one or more factors are held fixed (in this case, capital), there will come a point beyond which the extra output from utilising additional units of the variable factor (in this case, labour) will diminish. Option D describes increasing marginal returns.
Incorrect
Answer C: Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs (including both labour and capital) by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Option B can be ruled out because the inputs are not all being increased by the same amount (the relative amounts of labour and capital are being changed).
Option A is an example of the concept of diminishing marginal returns, which states that when one or more factors are held fixed (in this case, capital), there will come a point beyond which the extra output from utilising additional units of the variable factor (in this case, labour) will diminish. Option D describes increasing marginal returns.
-
Question 612 of 999CB2031518
Question 612
FlagThe following table gives a breakdown of a firm’s average cost and average revenue at various levels of output.
\begin{array}{ccc}
Output & \text{Average cost (£)} & \text{Average revenue (£)} \\
1 & 15 & 20 \\
2 & 13 & 19 \\
3 & 12 & 18 \\
4 & 12 & 15 \\
5 & 14 & 12 \\
6 & 16 & 9
\end{array}Which of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D :The table becomes:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline Output & \text{Average cost} & \text{Total cost} & \text{Marginal cost} & \text{Average revenue} & \text{Total revenue} & \text{Marginal revenue} \\
\hline 1 & 15 & 15 & 15 & 20 & 20 & 20 \\
\hline 2 & 13 & 26 & 11 & 19 & 38 & 18 \\
\hline 3 & 12 & 36 & 10 & 18 & 54 & 16 \\
\hline 4 & 12 & 48 & 12 & 15 & 60 & 6 \\
\hline 5 & 14 & 70 & 22 & 12 & 60 & 0 \\
\hline 6 & 16 & 96 & 26 & 9 & 54 & -6 \\
\hline
\end{array}The figures in the table show that Option D is the correct answer:
– Option A is incorrect because $\mathrm{MC}(4)=12<15=\mathrm{MC}(1)$
– Option B is incorrect because $\mathrm{MC}(4)=12>6=\mathrm{MR}(4)$
– Option C is incorrect because MR(6) is negative (-6)
– Option D is correct because $\mathrm{MR}(3)=16>10=\mathrm{MC}(3)$.Incorrect
Answer D :The table becomes:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline Output & \text{Average cost} & \text{Total cost} & \text{Marginal cost} & \text{Average revenue} & \text{Total revenue} & \text{Marginal revenue} \\
\hline 1 & 15 & 15 & 15 & 20 & 20 & 20 \\
\hline 2 & 13 & 26 & 11 & 19 & 38 & 18 \\
\hline 3 & 12 & 36 & 10 & 18 & 54 & 16 \\
\hline 4 & 12 & 48 & 12 & 15 & 60 & 6 \\
\hline 5 & 14 & 70 & 22 & 12 & 60 & 0 \\
\hline 6 & 16 & 96 & 26 & 9 & 54 & -6 \\
\hline
\end{array}The figures in the table show that Option D is the correct answer:
– Option A is incorrect because $\mathrm{MC}(4)=12<15=\mathrm{MC}(1)$
– Option B is incorrect because $\mathrm{MC}(4)=12>6=\mathrm{MR}(4)$
– Option C is incorrect because MR(6) is negative (-6)
– Option D is correct because $\mathrm{MR}(3)=16>10=\mathrm{MC}(3)$. -
Question 613 of 999CB2031519
Question 613
FlagWhich of the following is an example of economies of scope?
Correct
Answer C: Economies of scope arise when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer. Option A is an example of increasing returns to scale.
Incorrect
Answer C: Economies of scope arise when increasing the range of goods produced reduces the cost of producing each good, eg due to shared marketing. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer. Option A is an example of increasing returns to scale.
-
Question 614 of 999CB2031520
Question 614
FlagIf private savings exceed private investment by $£ 300$ million and government expenditure on goods and services exceeds government tax revenue by $£ 200$ million then net exports will be:
Correct
Calculation questions like this normally assume that (planned) injections and (planned) withdrawals are equal (so that the economy is in equilibrium), ie:
$$
I+G+X=S+T+M
$$So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(X-M) & =(T-G)+(S-1) \\
& =-200+300 \\
& =+100
\end{aligned}
$$Answer: B
Incorrect
Calculation questions like this normally assume that (planned) injections and (planned) withdrawals are equal (so that the economy is in equilibrium), ie:
$$
I+G+X=S+T+M
$$So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(X-M) & =(T-G)+(S-1) \\
& =-200+300 \\
& =+100
\end{aligned}
$$Answer: B
-
Question 615 of 999CB2031521
Question 615
FlagThe following data on an economy is provided for 2005 and 2013:
\begin{array}{lrc}
& 2005 & 2013 \\
Money supply & 400 & 600 \\
Real output & 100 & 150 \\
Price level & 10 & ?
\end{array}According to the equation of exchange, what would be the value of the price level in 2013 assuming that the velocity of circulation remains unchanged?
Correct
\begin{aligned}
&\text { It states that: }\\
&M \times V=P \times Y
\end{aligned}
where:
– $M=$ nominal money supply
– $V=$ velocity of circulation (the number of times per year a unit of currency is spent on buying goods and services that make up GDP)
– $P=$ average price level
– $Y=$ real national income, ie real GDP.Using the figures in the question, we can first find the velocity of circulation for 2005:
$$
400 \times V=10 \times 100
$$
ie
$$
V=2.5
$$Assuming that V remains unchanged until 2013, the average price level P in 2013 is given by:
$$
600 \times 2.5=P \times 150
$$
ie
$$
P=10
$$Hence the answer is Option C.
Incorrect
\begin{aligned}
&\text { It states that: }\\
&M \times V=P \times Y
\end{aligned}
where:
– $M=$ nominal money supply
– $V=$ velocity of circulation (the number of times per year a unit of currency is spent on buying goods and services that make up GDP)
– $P=$ average price level
– $Y=$ real national income, ie real GDP.Using the figures in the question, we can first find the velocity of circulation for 2005:
$$
400 \times V=10 \times 100
$$
ie
$$
V=2.5
$$Assuming that V remains unchanged until 2013, the average price level P in 2013 is given by:
$$
600 \times 2.5=P \times 150
$$
ie
$$
P=10
$$Hence the answer is Option C.
-
Question 616 of 999CB2031522
Question 616
FlagIncreasing long-run average costs are associated with:
Correct
Answer B: Remember that:
– The long run is the period of time when all factors of production can be varied, so the whole scale of production can change.
– Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that also do not vary with the scale of production.
– Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production.
– Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that increase with the scale of production.The answer is therefore Option B.
Option D is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns applies to the short run only. The law states that as more of a variable factor is added to the fixed factors, ultimately the marginal physical product of the variable factor will fall. Since this theory assumes that there are fixed factors, it must apply to the short run only.Incorrect
Answer B: Remember that:
– The long run is the period of time when all factors of production can be varied, so the whole scale of production can change.
– Constant returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to the same percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that also do not vary with the scale of production.
– Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production.
– Decreasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a smaller percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that increase with the scale of production.The answer is therefore Option B.
Option D is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns applies to the short run only. The law states that as more of a variable factor is added to the fixed factors, ultimately the marginal physical product of the variable factor will fall. Since this theory assumes that there are fixed factors, it must apply to the short run only. -
Question 617 of 999CB2031523
Question 617
FlagIn the model of the circular flow of income if injections are greater than withdrawals:
Correct
Answer: A
Recall that if injections of spending into the circular flow $(1+G+X)$ exceed withdrawals of spending from the circular flow ( $S+T+M$ ), then total spending or aggregate demand ( $A D=C_d+I+G+X$ ) will exceed total output ( $Y$ ). Consequently, firms will respond by increasing output to meet the excess demand and will pay increased factor incomes resulting in further subsequent increases in spending, output and income. Option A is therefore the correct answerand Option B is not.
Note that though unemployment is likely to fall, production will rise – ruling out Option C. Also, the increase in demand is likely to result in rising rather than falling prices, ruling out Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Recall that if injections of spending into the circular flow $(1+G+X)$ exceed withdrawals of spending from the circular flow ( $S+T+M$ ), then total spending or aggregate demand ( $A D=C_d+I+G+X$ ) will exceed total output ( $Y$ ). Consequently, firms will respond by increasing output to meet the excess demand and will pay increased factor incomes resulting in further subsequent increases in spending, output and income. Option A is therefore the correct answerand Option B is not.
Note that though unemployment is likely to fall, production will rise – ruling out Option C. Also, the increase in demand is likely to result in rising rather than falling prices, ruling out Option D.
-
Question 618 of 999CB2031524
Question 618
FlagWhich of the following statements is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D: Marginal physical product (MPP) is the extra output produced by employing one extra unit of the variable factor of production (usually taken to be labour), when the input of the other factors is held constant.
Average physical product (APP) is equal to total physical product (TPP) per unit of a variable factor, ie TPP divided by the number of units of the variable factor (eg labour).
Since APP is equal to TPP divided by the number of units of labour, TPP divided by APP will simply be the number of units of labour. So Option A is FALSE, and therefore is not the correct answer.The MPP curve cuts the APP curve at its maximum point, therefore if the APP is rising, the MPP will exceed the APP, whereas if the APP is falling, the MPP will be less than the APP. So Option B is FALSE, and therefore is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D: Marginal physical product (MPP) is the extra output produced by employing one extra unit of the variable factor of production (usually taken to be labour), when the input of the other factors is held constant.
Average physical product (APP) is equal to total physical product (TPP) per unit of a variable factor, ie TPP divided by the number of units of the variable factor (eg labour).
Since APP is equal to TPP divided by the number of units of labour, TPP divided by APP will simply be the number of units of labour. So Option A is FALSE, and therefore is not the correct answer.The MPP curve cuts the APP curve at its maximum point, therefore if the APP is rising, the MPP will exceed the APP, whereas if the APP is falling, the MPP will be less than the APP. So Option B is FALSE, and therefore is not the correct answer.
-
Question 619 of 999CB2031525
Question 619
FlagAssume that the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods is 0.7 and there are no taxes. The government decides to increase public spending by $£ 100$ million. According to simple Keynesian multiplier analysis, what is likely to be the total change in national income resulting from this increase in government expenditure (to the nearest million)?
Correct
Answer: D
This is a standard calculation question on the injections multiplier that appears in the Keynesian $45^{\circ}$ model.
In terms of the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services, $m p c_d$, the injections multiplier, $k$, is equal to:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}
$$Here the $m p c_d=0.7$ and so:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-0.7}=\frac{10}{3}=3.33
$$Consequently, the increase in national income resulting from on increase in government spending of $£ 100$ million will be:
$$
3.33 \times £ 100=£ 333 \text { million }
$$Note that:
– The marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services is the proportion of each extra unit of income that is spent on domestically produced goods and services – as opposed to being saved, paid as tax or spent on imports.
– Although the government has decided to increase its spending by $£ 100$ million, we are told there are no taxes to fund that spending.Incorrect
Answer: D
This is a standard calculation question on the injections multiplier that appears in the Keynesian $45^{\circ}$ model.
In terms of the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services, $m p c_d$, the injections multiplier, $k$, is equal to:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}
$$Here the $m p c_d=0.7$ and so:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-0.7}=\frac{10}{3}=3.33
$$Consequently, the increase in national income resulting from on increase in government spending of $£ 100$ million will be:
$$
3.33 \times £ 100=£ 333 \text { million }
$$Note that:
– The marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services is the proportion of each extra unit of income that is spent on domestically produced goods and services – as opposed to being saved, paid as tax or spent on imports.
– Although the government has decided to increase its spending by $£ 100$ million, we are told there are no taxes to fund that spending. -
Question 620 of 999CB2031526
Question 620
FlagIn a simple economy, consumption is given by the relationship
$$
C=0.75 Y
$$
where $C$ is consumption expenditure and $Y$ is gross domestic product.
Government expenditure is $£ 150$ million, investment is $£ 50$ million and there is no taxation or international trade. What will be the equilibrium value of gross domestic product of the economy?Correct
Answer: D
The equilibrium level of GDP can be calculated either by equating injections ((investment, government spending and exports, ie I, G and X) and withdrawals (savings, taxation and imports, ie $S, T$ and $M$ ), or by equating actual output ( $Y$ ) to aggregate demand (AD). Here there is sufficient information to use either approach.
Before doing so, note that:
– there is no taxation, so $T=0$ (which seems a little odd given that government spending is £150 million)
– there is no international trade, so $X=M=0$
– consumption is given by $C=0.75 Y$. As there are no imports, ‘consumption’ here refers to consumption of domestic goods and services only.By definition, the circular flow of income model, which underlies these calculations, assumes that all income received is spent either on consumption ( $C$ ) or on the three withdrawals, $S, T$ and $M$. As, $T=M=0$, savings are the only withdrawal in this model. Therefore:
$$
Y=C+S=0.75 Y+S
$$So:
$$
S=0.25 Y
$$Hence, using the injections equals withdrawals approach gives:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& I+G+X=S+T+M \\
\Rightarrow \quad & 50+150+0=0.25 Y+0+0 \\
\text { ie } \quad & Y=800
\end{aligned}
$$Alternatively, equating $Y$ to AD gives:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Y=C+I+G+X-M \\
\Rightarrow \quad & Y=0.75 Y+50+150+0-0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad & 0.25 Y=200 \\
\text { ie } \quad & Y=800
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer: D
The equilibrium level of GDP can be calculated either by equating injections ((investment, government spending and exports, ie I, G and X) and withdrawals (savings, taxation and imports, ie $S, T$ and $M$ ), or by equating actual output ( $Y$ ) to aggregate demand (AD). Here there is sufficient information to use either approach.
Before doing so, note that:
– there is no taxation, so $T=0$ (which seems a little odd given that government spending is £150 million)
– there is no international trade, so $X=M=0$
– consumption is given by $C=0.75 Y$. As there are no imports, ‘consumption’ here refers to consumption of domestic goods and services only.By definition, the circular flow of income model, which underlies these calculations, assumes that all income received is spent either on consumption ( $C$ ) or on the three withdrawals, $S, T$ and $M$. As, $T=M=0$, savings are the only withdrawal in this model. Therefore:
$$
Y=C+S=0.75 Y+S
$$So:
$$
S=0.25 Y
$$Hence, using the injections equals withdrawals approach gives:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& I+G+X=S+T+M \\
\Rightarrow \quad & 50+150+0=0.25 Y+0+0 \\
\text { ie } \quad & Y=800
\end{aligned}
$$Alternatively, equating $Y$ to AD gives:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Y=C+I+G+X-M \\
\Rightarrow \quad & Y=0.75 Y+50+150+0-0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad & 0.25 Y=200 \\
\text { ie } \quad & Y=800
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 621 of 999CB2031527
Question 621
FlagGiven the following data, at what levels of employment are the average physical product and marginal physical products of labour at a maximum?
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\textbf{Labour (units per day)} & \textbf{Output (units per day)} \\ \hline
0 & 0 \\ \hline
1 & 5 \\ \hline
2 & 14 \\ \hline
3 & 22 \\ \hline
4 & 28 \\ \hline
5 & 33 \\ \hline
\end{array}Correct
Answer B: The average and marginal physical product at each level of output are as follows:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Labour (units per day)} & \text{Output (units per day)} & \text{Average physical product} & \text{Marginal physical product} \\
\hline 0 & 0 & – & – \\
\hline 1 & 5 & 5 & 5 \\
\hline 2 & 14 & 7 & 9 \\
\hline 3 & 22 & 7.3 & 8 \\
\hline 4 & 28 & 7 & 6 \\
\hline 5 & 33 & 6.6 & 5 \\
\hline
\end{array}The table reveals that average physical product is maximised at 3 units of labour and marginal physical product is maximised at 2 units of labour, and so Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B: The average and marginal physical product at each level of output are as follows:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Labour (units per day)} & \text{Output (units per day)} & \text{Average physical product} & \text{Marginal physical product} \\
\hline 0 & 0 & – & – \\
\hline 1 & 5 & 5 & 5 \\
\hline 2 & 14 & 7 & 9 \\
\hline 3 & 22 & 7.3 & 8 \\
\hline 4 & 28 & 7 & 6 \\
\hline 5 & 33 & 6.6 & 5 \\
\hline
\end{array}The table reveals that average physical product is maximised at 3 units of labour and marginal physical product is maximised at 2 units of labour, and so Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 622 of 999CB2031528
Question 622
FlagA firm producing carpets has average variable costs of production of £ 420, marginal costs of production of £ 500 and operates in a perfectly competitive market. A decrease in the demand for carpets that reduces the price from £ 600 to £ 400 will mean that in the short run the firm will:
Correct
Answer A: In the short run, the firm has fixed costs. These must be paid even if it produces no output. Therefore, it is worth producing the profit-maximising (ie loss-minimising) level of output only if the total revenue is greater than the total variable cost of production (or equivalently, if average revenue (AR) (or price) exceeds the average variable cost (AVC) of production). This is because the variable costs of producing the output will be covered by the revenue brought in from that production and any surplus is a contribution towards the fixed costs, so that the loss will be less than the loss from producing nothing.
In this case, the average variable cost is $£ 420$, so if the price falls from $£ 600$ to $£ 400$, $\mathrm{AR}<\mathrm{AVC}$ and the firm should shut down. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Alternatively, the profit (or loss) could be calculated for each option in order to identify the largest profit (or smallest loss).
Incorrect
Answer A: In the short run, the firm has fixed costs. These must be paid even if it produces no output. Therefore, it is worth producing the profit-maximising (ie loss-minimising) level of output only if the total revenue is greater than the total variable cost of production (or equivalently, if average revenue (AR) (or price) exceeds the average variable cost (AVC) of production). This is because the variable costs of producing the output will be covered by the revenue brought in from that production and any surplus is a contribution towards the fixed costs, so that the loss will be less than the loss from producing nothing.
In this case, the average variable cost is $£ 420$, so if the price falls from $£ 600$ to $£ 400$, $\mathrm{AR}<\mathrm{AVC}$ and the firm should shut down. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Alternatively, the profit (or loss) could be calculated for each option in order to identify the largest profit (or smallest loss).
-
Question 623 of 999CB2031529
Question 623
FlagFor a monopoly, price exceeds marginal revenue because:
Correct
Answer C: Recall that whenever a firm faces a downward-sloping demand, or average revenue curve, as is the case with a monopoly, the corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. This is because in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product including all previous units (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the additional unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling the additional unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price.
Thus, Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C: Recall that whenever a firm faces a downward-sloping demand, or average revenue curve, as is the case with a monopoly, the corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. This is because in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product including all previous units (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the additional unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling the additional unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price.
Thus, Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 624 of 999CB2031530
Question 624
FlagA firm is producing 1,000 units of output at a price of € 20, with a marginal cost of € 5 and average cost of €8 at that level of output. What is the supernormal profit that the monopoly firm is making?
Correct
Answer D: Normal profit is the opportunity cost of being in business, ie the amount that the business’s resources could earn in their next best alternative use. It is therefore the amount required by the owners to keep them in the business. As such, normal profit is included in the cost curves. Therefore, if total revenue (TR) exactly covers the total cost (TC), the business would make normal profit and would remain in the industry in the long run.
Supernormal profit is profit in excess of normal profit. If TR $>$ TC, then the firm is earning supernormal profit.
From the information in the question:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{TR}=1,000 \times 20 = 20,000 \\
& \mathrm{TC}=1,000 \times 8 = 8,000
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore, supernormal profit is $ 12,000$ and so Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D: Normal profit is the opportunity cost of being in business, ie the amount that the business’s resources could earn in their next best alternative use. It is therefore the amount required by the owners to keep them in the business. As such, normal profit is included in the cost curves. Therefore, if total revenue (TR) exactly covers the total cost (TC), the business would make normal profit and would remain in the industry in the long run.
Supernormal profit is profit in excess of normal profit. If TR $>$ TC, then the firm is earning supernormal profit.
From the information in the question:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{TR}=1,000 \times 20 = 20,000 \\
& \mathrm{TC}=1,000 \times 8 = 8,000
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore, supernormal profit is $ 12,000$ and so Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 625 of 999CB2031531
Question 625
FlagDuring the winter, a profit maximising hotel in a seaside resort should close when average revenue is below:
Correct
Answer A :If firms are producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, but they are still making a loss, then:
– in the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if AR $>$ AVC , and if not, they should shut down (cease) production
– in the long run, they should exit the industry.The question is asking what a seaside resort should do in the winter season. This indicates that the scenario under consideration is a short run one, ie considering what the hotel will do during the winter season, and not what the hotel will do ultimately.
According to the above, the resort should close in the winter if AR < AVC, hence Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A :If firms are producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, but they are still making a loss, then:
– in the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if AR $>$ AVC , and if not, they should shut down (cease) production
– in the long run, they should exit the industry.The question is asking what a seaside resort should do in the winter season. This indicates that the scenario under consideration is a short run one, ie considering what the hotel will do during the winter season, and not what the hotel will do ultimately.
According to the above, the resort should close in the winter if AR < AVC, hence Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 626 of 999CB2031532
Question 626
FlagIn Country A, government expenditure is $£ 250$ billion, tax revenue is $£ 275$ billion, aggregate saving is $£ 300$ billion and aggregate investment is $£ 250$ billion. The net exports of Country A are equal to a:
Correct
Answer: C
Actual injections $(J)$ always equal actual withdrawals ( $W$ ). Injections include investment ( $I$ ), government spending ( $G$ ) and exports ( $X$ ). Withdrawals include savings ( $S$ ), taxation ( $T$ ) and imports ( $M$ ).
In this case:
$$
\begin{aligned}
1+G+X & =S+T+M \\
250+250+X & =300+275+M \\
500+X & =575+M \\
X-M & =575-500=+75
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore, net exports must be a surplus of $£ 75$ billion.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Actual injections $(J)$ always equal actual withdrawals ( $W$ ). Injections include investment ( $I$ ), government spending ( $G$ ) and exports ( $X$ ). Withdrawals include savings ( $S$ ), taxation ( $T$ ) and imports ( $M$ ).
In this case:
$$
\begin{aligned}
1+G+X & =S+T+M \\
250+250+X & =300+275+M \\
500+X & =575+M \\
X-M & =575-500=+75
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore, net exports must be a surplus of $£ 75$ billion.
-
Question 627 of 999CB2031533
Question 627
FlagIf private savings exceeds private investment by $£ 300$ million and government expenditure on goods and services exceeds government tax revenue by $£ 200$ million then net exports will be:
Correct
Answer: B
This is a question on the injections and withdrawals into and out of the circular flow of income.
Calculation questions like this normally assume that the economy is in equilibrium, which means that planned injections are equal to planned withdrawals, ie:
$$
I+G+X=S+T+M
$$So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(X-M) & =(T-G)+(S-I) \\
& =-200+300 \\
& =+100
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer: B
This is a question on the injections and withdrawals into and out of the circular flow of income.
Calculation questions like this normally assume that the economy is in equilibrium, which means that planned injections are equal to planned withdrawals, ie:
$$
I+G+X=S+T+M
$$So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(X-M) & =(T-G)+(S-I) \\
& =-200+300 \\
& =+100
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 628 of 999CB2031534
Question 628
FlagThe marginal cost curve:
-
Question 629 of 999CB2031535
Question 629
FlagWhat type of cost best describes the repayment of a bank loan for a firm?
Correct
Answer D: Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with the amount of output produced.
Variable costs are the costs that do vary with the amount of output produced.
Total costs are made up of fixed plus variable costs.
Marginal costs are the additional costs incurred in producing an additional unit of output. The marginal cost curve is the derivative of the derivative (or gradient) of the total cost curve.The repayment of a bank loan for a firm does not vary with the amount of output produced, so it is neither a variable cost (Option B), nor a marginal cost (Option C).
As the firm will almost certainly have other costs, it cannot be the firm’s total costs (Option A).
It must therefore be a fixed cost (Option D).
Incorrect
Answer D: Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with the amount of output produced.
Variable costs are the costs that do vary with the amount of output produced.
Total costs are made up of fixed plus variable costs.
Marginal costs are the additional costs incurred in producing an additional unit of output. The marginal cost curve is the derivative of the derivative (or gradient) of the total cost curve.The repayment of a bank loan for a firm does not vary with the amount of output produced, so it is neither a variable cost (Option B), nor a marginal cost (Option C).
As the firm will almost certainly have other costs, it cannot be the firm’s total costs (Option A).
It must therefore be a fixed cost (Option D).
-
Question 630 of 999CB2031536
Question 630
FlagIn the long run, firms will produce as long as the price they charge:
Correct
C or D
If firms are producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, but they are still making a loss, then:
– in the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if AR > AVC, and if not, they should shut down (cease) production
– in the long run, they should exit the industry.In other words, a firm will exit the industry if it is making a loss in the long run, ie if $\mathrm{TR}<\mathrm{TC}$, or equivalently, if $\mathrm{P}=\mathrm{AR}<\mathrm{AC}$.
Firms will therefore remain in the industry (and continue to produce) as long as $\mathrm{P}=\mathrm{AR}<\mathrm{AC}$. In the long run, all costs are variable and so $\mathrm{AC}=\mathrm{AVC}$, hence Options C and D are both correct.
Incorrect
C or D
If firms are producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, but they are still making a loss, then:
– in the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if AR > AVC, and if not, they should shut down (cease) production
– in the long run, they should exit the industry.In other words, a firm will exit the industry if it is making a loss in the long run, ie if $\mathrm{TR}<\mathrm{TC}$, or equivalently, if $\mathrm{P}=\mathrm{AR}<\mathrm{AC}$.
Firms will therefore remain in the industry (and continue to produce) as long as $\mathrm{P}=\mathrm{AR}<\mathrm{AC}$. In the long run, all costs are variable and so $\mathrm{AC}=\mathrm{AVC}$, hence Options C and D are both correct.
-
Question 631 of 999CB2031537
Question 631
FlagEconomies of scale means:
Correct
Answer B: Economies of scale refer to the situation in which long-run average costs fall as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B: Economies of scale refer to the situation in which long-run average costs fall as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 632 of 999CB2031538
Question 632
FlagA firm’s short-run total costs are £ 250 when ten units are produced and its total variable costs are £ 100. The marginal cost of producing the tenth unit is £ 27 and the marginal cost of producing the eleventh unit is £ 23. Which of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D :The following table summarises the information given in the question together with some additional calculated key values:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline Output & \text{Total cost} & \text{Total variable cost} & \text{Total fixed cost} & \text{Average cost} & \text{Average variable cost} & \text{Average fixed cost} & \text{Marginal cost} \\
\hline 10 & £250 & £100 & £150 & £25 & £10 & £15 & £27 \\
\hline 11 & £273 & £123 & £150 & £24.82 & £11.18 & £13.64 & £23 \\
\hline
\end{array}Option A is false, since the average cost of producing eleven units ( £ 24.82 ) is less than the average cost of producing ten units ( £ 25 ).
Option B is false, since the total fixed cost (for any level of output) is £ 150.
Option C is false, since the average fixed cost of producing eleven units ( £ 13.64 ) is less than the marginal cost of producing the eleventh unit ( £ 23 ).Incorrect
Answer D :The following table summarises the information given in the question together with some additional calculated key values:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline Output & \text{Total cost} & \text{Total variable cost} & \text{Total fixed cost} & \text{Average cost} & \text{Average variable cost} & \text{Average fixed cost} & \text{Marginal cost} \\
\hline 10 & £250 & £100 & £150 & £25 & £10 & £15 & £27 \\
\hline 11 & £273 & £123 & £150 & £24.82 & £11.18 & £13.64 & £23 \\
\hline
\end{array}Option A is false, since the average cost of producing eleven units ( £ 24.82 ) is less than the average cost of producing ten units ( £ 25 ).
Option B is false, since the total fixed cost (for any level of output) is £ 150.
Option C is false, since the average fixed cost of producing eleven units ( £ 13.64 ) is less than the marginal cost of producing the eleventh unit ( £ 23 ). -
Question 633 of 999CB2031539
Question 633
FlagA firm with falling long-run average costs is experiencing:
Correct
Answer A: Long-run average costs are associated with returns to scale (Options A, B and D). Option C (the law of diminishing returns (to labour)) is a short-run concept, so cannot be the correct answer.
The situation described (falling long run average costs) is consistent with economies of scale, which occur when increasing the scale of production leads to a lower cost per unit of output. If all factor costs are constant, then increasing returns to scale will result in economies of scale.
Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production. The answer is therefore Option A.
Incorrect
Answer A: Long-run average costs are associated with returns to scale (Options A, B and D). Option C (the law of diminishing returns (to labour)) is a short-run concept, so cannot be the correct answer.
The situation described (falling long run average costs) is consistent with economies of scale, which occur when increasing the scale of production leads to a lower cost per unit of output. If all factor costs are constant, then increasing returns to scale will result in economies of scale.
Increasing returns to scale arise when changing all inputs by the same percentage leads to a greater percentage change in output. If factor costs (per unit of input) do not change, then this will result in long-run average costs that decrease with the scale of production. The answer is therefore Option A.
-
Question 634 of 999CB2031540
Question 634
FlagIn the short run a rise in wages will:
Correct
Answer D: Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with the amount of output produced. Variable costs are the costs that do vary with the amount of output produced. Total costs are made up of fixed plus variable costs.
Marginal costs are the additional costs incurred in producing an additional unit of output. The marginal cost curve is the derivative of the derivative (or gradient) of the total cost curve.
Wages are paid to workers whose job it is to produce goods and services. The more that is produced, the greater the total wage outgo will be, so wages are a variable cost.
Variable costs are linked to marginal costs, ie the cost of producing additional units of output. Therefore Option A is not the correct answer, but Options B, C and D are possible in that a change in wages will affect each of total, variable and marginal costs.
A rise in wages will increase each of the variable, marginal and total costs. This rules out Options B and C, and so Option D must be the correct answer.
In the short run, costs can be fixed or variable, but in the long run, all costs are variable.
Incorrect
Answer D: Fixed costs are the costs that do not vary with the amount of output produced. Variable costs are the costs that do vary with the amount of output produced. Total costs are made up of fixed plus variable costs.
Marginal costs are the additional costs incurred in producing an additional unit of output. The marginal cost curve is the derivative of the derivative (or gradient) of the total cost curve.
Wages are paid to workers whose job it is to produce goods and services. The more that is produced, the greater the total wage outgo will be, so wages are a variable cost.
Variable costs are linked to marginal costs, ie the cost of producing additional units of output. Therefore Option A is not the correct answer, but Options B, C and D are possible in that a change in wages will affect each of total, variable and marginal costs.
A rise in wages will increase each of the variable, marginal and total costs. This rules out Options B and C, and so Option D must be the correct answer.
In the short run, costs can be fixed or variable, but in the long run, all costs are variable.
-
Question 635 of 999CB2031541
Question 635
FlagWhat is the minimum information necessary to determine a company’s short run shut down point?
Correct
Answer B :If firms are producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, but they are still making a loss, then in the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if AR > AVC, and if not, they should shut down (cease) production.
Since it is necessary to compare average revenue with average variable cost to make this decision, Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B :If firms are producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, but they are still making a loss, then in the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if AR > AVC, and if not, they should shut down (cease) production.
Since it is necessary to compare average revenue with average variable cost to make this decision, Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 636 of 999CB2031542
Question 636
FlagConstant returns to scale means:
Correct
Answer B: Economies and diseconomies of scale are a long-run concept, ie they affect production in the long run. This rules out Options A and C.
More specifically, constant returns to scale refer to the situation in which long-run average costs remain the same as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B: Economies and diseconomies of scale are a long-run concept, ie they affect production in the long run. This rules out Options A and C.
More specifically, constant returns to scale refer to the situation in which long-run average costs remain the same as the scale of production (ie output) is increased. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 637 of 999CB2031543
Question 637
FlagA firm decides to increase sales from 10 units to 11 units by reducing its price from $£ 10$ to $£ 9$ while its marginal cost of production of the 11 th unit is $£ 1$. This implies that the firm:
Correct
Answer C: If a firm increases sales from 10 units to 11 units by reducing its price from £ 10 to £ 9, this means that total revenue:
– was $10 \times 10 = £ 100$ initially
– is $11 \times 9 = £ 99$ after the price reduction.Total revenue therefore decreases by £ 1 when the 11th unit is sold, therefore the marginal revenue from the 11th unit is -£ 1. This rules out Option D.
Since the marginal cost of production of the 11 th unit is £ 1, this will reduce profits by £ 2, so Option A is incorrect and Option C is correct.
Although the firm is reducing price to increase sales, if it reduced price even more, this would likely increase sales even more, so it is not sales-maximising, so Option B is also incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer C: If a firm increases sales from 10 units to 11 units by reducing its price from £ 10 to £ 9, this means that total revenue:
– was $10 \times 10 = £ 100$ initially
– is $11 \times 9 = £ 99$ after the price reduction.Total revenue therefore decreases by £ 1 when the 11th unit is sold, therefore the marginal revenue from the 11th unit is -£ 1. This rules out Option D.
Since the marginal cost of production of the 11 th unit is £ 1, this will reduce profits by £ 2, so Option A is incorrect and Option C is correct.
Although the firm is reducing price to increase sales, if it reduced price even more, this would likely increase sales even more, so it is not sales-maximising, so Option B is also incorrect.
-
Question 638 of 999CB2031544
Question 638
FlagAccording to the law of diminishing returns, as the input of the variable factor of production is increased, total product will:
Correct
Answer C: As input of a variable factor of production (typically labour) is increased, output initially rises at an increasing rate due to the benefits of specialisation. Once the benefits of specialisation have been fully utilised, further increases in the factor will result in output increasing at a decreasing rate due to diminishing returns setting in. This corresponds to Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C: As input of a variable factor of production (typically labour) is increased, output initially rises at an increasing rate due to the benefits of specialisation. Once the benefits of specialisation have been fully utilised, further increases in the factor will result in output increasing at a decreasing rate due to diminishing returns setting in. This corresponds to Option C.
-
Question 639 of 999CB2031545
Question 639
FlagConsider the following table:
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text{Units of labour} & \text{Units of capital} & Output \\
\hline 1 & 1 & 100 \\
\hline 2 & 2 & 180 \\
\hline 3 & 3 & 250 \\
\hline 4 & 4 & 300 \\
\hline 5 & 5 & 340 \\
\hline
\end{array}The price of labour is $£ 50$ per unit and the price of capital is £ 100 per unit.
The table illustrates which of the following?Correct
Answer B: As the number of units of labour and capital increase, output increases at a decreasing rate. Therefore the answer initially looks to be either diminishing marginal returns (Option A) or decreasing returns to scale (Option B).
The difference between these two options is the time period under consideration: diminishing marginal returns is a short-run concept whereas decreasing returns to scale relate to diseconomies of scale, which is a long-run concept.
As the number of units of capital given in the table in the question can vary, this implies that the level of capital is variable, and hence this is a long-run scenario. Hence the correct answer is Option B.
The prices of labour and capital, given in the question, are irrelevant.
Incorrect
Answer B: As the number of units of labour and capital increase, output increases at a decreasing rate. Therefore the answer initially looks to be either diminishing marginal returns (Option A) or decreasing returns to scale (Option B).
The difference between these two options is the time period under consideration: diminishing marginal returns is a short-run concept whereas decreasing returns to scale relate to diseconomies of scale, which is a long-run concept.
As the number of units of capital given in the table in the question can vary, this implies that the level of capital is variable, and hence this is a long-run scenario. Hence the correct answer is Option B.
The prices of labour and capital, given in the question, are irrelevant.
-
Question 640 of 999CB2031546
Question 640
FlagThe owner of a business has used all of their own funds to set up the business. Which of the following is associated with an implicit cost incurred by the firm?
Correct
Answer C: Implicit costs are costs that do not involve a direct payment of money to a third party, but which nevertheless involve a sacrifice of some alternative.
Utility costs for the office (Option A), delivery fees paid to subcontractors (Option B) and the rental cost of storage units to hold produce (Option D) all involve a direct payment of money to a third party, so are not correct.
The question states that the business owner’s own funds have been used, so they are sacrificing interest that could have been earned on savings (had they not been used). Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C: Implicit costs are costs that do not involve a direct payment of money to a third party, but which nevertheless involve a sacrifice of some alternative.
Utility costs for the office (Option A), delivery fees paid to subcontractors (Option B) and the rental cost of storage units to hold produce (Option D) all involve a direct payment of money to a third party, so are not correct.
The question states that the business owner’s own funds have been used, so they are sacrificing interest that could have been earned on savings (had they not been used). Hence the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 641 of 999CB2031547
Question 641
FlagIn the short run, a firm should cease production if its price does not cover its:
Correct
Answer A: If firms are producing where $M R=M C$, but they are still making a loss, then:
– In the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if $A R>A V C$, and if not, they should shut down (cease) production
– In the long run, they should exit the industry.If a firm should cease production in the short run if $A R>A V C$ then, since average revenue is equivalent to price (assuming all units are sold at the same price), this is the same as price $<A V C$. Therefore option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A: If firms are producing where $M R=M C$, but they are still making a loss, then:
– In the short run, they should continue producing as long as they are covering their variable costs, ie if $A R>A V C$, and if not, they should shut down (cease) production
– In the long run, they should exit the industry.If a firm should cease production in the short run if $A R>A V C$ then, since average revenue is equivalent to price (assuming all units are sold at the same price), this is the same as price $<A V C$. Therefore option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 642 of 999CB2031548
Question 642
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option A.
The bygones principle is as stated in Option C. Sunk costs are those that cannot be recouped, eg the costs of an advertising campaign or the cost of a tailor-made display cabinet that is of no use to anyone else. When choosing a particular course of action, eg whether or not to shut down, sunk costs are ignored because they have no opportunity cost. Most fixed costs are sunk costs. However, if a machine did have an opportunity cost, eg if another firm was interested in buying it, then its resale value would be considered when making the shut-down decision.For simplicity, we usually assume that all fixed costs are sunk costs. Therefore, we say that the firm would, in the short run, remain in production as long as the revenue earned from production exceeds the extra costs incurred in production, ie as long as total revenue is greater than or equal to total variable cost.
Incorrect
Option A.
The bygones principle is as stated in Option C. Sunk costs are those that cannot be recouped, eg the costs of an advertising campaign or the cost of a tailor-made display cabinet that is of no use to anyone else. When choosing a particular course of action, eg whether or not to shut down, sunk costs are ignored because they have no opportunity cost. Most fixed costs are sunk costs. However, if a machine did have an opportunity cost, eg if another firm was interested in buying it, then its resale value would be considered when making the shut-down decision.For simplicity, we usually assume that all fixed costs are sunk costs. Therefore, we say that the firm would, in the short run, remain in production as long as the revenue earned from production exceeds the extra costs incurred in production, ie as long as total revenue is greater than or equal to total variable cost.
-
Question 643 of 999CB2031549
Question 643
FlagThe area below the firm’s marginal cost curve represents:
Correct
Option B. Remember that:
– marginal cost can be thought of as the derivative of total cost. So, summing or integrating the area under the marginal cost curve reverts back to (some form of) total costs.
– marginal cost indicates how costs vary with the level of output. It therefore reflects variable costs, but not fixed costs, which do not vary with the level of output.Incorrect
Option B. Remember that:
– marginal cost can be thought of as the derivative of total cost. So, summing or integrating the area under the marginal cost curve reverts back to (some form of) total costs.
– marginal cost indicates how costs vary with the level of output. It therefore reflects variable costs, but not fixed costs, which do not vary with the level of output. -
Question 644 of 999CB2031550
Question 644
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a source of economies of scale?
Correct
Option C. Industrial relations that deteriorate with distant management, poor communication and specialisation are a possible reason for diseconomies of scale.
Incorrect
Option C. Industrial relations that deteriorate with distant management, poor communication and specialisation are a possible reason for diseconomies of scale.
-
Question 645 of 999CB2031551
Question 645
FlagWhat is normally regarded as the main reason for diseconomies of scale?
Correct
Option B. Option A is an economy of scale. Options C and D are neither economies nor diseconomies of scale.
Incorrect
Option B. Option A is an economy of scale. Options C and D are neither economies nor diseconomies of scale.
-
Question 646 of 999CB2031552
Question 646
FlagA monopolist can sell 25 units of output per day for a price of £ 11.50 each and 26 units of output per day for a price of $\mathbf{£ 1 1 . 2 5}$ each. The marginal revenue earned from the 26th unit sold is:
Correct
Option C.
Total revenue at 25 units of output is $25 \times £11.50 = £287.50$.
Total revenue at 26 units of output is $26 \times £11.25 = £292.50$.
So the marginal revenue of the 26 th unit of output is $£ 5$.Incorrect
Option C.
Total revenue at 25 units of output is $25 \times £11.50 = £287.50$.
Total revenue at 26 units of output is $26 \times £11.25 = £292.50$.
So the marginal revenue of the 26 th unit of output is $£ 5$. -
Question 647 of 999CB2031553
Question 647
FlagIf labour is a variable factor, and capital a fixed factor, which of the following statements describes the law of diminishing returns?
1 The relative shortage of capital will eventually cause increases in total product to become progressively smaller.
II The cost of the product will eventually rise as increasingly scarce labour forces the wage rate upwards.
III The marginal revenue obtained from each additional unit produced will decline.
Correct
Option C.
The law of diminishing marginal returns suggests that as successive units of a variable factor such as a labour are combined with a fixed quantity of a fixed factor such as capital, then the increments in total output will eventually decrease. This corresponds to the scenario outlined in Statement I.The law of diminishing marginal returns means that the cost of production is likely to increase, but not due to a rise in wages arising from scarcity of labour as wages are assumed constant. So Statement II is incorrect. Also, whether the marginal revenue obtained from each additional unit produced declines or not depends upon demand conditions and is independent of production costs. So Statement III is incorrect.
Incorrect
Option C.
The law of diminishing marginal returns suggests that as successive units of a variable factor such as a labour are combined with a fixed quantity of a fixed factor such as capital, then the increments in total output will eventually decrease. This corresponds to the scenario outlined in Statement I.The law of diminishing marginal returns means that the cost of production is likely to increase, but not due to a rise in wages arising from scarcity of labour as wages are assumed constant. So Statement II is incorrect. Also, whether the marginal revenue obtained from each additional unit produced declines or not depends upon demand conditions and is independent of production costs. So Statement III is incorrect.
-
Question 648 of 999CB2031554
Question 648
FlagWhich of the following best describes the economic concept of normal profit?
Correct
Option C.
Normal profit is defined as the opportunity cost of being in business. It therefore represents the level of profit needed to persuade a firm to stay in its current business, rather than to leave the current industry and produce elsewhere. So Option C is correct.
Equating marginal cost and marginal revenue gives the profit-maximising output, which could correspond to a level of profits greater or less than normal profits. So Option A is incorrect.
Both the level of profits that firms would tend to make under normal conditions of trade and the level of profits made by a typical firm in an industry will depend upon many factors including the structure of the industry. So Options B and D are incorrect.
Incorrect
Option C.
Normal profit is defined as the opportunity cost of being in business. It therefore represents the level of profit needed to persuade a firm to stay in its current business, rather than to leave the current industry and produce elsewhere. So Option C is correct.
Equating marginal cost and marginal revenue gives the profit-maximising output, which could correspond to a level of profits greater or less than normal profits. So Option A is incorrect.
Both the level of profits that firms would tend to make under normal conditions of trade and the level of profits made by a typical firm in an industry will depend upon many factors including the structure of the industry. So Options B and D are incorrect.
-
Question 649 of 999CB2031555
Question 649
FlagWhich of the following situations will lead to the closure of a profit-maximising firm in the short run?
I total revenue is less than total variable cost
II total cost is greater than total revenue
III fixed costs are greater than total revenueCorrect
Option C.
A profit-maximising firm will continue to produce output in the short run provided that it is covering its variable costs and making some contribution to its fixed costs. This is because it would have to pay the fixed costs in the short run even if it did shut down. In the short run, the firm will therefore close down only if its total revenue is less than its total variable cost.Total cost being greater than total revenue (Statement II) is the condition for shutting down (ie exiting the industry) in the long run.
Incorrect
Option C.
A profit-maximising firm will continue to produce output in the short run provided that it is covering its variable costs and making some contribution to its fixed costs. This is because it would have to pay the fixed costs in the short run even if it did shut down. In the short run, the firm will therefore close down only if its total revenue is less than its total variable cost.Total cost being greater than total revenue (Statement II) is the condition for shutting down (ie exiting the industry) in the long run.
-
Question 650 of 999CB2031556
Question 650
FlagWhich of the following statements is/are TRUE?
I Whether marginal revenue falls or rises with output depends upon the balance of the gain from selling extra units against the loss from reducing the selling price of existing units.
II Whether marginal cost increases or decreases with output depends upon the balance of the gain from the further spreading of fixed costs against the loss from increasing capacity constraints.
III Whether profits increase as output falls depends upon the balance between the gain from a positive level of marginal costs against the loss from a positive level of marginal revenue.
Correct
Option D.
Reducing output by one unit will increase profit so long as marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, so the cost saving from producing one fewer unit is greater than the reduction in revenue. So Statement III is correct.The balance of the gain from selling extra units against the loss from reducing the selling price of existing units determines whether marginal revenue is positive or negative and not whether it is falling or rising. So Statement $I$ is incorrect.
Whether marginal cost increases or decreases with output depends upon whether production is taking place under increasing or diminishing returns to labour. By definition, fixed costs do not vary with output and so cannot influence marginal cost. So Statement II is incorrect.
Incorrect
Option D.
Reducing output by one unit will increase profit so long as marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, so the cost saving from producing one fewer unit is greater than the reduction in revenue. So Statement III is correct.The balance of the gain from selling extra units against the loss from reducing the selling price of existing units determines whether marginal revenue is positive or negative and not whether it is falling or rising. So Statement $I$ is incorrect.
Whether marginal cost increases or decreases with output depends upon whether production is taking place under increasing or diminishing returns to labour. By definition, fixed costs do not vary with output and so cannot influence marginal cost. So Statement II is incorrect.
-
Question 651 of 999CB2031557
Question 651
FlagA firm’s total fixed costs are \$1,200. If at a certain output level, its average costs per unit are \$12 and the average variable cost per unit is \$8, then the level of output is:
Correct
Option C.
If the total average cost is \$ 12 and the average variable cost is \$ 8, then the average fixed cost must be \$ 4. Given that total fixed costs are \$ 1,200, the number of units produced must be:
$$
\frac{\$ 1200}{\$ 4}=300
$$Incorrect
Option C.
If the total average cost is \$ 12 and the average variable cost is \$ 8, then the average fixed cost must be \$ 4. Given that total fixed costs are \$ 1,200, the number of units produced must be:
$$
\frac{\$ 1200}{\$ 4}=300
$$ -
Question 652 of 999CB2031558
Question 652
FlagWhich of the following statements relating to physical product of labour curves is/are TRUE?
1 A marginal physical product of labour curve initially slopes upwards then downwards because of increasing returns to labour then then diminishing returns to labour.
II The marginal physical product of labour curve intersects with the average physical product of labour curve at its minimum point.
III The total physical product of labour curve cannot slope downwards.
Correct
Option A.
The marginal physical product of labour curve intersects with the average physical product of labour curve at its maximum point, so Statement II is incorrect.
The total physical product of labour curve can slope downwards, so Statement III is incorrect. This will happen when marginal physical product of labour is negative, which might be caused by too many workers getting in each other’s way.
Incorrect
Option A.
The marginal physical product of labour curve intersects with the average physical product of labour curve at its maximum point, so Statement II is incorrect.
The total physical product of labour curve can slope downwards, so Statement III is incorrect. This will happen when marginal physical product of labour is negative, which might be caused by too many workers getting in each other’s way.
-
Question 653 of 999CB2031559
Question 653
FlagThe short-run marginal cost curve will eventually slope upwards because of the law of:
Correct
Option B. It is the marginal returns to a variable factor of production that will determine the shape of the marginal cost curve in the short run. As successive units of the variable factor of production are added to a fixed quantity of the fixed factors of production, the law of diminishing marginal returns says that, after a certain level of output, each extra unit of the variable factor will add less to total production than the previous unit. If each unit costs the same to employ, then marginal costs will start to rise.
Incorrect
Option B. It is the marginal returns to a variable factor of production that will determine the shape of the marginal cost curve in the short run. As successive units of the variable factor of production are added to a fixed quantity of the fixed factors of production, the law of diminishing marginal returns says that, after a certain level of output, each extra unit of the variable factor will add less to total production than the previous unit. If each unit costs the same to employ, then marginal costs will start to rise.
-
Question 654 of 999CB2031560
Question 654
FlagIf MC>A C :
Correct
Option D. AC will be rising if, and only if, $MC>AC$. This is because $MC$ is, in effect, pulling up the $AC . AC$ will not rise faster than $MC$.
Recall the diagram showing the typical relationship between the MC and AC curves.
-
Question 655 of 999CB2031561
Question 655
FlagDecreasing returns to scale occur when:
Correct
Option C.
When a firm experiences decreasing returns to scale, its long-run average cost (LRAC) curve slopes upwards (assuming that factor prices are constant). As the long-run marginal cost curve cuts the LRAC curve at the minimum point on the LRAC curve, long-run marginal cost must exceed long-run average cost.
Remember that returns to scale is a long-run phenomenon.
Incorrect
Option C.
When a firm experiences decreasing returns to scale, its long-run average cost (LRAC) curve slopes upwards (assuming that factor prices are constant). As the long-run marginal cost curve cuts the LRAC curve at the minimum point on the LRAC curve, long-run marginal cost must exceed long-run average cost.
Remember that returns to scale is a long-run phenomenon.
-
Question 656 of 999CB2031562
Question 656
FlagDiminishing marginal productivity:
Correct
Option D. Diminishing marginal productivity suggests that the marginal product of labour may eventually become negative, but not that it must necessarily do so. It is relevant only in the short run, when capital is assumed to be fixed, as it assumes that additional units of labour are added to a fixed amount of capital. It occurs when each additional worker adds less to output than the previous worker, with capital being fixed.
Incorrect
Option D. Diminishing marginal productivity suggests that the marginal product of labour may eventually become negative, but not that it must necessarily do so. It is relevant only in the short run, when capital is assumed to be fixed, as it assumes that additional units of labour are added to a fixed amount of capital. It occurs when each additional worker adds less to output than the previous worker, with capital being fixed.
-
Question 657 of 999CB2031563
Question 657
FlagIn a simple closed economy with no government sector the consumption function relating consumption expenditure $(\mathrm{C})$ to income $(\mathrm{Y})$ is given by the expression:
$$
\mathrm{C}=£ 40 \text { million + } 0.7 \mathrm{Y}
$$Planned investment is constant at $£ 50$ million.
Which one of the following is TRUE?Correct
Answer: C
The question has stated that it is a simple, closed economy with no government sector. This means that there is no international trade (exports and imports) and there is no government spending or taxation.
The economy is in equilibrium where income $(\mathrm{Y})$ is equal to expenditure (in this case, consumption (C) and investment (I)):
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =C+I \\
& =40+0.7 Y+50 \\
& =90+0.7 Y \\
0.3 Y & =90 \\
Y & =300
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore Option C is true and so is the correct answer. (Since Option C is true, this also rules out Option D.)
Looking at Options A and B:
– The multiplier can be calculated as $k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}$, where $m p c_d$ is the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services. In this case, it is simply the part of each additional unit of income that is spent, ie 0.7 . Therefore the multiplier is $\frac{1}{1-0.7}=3.33$. So Option A is false.
– In equilibrium, $Y=300$, so:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C & =40+0.7 \times 300 \\
& =250
\end{aligned}
$$
so Option B is false.Incorrect
Answer: C
The question has stated that it is a simple, closed economy with no government sector. This means that there is no international trade (exports and imports) and there is no government spending or taxation.
The economy is in equilibrium where income $(\mathrm{Y})$ is equal to expenditure (in this case, consumption (C) and investment (I)):
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =C+I \\
& =40+0.7 Y+50 \\
& =90+0.7 Y \\
0.3 Y & =90 \\
Y & =300
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore Option C is true and so is the correct answer. (Since Option C is true, this also rules out Option D.)
Looking at Options A and B:
– The multiplier can be calculated as $k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}$, where $m p c_d$ is the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services. In this case, it is simply the part of each additional unit of income that is spent, ie 0.7 . Therefore the multiplier is $\frac{1}{1-0.7}=3.33$. So Option A is false.
– In equilibrium, $Y=300$, so:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C & =40+0.7 \times 300 \\
& =250
\end{aligned}
$$
so Option B is false. -
Question 658 of 999CB2031564
Question 658
FlagWhich of the following will increase the size of the multiplier?
Correct
Answer: C
The multiplier can be calculated as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{m p s+m p t+m p m}
$$
where: $m p c_d$ is the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services $m p s$ is the marginal propensity to save $m p t$ is the marginal propensity to be taxed (ie the marginal tax rate) $m p m$ is the marginal propensity to import.Therefore the multiplier will increase if there is an increase in $m p c_d$ (Option C) or a decrease in mps (the opposite of Option A), mpt (the opposite of Option D) or mpm.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Note that if there is an increase in government expenditure (Option B), then this will increase income by a multiplied amount (the multiplier effect), but it will not necessarily change the value of the multiplier itself.Incorrect
Answer: C
The multiplier can be calculated as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{m p s+m p t+m p m}
$$
where: $m p c_d$ is the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services $m p s$ is the marginal propensity to save $m p t$ is the marginal propensity to be taxed (ie the marginal tax rate) $m p m$ is the marginal propensity to import.Therefore the multiplier will increase if there is an increase in $m p c_d$ (Option C) or a decrease in mps (the opposite of Option A), mpt (the opposite of Option D) or mpm.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Note that if there is an increase in government expenditure (Option B), then this will increase income by a multiplied amount (the multiplier effect), but it will not necessarily change the value of the multiplier itself. -
Question 659 of 999CB2031565
Question 659
FlagYou are given the following data on a firm:
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Output} & \text{Marginal cost of the next unit} & \text{Marginal revenue from the next unit} & \text{Average cost} & \text{Average revenue} \\
\hline 5 & £14 & £23 & £26 & £35 \\
\hline 6 & £10 & £19 & £24 & £33 \\
\hline 7 & £6 & £15 & £22 & £31 \\
\hline 8 & £29 & £11 & £20 & £29 \\
\hline 9 & £41 & £7 & £21 & £27 \\
\hline
\end{array}What is the supernormal profit at the profit-maximising output?
Correct
Option D.
The profit-maximising firm will increase output as long as the extra revenue from selling the next unit is greater than (or equal to) the extra cost incurred in producing it. This firm will therefore produce eight units. The supernormal profit is then:
$$
\text { quantity × (average revenue – average cost) }=8 \times(29-20)=72
$$Notice that the MC and the MR refer to the next unit.
Incorrect
Option D.
The profit-maximising firm will increase output as long as the extra revenue from selling the next unit is greater than (or equal to) the extra cost incurred in producing it. This firm will therefore produce eight units. The supernormal profit is then:
$$
\text { quantity × (average revenue – average cost) }=8 \times(29-20)=72
$$Notice that the MC and the MR refer to the next unit.
-
Question 660 of 999CB2031566
Question 660
Flag‘Supply creates its own demand’ is also known as:
Correct
Answer: C
Say’s law – which is a classical theory – states that supply creates its own demand. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Gold’s law doesn’t exist (in the Subject CB2 course at least). However, classical theory does believe that, as a result of the flexibility of the exchange rate and the Gold standard, exports will equal imports. (There is also a golden rule, under which the UK’s Labour government of 1997 pledged to achieve a current budget balance over the business cycle.)
Austrian law (ie the legal system in place in Austria) isn’t covered by the Subject CB2 course, although the Austrian economic school of thought is covered.
Quantity law also doesn’t exist in an economic context. The quantity theory of money is an identity that equates the product of the nominal money supply and the velocity of circulation of that money with the product of the real level of output and the price level.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Say’s law – which is a classical theory – states that supply creates its own demand. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Gold’s law doesn’t exist (in the Subject CB2 course at least). However, classical theory does believe that, as a result of the flexibility of the exchange rate and the Gold standard, exports will equal imports. (There is also a golden rule, under which the UK’s Labour government of 1997 pledged to achieve a current budget balance over the business cycle.)
Austrian law (ie the legal system in place in Austria) isn’t covered by the Subject CB2 course, although the Austrian economic school of thought is covered.
Quantity law also doesn’t exist in an economic context. The quantity theory of money is an identity that equates the product of the nominal money supply and the velocity of circulation of that money with the product of the real level of output and the price level.
-
Question 661 of 999CB2031567
Question 661
FlagAccording to the quantity theory of money, a 10 per cent increase in the nominal money supply will lead to an increase in the real output level of the economy of:
Correct
Answer: A
The quantity theory of money states that:
$$
M \times V=P \times Y
$$
where M is the nominal money supply, V is the velocity of circulation, P is the average price level and $Y$ is real national income (or output), and that $V$ and $Y$ are fixed, so that an increase in M leads to a corresponding proportional increase in P .Hence, a $10 \%$ in the nominal money supply must lead to a $10 \%$ increase in prices, with no impact on the real output level of the economy.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The quantity theory of money states that:
$$
M \times V=P \times Y
$$
where M is the nominal money supply, V is the velocity of circulation, P is the average price level and $Y$ is real national income (or output), and that $V$ and $Y$ are fixed, so that an increase in M leads to a corresponding proportional increase in P .Hence, a $10 \%$ in the nominal money supply must lead to a $10 \%$ increase in prices, with no impact on the real output level of the economy.
-
Question 662 of 999CB2031568
Question 662
Flag‘Crowding out’ describes the:
Correct
Answer: A
Crowding out is defined in Module 17 as the process whereby increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector. (For example, an increase in government spending on health services might lead to a reduction in spending on private healthcare.)
In Module 18, financial crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government borrowing (and spending) diverts money away from the private sector. It is argued that this occurs because the consequent rise in interest rates decreases consumption and investment, and might also reduce net exports if the rise in interest rates causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.
The effect of crowding out will therefore be to reduce the size of the multiplier effect resulting from an increase in government spending. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Note that the above analysis assumes a fixed money supply, ie the government borrows from the non-bank private sector. In these circumstances, an increase in the demand for money (as a result of the increase in national income resulting from the increase in government spending) causes a rise in interest rates. Financial crowding out will not occur if the money supply is allowed to rise in line with the increase in the demand for money, eg if the government borrows in the form of Treasury bills from the banking sector.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Crowding out is defined in Module 17 as the process whereby increased government spending diverts money or resources away from the private sector. (For example, an increase in government spending on health services might lead to a reduction in spending on private healthcare.)
In Module 18, financial crowding out is defined as the process whereby increased government borrowing (and spending) diverts money away from the private sector. It is argued that this occurs because the consequent rise in interest rates decreases consumption and investment, and might also reduce net exports if the rise in interest rates causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.
The effect of crowding out will therefore be to reduce the size of the multiplier effect resulting from an increase in government spending. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Note that the above analysis assumes a fixed money supply, ie the government borrows from the non-bank private sector. In these circumstances, an increase in the demand for money (as a result of the increase in national income resulting from the increase in government spending) causes a rise in interest rates. Financial crowding out will not occur if the money supply is allowed to rise in line with the increase in the demand for money, eg if the government borrows in the form of Treasury bills from the banking sector.
-
Question 663 of 999CB2031569
Question 663
FlagThe accelerator principle states that:
Correct
Answer: B
As national income increases, firms need to invest in order to be able to cope with the increased level of aggregate demand, ie to provide additional capacity. The accelerator principle states that ‘the level of investment depends on the rate of change of national income, and as a result tends to be subject to substantial fluctuations’.
New investment will:
– increase if the rate at which national income is increasing is increasing
– be constant if the rate at which national income is increasing is constant
– decrease if the rate at which national income is increasing is decreasing.A consequence of the accelerator principle is that changes in investment are much more dramatic than changes in national income. So Option B is correct.
Option A is incorrect because the accelerator theory has nothing to do with interest rates. The direction of causation is incorrect in Option C. The direction of causation is also incorrect in Option D, and in addition, it is the level of investment that depends on the rate of change of output, not the rate of change of investment.
Incorrect
Answer: B
As national income increases, firms need to invest in order to be able to cope with the increased level of aggregate demand, ie to provide additional capacity. The accelerator principle states that ‘the level of investment depends on the rate of change of national income, and as a result tends to be subject to substantial fluctuations’.
New investment will:
– increase if the rate at which national income is increasing is increasing
– be constant if the rate at which national income is increasing is constant
– decrease if the rate at which national income is increasing is decreasing.A consequence of the accelerator principle is that changes in investment are much more dramatic than changes in national income. So Option B is correct.
Option A is incorrect because the accelerator theory has nothing to do with interest rates. The direction of causation is incorrect in Option C. The direction of causation is also incorrect in Option D, and in addition, it is the level of investment that depends on the rate of change of output, not the rate of change of investment.
-
Question 664 of 999CB2031570
Question 664
FlagAccording to Keynesian analysis, once a closed economy is in macroeconomic equilibrium such that planned savings equals planned investment, then:
Correct
Answer: D
One of the major conclusions of Keynesian theory is that equilibrium can occur at any level of unemployment, hence Option A is incorrect and Option D is the correct answer.
In equilibrium, national income ( Y ) equals aggregate demand (AD). Recall that aggregate demand in a closed economy equals consumption ( C ) plus investment ( I ) plus government spending (G). Assuming that I +G is non-zero, national income must be greater than consumption, and hence Option C is incorrect.
Being in equilibrium reveals nothing about the marginal propensities to consume and save, so Option B is incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer: D
One of the major conclusions of Keynesian theory is that equilibrium can occur at any level of unemployment, hence Option A is incorrect and Option D is the correct answer.
In equilibrium, national income ( Y ) equals aggregate demand (AD). Recall that aggregate demand in a closed economy equals consumption ( C ) plus investment ( I ) plus government spending (G). Assuming that I +G is non-zero, national income must be greater than consumption, and hence Option C is incorrect.
Being in equilibrium reveals nothing about the marginal propensities to consume and save, so Option B is incorrect.
-
Question 665 of 999CB2031571
Question 665
FlagIn a simple economy, consumption is given by the relationship:
$$
C=0.75 \mathrm{Y}
$$Where C is consumption expenditure and Y is gross domestic product (GDP).
If government expenditure is $£ 150$ million, investment is $£ 50$ million and there is no taxation or international trade, the equilibrium value of GDP of the economy will be:Correct
Answer: D
The level of national income ( Y ) will be in equilibrium when:
Injections (J) = Withdrawals (W)
where injections include investment (I), government spending (G) and exports (X) and withdrawals include savings (S), taxation (T) and imports (M).Another (equivalent) condition for when Y will be in equilibrium is:
(2) Aggregate demand (AD) = Income (Y).The question has given the following information:
$$
I=50, \quad G=150, \quad T=X=M=0, \quad C=0.75 Y
$$
and since $\mathrm{Y}=\mathrm{T}+\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{S}$, it must be the case that $\mathrm{S}=0.25 \mathrm{Y}$.Method 1
$$
\begin{aligned}
J & =W \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
50+150 & =0.25 Y \\
Y & =800
\end{aligned}
$$Method 2
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =A D \\
& =C+I+G+X-M \\
& =0.75 Y+50+150 \\
0.25 Y & =200 \\
Y & =800
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer: D
The level of national income ( Y ) will be in equilibrium when:
Injections (J) = Withdrawals (W)
where injections include investment (I), government spending (G) and exports (X) and withdrawals include savings (S), taxation (T) and imports (M).Another (equivalent) condition for when Y will be in equilibrium is:
(2) Aggregate demand (AD) = Income (Y).The question has given the following information:
$$
I=50, \quad G=150, \quad T=X=M=0, \quad C=0.75 Y
$$
and since $\mathrm{Y}=\mathrm{T}+\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{S}$, it must be the case that $\mathrm{S}=0.25 \mathrm{Y}$.Method 1
$$
\begin{aligned}
J & =W \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
50+150 & =0.25 Y \\
Y & =800
\end{aligned}
$$Method 2
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =A D \\
& =C+I+G+X-M \\
& =0.75 Y+50+150 \\
0.25 Y & =200 \\
Y & =800
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 666 of 999CB2031572
Question 666
FlagIn Country A, government expenditure is $£ 350$ billion, tax revenue is $£ 275$ billion, aggregate saving is $£ 300$ billion and aggregate investment is $£ 250$ billion. The net exports of Country A are equal to a:
Correct
Answer: D
In equilibrium, injections (J) equal withdrawals (W).
Using the figures given:
$$
\begin{aligned}
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
250+350+X & =300+275+M \\
600+X & =575+M \\
X-M & =575-600=-25
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore, net exports must be a deficit of $£ 25$ billion.
Incorrect
Answer: D
In equilibrium, injections (J) equal withdrawals (W).
Using the figures given:
$$
\begin{aligned}
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
250+350+X & =300+275+M \\
600+X & =575+M \\
X-M & =575-600=-25
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore, net exports must be a deficit of $£ 25$ billion.
-
Question 667 of 999CB2031573
Question 667
FlagWhich of the following statements is NOT correct in relation to Say’s Law?
Correct
Answer: A
Say’s Law states that supply creates its own demand. This means that the production of goods and services generate expenditures sufficient to ensure that they are sold. This rules out Options B and D.
According to Say’s Law, there will be no deficiency of demand or demand-deficient unemployment. Option A is therefore not true and hence is the correct answer.
Say’s Law implies that there might be some structural and frictional unemployment in the market, the levels of which will depend on how flexible wages are, and how willing and able are workers to move industries and location. Option C is therefore true and hence is not the correct answer.
In an oligopolistic market structure, there are a small number of firms, whereas under monopoly, there is just one firm.
Unlike under oligopoly, the lack of competitors means that a monopolist does not have to worry about its interdependence with other firms when making pricing and output decisions, …
… however, it may decide to moderate price increases for fear of attracting competitors.
Under oligopoly, each firm may be selling either identical or differentiated products and they tend to compete with each other on both price and quality. A monopolist may produce just one good or a variety of goods.
Under oligopoly, each firm only has a share of the market demand, whereas for a monopoly, the market demand curve is the firm’s demand curve.
Additional points
There are barriers to entry in both market structures, although they tend to be stronger in the case of a monopoly.Although firms in both market structures can earn a supernormal profit in the long run due to the existence of barriers to entry, a monopolist has the potential to capture all supernormal profits available in the industry, whereas oligopolists must share such profits.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Say’s Law states that supply creates its own demand. This means that the production of goods and services generate expenditures sufficient to ensure that they are sold. This rules out Options B and D.
According to Say’s Law, there will be no deficiency of demand or demand-deficient unemployment. Option A is therefore not true and hence is the correct answer.
Say’s Law implies that there might be some structural and frictional unemployment in the market, the levels of which will depend on how flexible wages are, and how willing and able are workers to move industries and location. Option C is therefore true and hence is not the correct answer.
In an oligopolistic market structure, there are a small number of firms, whereas under monopoly, there is just one firm.
Unlike under oligopoly, the lack of competitors means that a monopolist does not have to worry about its interdependence with other firms when making pricing and output decisions, …
… however, it may decide to moderate price increases for fear of attracting competitors.
Under oligopoly, each firm may be selling either identical or differentiated products and they tend to compete with each other on both price and quality. A monopolist may produce just one good or a variety of goods.
Under oligopoly, each firm only has a share of the market demand, whereas for a monopoly, the market demand curve is the firm’s demand curve.
Additional points
There are barriers to entry in both market structures, although they tend to be stronger in the case of a monopoly.Although firms in both market structures can earn a supernormal profit in the long run due to the existence of barriers to entry, a monopolist has the potential to capture all supernormal profits available in the industry, whereas oligopolists must share such profits.
-
Question 668 of 999CB2031574
Question 668
FlagIf the rate of income tax is cut from $30 \%$ to $25 \%$ while the marginal propensity to import falls from $20 \%$ to $15 \%$, the effect on the open economy fiscal multiplier will be:
Correct
Answer: A
The (injections) multiplier is the number of times by which a rise in national income exceeds the rise in injections that caused it. It would follow from this that the fiscal multiplier might be the number of times by which a rise in national income exceeds the rise in fiscal spending that caused it. As fiscal spending is one of the three possible injections, the calculation will be the same.
The multiplier can be calculated as:
$$
\mathrm{k}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{mps}+\mathrm{mpt}+\mathrm{mpm}}
$$
where:
– mps is the marginal propensity to save
– mpt is the marginal propensity to be taxed (ie the marginal tax rate)
– mpm is the marginal propensity to import.Therefore the multiplier will increase if there is a decrease in mps, mpt or mpm. The multiplier will decrease if there is a decrease in $\mathrm{mpc}_{\mathrm{d}}$ or an increase in mps, mpt or mpm.
In this scenario, both income tax (and so the mpt) and the mpm decrease and so the multiplier will increase. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The (injections) multiplier is the number of times by which a rise in national income exceeds the rise in injections that caused it. It would follow from this that the fiscal multiplier might be the number of times by which a rise in national income exceeds the rise in fiscal spending that caused it. As fiscal spending is one of the three possible injections, the calculation will be the same.
The multiplier can be calculated as:
$$
\mathrm{k}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{mps}+\mathrm{mpt}+\mathrm{mpm}}
$$
where:
– mps is the marginal propensity to save
– mpt is the marginal propensity to be taxed (ie the marginal tax rate)
– mpm is the marginal propensity to import.Therefore the multiplier will increase if there is a decrease in mps, mpt or mpm. The multiplier will decrease if there is a decrease in $\mathrm{mpc}_{\mathrm{d}}$ or an increase in mps, mpt or mpm.
In this scenario, both income tax (and so the mpt) and the mpm decrease and so the multiplier will increase. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 669 of 999CB2031575
Question 669
FlagA short-run fall in real gross domestic product (GDP) would result from an increase in all of the following with the exception of:
Correct
Answer:B
Autonomous consumption is the part of consumption that does not depend on income and autonomous saving is the level of saving that does not depend on income. An increase in the level of autonomous saving will decrease the level of consumption. Since consumption is one component of aggregate demand, a decrease in consumption will decrease aggregate demand and so decrease real gross domestic product in order to restore equilibrium in the goods market. Option A is therefore incorrect.
An increase in the marginal propensity to consume means that more of each additional unit of income will be spent on goods and services, or in other words, a higher proportion of the last unit of income will be spent on goods and services, and hence consumption will increase. An increase in consumption will increase aggregate demand so and increase real gross domestic product. An increase in the marginal propensity to consume will therefore increase gross domestic product and so Option B is the correct answer.
An increase in either the marginal propensity to import (Option C) or the marginal rate of taxation (Option D) will reduce levels of domestic consumption, which will in turn decrease aggregate demand and decrease gross domestic product.
An alternative approach to deriving the correct answer is to recognise that savings, imports, and taxation are all withdrawals, and an increase in withdrawals leads to a decrease in GDP. Savings, imports and taxation correspond to Options A, C and D respectively and so none of these cannot be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer:B
Autonomous consumption is the part of consumption that does not depend on income and autonomous saving is the level of saving that does not depend on income. An increase in the level of autonomous saving will decrease the level of consumption. Since consumption is one component of aggregate demand, a decrease in consumption will decrease aggregate demand and so decrease real gross domestic product in order to restore equilibrium in the goods market. Option A is therefore incorrect.
An increase in the marginal propensity to consume means that more of each additional unit of income will be spent on goods and services, or in other words, a higher proportion of the last unit of income will be spent on goods and services, and hence consumption will increase. An increase in consumption will increase aggregate demand so and increase real gross domestic product. An increase in the marginal propensity to consume will therefore increase gross domestic product and so Option B is the correct answer.
An increase in either the marginal propensity to import (Option C) or the marginal rate of taxation (Option D) will reduce levels of domestic consumption, which will in turn decrease aggregate demand and decrease gross domestic product.
An alternative approach to deriving the correct answer is to recognise that savings, imports, and taxation are all withdrawals, and an increase in withdrawals leads to a decrease in GDP. Savings, imports and taxation correspond to Options A, C and D respectively and so none of these cannot be the correct answer.
-
Question 670 of 999CB2031576
Question 670
FlagIn a simple closed economy with no government sector, the consumption function relating consumption $(\mathrm{C})$ to income $(\mathrm{Y})$ is given by the expression:
$$
C=£ 80 \text { million }+0.75 Y
$$Planned investment is constant at $£ 50$ million.
Which of the following is TRUE?Correct
Answer:B
The question has stated that it is a simple, closed economy with no government sector. This means that there is no international trade (exports and imports) and there is no government spending or taxation.
The economy is in equilibrium where income is equal to expenditure (ie consumption plus investment):
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Y=C+I \\
& =80+0.75 Y+50 \\
& =0.75 Y+130 \\
& \Rightarrow Y=520
\end{aligned}
$$Then:
$$
C=80+0.75 \times 520=470
$$Hence Option B is true and is the correct answer.
Looking at Options A and C:– In this economy, the only injection is investment (hence why the multiplier is referred to as the investment multiplier). The multiplier is $\frac{1}{1-0.75}=4$. So Option A is false.
– In equilibrium $Y=520$, so Option C is false.Incorrect
Answer:B
The question has stated that it is a simple, closed economy with no government sector. This means that there is no international trade (exports and imports) and there is no government spending or taxation.
The economy is in equilibrium where income is equal to expenditure (ie consumption plus investment):
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Y=C+I \\
& =80+0.75 Y+50 \\
& =0.75 Y+130 \\
& \Rightarrow Y=520
\end{aligned}
$$Then:
$$
C=80+0.75 \times 520=470
$$Hence Option B is true and is the correct answer.
Looking at Options A and C:– In this economy, the only injection is investment (hence why the multiplier is referred to as the investment multiplier). The multiplier is $\frac{1}{1-0.75}=4$. So Option A is false.
– In equilibrium $Y=520$, so Option C is false. -
Question 671 of 999CB2031577
Question 671
FlagThe marginal propensity to consume is 0.8 , the rate of income tax is $25 \%$ of all income and government expenditure is $£ 50$ million. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Correct
Answer:C
It’s not clear from the question whether the marginal propensity to consume relates to all income or disposable income (ie income after tax). However, it cannot relate to all income since the rate of income tax is too high (the marginal propensity to consume from all income plus the marginal propensities to tax, import and save cannot exceed one).
In addition, it is not clear whether consumption relates to domestic consumption or consumption including imports. Since the question does not give any details of imports, it is sensible to assume this relates to domestic consumption only or there would not be enough information to answer the question.
The multiplier is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{1-0.75 \times 0.8}=2.5
$$Hence an increase in government spending of $£ 10$ million would increase national income by $10 \times 2.5=25$.
Incorrect
Answer:C
It’s not clear from the question whether the marginal propensity to consume relates to all income or disposable income (ie income after tax). However, it cannot relate to all income since the rate of income tax is too high (the marginal propensity to consume from all income plus the marginal propensities to tax, import and save cannot exceed one).
In addition, it is not clear whether consumption relates to domestic consumption or consumption including imports. Since the question does not give any details of imports, it is sensible to assume this relates to domestic consumption only or there would not be enough information to answer the question.
The multiplier is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{1-0.75 \times 0.8}=2.5
$$Hence an increase in government spending of $£ 10$ million would increase national income by $10 \times 2.5=25$.
-
Question 672 of 999CB2031578
Question 672
FlagIn a closed economy with no government, planned consumption is $£ 140$ million, planned investment is $£ 70$ million and total production is $£ 240$ million. Actual investment is:
Correct
Answer:D
According to the Keynesian model, an economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand $(A D)$ equals national output $(\eta)$, ie $A D=Y$.
Since:
$$
A D=C_d+J=C_d+I+G+X
$$
and:
$$
Y=C_d+W=C_d+S+T+M
$$
where:
$C_d=$ consumption of domestically-produced goods and services
| = investment
G = government spending
$X=$ exports
$M \quad=\quad$ importsand $C=C_d+M$, ie $C$ is consumption of all goods and services.
This can also be expressed as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C_d+I+G+X & =C_d+S+T+M \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
J & =W
\end{aligned}
$$
ie injections equals withdrawals.
In a closed economy with no government sector, the only withdrawal is saving and the only injection is investment.Hence, $Y=C_d+W$, so when $C_d=140$ and $Y=240$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
240 & =140+W \\
W & =100
\end{aligned}
$$Assuming the economy is in equilibrium, injections will equal withdrawals, and since the only injection is investment, hence $J=I=100$.
Incorrect
Answer:D
According to the Keynesian model, an economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand $(A D)$ equals national output $(\eta)$, ie $A D=Y$.
Since:
$$
A D=C_d+J=C_d+I+G+X
$$
and:
$$
Y=C_d+W=C_d+S+T+M
$$
where:
$C_d=$ consumption of domestically-produced goods and services
| = investment
G = government spending
$X=$ exports
$M \quad=\quad$ importsand $C=C_d+M$, ie $C$ is consumption of all goods and services.
This can also be expressed as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C_d+I+G+X & =C_d+S+T+M \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
J & =W
\end{aligned}
$$
ie injections equals withdrawals.
In a closed economy with no government sector, the only withdrawal is saving and the only injection is investment.Hence, $Y=C_d+W$, so when $C_d=140$ and $Y=240$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
240 & =140+W \\
W & =100
\end{aligned}
$$Assuming the economy is in equilibrium, injections will equal withdrawals, and since the only injection is investment, hence $J=I=100$.
-
Question 673 of 999CB2031579
Question 673
FlagIf a household’s income increases from $£ 20,000$ to $£ 25,000$ and, as a result, consumption increases from $£ 17,000$ to $£ 21,000$, what is the household’s marginal propensity to save?
Correct
answer: c or d
Using the relationship $Y=T+C+S$, when household income goes up it is either saved, taxed or spent on consumption. If income goes up by $£ 5,000$ and consumption goes up by $£ 4,000$ then the amount saved or taxed must go up by $£ 1,000$. The marginal propensity to save plus the marginal rate of tax is then:
$$
m p s+m p t=1000 / 5000=0.2
$$If marginal income tax is zero then $m p s$ equals 0.2 . If marginal income tax is non-zero then $m p s$ is less than 0.2 .
Incorrect
answer: c or d
Using the relationship $Y=T+C+S$, when household income goes up it is either saved, taxed or spent on consumption. If income goes up by $£ 5,000$ and consumption goes up by $£ 4,000$ then the amount saved or taxed must go up by $£ 1,000$. The marginal propensity to save plus the marginal rate of tax is then:
$$
m p s+m p t=1000 / 5000=0.2
$$If marginal income tax is zero then $m p s$ equals 0.2 . If marginal income tax is non-zero then $m p s$ is less than 0.2 .
-
Question 674 of 999CB2031580
Question 674
FlagGiven the following aggregate data for Country A, what is the value of leakages (withdrawals) into the circular flow of income?
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline & £ billions \\
\hline \text{Consumption expenditure} & 300 \\
\hline \text{Tax revenue} & 200 \\
\hline Exports & 200 \\
\hline Imports & 150 \\
\hline \text{Government expenditure} & 250 \\
\hline \text{Investment expenditure} & 100 \\
\hline Savings & 200 \\
\hline
\end{array}Correct
Answer: B
Withdrawals is the sum of savings, taxes and imports, so:
$$
\begin{aligned}
W & =S+T+M \\
& =200+200+150 \\
& =550
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer: B
Withdrawals is the sum of savings, taxes and imports, so:
$$
\begin{aligned}
W & =S+T+M \\
& =200+200+150 \\
& =550
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 675 of 999CB2031581
Question 675
FlagIn an economy, investment spending is $£ 240$ billion, savings are $£ 160$ billion, government spending is $£ 80$ billion, imports are $£ 120$ billion and tax is $£ 80$ billion. What is the value of exports in this economy?
Correct
Answer: A
According to the Keynesian model, an economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand $(A D)$ equals national output $(Y)$, ie $A D=Y$.
Since:
$$
A D=C_d+J=C_d+I+G+X
$$
and:
$$
Y=C_d+W=C_d+S+T+M
$$
where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C_d & =\text { consumption of domestically-produced goods and services } \\
I & =\text { investment } \\
G & =\text { government spending } \\
X & =\text { exports } \\
M & =\text { imports }
\end{aligned}
$$
and $C=C_d+M$, ie $C$ is consumption of all goods and services.This can also be expressed as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C_d+I+G+X & =C_d+S+T+M \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
J & =W
\end{aligned}
$$
$i e$ injections equals withdrawals. Hence, we can solve for $X$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
J & =W \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
240+80+X & =160+80+120 \\
X & =40
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer: A
According to the Keynesian model, an economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand $(A D)$ equals national output $(Y)$, ie $A D=Y$.
Since:
$$
A D=C_d+J=C_d+I+G+X
$$
and:
$$
Y=C_d+W=C_d+S+T+M
$$
where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C_d & =\text { consumption of domestically-produced goods and services } \\
I & =\text { investment } \\
G & =\text { government spending } \\
X & =\text { exports } \\
M & =\text { imports }
\end{aligned}
$$
and $C=C_d+M$, ie $C$ is consumption of all goods and services.This can also be expressed as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
C_d+I+G+X & =C_d+S+T+M \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
J & =W
\end{aligned}
$$
$i e$ injections equals withdrawals. Hence, we can solve for $X$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
J & =W \\
I+G+X & =S+T+M \\
240+80+X & =160+80+120 \\
X & =40
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 676 of 999CB2031582
Question 676
FlagIf the marginal propensity to consume is 0.6 , then the multiplier assuming no taxes is:
Correct
Answer: C
The multiplier, k , can be calculated as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{0.4}=2.5
$$Incorrect
Answer: C
The multiplier, k , can be calculated as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{0.4}=2.5
$$ -
Question 677 of 999CB2031583
Question 677
FlagIn a simple closed economy with no taxes, consumption is given by the relationship:
$$
C=£ 50 \text { million }+0.6 Y
$$
where $C$ is consumption expenditure and $Y$ is GDP.
If government expenditure is $£ 100$ million and investment is $£ 50$ million, what will be the equilibrium value of GDP of the economy?Correct
Answer: D
According to the Keynesian model, an economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand (AD) equals national output (Y), ie $A D=Y$.
Since:
$$
A D=C_d+J=C_d+I+G+X
$$
and:
$$
Y=C_d+W=C_d+S+T+M
$$
where:
$C_d=$ consumption of domestically produced goods and services
I $=$ investment
$\mathrm{G}=$ government spending
$\mathrm{X}=$ exports
M = imports
and $C=C_d+M$, ie $C$ is consumption of all goods and services.
Since we are told there is no international trade, $X=M=0$ and so $C=C_d$ :$$
\begin{aligned}
A D & =C_d+I+G+X \\
& =50+0.6 Y+50+100+0 \\
& =0.6 Y+200
\end{aligned}
$$Since, in equilibrium, $A D=Y$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =A D=0.6 Y+200 \\
0.4 Y & =200 \\
Y & =500
\end{aligned}
$$Hence none of the numerical options given are correct and so Option D is the answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
According to the Keynesian model, an economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand (AD) equals national output (Y), ie $A D=Y$.
Since:
$$
A D=C_d+J=C_d+I+G+X
$$
and:
$$
Y=C_d+W=C_d+S+T+M
$$
where:
$C_d=$ consumption of domestically produced goods and services
I $=$ investment
$\mathrm{G}=$ government spending
$\mathrm{X}=$ exports
M = imports
and $C=C_d+M$, ie $C$ is consumption of all goods and services.
Since we are told there is no international trade, $X=M=0$ and so $C=C_d$ :$$
\begin{aligned}
A D & =C_d+I+G+X \\
& =50+0.6 Y+50+100+0 \\
& =0.6 Y+200
\end{aligned}
$$Since, in equilibrium, $A D=Y$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =A D=0.6 Y+200 \\
0.4 Y & =200 \\
Y & =500
\end{aligned}
$$Hence none of the numerical options given are correct and so Option D is the answer.
-
Question 678 of 999CB2031584
Question 678
FlagIn a closed economy, planned investment is $£ 20$ million, government expenditure is $£ 40$ million, planned savings are $£ 15$ million and taxes are $£ 25$ million. Which of the following is most likely to occur?
Correct
Answer: A
In a closed economy, withdrawals are given by $S+T=40$ and injections are given by $I+G=60$. If injections exceed withdrawals, then expenditure will exceed output and stocks will be run down to meet the demand. To restore stocks to their previous level (and hence restore equilibrium) national output (national income) must increase. Hence Option A is correct and Option B is incorrect.
Unemployment and production tend to move in opposite directions, hence Option C is false.
Increased demand for a limited supply of goods will tend to push prices up, hence Option D is also false.
Incorrect
Answer: A
In a closed economy, withdrawals are given by $S+T=40$ and injections are given by $I+G=60$. If injections exceed withdrawals, then expenditure will exceed output and stocks will be run down to meet the demand. To restore stocks to their previous level (and hence restore equilibrium) national output (national income) must increase. Hence Option A is correct and Option B is incorrect.
Unemployment and production tend to move in opposite directions, hence Option C is false.
Increased demand for a limited supply of goods will tend to push prices up, hence Option D is also false.
-
Question 679 of 999CB2031585
Question 679
FlagAccording to the quantity theory of money, an increase in the money supply is least likely to lead to inflation if the:
Correct
Answer:C
The equation of exchange shows a theoretical relationship between money and GDP:
$$
M V=P Y
$$Where $M$ is the nominal money supply, $V$ is the velocity of circulation, $P$ is the average price level, and $Y$ is real national income. The quantity theory of money is the same relationship but with the assumptions that V and Y are fixed, or in other words, determined independently of the model.
The relationship tells us that an increase in the money supply when the velocity of circulation remains constant will lead to an increase in real GDP or an increase in prices (or some combination of the two). The more real GDP increases, the less prices must increase and hence the less inflation will there be.
Incorrect
Answer:C
The equation of exchange shows a theoretical relationship between money and GDP:
$$
M V=P Y
$$Where $M$ is the nominal money supply, $V$ is the velocity of circulation, $P$ is the average price level, and $Y$ is real national income. The quantity theory of money is the same relationship but with the assumptions that V and Y are fixed, or in other words, determined independently of the model.
The relationship tells us that an increase in the money supply when the velocity of circulation remains constant will lead to an increase in real GDP or an increase in prices (or some combination of the two). The more real GDP increases, the less prices must increase and hence the less inflation will there be.
-
Question 680 of 999CB2031586
Question 680
FlagIf the consumption function lies above the $45^{\circ}$ line, then:
Correct
Answer: D
The $45^{\circ}$ diagram consists of aggregate demand, or expenditure, on the vertical axis, and national income, or output, on the horizontal axis. The $45^{\circ}$ line shows all points at which expenditure equals national output, and so at points where the consumption function is above the $45^{\circ}$ line, expenditure is greater than output, or equivalently spending is greater than income.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The $45^{\circ}$ diagram consists of aggregate demand, or expenditure, on the vertical axis, and national income, or output, on the horizontal axis. The $45^{\circ}$ line shows all points at which expenditure equals national output, and so at points where the consumption function is above the $45^{\circ}$ line, expenditure is greater than output, or equivalently spending is greater than income.
-
Question 681 of 999CB2031587
Question 681
FlagA decrease in the average wage will:
Correct
Answer: D
If the average wage falls, there is an increase in the amount firms are able to produce for a given level of prices. This is represented by a downward (or rightward) shift of the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve. This rules out Options B and C.
According to the classical theory, the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve is vertical because wages and prices will adjust to shocks to restore the ‘natural’ level of output. A downward shift of a vertical curve leaves it unchanged, which rules out all of Options A, B and C . (In this case, the fall in labour costs will mean that consumers have less to spend, so reducing demand. This will shift the aggregate demand (AD) curve downward (or leftward), restoring the previous level of output, but at a lower level of prices.) Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: D
If the average wage falls, there is an increase in the amount firms are able to produce for a given level of prices. This is represented by a downward (or rightward) shift of the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve. This rules out Options B and C.
According to the classical theory, the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve is vertical because wages and prices will adjust to shocks to restore the ‘natural’ level of output. A downward shift of a vertical curve leaves it unchanged, which rules out all of Options A, B and C . (In this case, the fall in labour costs will mean that consumers have less to spend, so reducing demand. This will shift the aggregate demand (AD) curve downward (or leftward), restoring the previous level of output, but at a lower level of prices.) Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 682 of 999CB2031588
Question 682
FlagThe government of a closed economy with no taxes wishes to expand real GDP by $£ 12$ billion. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.667 , what is the approximate change in the level of government spending (in $£$ billion) on goods and services required to achieve this?
Correct
Answer: B
The multiplier ( $k$ ) is the ratio of the change in national income to the change in the injection(s) that caused it. It can be calculated as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{0.333}=3
$$Hence to increase real GDP by £12bn an injection of $12 / 3=4$ is needed.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The multiplier ( $k$ ) is the ratio of the change in national income to the change in the injection(s) that caused it. It can be calculated as:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{0.333}=3
$$Hence to increase real GDP by £12bn an injection of $12 / 3=4$ is needed.
-
Question 683 of 999CB2031589
Question 683
FlagIn the presence of an inflationary gap in the standard Keynesian model, an appropriate policy response would be:
Correct
Answer: A
An inflationary gap occurs when aggregate expenditure exceeds national income (or injections exceed withdrawals) at the full-employment level of national income (ie if the full employment level of national income is to the left of equilibrium output). This excess demand creates demand-pull inflation. To reduce demand, an appropriate policy response would be to reduce government expenditure (Option A).
Increasing protectionism by raising tariffs and implementing quotas (Option B) might lead to an increase in demand for domestically produced goods and services as individuals and firms look to import less.
Decreasing the rate of income tax (Option C) and increasing the level of unemployment benefits (Option D) will leave people with higher disposable incomes and so likely increase demand.
Incorrect
Answer: A
An inflationary gap occurs when aggregate expenditure exceeds national income (or injections exceed withdrawals) at the full-employment level of national income (ie if the full employment level of national income is to the left of equilibrium output). This excess demand creates demand-pull inflation. To reduce demand, an appropriate policy response would be to reduce government expenditure (Option A).
Increasing protectionism by raising tariffs and implementing quotas (Option B) might lead to an increase in demand for domestically produced goods and services as individuals and firms look to import less.
Decreasing the rate of income tax (Option C) and increasing the level of unemployment benefits (Option D) will leave people with higher disposable incomes and so likely increase demand.
-
Question 684 of 999CB2031590
Question 684
FlagIn an open economy with a high degree of unemployment, which one of the following will result in a fall in stocks of goods and a rise in output?
You are given: $\mathrm{S}=$ planned savings, $\mathrm{I}=$ planned investment, $\mathrm{T}=$ taxation, $\mathrm{G}=$ government expenditure, $\mathrm{M}=$ import expenditure, $\mathrm{X}=$ export receipts.
Correct
If aggregate demand is greater than output:
– there will be an unplanned fall in stocks
– output will need to rise to meet the higher level of output the following year.Aggregate demand will exceed output if injections exceed withdrawals, ie if $S+T+M<I+G+X$. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
If aggregate demand is greater than output:
– there will be an unplanned fall in stocks
– output will need to rise to meet the higher level of output the following year.Aggregate demand will exceed output if injections exceed withdrawals, ie if $S+T+M<I+G+X$. Hence Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 685 of 999CB2031591
Question 685
FlagIn a closed economy the following information is given:
– the tax rate is $25 \%$ of the national income
– consumption expenditure $(\mathrm{C})$ is related to current disposable income $(\mathrm{Yd})$ by the formula $\mathrm{C}=£ 20$ million +0.8 Yd
– investment expenditure is $£ 100$ million
– government expenditure is $£ 120$ million.Which of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Answer:D
since :
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =20+0.8 \times 0.75 Y \\
& =20+0.6 Y
\end{aligned}
$$
when $Y=800$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
C & =20+0.6 \times 800 \\
& =500
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option A is true and so is not the correct answer.
The economy is in equilibrium where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =A D=C+I+G \\
& =20+0.8 Y_d+100+120 \\
& =240+0.8 Y_d
\end{aligned}
$$Since $Y_d=(1-0.25) Y=0.75 Y$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Y=240+0.8 \times 0.75 Y \\
& 0.4 Y=240 \\
& Y=600
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option B is true and so is not the correct answer.
When $Y=600$, ie at its equilibrium, $T=0.25 Y=0.25 \times 600=150$.
Hence Option C is true and so is not the correct answer.
The marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services ( $m p c_d$ ) is $0.75 \times 0.8=0.6$, so the multiplier $(k)$ is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{1-0.6}=2.5
$$Hence Option D is false and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer:D
since :
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =20+0.8 \times 0.75 Y \\
& =20+0.6 Y
\end{aligned}
$$
when $Y=800$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
C & =20+0.6 \times 800 \\
& =500
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option A is true and so is not the correct answer.
The economy is in equilibrium where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
Y & =A D=C+I+G \\
& =20+0.8 Y_d+100+120 \\
& =240+0.8 Y_d
\end{aligned}
$$Since $Y_d=(1-0.25) Y=0.75 Y$ :
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Y=240+0.8 \times 0.75 Y \\
& 0.4 Y=240 \\
& Y=600
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option B is true and so is not the correct answer.
When $Y=600$, ie at its equilibrium, $T=0.25 Y=0.25 \times 600=150$.
Hence Option C is true and so is not the correct answer.
The marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods and services ( $m p c_d$ ) is $0.75 \times 0.8=0.6$, so the multiplier $(k)$ is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{1-0.6}=2.5
$$Hence Option D is false and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 686 of 999CB2031592
Question 686
FlagWhich of the following will increase the domestic national income if an open economy is at less than full employment?
Correct
Answer: A
A fall in the marginal propensity to save (Option A) will decrease the level of saving and increase the level of consumption. Since consumption is one component of aggregate demand, an increase in consumption will increase aggregate demand and so increase domestic national income in order to restore equilibrium in the goods market. Option A i therefore the correct answer.
A fall in foreign income (or net income from abroad) will decrease domestic national income, hence Option B is not the correct answer. (Recall from Module 10 that net income from abroad is part of national income.)
A rise in either the marginal propensity to import (Option C) or the marginal rate of taxation (Option D) will reduce levels of domestic consumption, which will in turn decrease aggregate demand and decrease domestic national income. Hence Options C and D are not correct.
Incorrect
Answer: A
A fall in the marginal propensity to save (Option A) will decrease the level of saving and increase the level of consumption. Since consumption is one component of aggregate demand, an increase in consumption will increase aggregate demand and so increase domestic national income in order to restore equilibrium in the goods market. Option A i therefore the correct answer.
A fall in foreign income (or net income from abroad) will decrease domestic national income, hence Option B is not the correct answer. (Recall from Module 10 that net income from abroad is part of national income.)
A rise in either the marginal propensity to import (Option C) or the marginal rate of taxation (Option D) will reduce levels of domestic consumption, which will in turn decrease aggregate demand and decrease domestic national income. Hence Options C and D are not correct.
-
Question 687 of 999CB2031593
Question 687
FlagIn 2022 a household has an annual income of $£ 20,000$ and annual spending of $£ 10,000$. In 2023 the household income rises to $£ 30,000$ and annual spending rises to $£ 12,000$. This indicates that for this household the:
Correct
Answer: A
When an individual or household’s (gross) income increases, the increase is either paid in tax, spent on goods and services, or saved.
If income goes up by $£ 10,000$ (ie from $£ 20,000$ to $£ 30,000$ ) and spending (consumption) goes up by $£ 2,000$ (from $£ 10,000$ to $£ 12,000$ ) then the amount saved or taxed must go up by the remaining $£ 8,000$.
The marginal propensity to consume is then:
$$
m p c=\frac{2,000}{10,000}=0.2
$$Hence the correct answer is Option A (and not Option C).
The marginal propensity to save plus the marginal rate of tax is then:
$$
m p s+m p t=\frac{8,000}{10,000}=0.8
$$Since no information is given on tax, it is not possible to determine what the marginal propensity to save is, so Options B and D are unlikely to be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
When an individual or household’s (gross) income increases, the increase is either paid in tax, spent on goods and services, or saved.
If income goes up by $£ 10,000$ (ie from $£ 20,000$ to $£ 30,000$ ) and spending (consumption) goes up by $£ 2,000$ (from $£ 10,000$ to $£ 12,000$ ) then the amount saved or taxed must go up by the remaining $£ 8,000$.
The marginal propensity to consume is then:
$$
m p c=\frac{2,000}{10,000}=0.2
$$Hence the correct answer is Option A (and not Option C).
The marginal propensity to save plus the marginal rate of tax is then:
$$
m p s+m p t=\frac{8,000}{10,000}=0.8
$$Since no information is given on tax, it is not possible to determine what the marginal propensity to save is, so Options B and D are unlikely to be the correct answer.
-
Question 688 of 999CB2031594
Question 688
FlagA change in consumer preference in favour of savings will lead to $\_\_\_\_$ (i) in the marginal propensity to consume and $\_\_\_\_$ (ii) $\_\_\_\_$ in the effect of the multiplier on aggregate demand.
Correct
Answer:C
A change in consumer preference in favour of savings will lead to an increase in the marginal propensity to save, and so – all else being equal – a decrease in the marginal propensity to consume. This rules out Options B and D.
An increase in the marginal propensity to save / a decrease in the marginal propensity to consume will decrease the multiplier (so a decrease in the effect of the multiplier on aggregate demand). This rules out Options A and B, so Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer:C
A change in consumer preference in favour of savings will lead to an increase in the marginal propensity to save, and so – all else being equal – a decrease in the marginal propensity to consume. This rules out Options B and D.
An increase in the marginal propensity to save / a decrease in the marginal propensity to consume will decrease the multiplier (so a decrease in the effect of the multiplier on aggregate demand). This rules out Options A and B, so Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 689 of 999CB2031595
Question 689
FlagMaking your selection from options A-D below, which of the following statements is NOT correct in relation to the Austrian school of thought?
Economists following the Austrian school of thought:
| place emphasis on individual subjective preferences.
II focus on market forces determining prices.
III believe in a centrally planned economic system.Correct
Answer C
Like the classicals, monetarists and new classicals, the Austrian school supports the free market (including market forces determining prices), so Statement (II) is correct and Statement (III) is not correct.
The main difference between the Austrian and new classical schools is that whereas the new classical view is that people have access to information, form rational expectations and behave rationally, the Austrian view is that people and firms operate in conditions of uncertainty, and people’s preferences are complex and not necessarily rational in the conventional sense. They therefore believe that more emphasis is needed on the individuals’ subjective preferences, so Statement (I) is also correct.
Statement (III) is therefore the only option that is NOT correct and so Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
Like the classicals, monetarists and new classicals, the Austrian school supports the free market (including market forces determining prices), so Statement (II) is correct and Statement (III) is not correct.
The main difference between the Austrian and new classical schools is that whereas the new classical view is that people have access to information, form rational expectations and behave rationally, the Austrian view is that people and firms operate in conditions of uncertainty, and people’s preferences are complex and not necessarily rational in the conventional sense. They therefore believe that more emphasis is needed on the individuals’ subjective preferences, so Statement (I) is also correct.
Statement (III) is therefore the only option that is NOT correct and so Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 690 of 999CB2031596
Question 690
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a feature of a capitalist economy?
Correct
Answer:C
Capitalism is not strictly defined in the Subject CB2 Core Reading, however features of capitalism include:
– the private ownership of the factors of production
– competitive markets – this suggests that Option D is a feature of a capitalist economy, so is not the correct answer
– minimal government intervention – this suggests that Options A and B are features of a capitalist economy, so are not the correct answer, whereas Option C involves significant government intervention, so this is the correct answer
– enforced property rights.Incorrect
Answer:C
Capitalism is not strictly defined in the Subject CB2 Core Reading, however features of capitalism include:
– the private ownership of the factors of production
– competitive markets – this suggests that Option D is a feature of a capitalist economy, so is not the correct answer
– minimal government intervention – this suggests that Options A and B are features of a capitalist economy, so are not the correct answer, whereas Option C involves significant government intervention, so this is the correct answer
– enforced property rights. -
Question 691 of 999CB2031597
Question 691
FlagFor a small open economy the imposition of a tariff on its imports of a good will normally:
Correct
Answer C
Recall that a tariff is a tax imposed on imported good and services, which should be passed on to consumers through higher prices. It is usually imposed in order to make imports more expensive and thereby reduce the volume of imports. It also has the beneficial side effect of raising tax revenue for the domestic government.
As the tariff raises the domestic price of the imported good, Option A can be ruled out. In addition, the likely fall in the volumes of imports means that Options B and D can also be ruled out, leaving Option C as the correct answer.
Increasing the cost of an imported good, means that the domestically produced equivalent will now be relatively cheaper and consequently domestic production of the good may increase. However, this will not be true of all goods. For example, imposing a tariff on oil will not increase the domestic production of oil if the country has no oil reserves.
Finally, note that an open economy is one that is open to international trade. Likewise, the term closed economy is often used to refer to an economy that is closed to international trade and so has no imports or exports.
Incorrect
Answer C
Recall that a tariff is a tax imposed on imported good and services, which should be passed on to consumers through higher prices. It is usually imposed in order to make imports more expensive and thereby reduce the volume of imports. It also has the beneficial side effect of raising tax revenue for the domestic government.
As the tariff raises the domestic price of the imported good, Option A can be ruled out. In addition, the likely fall in the volumes of imports means that Options B and D can also be ruled out, leaving Option C as the correct answer.
Increasing the cost of an imported good, means that the domestically produced equivalent will now be relatively cheaper and consequently domestic production of the good may increase. However, this will not be true of all goods. For example, imposing a tariff on oil will not increase the domestic production of oil if the country has no oil reserves.
Finally, note that an open economy is one that is open to international trade. Likewise, the term closed economy is often used to refer to an economy that is closed to international trade and so has no imports or exports.
-
Question 692 of 999CB2031598
Question 692
FlagWhich one of the following will result in an improvement in a country’s terms of trade?
Correct
Answer: A
The terms of trade is usually defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$An increase in its value is usually referred to as an improvement in the terms of trade. This is because it means that export prices have risen relative to import prices and consequently fewer exports need to be exchanged in return for the same volume of imports.
Working through each of the four options in turn – a rise in export prices together with a fall in import prices must result in an increase in the terms of trade and so Option A is likely to be the correct answer. However, it’s always safest to check the other options, so let’s do that.
A fall in the prices of both imports and exports may also result in an increase in the value of the terms of trade. This will be the case if import prices fall by a greater percentage than export prices. However, it will not necessarily lead to such an increase and so is a less convincing answer than Option A.
Likewise, a rise in the prices of both imports and exports may also result in an increase in the value of the terms of trade. This will be the case if import prices rise by a smaller percentage than export prices. Once again, however, it is not certain that this will lead to such an increase and so again this is a less convincing answer than Option A.
Finally, a rise in import prices combined with a fall in export prices must lead to a fall in the value of the terms of trade, which means that Option D is definitely incorrect. So, although Options B and C may lead to an improvement in the terms of trade, Option A is the best answer, as it will definitely do so.
Note that an increase in the value of the terms of trade is not necessarily a good thing, as it may result in a fall in the volume of exports and a rise in the volume of imports, possibility resulting in a balance of payments current account deficit.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The terms of trade is usually defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$An increase in its value is usually referred to as an improvement in the terms of trade. This is because it means that export prices have risen relative to import prices and consequently fewer exports need to be exchanged in return for the same volume of imports.
Working through each of the four options in turn – a rise in export prices together with a fall in import prices must result in an increase in the terms of trade and so Option A is likely to be the correct answer. However, it’s always safest to check the other options, so let’s do that.
A fall in the prices of both imports and exports may also result in an increase in the value of the terms of trade. This will be the case if import prices fall by a greater percentage than export prices. However, it will not necessarily lead to such an increase and so is a less convincing answer than Option A.
Likewise, a rise in the prices of both imports and exports may also result in an increase in the value of the terms of trade. This will be the case if import prices rise by a smaller percentage than export prices. Once again, however, it is not certain that this will lead to such an increase and so again this is a less convincing answer than Option A.
Finally, a rise in import prices combined with a fall in export prices must lead to a fall in the value of the terms of trade, which means that Option D is definitely incorrect. So, although Options B and C may lead to an improvement in the terms of trade, Option A is the best answer, as it will definitely do so.
Note that an increase in the value of the terms of trade is not necessarily a good thing, as it may result in a fall in the volume of exports and a rise in the volume of imports, possibility resulting in a balance of payments current account deficit.
-
Question 693 of 999CB2031599
Question 693
FlagGiven an initial terms of trade of 100, if the average price of exports has risen by $50 \%$ since the base year and the average price of imports has risen by $25 \%$ since the base year, what is the current figure for the terms of trade?
Correct
Answer: B
The terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$The initial value of the terms of trade was 100, so, for simplicity, let’s assume that in the base year, both the index of export prices and the index of import prices were 100. Then:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { terms of trade } & =\frac{100 \times 1.5}{100 \times 1.25} \times 100 \\
& =120
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$The initial value of the terms of trade was 100, so, for simplicity, let’s assume that in the base year, both the index of export prices and the index of import prices were 100. Then:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { terms of trade } & =\frac{100 \times 1.5}{100 \times 1.25} \times 100 \\
& =120
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 694 of 999CB2031600
Question 694
FlagFirms can benefit through specialisation and international trade due to:
Correct
Answer: D
– Country $X$ has an absolute advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ can produce a unit of that good using fewer scarce resources than Country $Y$.
– Country $X$ has a comparative advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ has a lower opportunity cost of producing that good than Country $Y$.The course shows that specialising according to absolute and/or comparative advantage increases total output, so Options A and B must be true. Let’s check on Option C.
Factor endowments get a brief mention on page 751 of the textbook (in the section about the law of comparative advantage). Factor endowments differ between countries due to differences in population density, labour skills, climate, raw materials, capital equipment etc. These lead to different relative costs of producing goods in different countries, which in turn leads to absolute and/or comparative advantage. Therefore the Option C is also correct.
Hence the correct answer is Option D.
Note that even if you are not sure what different factor endowments are, you should be able to deduce that the correct answer is Option D because both of the first two reasons are correct.Incorrect
Answer: D
– Country $X$ has an absolute advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ can produce a unit of that good using fewer scarce resources than Country $Y$.
– Country $X$ has a comparative advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ has a lower opportunity cost of producing that good than Country $Y$.The course shows that specialising according to absolute and/or comparative advantage increases total output, so Options A and B must be true. Let’s check on Option C.
Factor endowments get a brief mention on page 751 of the textbook (in the section about the law of comparative advantage). Factor endowments differ between countries due to differences in population density, labour skills, climate, raw materials, capital equipment etc. These lead to different relative costs of producing goods in different countries, which in turn leads to absolute and/or comparative advantage. Therefore the Option C is also correct.
Hence the correct answer is Option D.
Note that even if you are not sure what different factor endowments are, you should be able to deduce that the correct answer is Option D because both of the first two reasons are correct. -
Question 695 of 999CB2031601
Question 695
FlagAssume two countries, with the same level of technology and resources, do not presently trade. In Country X one unit of labour and one unit of capital can produce 20 units of Good A or 15 units of Good B. In Country Y one unit of labour and one unit of capital can produce 50 units of Good A or 25 units of Good B.
\begin{array}{ccc}
\text{Country} & \text{Good A} & \text{Good B} \\
X & 20 & 15 \\
Y & 50 & 25
\end{array}Which of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer:C
Absolute and comparative advantage are examined frequently and it is important to have a good understanding of how they work.
Let’s start by looking at absolute advantage. Country $X$ has an absolute advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ can produce a unit of that good using fewer resources than Country $Y$, (or, equivalently, when it produces more than Country $Y$ when given the same resources).
Here, using one unit of labour and one unit of capital, Country X can produce 20 units of Good A, whereas Country $Y$ can produce 50 units. Therefore Country $Y$ has the absolute advantage in producing Good A. This contradicts the statement in Option A, which is therefore an incorrect answer.
Using one unit of labour and one unit of capital, Country X can produce 15 units of Good A, whereas Country Y can produce 25 units. Therefore Country Y also has the absolute advantage in producing Good B. This contradicts the statement in Option B, which is therefore also an incorrect answer. So the correct answer must be either Option Cor Option D.
Turning next to comparative advantage; Country $X$ has a comparative advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ has a lower opportunity cost of producing that good than Country Y. So, in order to determine which country has the comparative advantage, it is necessary to look at opportunity cost.
In Country X, the opportunity cost of producing 20 units of Good A is 15 units of Good B, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good A is 0.75 units of Good B.
In Country Y, the opportunity cost of producing 50 units of Good A is 25 units of Good B, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good A is 0.5 units of Good B.
Since Country $Y$ has the lower opportunity cost of producing Good A, Country $Y$ has the comparative advantage in producing Good A. This suggests that Option C is the correct answer. However, to be on the safe side, it’s best to check Option D to be sure.
In Country $X$, the opportunity cost of producing 15 units of Good $B$ is 20 units of Good $A$, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good B is 1.33 units of Good A.
In Country Y, the opportunity cost of producing 25 units of Good B is 50 units of Good A, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good B is 2 units of Good A.
Since Country X has the lower opportunity cost of producing Good B, Country X has the comparative advantage in producing Good B. This means that Option D is incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer:C
Absolute and comparative advantage are examined frequently and it is important to have a good understanding of how they work.
Let’s start by looking at absolute advantage. Country $X$ has an absolute advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ can produce a unit of that good using fewer resources than Country $Y$, (or, equivalently, when it produces more than Country $Y$ when given the same resources).
Here, using one unit of labour and one unit of capital, Country X can produce 20 units of Good A, whereas Country $Y$ can produce 50 units. Therefore Country $Y$ has the absolute advantage in producing Good A. This contradicts the statement in Option A, which is therefore an incorrect answer.
Using one unit of labour and one unit of capital, Country X can produce 15 units of Good A, whereas Country Y can produce 25 units. Therefore Country Y also has the absolute advantage in producing Good B. This contradicts the statement in Option B, which is therefore also an incorrect answer. So the correct answer must be either Option Cor Option D.
Turning next to comparative advantage; Country $X$ has a comparative advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ has a lower opportunity cost of producing that good than Country Y. So, in order to determine which country has the comparative advantage, it is necessary to look at opportunity cost.
In Country X, the opportunity cost of producing 20 units of Good A is 15 units of Good B, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good A is 0.75 units of Good B.
In Country Y, the opportunity cost of producing 50 units of Good A is 25 units of Good B, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good A is 0.5 units of Good B.
Since Country $Y$ has the lower opportunity cost of producing Good A, Country $Y$ has the comparative advantage in producing Good A. This suggests that Option C is the correct answer. However, to be on the safe side, it’s best to check Option D to be sure.
In Country $X$, the opportunity cost of producing 15 units of Good $B$ is 20 units of Good $A$, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good B is 1.33 units of Good A.
In Country Y, the opportunity cost of producing 25 units of Good B is 50 units of Good A, hence the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of Good B is 2 units of Good A.
Since Country X has the lower opportunity cost of producing Good B, Country X has the comparative advantage in producing Good B. This means that Option D is incorrect.
-
Question 696 of 999CB2031602
Question 696
FlagFirms can benefit through specialisation and international trade due to:
Correct
Answer: D
Recall that:
– Country $X$ has an absolute advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ can produce $a$ unit of that good using fewer scarce resources than Country $Y$.
– Country $X$ has a comparative advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ has a lower opportunity cost of producing that good than Country $Y$.Factor endowments get a brief mention on page 751 of the textbook (in the section about the law of comparative advantage). Factor endowments differ between countries due to differences in population density, labour skills, climate, raw materials, capital equipment etc. These lead to different relative costs of producing goods in different countries, which in turn leads to absolute and/or comparative advantage. Therefore the third option is also correct.
Hence the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Recall that:
– Country $X$ has an absolute advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ can produce $a$ unit of that good using fewer scarce resources than Country $Y$.
– Country $X$ has a comparative advantage over Country $Y$ in producing a good when Country $X$ has a lower opportunity cost of producing that good than Country $Y$.Factor endowments get a brief mention on page 751 of the textbook (in the section about the law of comparative advantage). Factor endowments differ between countries due to differences in population density, labour skills, climate, raw materials, capital equipment etc. These lead to different relative costs of producing goods in different countries, which in turn leads to absolute and/or comparative advantage. Therefore the third option is also correct.
Hence the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 697 of 999CB2031603
Question 697
FlagThe terms of trade is initially set at 100 . If the average price of exports has risen by $50 \%$ since the base year and the average price of imports has risen by $20 \%$ since the base year, what is the current figure for the terms of trade to the nearest whole number?
Correct
Answer: B
The terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$The initial value of the terms of trade was 100, so, for simplicity, let’s assume that in the base year, both the index of export prices and the index of import prices were 100. Then the current figure is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { terms of trade } & =\frac{100 \times 1.5}{100 \times 1.2} \times 100 \\
& =125
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\text { terms of trade }=\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$The initial value of the terms of trade was 100, so, for simplicity, let’s assume that in the base year, both the index of export prices and the index of import prices were 100. Then the current figure is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { terms of trade } & =\frac{100 \times 1.5}{100 \times 1.2} \times 100 \\
& =125
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 698 of 999CB2031604
Question 698
FlagWhich of the following will result in an improvement in the domestic country’s terms of trade?
Correct
Answer: D
The terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$The first point to note is that the terms of trade is calculated using the prices of exports and imports, and so this rules out Options B and C.
An increase in the value of the terms of trade is regarded as an improvement. This will happen if the price of exports rises relative to the price of imports, which is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The terms of trade is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { index of export prices }}{\text { index of import prices }} \times 100
$$The first point to note is that the terms of trade is calculated using the prices of exports and imports, and so this rules out Options B and C.
An increase in the value of the terms of trade is regarded as an improvement. This will happen if the price of exports rises relative to the price of imports, which is Option D.
-
Question 699 of 999CB2031605
Question 699
FlagWhich of the following statements correctly describes the impact of removing a tariff?
Correct
Answer D
A tariff is a tax imposed on an imported good (or service). When a tariff is imposed:
– domestic customers pay a higher price (price rises from $P_{\text {world }}$ to $P_{\text {world }}+$ tariff on the diagram below) and domestic producers receive the same higher price
– the government gains tariff income from imports.When a tariff is removed, the opposite must apply, which corresponds to Option D.
Incorrect
Answer D
A tariff is a tax imposed on an imported good (or service). When a tariff is imposed:
– domestic customers pay a higher price (price rises from $P_{\text {world }}$ to $P_{\text {world }}+$ tariff on the diagram below) and domestic producers receive the same higher price
– the government gains tariff income from imports.When a tariff is removed, the opposite must apply, which corresponds to Option D.
-
Question 700 of 999CB2031606
Question 700
FlagA tariff is imposed on a specific good. Which group would benefit from the imposition of this tariff?
Correct
Answer: B
When a tariff is imposed, domestic customers pay a higher price, so Option A is incorrect, and domestic producers receive the same higher price, so Option B is correct.
Although the price charged in the domestic market will also be higher for the imported goods, the international producers will not benefit from additional income, because this will be absorbed by the tariff. Therefore Option C is incorrect.
It is difficult to see how international consumers (or producers) would benefit from a tariff that is imposed in another country, so Option D is also incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer: B
When a tariff is imposed, domestic customers pay a higher price, so Option A is incorrect, and domestic producers receive the same higher price, so Option B is correct.
Although the price charged in the domestic market will also be higher for the imported goods, the international producers will not benefit from additional income, because this will be absorbed by the tariff. Therefore Option C is incorrect.
It is difficult to see how international consumers (or producers) would benefit from a tariff that is imposed in another country, so Option D is also incorrect.
-
Question 701 of 999CB2031607
Question 701
FlagWhen countries engage in international trade, one of the advantages of specialisation is that it will enable a country to:
Correct
Answer B
The law of comparative advantage states that trade can benefit all countries if they specialise in (and so export) the goods in which they have a lower opportunity cost of production. This is Option B.
Terms of trade (Option A) reflects the relative prices of exports and imports. Specialisation might result in exports being produced at a lower price. This would actually act to worsen the terms of trade (ie exports are now relatively cheap compared to imports).
Importing cheaper labour (Option C) may reduce the price at which goods can be produced for, however, this is not an advantage of specialisation.
Similarly, although it might influence trade, attracting foreign direct investment is not an advantage of specialisation.
Incorrect
Answer B
The law of comparative advantage states that trade can benefit all countries if they specialise in (and so export) the goods in which they have a lower opportunity cost of production. This is Option B.
Terms of trade (Option A) reflects the relative prices of exports and imports. Specialisation might result in exports being produced at a lower price. This would actually act to worsen the terms of trade (ie exports are now relatively cheap compared to imports).
Importing cheaper labour (Option C) may reduce the price at which goods can be produced for, however, this is not an advantage of specialisation.
Similarly, although it might influence trade, attracting foreign direct investment is not an advantage of specialisation.
-
Question 702 of 999CB2031608
Question 702
FlagWhich of the following does NOT necessarily apply to a perfectly competitive firm producing in both the short run and the long run?
Correct
Option D is the correct answer.
Any firm that aims to maximise its profits will produce where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, and this is true in both the short run and the long run. So Option B does apply to perfectly competitive firms in both the short and the long run, and so it is not the correct answer.
Perfectly competitive firms face a horizontal demand, ie average revenue, curve. Given a straight line average revenue curve, the marginal revenue curve is also a straight line, but with twice the gradient. Since a horizontal average revenue curve has a gradient of zero, the marginal revenue curve will also have a gradient of zero, ie the average and marginal revenue curves are the same. Option A is therefore the same as Option B for perfectly competitive firms, and so is not the correct answer.
In the short run, any firm will only continue producing if it is covering its average variable costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average variable cost. (Any losses would then be less than the fixed cost, which would be the loss if the firm shut down and produced nothing.)
In the long run, any firm will only stay in the market if it is covering all of its costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average total cost (which is made up of average fixed costs and average variable costs). Therefore firms will only continue producing if average revenue exceeds average variable costs, and so Option C is true and so is not the correct answer.
In the long run, perfectly competitive firms will only make normal profits. However, in the short run, perfectly competitive firms can make supernormal profits, normal profits or losses. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Option D is the correct answer.
Any firm that aims to maximise its profits will produce where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, and this is true in both the short run and the long run. So Option B does apply to perfectly competitive firms in both the short and the long run, and so it is not the correct answer.
Perfectly competitive firms face a horizontal demand, ie average revenue, curve. Given a straight line average revenue curve, the marginal revenue curve is also a straight line, but with twice the gradient. Since a horizontal average revenue curve has a gradient of zero, the marginal revenue curve will also have a gradient of zero, ie the average and marginal revenue curves are the same. Option A is therefore the same as Option B for perfectly competitive firms, and so is not the correct answer.
In the short run, any firm will only continue producing if it is covering its average variable costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average variable cost. (Any losses would then be less than the fixed cost, which would be the loss if the firm shut down and produced nothing.)
In the long run, any firm will only stay in the market if it is covering all of its costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average total cost (which is made up of average fixed costs and average variable costs). Therefore firms will only continue producing if average revenue exceeds average variable costs, and so Option C is true and so is not the correct answer.
In the long run, perfectly competitive firms will only make normal profits. However, in the short run, perfectly competitive firms can make supernormal profits, normal profits or losses. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 703 of 999CB2031609
Question 703
FlagWhen a monopolist maximises profits, price exceeds marginal revenue. The difference between price and marginal revenue occurs because:
Correct
Answer: C
A monopoly typically faces a downward-sloping demand curve. This means that it will need to reduce its price in order to sell more units.
Suppose it drops its price a little in order to sell exactly one more unit. Then the marginal revenue of this extra unit will be equal to the additional revenue received from selling that particular unit (ie the new and reduced selling price) less the loss of revenue from all of the previous units, which are now being sold for a lower price than before. It is this loss of revenue from the previous units which means that the marginal revenue must be less than the price.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Note that Option B is the opposite to Option C, and so is not the correct answer. Option A refers to cost, whereas the question is asking about the relationship between revenues (rather than costs). Option D (diminishing returns) relates to production in the short run-and so the law of diminishing returns affects costs, and hence price in the short run. However, it is not the reason why price exceeds marginal revenue.Incorrect
Answer: C
A monopoly typically faces a downward-sloping demand curve. This means that it will need to reduce its price in order to sell more units.
Suppose it drops its price a little in order to sell exactly one more unit. Then the marginal revenue of this extra unit will be equal to the additional revenue received from selling that particular unit (ie the new and reduced selling price) less the loss of revenue from all of the previous units, which are now being sold for a lower price than before. It is this loss of revenue from the previous units which means that the marginal revenue must be less than the price.
Hence the correct answer is Option C.
Note that Option B is the opposite to Option C, and so is not the correct answer. Option A refers to cost, whereas the question is asking about the relationship between revenues (rather than costs). Option D (diminishing returns) relates to production in the short run-and so the law of diminishing returns affects costs, and hence price in the short run. However, it is not the reason why price exceeds marginal revenue. -
Question 704 of 999CB2031610
Question 704
FlagUnder perfect competition:
Correct
Answer: B
Recall that a key assumption of perfect competition is that there are no barriers to entry. This means that it is quick and easy for new firms to enter the industry, which they will do if the industry presents an opportunity to make excess, or supernormal, profits. As new firms enter the industry, the resulting increase in total market supply will reduce the market price. This process will continue until the market price has reduced to such an extent that the supernormal profits have been competed away and all firms in the industry are once again earning normal profits. The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Note also that:
– Under perfect competition, losses will likewise disappear in the long run, as firms leave the industry resulting in a decrease in market supply and a rise in the price until the remaining firms all earn normal profits.
– The absence of barriers to entry means that a similar process to that described above will lead to the competing away of supernormal profits in the long run under monopolistic competition.Incorrect
Answer: B
Recall that a key assumption of perfect competition is that there are no barriers to entry. This means that it is quick and easy for new firms to enter the industry, which they will do if the industry presents an opportunity to make excess, or supernormal, profits. As new firms enter the industry, the resulting increase in total market supply will reduce the market price. This process will continue until the market price has reduced to such an extent that the supernormal profits have been competed away and all firms in the industry are once again earning normal profits. The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Note also that:
– Under perfect competition, losses will likewise disappear in the long run, as firms leave the industry resulting in a decrease in market supply and a rise in the price until the remaining firms all earn normal profits.
– The absence of barriers to entry means that a similar process to that described above will lead to the competing away of supernormal profits in the long run under monopolistic competition. -
Question 705 of 999CB2031611
Question 705
FlagThe short-run supply curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry is its:
Correct
Answer: C
Just like any other firm, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue, ie $M C=M R$. As the $M R$ of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to average revenue (AR) and hence the price of the good, this means that output occurs where MC intersects the horizontal demand curve faced by the firm.
Moreover, as $M R=A R=$ price changes, so the profit-maximising output moves up or down the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the AR or demand curve with the MC curve that determines the output of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
However, in the short run, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will choose to keep producing where $M C=M R$, provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. The firm’s supply curve is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Just like any other firm, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue, ie $M C=M R$. As the $M R$ of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to average revenue (AR) and hence the price of the good, this means that output occurs where MC intersects the horizontal demand curve faced by the firm.
Moreover, as $M R=A R=$ price changes, so the profit-maximising output moves up or down the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the AR or demand curve with the MC curve that determines the output of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
However, in the short run, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will choose to keep producing where $M C=M R$, provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. The firm’s supply curve is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve.
-
Question 706 of 999CB2031612
Question 706
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is TRUE?
Correct
Answer: D
Although perfect competition assumes there are no barriers to entry, this assumption is also true of monopolistic competition. Consequently, Statement A is not true.
Next, each firm under monopolistic competition is assumed to produce a (slightly) different product from those of its competitors. As a result, it faces a downward-sloping demand curve and not a horizontal one. So, Statement B is also not true.
Although it is normally assumed that a monopoly will enjoy supernormal profits consistent with average revenues that exceed average costs, this is not necessarily the case. For example, it is possible that following a sudden fall in demand and/or increase in production costs even a monopoly could make losses. Consequently, its average revenue may not always be greater than it average cost, meaning that Statement C is not true.
Finally, the absence of barriers to entry means that in the long run under perfect competition, each firm will make only normal profits, with average revenue equal to average cost at the minimum point on the average cost curve. This will also be the point at which the marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve. So, Statement D is true and is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Although perfect competition assumes there are no barriers to entry, this assumption is also true of monopolistic competition. Consequently, Statement A is not true.
Next, each firm under monopolistic competition is assumed to produce a (slightly) different product from those of its competitors. As a result, it faces a downward-sloping demand curve and not a horizontal one. So, Statement B is also not true.
Although it is normally assumed that a monopoly will enjoy supernormal profits consistent with average revenues that exceed average costs, this is not necessarily the case. For example, it is possible that following a sudden fall in demand and/or increase in production costs even a monopoly could make losses. Consequently, its average revenue may not always be greater than it average cost, meaning that Statement C is not true.
Finally, the absence of barriers to entry means that in the long run under perfect competition, each firm will make only normal profits, with average revenue equal to average cost at the minimum point on the average cost curve. This will also be the point at which the marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve. So, Statement D is true and is the correct answer.
-
Question 707 of 999CB2031613
Question 707
FlagThe short-run supply curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry is its:
Correct
Answer: C
Just like any other firm, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue, ie $M C=M R$. As the $M R$ of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to average revenue (AR) and hence the price of the good, this means that the $M R=A R$ curve represents the demand curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
In addition, as the $M R=A R=$ demand curve shifts, so the profit-maximising output moves up or down the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the MR = demand curve with the MC curve that determines the supply of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm.
In the short run, if the price or average revenue is less than the average cost, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will choose to keep producing where $M C=M R$, provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. This is because by doing so the firm is covering its variable costs and also making some contribution towards its fixed costs. If this is the case, then it will make a smaller loss than if it closed down (in which case its loss would equal the total of its fixed costs), and so it will continue to produce in the short run. The short-run supply curve of an individual firm under perfect competition is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Just like any other firm, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue, ie $M C=M R$. As the $M R$ of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to average revenue (AR) and hence the price of the good, this means that the $M R=A R$ curve represents the demand curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
In addition, as the $M R=A R=$ demand curve shifts, so the profit-maximising output moves up or down the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the MR = demand curve with the MC curve that determines the supply of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm.
In the short run, if the price or average revenue is less than the average cost, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will choose to keep producing where $M C=M R$, provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. This is because by doing so the firm is covering its variable costs and also making some contribution towards its fixed costs. If this is the case, then it will make a smaller loss than if it closed down (in which case its loss would equal the total of its fixed costs), and so it will continue to produce in the short run. The short-run supply curve of an individual firm under perfect competition is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve.
-
Question 708 of 999CB2031614
Question 708
FlagA market is defined as perfectly contestable if entry to it:
Correct
A perfectly contestable market is a market where there is free and costless entry and exit. Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Answer: A
Incorrect
A perfectly contestable market is a market where there is free and costless entry and exit. Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Answer: A
-
Question 709 of 999CB2031615
Question 709
FlagThe managing director of a monopoly firm is given the following data:
Marginal revenue $=£ 11$, Marginal cost $=£ 10$
Average cost $=£ 13$, Average revenue $=£ 15$
To maximise profits the firm should:Correct
Answer: A
In general, the profit-maximising level of output is found by equating marginal cost (MC) to marginal revenue (MR).
Here the question states that $M C=£ 10$, while $M R=£ 11$. In other words, $M R>M C$. This means that if the firm were to increase its output by an additional unit, total profit would increase by $£ 1$. So, to maximise profits the firm should increase its output, which in turn rules out Options B and D.
In fact, the equilibrium diagram below shows that if $M R>M C$, the firm must be operating to the left of the profit-maximising level of output, $Q_1$. So in order to increase its profits, the monopoly should produce more units.
Recall that, as the diagram shows, a monopoly firm is assumed to always face a downwardsloping demand curve. This means that in order to sell more units, it will need to reduce its price. Consequently, we can rule out Option C, so the correct answer must be Option A.
Note that $M C=M R$ is the profit-maximising condition for all four of the market structures, ie perfect competition, monopolistic competition and oligopoly, as well as monopoly. So, if MR > MC, the firm should increase its output to maximise its profits regardless of the market structure in which it operates.
Furthermore, firms operating under monopolistic competition and oligopoly also face downwardsloping demand curves, and so they will need to drop their prices in order sell more units. However, this is not the case under perfect competition, where the individual firm is a price taker, facing a horizontal demand curve, and so can sell as many units as it likes at the given market price.
Incorrect
Answer: A
In general, the profit-maximising level of output is found by equating marginal cost (MC) to marginal revenue (MR).
Here the question states that $M C=£ 10$, while $M R=£ 11$. In other words, $M R>M C$. This means that if the firm were to increase its output by an additional unit, total profit would increase by $£ 1$. So, to maximise profits the firm should increase its output, which in turn rules out Options B and D.
In fact, the equilibrium diagram below shows that if $M R>M C$, the firm must be operating to the left of the profit-maximising level of output, $Q_1$. So in order to increase its profits, the monopoly should produce more units.
Recall that, as the diagram shows, a monopoly firm is assumed to always face a downwardsloping demand curve. This means that in order to sell more units, it will need to reduce its price. Consequently, we can rule out Option C, so the correct answer must be Option A.
Note that $M C=M R$ is the profit-maximising condition for all four of the market structures, ie perfect competition, monopolistic competition and oligopoly, as well as monopoly. So, if MR > MC, the firm should increase its output to maximise its profits regardless of the market structure in which it operates.
Furthermore, firms operating under monopolistic competition and oligopoly also face downwardsloping demand curves, and so they will need to drop their prices in order sell more units. However, this is not the case under perfect competition, where the individual firm is a price taker, facing a horizontal demand curve, and so can sell as many units as it likes at the given market price.
-
Question 710 of 999CB2031616
Question 710
FlagThe short-run supply curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry is its:
Correct
Answer: D
Just like a firm operating under any of the other market structures, the typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue, ie $M C=M R$. As the $M R$ of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to average revenue (AR) and hence the price of the good, this means that the horizontal $M R=A R$ curve represents the demand curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
In addition, as the $M R(=A R=$ demand) curve shifts, so the profit-maximising output moves along the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the MR (= demand) curve with the MC curve that determines the supply of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
In the short run, if the price, ie average revenue, is less than the average cost, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will choose to keep producing (where MC $=$ MR), provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. This is because by doing so, the firm is covering its variable costs and also making some contribution towards its fixed costs. If this is the case, then it will make a smaller loss than if it shut down (in which case its loss would equal the total of its fixed costs), and so it will continue to produce in the short run. The short-run supply curve of an individual firm under perfect competition is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve. Hence the correct answer is Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Just like a firm operating under any of the other market structures, the typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue, ie $M C=M R$. As the $M R$ of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to average revenue (AR) and hence the price of the good, this means that the horizontal $M R=A R$ curve represents the demand curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
In addition, as the $M R(=A R=$ demand) curve shifts, so the profit-maximising output moves along the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the MR (= demand) curve with the MC curve that determines the supply of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
In the short run, if the price, ie average revenue, is less than the average cost, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will choose to keep producing (where MC $=$ MR), provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. This is because by doing so, the firm is covering its variable costs and also making some contribution towards its fixed costs. If this is the case, then it will make a smaller loss than if it shut down (in which case its loss would equal the total of its fixed costs), and so it will continue to produce in the short run. The short-run supply curve of an individual firm under perfect competition is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve. Hence the correct answer is Option D.
-
Question 711 of 999CB2031617
Question 711
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is TRUE?
Correct
Answer:D
The absence of barriers to entry under perfect competition means that if firms are making excess (ie supernormal) profits, then, in the long run, other firms will enter the industry and drive prices down until all firms are just making normal profits again. Therefore Option A is false.
One of the key features of oligopoly is interdependence, ie the fact that each firm will be affected by its rivals’ decisions, and likewise, its decisions will affect its rivals. It is therefore very important to take into account the possible reactions of competitors, so Option B is false.
Since most firms (and in the case of Option C, monopolists) are generally able to sell more units if they reduce their price, they will face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves. Consequently, the marginal revenue curve also slopes downwards, and in fact, will slope downwards more steeply than the average revenue curve. (This is because the marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned from selling the last unit less the revenue lost by selling previous units at a lower price.) Therefore, at any level of output, average revenue will always be more than marginal revenue and so Option C is false.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium position for a monopolist making supernormal profits.
Firms under monopolistic competition also face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves, and therefore (for the reasons given above), the marginal revenue curve will be below the average revenue curve. Since the average revenue curve reflects price, price will be more than marginal revenue and hence Option D is correct.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium diagram for a firm under monopolistic competition making normal profits.
Incorrect
Answer:D
The absence of barriers to entry under perfect competition means that if firms are making excess (ie supernormal) profits, then, in the long run, other firms will enter the industry and drive prices down until all firms are just making normal profits again. Therefore Option A is false.
One of the key features of oligopoly is interdependence, ie the fact that each firm will be affected by its rivals’ decisions, and likewise, its decisions will affect its rivals. It is therefore very important to take into account the possible reactions of competitors, so Option B is false.
Since most firms (and in the case of Option C, monopolists) are generally able to sell more units if they reduce their price, they will face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves. Consequently, the marginal revenue curve also slopes downwards, and in fact, will slope downwards more steeply than the average revenue curve. (This is because the marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned from selling the last unit less the revenue lost by selling previous units at a lower price.) Therefore, at any level of output, average revenue will always be more than marginal revenue and so Option C is false.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium position for a monopolist making supernormal profits.
Firms under monopolistic competition also face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves, and therefore (for the reasons given above), the marginal revenue curve will be below the average revenue curve. Since the average revenue curve reflects price, price will be more than marginal revenue and hence Option D is correct.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium diagram for a firm under monopolistic competition making normal profits.
-
Question 712 of 999CB2031618
Question 712
FlagA perfectly competitive firm has fixed and variable costs of production. It produces output at the long-run profit-maximising level. Which of the following statements is correct?
Correct
Answer: C
Freedom of entry and exit means that, in the long run, firms in perfect competition make normal profits. In doing so, they produce at the lowest point on their average total cost (AC) curve (where it is tangential to the horizontal $A R=M R$ curve). As is the case in any market form, the MC curve cuts the AC curve at its lowest point, which rules out Option A.
If $M C=A C$ and, as is the case here, the firm has fixed costs, then $A C$ must be greater than average variable cost (AVC). It therefore follows that, MC $=A C>A V C$ and so the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Freedom of entry and exit means that, in the long run, firms in perfect competition make normal profits. In doing so, they produce at the lowest point on their average total cost (AC) curve (where it is tangential to the horizontal $A R=M R$ curve). As is the case in any market form, the MC curve cuts the AC curve at its lowest point, which rules out Option A.
If $M C=A C$ and, as is the case here, the firm has fixed costs, then $A C$ must be greater than average variable cost (AVC). It therefore follows that, MC $=A C>A V C$ and so the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 713 of 999CB2031619
Question 713
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Answer: B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option C is true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option C isn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option C is true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option C isn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
-
Question 714 of 999CB2031620
Question 714
FlagWhich one of the following characteristics does NOT apply to a firm in an industry characterised by perfect competition?
Correct
Firms in perfect competition each face a horizontal demand curve so that price $=A R=M R$. Therefore, Option D is true and is not the correct answer.
Freedom of entry and exit means that, in the long run, firms in perfect competition make normal profits. Therefore, Options A and B are true and so neither is the correct answer here.
Although firms in perfect competition can make only normal profits in the long run, they may be able to make supernormal profits in the short run. Therefore, Option C is untrue and is the correct answer.
Answer: C
Incorrect
Firms in perfect competition each face a horizontal demand curve so that price $=A R=M R$. Therefore, Option D is true and is not the correct answer.
Freedom of entry and exit means that, in the long run, firms in perfect competition make normal profits. Therefore, Options A and B are true and so neither is the correct answer here.
Although firms in perfect competition can make only normal profits in the long run, they may be able to make supernormal profits in the short run. Therefore, Option C is untrue and is the correct answer.
Answer: C
-
Question 715 of 999CB2031621
Question 715
FlagA monopoly firm faces a linear demand schedule and has positive but constant marginal costs which are currently below its marginal revenue. If the firm wishes to maximise profits then it should:
Correct
Answer: A
The monopolist’s position is shown in the following diagram:
Suppose the monopolist is producing at $Q_1$ where $M R>M C$. The profit-maximising level of output is $Q^*$ where $M R=M C$. Thus, the firm should lower prices and increase output to reach the profit-maximising level of output. Remember the demand curve is the AR curve. This shows the price at which a firm can sell its output. If the firm wishes to sell more, it must reduce its price from $P_1$ to $P^*$.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The monopolist’s position is shown in the following diagram:
Suppose the monopolist is producing at $Q_1$ where $M R>M C$. The profit-maximising level of output is $Q^*$ where $M R=M C$. Thus, the firm should lower prices and increase output to reach the profit-maximising level of output. Remember the demand curve is the AR curve. This shows the price at which a firm can sell its output. If the firm wishes to sell more, it must reduce its price from $P_1$ to $P^*$.
-
Question 716 of 999CB2031622
Question 716
FlagA perfectly contestable market is a market where the:
Correct
A perfectly contestable market is a market where there is free and costless entry and exit. As a result of this, potential entrants can enter the market quickly. Hence Option A is the correct answer.
Note that:
– Option B relates either to perfect competition or collusive oligopoly.
– Option C states that the barriers to entry are substantial, which is not consistent with a perfectly contestable market; furthermore, it does not mention exit costs, which are a major part of the definition of a perfectly contestable market, as significant exit costs will also discourage new firms from entering the market.
– Option D is not correct, since there is no reference to freedom of entry or exit, which is the definition of a perfectly contestable market.Answer: A
Incorrect
A perfectly contestable market is a market where there is free and costless entry and exit. As a result of this, potential entrants can enter the market quickly. Hence Option A is the correct answer.
Note that:
– Option B relates either to perfect competition or collusive oligopoly.
– Option C states that the barriers to entry are substantial, which is not consistent with a perfectly contestable market; furthermore, it does not mention exit costs, which are a major part of the definition of a perfectly contestable market, as significant exit costs will also discourage new firms from entering the market.
– Option D is not correct, since there is no reference to freedom of entry or exit, which is the definition of a perfectly contestable market.Answer: A
-
Question 717 of 999CB2031623
Question 717
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Answer D
This question concerns the typical features of three of the four main market structures.
Let’s consider the options in turn, bearing in mind that multiple-choice questions like this very much focus on the typical features of firms under each of the market structures.In monopolistic competition, it is generally assumed that the firms make normal profits in the long run. This is because the absence of barriers to entry means that any supernormal profits will eventually be competed away by the entry of new firms. This suggests that Option A is unlikely to be the correct answer.
Note that although it may be possible for some firms under monopolistic competition to earn supernormal profits in the long run, eg if they have lower costs, or if there is imperfect information, this isn’t typically the case. Consequently, in a question like this, as opposed to a longer question requiring a detailed discussion of monopolistic competition, we should assume this not to be the case.
Turning to Option B, price discrimination requires that the firm has some control over the price(s) it is able to charge customers. In other words, the firm needs to be a price maker. This is not the case under perfect competition, where each firm simply takes the market price as given and so is said to be a price taker. Consequently, this option represents a true statement.
Collusion is a key distinguishing feature of oligopoly compared to the other market structures and so Option C is a true statement.
Incorrect
Answer D
This question concerns the typical features of three of the four main market structures.
Let’s consider the options in turn, bearing in mind that multiple-choice questions like this very much focus on the typical features of firms under each of the market structures.In monopolistic competition, it is generally assumed that the firms make normal profits in the long run. This is because the absence of barriers to entry means that any supernormal profits will eventually be competed away by the entry of new firms. This suggests that Option A is unlikely to be the correct answer.
Note that although it may be possible for some firms under monopolistic competition to earn supernormal profits in the long run, eg if they have lower costs, or if there is imperfect information, this isn’t typically the case. Consequently, in a question like this, as opposed to a longer question requiring a detailed discussion of monopolistic competition, we should assume this not to be the case.
Turning to Option B, price discrimination requires that the firm has some control over the price(s) it is able to charge customers. In other words, the firm needs to be a price maker. This is not the case under perfect competition, where each firm simply takes the market price as given and so is said to be a price taker. Consequently, this option represents a true statement.
Collusion is a key distinguishing feature of oligopoly compared to the other market structures and so Option C is a true statement.
-
Question 718 of 999CB2031624
Question 718
FlagWhen a monopolist maximises profits, price exceeds marginal revenue. The difference between price and marginal revenue occurs because:
Correct
Answer: C
Recall that whenever a firm faces a downward-sloping demand, or average revnue, curve, as is the case with a monopoly, the corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. This is because in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the additional unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling the additional unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price.
Thus, Option C is the correct answer.
As an example, suppose that currently the firm sells 10 units at $\$ 10$ each, so its total revenue is \$100. Suppose that it then drops the price to \$9 in order to increase sales to 11 units.The effect of this is that its average revenue, or price per unit, will now be \$9 and its total revenue will fall to \$99. So, the marginal revenue of the 11th unit will be -\$1, which represents the revenue of $+\$ 9$ from the additional unit, which is the price of that unit, less the loss of \$1 per unit on the 10 units it sold previously.
Recall that under perfect competition, each firm is so small that its actions do not affect the market price and so it can sell as many units as it likes at that market price. Consequently, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve and the price charged and the marginal revenue are the same.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Recall that whenever a firm faces a downward-sloping demand, or average revnue, curve, as is the case with a monopoly, the corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. This is because in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the additional unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling the additional unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price.
Thus, Option C is the correct answer.
As an example, suppose that currently the firm sells 10 units at $\$ 10$ each, so its total revenue is \$100. Suppose that it then drops the price to \$9 in order to increase sales to 11 units.The effect of this is that its average revenue, or price per unit, will now be \$9 and its total revenue will fall to \$99. So, the marginal revenue of the 11th unit will be -\$1, which represents the revenue of $+\$ 9$ from the additional unit, which is the price of that unit, less the loss of \$1 per unit on the 10 units it sold previously.
Recall that under perfect competition, each firm is so small that its actions do not affect the market price and so it can sell as many units as it likes at that market price. Consequently, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve and the price charged and the marginal revenue are the same.
-
Question 719 of 999CB2031625
Question 719
FlagA profit maximising monopoly facing a linear demand schedule and having positive marginal costs will set its price in the region of the demand curve where the absolute price elasticity of demand is:
Correct
Answer A
the following graph shows for a monopoly:
Recall that along any straight-line demand curve:
– demand is elastic, ie has an absolute value of greater than one, throughout the top half of the curve (where MR is positive and output is less than Q1)
– demand has unit elasticity, ie has an absolute value of one, at the midway point (where MR is equal to zero, at output level Q1)
– demand is inelastic, ie has an absolute value of less than one, throughout the bottom half of the curve (where MR is negative and output exceeds Q1).The monopolist maximises profit where $\mathrm{MC}=\mathrm{MR}$, at output $\mathrm{Q}^*$ on the diagram above. So, as MC is positive, MR must also be positive at $\mathrm{Q}^*$. The profit-maximising price, $\mathrm{P}^*$, is therefore above the midway point along the AR curve, which implies that price elasticity of demand must have an absolute value of greater than one.
Incorrect
Answer A
the following graph shows for a monopoly:
Recall that along any straight-line demand curve:
– demand is elastic, ie has an absolute value of greater than one, throughout the top half of the curve (where MR is positive and output is less than Q1)
– demand has unit elasticity, ie has an absolute value of one, at the midway point (where MR is equal to zero, at output level Q1)
– demand is inelastic, ie has an absolute value of less than one, throughout the bottom half of the curve (where MR is negative and output exceeds Q1).The monopolist maximises profit where $\mathrm{MC}=\mathrm{MR}$, at output $\mathrm{Q}^*$ on the diagram above. So, as MC is positive, MR must also be positive at $\mathrm{Q}^*$. The profit-maximising price, $\mathrm{P}^*$, is therefore above the midway point along the AR curve, which implies that price elasticity of demand must have an absolute value of greater than one.
-
Question 720 of 999CB2031626
Question 720
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a feature of perfect competition?
Correct
Answer: C
The main assumptions underlying perfect competition are:
– firms are price takers – this means that all firms face horizontal demand (AR) curves, and their marginal revenue (MR) curves are the same line (which means that Option C is not a feature of perfect competition); furthermore, the equilibrium price (determined by the AR curve) will be equal to marginal cost (MC) because the profit-maximising firm will produce where $M C=M R(=A R)$
– there is complete freedom of entry into the industry for new firms – so Option B is a feature of perfect competition; furthermore, as a result of free entry, if supernormal profits are made in the short run, then new firms will enter the industry and the increased competition will compete away the supernormal profits, leaving only normal profits (so Option D is also a feature of perfect competition)
– all firms produce an identical product
– producers and consumers have perfect knowledge of the market.Incorrect
Answer: C
The main assumptions underlying perfect competition are:
– firms are price takers – this means that all firms face horizontal demand (AR) curves, and their marginal revenue (MR) curves are the same line (which means that Option C is not a feature of perfect competition); furthermore, the equilibrium price (determined by the AR curve) will be equal to marginal cost (MC) because the profit-maximising firm will produce where $M C=M R(=A R)$
– there is complete freedom of entry into the industry for new firms – so Option B is a feature of perfect competition; furthermore, as a result of free entry, if supernormal profits are made in the short run, then new firms will enter the industry and the increased competition will compete away the supernormal profits, leaving only normal profits (so Option D is also a feature of perfect competition)
– all firms produce an identical product
– producers and consumers have perfect knowledge of the market. -
Question 721 of 999CB2031627
Question 721
FlagA managing director of a monopoly firm with constant marginal costs has the following data:
\begin{array}{ll}
\text{Average revenue} & £ 15 \\
\text{Marginal revenue} & £ 10 \\
\text{Marginal cost} & £ 11 \\
\text{Average variable cost} & £ 11 \\
\text{Average total cost} & £ 13
\end{array}To maximise profits/minimise losses in the short run the firm should:
Correct
Answer: A
When the question has given cost and revenue figures like this, it might help to draw a diagram. In this case, the relevant diagram is for a monopoly firm in the short run. It is then possible to mark on the diagram the profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) output level and price and compare this to the position described by the values given in the question.
A The average revenue (AR) curve is typically drawn as a downward-sloping straight line and the corresponding marginal revenue (MR) curve is also a downward-sloping straight line, but with twice the gradient.
The question states that marginal costs (MC) (and hence average variable costs (AVC)) are constant, so can be drawn as a horizontal line at $£ 11$.
The figures given show an output level at which $A R(15)>M C(11)>M R(10)$, so the firm is producing at output level $Q_1$.
(At this output level, average (total) costs are $£ 13$. Constant marginal costs can be consistent with a downward-sloping average cost (AC) curve. This is because average (total) costs are made up of fixed and variable costs: average fixed cost falls with output and the average variable cost curve is constant. The AC curve can therefore be drawn in, although this isn’t actually needed in order to determine the correct answer.)To maximise profits, the firm should produce where $M R=M C$, ie at output level $Q^*$ in the diagram. This is below $Q_1$, so in order to maximise profits, the firm should reduce output.
Price is determined using the AR curve. Since this is downward-sloping, reduced output will be associated with higher prices, so in order to maximise profits, the firm should increase price.
Hence Option A is the correct answer.
Note that a firm should only close down in the short run (Option D) if it is not covering its variable costs of production. Since $A R>A V C$, it is covering its variable costs, so should continue producing.Incorrect
Answer: A
When the question has given cost and revenue figures like this, it might help to draw a diagram. In this case, the relevant diagram is for a monopoly firm in the short run. It is then possible to mark on the diagram the profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) output level and price and compare this to the position described by the values given in the question.
A The average revenue (AR) curve is typically drawn as a downward-sloping straight line and the corresponding marginal revenue (MR) curve is also a downward-sloping straight line, but with twice the gradient.
The question states that marginal costs (MC) (and hence average variable costs (AVC)) are constant, so can be drawn as a horizontal line at $£ 11$.
The figures given show an output level at which $A R(15)>M C(11)>M R(10)$, so the firm is producing at output level $Q_1$.
(At this output level, average (total) costs are $£ 13$. Constant marginal costs can be consistent with a downward-sloping average cost (AC) curve. This is because average (total) costs are made up of fixed and variable costs: average fixed cost falls with output and the average variable cost curve is constant. The AC curve can therefore be drawn in, although this isn’t actually needed in order to determine the correct answer.)To maximise profits, the firm should produce where $M R=M C$, ie at output level $Q^*$ in the diagram. This is below $Q_1$, so in order to maximise profits, the firm should reduce output.
Price is determined using the AR curve. Since this is downward-sloping, reduced output will be associated with higher prices, so in order to maximise profits, the firm should increase price.
Hence Option A is the correct answer.
Note that a firm should only close down in the short run (Option D) if it is not covering its variable costs of production. Since $A R>A V C$, it is covering its variable costs, so should continue producing. -
Question 722 of 999CB2031628
Question 722
FlagWhich one of the following conditions indicates that a firm is operating in a perfectly competitive industry rather than a monopolistic industry?
Correct
Answer: C
Option A states the profit-maximising condition for any firm operating in any industry.
Option B relates to cost curves and is also true for any firm.
Option D states an arithmetic relationship between marginal and average for any firm.
Option C describes a situation where marginal revenue equals average revenue. For a straight-line downward-sloping demand (average revenue) curve, the marginal revenue curve is also a straight line, but is twice as steep. Therefore the only way these curves can be equal is if they both have a gradient of zero, ie they are horizontal. This is the case under perfect competition, hence the answer is Option C.Note that in the case of a monopolistic firm operating first-degree price discrimination, the marginal revenue and demand curves could also be equal, but this is a special situation. When you think of the distinguishing feature of perfect competition, it must be the horizontal demand curve, giving $A R=M R$.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Option A states the profit-maximising condition for any firm operating in any industry.
Option B relates to cost curves and is also true for any firm.
Option D states an arithmetic relationship between marginal and average for any firm.
Option C describes a situation where marginal revenue equals average revenue. For a straight-line downward-sloping demand (average revenue) curve, the marginal revenue curve is also a straight line, but is twice as steep. Therefore the only way these curves can be equal is if they both have a gradient of zero, ie they are horizontal. This is the case under perfect competition, hence the answer is Option C.Note that in the case of a monopolistic firm operating first-degree price discrimination, the marginal revenue and demand curves could also be equal, but this is a special situation. When you think of the distinguishing feature of perfect competition, it must be the horizontal demand curve, giving $A R=M R$.
-
Question 723 of 999CB2031629
Question 723
FlagA profit maximising monopoly facing a linear demand schedule and with positive marginal costs will set its price in the region of the demand curve where the absolute price elasticity of demand is:
Correct
Answer: A
A The average revenue curve (AR) or demand curve, marginal revenue curve (MR) and marginal cost curve (MC) for a monopoly generally look as follows:
Recall that along any straight-line demand curve:
– demand is elastic throughout the top half of the curve (where MR is positive and output is less than Q1)
– demand has unit elasticity at the midway point (where MR is equal to zero, at output level Q1)
– demand is inelastic throughout the bottom half of the curve (where MR is negative and output exceeds Q1).The monopolist maximises profit where $\mathrm{MC}=\mathrm{MR}$, at output $\mathrm{Q}^*$ on the diagram above. So, as MC is positive, MR must also be positive at $\mathrm{Q}^*$. The profit-maximising price, $\mathrm{P}^*$, is therefore above the midway point along the AR curve, which implies that the price of elasticity of demand must be elastic.
Incorrect
Answer: A
A The average revenue curve (AR) or demand curve, marginal revenue curve (MR) and marginal cost curve (MC) for a monopoly generally look as follows:
Recall that along any straight-line demand curve:
– demand is elastic throughout the top half of the curve (where MR is positive and output is less than Q1)
– demand has unit elasticity at the midway point (where MR is equal to zero, at output level Q1)
– demand is inelastic throughout the bottom half of the curve (where MR is negative and output exceeds Q1).The monopolist maximises profit where $\mathrm{MC}=\mathrm{MR}$, at output $\mathrm{Q}^*$ on the diagram above. So, as MC is positive, MR must also be positive at $\mathrm{Q}^*$. The profit-maximising price, $\mathrm{P}^*$, is therefore above the midway point along the AR curve, which implies that the price of elasticity of demand must be elastic.
-
Question 724 of 999CB2031630
Question 724
FlagWhich one of the following characteristics does NOT apply to a firm in an industry characterised by perfect competition?
Correct
Answer:B
Firms in perfect competition each face a horizontal demand curve so that price $=A R=M R$. Therefore, Option D is true and so is not the correct answer.
In the short run, firms in perfect competition can make losses, normal profits or supernormal profits. Therefore Option A is true and so is not the correct answer.
Freedom of entry and exit means that, in the long run, firms in perfect competition make normal profits. Therefore Option C is true and so is not the correct answer. Freedom of entry also means that there are no barriers to entry, so Option B is false and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer:B
Firms in perfect competition each face a horizontal demand curve so that price $=A R=M R$. Therefore, Option D is true and so is not the correct answer.
In the short run, firms in perfect competition can make losses, normal profits or supernormal profits. Therefore Option A is true and so is not the correct answer.
Freedom of entry and exit means that, in the long run, firms in perfect competition make normal profits. Therefore Option C is true and so is not the correct answer. Freedom of entry also means that there are no barriers to entry, so Option B is false and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 725 of 999CB2031631
Question 725
FlagThe short-run supply curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry is its:
Correct
Answer: D
Just like any other firm, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost ( MC ), ie $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. One of the features of perfect competition is a horizontal demand (or average revenue (AR)) curve for the individual firm, and hence an identical (horizontal) MR curve. As the MR of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to AR, and hence the price of the good, this means that output occurs where MC intersects the horizontal demand curve faced by the firm.
Moreover, as $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{AR}$ (= price) changes, the profit-maximising output moves up or down the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the AR or demand curve with the MC curve that determines the output of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
However, in the short run, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will only choose to keep producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. The firm’s supply curve is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Just like any other firm, a firm in a perfectly competitive industry will aim to maximise profits. This occurs at the output level at which marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost ( MC ), ie $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. One of the features of perfect competition is a horizontal demand (or average revenue (AR)) curve for the individual firm, and hence an identical (horizontal) MR curve. As the MR of the perfectly competitive firm is always equal to AR, and hence the price of the good, this means that output occurs where MC intersects the horizontal demand curve faced by the firm.
Moreover, as $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{AR}$ (= price) changes, the profit-maximising output moves up or down the firm’s MC curve. So, it is the intersection of the AR or demand curve with the MC curve that determines the output of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. In other words, the MC curve is effectively the supply curve of the individual firm under perfect competition.
However, in the short run, any firm (including a perfectly competitive one) will only choose to keep producing where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, provided that average revenue exceeds average variable costs. The firm’s supply curve is therefore that part of its MC curve above the average variable cost curve.
-
Question 726 of 999CB2031632
Question 726
FlagIn an industry characterised by perfect competition:
Correct
Answer: A
In a perfectly competitive market, the industry demand curve is downward-sloping, which rules out Option B, and firms are free to enter and exit the industry, which rules out Option C.
It is possible for firms to make supernormal profits in the short run because it takes time for new firms to enter markets and compete the excess profits away. This rules out Option D. It is only in the long run that there are no supernormal profits under perfect competition.
Firms operating under perfect competition are price takers – this means that all firms face a horizontal demand (AR) curve, and their marginal revenue (MR) curves are the same line. A profit-maximising firm will produce where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, and since $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{AR}, \mathrm{AR}=\mathrm{MC}$ and so Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
In a perfectly competitive market, the industry demand curve is downward-sloping, which rules out Option B, and firms are free to enter and exit the industry, which rules out Option C.
It is possible for firms to make supernormal profits in the short run because it takes time for new firms to enter markets and compete the excess profits away. This rules out Option D. It is only in the long run that there are no supernormal profits under perfect competition.
Firms operating under perfect competition are price takers – this means that all firms face a horizontal demand (AR) curve, and their marginal revenue (MR) curves are the same line. A profit-maximising firm will produce where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$, and since $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{AR}, \mathrm{AR}=\mathrm{MC}$ and so Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 727 of 999CB2031633
Question 727
FlagA monopoly firm faces a linear demand schedule, has positive but constant marginal costs and is currently producing where its marginal cost is below its marginal revenue. If the firm wishes to maximise profits then it should:
Correct
Answer: C
The monopolist’s position (as described in the question) is shown in the following diagram:
The question states that the monopolist is currently producing where $\mathrm{MR}>\mathrm{MC}$, eg at an output level $\mathrm{Q}_1$ with corresponding price $\mathrm{P}_1$. The profit-maximising level of output is $Q^*$, where $M R=M C$. Thus, the firm should lower prices (from $P_1$ to $P^*$ ) and increase output (from $\mathrm{Q}_1$ to $\mathrm{Q}^*$ ) to reach the profit-maximising level of output. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
The monopolist’s position (as described in the question) is shown in the following diagram:
The question states that the monopolist is currently producing where $\mathrm{MR}>\mathrm{MC}$, eg at an output level $\mathrm{Q}_1$ with corresponding price $\mathrm{P}_1$. The profit-maximising level of output is $Q^*$, where $M R=M C$. Thus, the firm should lower prices (from $P_1$ to $P^*$ ) and increase output (from $\mathrm{Q}_1$ to $\mathrm{Q}^*$ ) to reach the profit-maximising level of output. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 728 of 999CB2031634
Question 728
FlagOther things being equal, a fall in a monopolist’s fixed costs of production, which does not lead to new entrants, causes:
Correct
Answer: D
A fall in fixed costs reduces the average cost of production but has no effect on the marginal cost of production (which reflects variable costs only and is independent of fixed costs).
The profit-maximising level of output occurs where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. From the above, the marginal cost is unaffected. Furthermore, the question states that there are no new competitors in the market, so the demand curve and the MR curve are also unaffected.
Since MC and MR are unaffected by the change in fixed costs, both the profit-maximising level of output and market price are unchanged and so Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
A fall in fixed costs reduces the average cost of production but has no effect on the marginal cost of production (which reflects variable costs only and is independent of fixed costs).
The profit-maximising level of output occurs where $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$. From the above, the marginal cost is unaffected. Furthermore, the question states that there are no new competitors in the market, so the demand curve and the MR curve are also unaffected.
Since MC and MR are unaffected by the change in fixed costs, both the profit-maximising level of output and market price are unchanged and so Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 729 of 999CB2031635
Question 729
FlagIn a perfectly competitive market, a typical firm cannot affect the price of its output, and so it maximises profits when marginal cost is:
Correct
Answer C
The profit-maximising level of output in any market structure occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost ( $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$ ). In the case of perfect competition, where firms have no control over price and so sell at a constant price, the marginal revenue from an extra sale is equal to the price received for that extra unit. Therefore, $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$ becomes Price = MC and so Option C is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer C
The profit-maximising level of output in any market structure occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost ( $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$ ). In the case of perfect competition, where firms have no control over price and so sell at a constant price, the marginal revenue from an extra sale is equal to the price received for that extra unit. Therefore, $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$ becomes Price = MC and so Option C is the correct answer. -
Question 730 of 999CB2031636
Question 730
FlagAssuming that the marginal and average cost curves are unchanged, then following an increase in demand, firms in a perfectly competitive industry will:
Correct
Answer A
In the short run, an increase in demand will increase the price level and hence lead to supernormal profits being earned by firms in a perfectly competitive market. This rules out Options B and D.
In the long run, new firms will enter the market, attracted by the supernormal profits being made by the existing firms. The increase in supply from these new firms will reduce the price level in the market. New firms will continue to enter, and so the price level will continue to fall, until supernormal profits are no longer being made, ie until the price level is back to its original level. This rules out Options C and D.
Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A
In the short run, an increase in demand will increase the price level and hence lead to supernormal profits being earned by firms in a perfectly competitive market. This rules out Options B and D.
In the long run, new firms will enter the market, attracted by the supernormal profits being made by the existing firms. The increase in supply from these new firms will reduce the price level in the market. New firms will continue to enter, and so the price level will continue to fall, until supernormal profits are no longer being made, ie until the price level is back to its original level. This rules out Options C and D.
Option A is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 731 of 999CB2031637
Question 731
FlagA firm is operating in a perfectly competitive industry and in long-run equilibrium. An increase in wages would lead to:
Correct
Answer C
In the short run, an increase in wages for perfectly competitive firms would shift their cost curves upwards. Since wages are likely to be a variable cost, this will include both marginal costs and average costs. If marginal costs increase, then firms will need to find the new profit-maximising output level where the (new) marginal costs are equal to the (original) marginal revenues. This is shown on the diagram below, where the original curves are labelled with 1 s and the new cost curves are labelled with 2 s :
The new profit-maximising (or in this case loss-minimising) output level for firms is $Q_2$, and the firms are making losses equal to $Q_2 \times\left(C-P_1\right)$. As Option C is the only option that suggests losses, this is likely to be the correct answer.
In the long run, the losses being made will lead to some firms exiting the industry. This is also consistent with Option C.
As firms exit the industry, the industry supply curve will shift to the left. This will increase the prices that the (remaining) perfectly competitive firms must charge for the good. The average and marginal revenue curves will shift up to reflect this until the remaining perfectly competitive firms are again making normal profits.
Incorrect
Answer C
In the short run, an increase in wages for perfectly competitive firms would shift their cost curves upwards. Since wages are likely to be a variable cost, this will include both marginal costs and average costs. If marginal costs increase, then firms will need to find the new profit-maximising output level where the (new) marginal costs are equal to the (original) marginal revenues. This is shown on the diagram below, where the original curves are labelled with 1 s and the new cost curves are labelled with 2 s :
The new profit-maximising (or in this case loss-minimising) output level for firms is $Q_2$, and the firms are making losses equal to $Q_2 \times\left(C-P_1\right)$. As Option C is the only option that suggests losses, this is likely to be the correct answer.
In the long run, the losses being made will lead to some firms exiting the industry. This is also consistent with Option C.
As firms exit the industry, the industry supply curve will shift to the left. This will increase the prices that the (remaining) perfectly competitive firms must charge for the good. The average and marginal revenue curves will shift up to reflect this until the remaining perfectly competitive firms are again making normal profits.
-
Question 732 of 999CB2031638
Question 732
FlagThe marginal revenue curve for a monopoly is:
Correct
Answer C
the long run equilibrium for a monopoly for a firm is as follows:
The demand (or $A R$ ) curve for a monopoly firm is the same as the demand curve for the whole industry. It is therefore (usually) downward-sloping.
Given a downward-sloping $A R$ curve, the $M R$ curve will also be downward-sloping, but it will be steeper. This is because, in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product including all previous units (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the next unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling this unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
For a perfectly competitive firm, the MR curve is the same as the AR curve, ie the demand curve, (Option A), and these curves are horizontal (Option D).
Incorrect
Answer C
the long run equilibrium for a monopoly for a firm is as follows:
The demand (or $A R$ ) curve for a monopoly firm is the same as the demand curve for the whole industry. It is therefore (usually) downward-sloping.
Given a downward-sloping $A R$ curve, the $M R$ curve will also be downward-sloping, but it will be steeper. This is because, in order to sell more units, the firm has to reduce the price of the product including all previous units (in order to find some additional consumers who are now willing to buy the good at the lower price). Consequently, the marginal revenue of the next unit is equal to the additional revenue earned from selling this unit alone less the revenue lost by selling the existing output at a lower price. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
For a perfectly competitive firm, the MR curve is the same as the AR curve, ie the demand curve, (Option A), and these curves are horizontal (Option D).
-
Question 733 of 999CB2031639
Question 733
FlagWhich of the following does NOT necessarily apply to a perfectly competitive firm that produces in both the short run and the long run?
Correct
Answer D
the long run equilibrium position for a perfectly competitive firm is as follows:
The firm’s average revenue ( $A R$ ) and marginal revenue ( $M R$ ) curves are (the same) horizontal lines.
The marginal cost $(M C)$ curve has a standard ‘ $J$ ‘ shape, and profit is maximised at the output level at which $M R=M C$, ie $Q_1$. Any firm that aims to maximise its profits will produce where $M R=M C$, and this is true in both the short run and the long run. So Option B does apply to perfectly competitive firms in both the short and the long run, and so it is not the correct answer.
Since perfectly competitive firms can only make normal profits in the long run, $A R=A C$ at $Q_1$. This means they produce at the lowest point on their average (total) cost (AC) curve, ie where it is tangential to the (horizontal) $A R=M R$ curve. Since $A R=M R$, Option A is the same as Option B for perfectly competitive firms, and so Option A is not the correct answer.
In the short run, any firm will only continue producing if it is covering its average variable costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average variable cost. (Any losses would then be less than the fixed cost, which would be the loss if the firm shut down and produced nothing.)
In the long run, any firm will only stay in the market if it is covering all of its costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average total cost (which is made up of average fixed costs and average variable costs). Therefore, firms will only continue producing if average revenue exceeds average variable costs, and so Option C is true and so is not the correct answer.In the long run, perfectly competitive firms will only make normal profits. However, in the short run, perfectly competitive firms can make supernormal profits, normal profits or losses. Therefore Option D is false and so is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer D
the long run equilibrium position for a perfectly competitive firm is as follows:
The firm’s average revenue ( $A R$ ) and marginal revenue ( $M R$ ) curves are (the same) horizontal lines.
The marginal cost $(M C)$ curve has a standard ‘ $J$ ‘ shape, and profit is maximised at the output level at which $M R=M C$, ie $Q_1$. Any firm that aims to maximise its profits will produce where $M R=M C$, and this is true in both the short run and the long run. So Option B does apply to perfectly competitive firms in both the short and the long run, and so it is not the correct answer.
Since perfectly competitive firms can only make normal profits in the long run, $A R=A C$ at $Q_1$. This means they produce at the lowest point on their average (total) cost (AC) curve, ie where it is tangential to the (horizontal) $A R=M R$ curve. Since $A R=M R$, Option A is the same as Option B for perfectly competitive firms, and so Option A is not the correct answer.
In the short run, any firm will only continue producing if it is covering its average variable costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average variable cost. (Any losses would then be less than the fixed cost, which would be the loss if the firm shut down and produced nothing.)
In the long run, any firm will only stay in the market if it is covering all of its costs, ie if average revenue exceeds average total cost (which is made up of average fixed costs and average variable costs). Therefore, firms will only continue producing if average revenue exceeds average variable costs, and so Option C is true and so is not the correct answer.In the long run, perfectly competitive firms will only make normal profits. However, in the short run, perfectly competitive firms can make supernormal profits, normal profits or losses. Therefore Option D is false and so is the correct answer. -
Question 734 of 999CB2031640
Question 734
FlagGlobal Airways, which is a profit-maximising firm, has to decide whether or not to run an extra daily flight between London and Manchester. The total daily fixed costs of the airline are $£ 4,000$, the total variable costs of the extra flight are $£ 4,500$ and the expected average revenue from the extra flight is $£ 50$ with 85 passengers. In such circumstances, Global Airways will:
Correct
Answer A
The question is asking whether an airline should run an extra flight. It has specified that there are fixed costs, which indicates that the scenario under consideration is a short-run one. A firm should cease production in the short run (or in this case not run the extra flight) if $A R<A V C$, or in other words, if the total revenue from the extra flight is less than the total variable cost of running it.
Although the existence of (daily) fixed costs of the airline provide information on the time frame, the specific amount of these fixed costs will not be used in deciding whether or not the extra flight should run, so this piece of information can be ignored.
By running the extra flight:
– total fixed costs will remain unchanged
– total variable costs will increase by $£ 4,500$
– total revenue will increase by $£ 50 \times 85=£ 4,250$.Since the additional revenue is less than the additional variable costs, the airline should not run the extra flight. This rules out Options C and D.
Total profit (the difference between total revenue and total costs) will decrease by $£ 250$ ( $£ 4,250-£ 4,500$ ), ie there will be an expected loss of $£ 250$ on the extra flight. Therefore Option B is not the correct answer. If running the flight decreases profit, then it is not worth running the extra flight.
Incorrect
Answer A
The question is asking whether an airline should run an extra flight. It has specified that there are fixed costs, which indicates that the scenario under consideration is a short-run one. A firm should cease production in the short run (or in this case not run the extra flight) if $A R<A V C$, or in other words, if the total revenue from the extra flight is less than the total variable cost of running it.
Although the existence of (daily) fixed costs of the airline provide information on the time frame, the specific amount of these fixed costs will not be used in deciding whether or not the extra flight should run, so this piece of information can be ignored.
By running the extra flight:
– total fixed costs will remain unchanged
– total variable costs will increase by $£ 4,500$
– total revenue will increase by $£ 50 \times 85=£ 4,250$.Since the additional revenue is less than the additional variable costs, the airline should not run the extra flight. This rules out Options C and D.
Total profit (the difference between total revenue and total costs) will decrease by $£ 250$ ( $£ 4,250-£ 4,500$ ), ie there will be an expected loss of $£ 250$ on the extra flight. Therefore Option B is not the correct answer. If running the flight decreases profit, then it is not worth running the extra flight.
-
Question 735 of 999CB2031641
Question 735
FlagA perfectly competitive firm will:
Correct
Answer C
The main assumptions underlying perfect competition are:
– firms are price takers, ie all firms face horizontal demand, or average revenue (AR), curves and so Option D is false
– there is complete freedom of entry into the industry for new firms, so Option A is false, however, as setting up a business takes time, this only applies in the long run
– all firms produce an identical product
– producers and consumers have perfect knowledge of the market.In a perfectly competitive market, the industry demand curve is downward-sloping.
As a result of these assumptions:
– all firms face horizontal marginal revenue (MR) curves (ie their MR curves are the same line as their AR curves)
– in the short run, firms can make losses, normal profits or supernormal profits
– if supernormal profits are made in the short run, then – as there are no entry costs – new firms will enter the industry and the increased competition will compete away the supernormal profits, leaving only normal profits in the long run, so Option A is false
– the equilibrium price is determined by the intersection of the demand (ie AR) curve and supply (ie MC ) curve, and this will also be the profit-maximising price because the profit-maximising firm will produce where $\mathrm{MC}=\mathrm{MR}(=\mathrm{AR}=\mathrm{P})$, so Option C is true and is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer C
The main assumptions underlying perfect competition are:
– firms are price takers, ie all firms face horizontal demand, or average revenue (AR), curves and so Option D is false
– there is complete freedom of entry into the industry for new firms, so Option A is false, however, as setting up a business takes time, this only applies in the long run
– all firms produce an identical product
– producers and consumers have perfect knowledge of the market.In a perfectly competitive market, the industry demand curve is downward-sloping.
As a result of these assumptions:
– all firms face horizontal marginal revenue (MR) curves (ie their MR curves are the same line as their AR curves)
– in the short run, firms can make losses, normal profits or supernormal profits
– if supernormal profits are made in the short run, then – as there are no entry costs – new firms will enter the industry and the increased competition will compete away the supernormal profits, leaving only normal profits in the long run, so Option A is false
– the equilibrium price is determined by the intersection of the demand (ie AR) curve and supply (ie MC ) curve, and this will also be the profit-maximising price because the profit-maximising firm will produce where $\mathrm{MC}=\mathrm{MR}(=\mathrm{AR}=\mathrm{P})$, so Option C is true and is the correct answer. -
Question 736 of 999CB2031642
Question 736
FlagA perfectly competitive market is operating in long-run equilibrium and a new innovation is implemented that results in a downward shift in the firms’ average cost curve. Which of the following is likely to occur as a result of this innovation in the short run?
Correct
Answer D
The long-run equilibrium position for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market is as follows (prior to the new innovation being implemented):
The $A R$ and $M R$ curves are (the same) horizontal lines, because all firms in a perfectly competitive industry must share the same price, which can be determined by the whole industry supply and demand curves.
The $M C$ curve has a standard ‘ $J$ ‘ shape, and profit is maximised at the output level at which $M R=M C$, ie $Q_1$.
Since perfectly competitive firms can only make normal profits in the long run, $A R=A C$ at $Q_1$. This means they produce at the lowest point on their average (total) cost (AC) curve, ie where it is tangential to the (horizontal) $A R=M R$ curve.
As is always the case, the $M C$ curve intersects the $A C$ curve at its minimum point.
As a result of this new innovation, in the short run, there is a downward shift in the average cost curve. With price now above average cost, firms will make excess profit. Hence Option D is correct.It is possible that the marginal cost curve may also shift downwards (if it is variable rather than fixed costs which the innovation reduces), which may also lead to an increased level of output so that (new) $M C$ equals $M R$. However, there should be no change in the price charged (and so total revenue will either stay the same or increase), therefore leading to excess profits for firms.
This question specifically asks for the impact in the short run. However, you may find it helpful to consider the long run, partly as it may be asked in a similar question, and partly as it may help to demonstrate why the other possible answers are incorrect.
The innovation has reduced costs (potentially including average variable costs and hence marginal costs) for all firms in the industry, allowing excess or supernormal profits to be made. In the long run, other firms will likely enter the industry, attracted by the supernormal profits being made. This will increase industry supply, which will increase industry output (so Option A is not correct). An increase in industry output (and supply) will put downward pressure on prices, so Option B is not correct. For perfectly competitive firms, the marginal revenue curve is horizontal, so marginal revenues will decrease, meaning Option C is not correct.
Incorrect
Answer D
The long-run equilibrium position for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market is as follows (prior to the new innovation being implemented):
The $A R$ and $M R$ curves are (the same) horizontal lines, because all firms in a perfectly competitive industry must share the same price, which can be determined by the whole industry supply and demand curves.
The $M C$ curve has a standard ‘ $J$ ‘ shape, and profit is maximised at the output level at which $M R=M C$, ie $Q_1$.
Since perfectly competitive firms can only make normal profits in the long run, $A R=A C$ at $Q_1$. This means they produce at the lowest point on their average (total) cost (AC) curve, ie where it is tangential to the (horizontal) $A R=M R$ curve.
As is always the case, the $M C$ curve intersects the $A C$ curve at its minimum point.
As a result of this new innovation, in the short run, there is a downward shift in the average cost curve. With price now above average cost, firms will make excess profit. Hence Option D is correct.It is possible that the marginal cost curve may also shift downwards (if it is variable rather than fixed costs which the innovation reduces), which may also lead to an increased level of output so that (new) $M C$ equals $M R$. However, there should be no change in the price charged (and so total revenue will either stay the same or increase), therefore leading to excess profits for firms.
This question specifically asks for the impact in the short run. However, you may find it helpful to consider the long run, partly as it may be asked in a similar question, and partly as it may help to demonstrate why the other possible answers are incorrect.
The innovation has reduced costs (potentially including average variable costs and hence marginal costs) for all firms in the industry, allowing excess or supernormal profits to be made. In the long run, other firms will likely enter the industry, attracted by the supernormal profits being made. This will increase industry supply, which will increase industry output (so Option A is not correct). An increase in industry output (and supply) will put downward pressure on prices, so Option B is not correct. For perfectly competitive firms, the marginal revenue curve is horizontal, so marginal revenues will decrease, meaning Option C is not correct.
-
Question 737 of 999CB2031644
Question 737
FlagThe prisoners’ dilemma, applied to a situation involving the only two firms in an oligopoly industry, illustrates that:
Correct
The prisoners’ dilemma is a scenario under which there are two or more firms (or prisoners) who, by attempting independently to choose the best strategy, based on what other(s) are likely to do, end up in a worse position than if they had co-operated from the start. This description corresponds best with Option C.
Answer: C
Incorrect
The prisoners’ dilemma is a scenario under which there are two or more firms (or prisoners) who, by attempting independently to choose the best strategy, based on what other(s) are likely to do, end up in a worse position than if they had co-operated from the start. This description corresponds best with Option C.
Answer: C
-
Question 738 of 999CB2031645
Question 738
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D
Although perfect competition assumes there are no barriers to entry, this assumption is also true of monopolistic competition. Consequently, Statement A is not true.Next, each firm under monopolistic competition is assumed to produce a (slightly) different product from those of its competitors. As a result, it faces a downward-sloping demand curve and not a horizontal one. So, Statement B is also not true.
Although it is normally assumed that a monopoly will enjoy supernormal profits consistent with average revenues that exceed average costs, this is not necessarily the case. For example, it is possible that following a sudden fall in demand and/or increase in production costs even a monopoly could make losses. Consequently, its average revenue may not always be greater than it average cost, meaning that Statement C is not true.
Finally, the absence of barriers to entry means that in the long run under perfect competition, each firm will make only normal profits, with average revenue equal to average cost at the minimum point on the average cost curve. This will also be the point at which the marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve. So, Statement D is true and is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D
Although perfect competition assumes there are no barriers to entry, this assumption is also true of monopolistic competition. Consequently, Statement A is not true.Next, each firm under monopolistic competition is assumed to produce a (slightly) different product from those of its competitors. As a result, it faces a downward-sloping demand curve and not a horizontal one. So, Statement B is also not true.
Although it is normally assumed that a monopoly will enjoy supernormal profits consistent with average revenues that exceed average costs, this is not necessarily the case. For example, it is possible that following a sudden fall in demand and/or increase in production costs even a monopoly could make losses. Consequently, its average revenue may not always be greater than it average cost, meaning that Statement C is not true.
Finally, the absence of barriers to entry means that in the long run under perfect competition, each firm will make only normal profits, with average revenue equal to average cost at the minimum point on the average cost curve. This will also be the point at which the marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve. So, Statement D is true and is the correct answer.
-
Question 739 of 999CB2031647
Question 739
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a prediction of the theory of monopolistic competition?
Correct
Answer: D
Here is the long-run equilibrium diagram for the firm in monopolistic competition.
The question asks for the incorrect statement, so let’s go through each option in turn.
Option A is correct. The diagram shows that at output $q_1, P>M C$. (Note that this means that the social optimum is not reached; in fact, the social optimum (where $P=M C$ ) is only achieved in perfect competition.)
Option B is correct. Firms in monopolistic competition all make slightly different products. This means that they have some power in the market to determine price, ie they are price makers and each faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
Option C is correct. Unless there is price discrimination, the price is equal to the average revenue in all market structures.
This means that Option D must be incorrect. Let’s check. Monopolistic firms do not make supernormal profit in the long run because other firms are free to enter the industry in the long run. Any supernormal profit earned in the short run would be competed away by the entry of new firms in the long run.
Answer: D
Incorrect
Answer: D
Here is the long-run equilibrium diagram for the firm in monopolistic competition.
The question asks for the incorrect statement, so let’s go through each option in turn.
Option A is correct. The diagram shows that at output $q_1, P>M C$. (Note that this means that the social optimum is not reached; in fact, the social optimum (where $P=M C$ ) is only achieved in perfect competition.)
Option B is correct. Firms in monopolistic competition all make slightly different products. This means that they have some power in the market to determine price, ie they are price makers and each faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
Option C is correct. Unless there is price discrimination, the price is equal to the average revenue in all market structures.
This means that Option D must be incorrect. Let’s check. Monopolistic firms do not make supernormal profit in the long run because other firms are free to enter the industry in the long run. Any supernormal profit earned in the short run would be competed away by the entry of new firms in the long run.
Answer: D
-
Question 740 of 999CB2031648
Question 740
FlagIn the long run, profit-maximising firms operating under conditions of monopolistic competition will produce at a level of output where price equals:
Correct
Answer: B
The standard model of monopolistic competition assumes there are no barriers to entry to prevent new firms entering the market in response to supernormal profits. Consequently, in the long run, firms operating under conditions of monopolistic competition will make normal profits. This means that total revenue must equal total cost at the profit-maximising output level and that average revenue, or price, must likewise equal average (total) cost.
Note also that at the profit-maximising output level for a firm in monopolistic competition:
– Price will exceed both average fixed and average variable cost (assuming there is a fixed cost).
– Price will exceed marginal cost. (To see this, draw the long-run equilibrium diagram.)Incorrect
Answer: B
The standard model of monopolistic competition assumes there are no barriers to entry to prevent new firms entering the market in response to supernormal profits. Consequently, in the long run, firms operating under conditions of monopolistic competition will make normal profits. This means that total revenue must equal total cost at the profit-maximising output level and that average revenue, or price, must likewise equal average (total) cost.
Note also that at the profit-maximising output level for a firm in monopolistic competition:
– Price will exceed both average fixed and average variable cost (assuming there is a fixed cost).
– Price will exceed marginal cost. (To see this, draw the long-run equilibrium diagram.) -
Question 741 of 999CB2031649
Question 741
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a feature of an industry characterised by monopolistic competition?
Correct
Answer: A
monopolistic competition is characterised by free entry and exit of firms, which means that Option B is a true statement and hence isn’t the correct answer.
Free entry and exit also means that although supernormal profits may be made in the short run, such profits will attract new entrants into the industry, increasing supply and forcing down the market price. This will continue until only normal profits are being made. Hence, in the long run, firms can make only normal profits. This suggests that Option A is false and hence is the correct answer.
In addition, under monopolistic competition:
– Firms produce differentiated products. So, Option C is a true statement.
– Profit is maximised when $M C=M R$ and, in the long run, free entry and exit ensures that $A C=A R$, ie normal profits are earned. As $A R$ is always greater than $M R$ for a firm operating under monopolistic competition (see the second diagram in Solution 12 below), it must be the case that when profit is maximised, $A R>M C$, ie prices are above marginal cost. So, Option D is also a true statement.Incorrect
Answer: A
monopolistic competition is characterised by free entry and exit of firms, which means that Option B is a true statement and hence isn’t the correct answer.
Free entry and exit also means that although supernormal profits may be made in the short run, such profits will attract new entrants into the industry, increasing supply and forcing down the market price. This will continue until only normal profits are being made. Hence, in the long run, firms can make only normal profits. This suggests that Option A is false and hence is the correct answer.
In addition, under monopolistic competition:
– Firms produce differentiated products. So, Option C is a true statement.
– Profit is maximised when $M C=M R$ and, in the long run, free entry and exit ensures that $A C=A R$, ie normal profits are earned. As $A R$ is always greater than $M R$ for a firm operating under monopolistic competition (see the second diagram in Solution 12 below), it must be the case that when profit is maximised, $A R>M C$, ie prices are above marginal cost. So, Option D is also a true statement. -
Question 742 of 999CB2031650
Question 742
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is TRUE?
Correct
answer d
The absence of barriers to entry under perfect competition means that if firms are making excess (ie supernormal) profits, then, in the long run, other firms will enter the industry and drive prices down until all firms are just making normal profits again. Therefore Option A is false.
One of the key features of oligopoly is interdependence, ie the fact that each firm will be affected by its rivals’ decisions, and likewise, its decisions will affect its rivals. It is therefore very important to take into account the possible reactions of competitors, so Option B is false.
Since most firms (and in the case of Option C, monopolists) are generally able to sell more units if they reduce their price, they will face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves. Consequently, the marginal revenue curve also slopes downwards, and in fact, will slope downwards more steeply than the average revenue curve. (This is because the marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned from selling the last unit less the revenue lost by selling previous units at a lower price.) Therefore, at any level of output, average revenue will always be more than marginal revenue and so Option C is false.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium position for a monopolist making supernormal profits.
Firms under monopolistic competition also face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves, and therefore (for the reasons given above), the marginal revenue curve will be below the average revenue curve. Since the average revenue curve reflects price, price will be more than marginal revenue and hence Option D is correct.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium diagram for a firm under monopolistic competition making normal profits.
Incorrect
answer d
The absence of barriers to entry under perfect competition means that if firms are making excess (ie supernormal) profits, then, in the long run, other firms will enter the industry and drive prices down until all firms are just making normal profits again. Therefore Option A is false.
One of the key features of oligopoly is interdependence, ie the fact that each firm will be affected by its rivals’ decisions, and likewise, its decisions will affect its rivals. It is therefore very important to take into account the possible reactions of competitors, so Option B is false.
Since most firms (and in the case of Option C, monopolists) are generally able to sell more units if they reduce their price, they will face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves. Consequently, the marginal revenue curve also slopes downwards, and in fact, will slope downwards more steeply than the average revenue curve. (This is because the marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned from selling the last unit less the revenue lost by selling previous units at a lower price.) Therefore, at any level of output, average revenue will always be more than marginal revenue and so Option C is false.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium position for a monopolist making supernormal profits.
Firms under monopolistic competition also face downward-sloping demand (ie average revenue) curves, and therefore (for the reasons given above), the marginal revenue curve will be below the average revenue curve. Since the average revenue curve reflects price, price will be more than marginal revenue and hence Option D is correct.
The diagram below shows the long-run equilibrium diagram for a firm under monopolistic competition making normal profits.
-
Question 743 of 999CB2031651
Question 743
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Answer B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option C is true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option Cisn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
Answer: B
Incorrect
Answer B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option C is true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option Cisn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
Answer: B
-
Question 744 of 999CB2031652
Question 744
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a barrier to entry in an oligopolistic industry?
Correct
Answer B
In an oligopoly (and also a monopoly) barriers prevent new firms entering the industry. These can be structural (ie natural) barriers, such as economies of scale, or strategic (ie deliberate) barriers erected by the existing firms, such as:
– product proliferation, ie producing many variations of a product so as to cover every niche in the market (Option A)
– investing in spare capacity, to ensure that all future demand can be met, even if prices were to reduce and demand were to increase (Option C)
– high advertising expenditure, to increase brand loyalty and the cost of entry for potential competitors (Option D).As Options A, C and D are all potential barriers to entry, Option B must be the correct answer.
If an industry experiences constant returns to scale, then assuming that prices are fixed, long-run average cost is constant as output increases. This corresponds to a situation where firms experience neither economies nor diseconomies of scale. Large firms therefore have no cost advantage over smaller firms, and production costs do not deter the entry of new firms into the industry.So, Option B is indeed the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B
In an oligopoly (and also a monopoly) barriers prevent new firms entering the industry. These can be structural (ie natural) barriers, such as economies of scale, or strategic (ie deliberate) barriers erected by the existing firms, such as:
– product proliferation, ie producing many variations of a product so as to cover every niche in the market (Option A)
– investing in spare capacity, to ensure that all future demand can be met, even if prices were to reduce and demand were to increase (Option C)
– high advertising expenditure, to increase brand loyalty and the cost of entry for potential competitors (Option D).As Options A, C and D are all potential barriers to entry, Option B must be the correct answer.
If an industry experiences constant returns to scale, then assuming that prices are fixed, long-run average cost is constant as output increases. This corresponds to a situation where firms experience neither economies nor diseconomies of scale. Large firms therefore have no cost advantage over smaller firms, and production costs do not deter the entry of new firms into the industry.So, Option B is indeed the correct answer.
-
Question 745 of 999CB2031654
Question 745
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
answer d
Let’s consider the options in turn, bearing in mind that multiple-choice questions like this very much focus on the typical features of firms under each of the market structures.In monopolistic competition, it is generally assumed that the firms make normal profits in the long run. This is because the absence of barriers to entry means that any supernormal profits will eventually be competed away by the entry of new firms. This suggests that Option $A$ is unlikely to be the correct answer.
Note that although it may be possible for some firms under monopolistic competition to earn supernormal profits in the long run, eg if they have lower costs, or if there is imperfect information, this isn’t typically the case. Consequently, in a question like this, as opposed to a longer question requiring a detailed discussion of monopolistic competition, we should assume this not to be the case.
Turning to Option B, price discrimination requires that the firm has some control over the price(s) it is able to charge customers. In other words, the firm needs to be a price maker. This is not the case under perfect competition, where each firm simply takes the market price as given and so is said to be a price taker. Consequently, this option represents a true statement.
Collusion is a key distinguishing feature of oligopoly compared to the other market structures and so Option C is a true statement.
As mentioned above, under perfect competition each firm takes the market price as given. It is then assumed that it can sell as much or as little as it chooses at the given market price and so it faces a horizontal, ie a perfectly elastic, demand curve. Option D is therefore a false statement and hence the correct answer.
Answer: D
Incorrect
answer d
Let’s consider the options in turn, bearing in mind that multiple-choice questions like this very much focus on the typical features of firms under each of the market structures.In monopolistic competition, it is generally assumed that the firms make normal profits in the long run. This is because the absence of barriers to entry means that any supernormal profits will eventually be competed away by the entry of new firms. This suggests that Option $A$ is unlikely to be the correct answer.
Note that although it may be possible for some firms under monopolistic competition to earn supernormal profits in the long run, eg if they have lower costs, or if there is imperfect information, this isn’t typically the case. Consequently, in a question like this, as opposed to a longer question requiring a detailed discussion of monopolistic competition, we should assume this not to be the case.
Turning to Option B, price discrimination requires that the firm has some control over the price(s) it is able to charge customers. In other words, the firm needs to be a price maker. This is not the case under perfect competition, where each firm simply takes the market price as given and so is said to be a price taker. Consequently, this option represents a true statement.
Collusion is a key distinguishing feature of oligopoly compared to the other market structures and so Option C is a true statement.
As mentioned above, under perfect competition each firm takes the market price as given. It is then assumed that it can sell as much or as little as it chooses at the given market price and so it faces a horizontal, ie a perfectly elastic, demand curve. Option D is therefore a false statement and hence the correct answer.
Answer: D
-
Question 746 of 999CB2031655
Question 746
FlagWhich one of the following characteristics applies to an oligopolistic market structure?
Correct
Answer: D
This question concerns the main features of oligopolies.
One of the distinctive features of oligopoly is the interdependence of firms in the industry, ie the output (and other) decisions of each firm may exert a significant influence on the other decisions of the firms in the industry. This corresponds to Option D, which is therefore the correct answer.Typically:
– There are just a few firms in an oligopolistic market, which contradicts Option A.
– There are significant barriers to entry in the market, which contradicts Option B.
– The firms have market power and thus are price makers, each with a downward-sloping demand curve, (unlike the price takers in perfect competition who face a perfectly elastic demand curve). This contradicts Option C.Incorrect
Answer: D
This question concerns the main features of oligopolies.
One of the distinctive features of oligopoly is the interdependence of firms in the industry, ie the output (and other) decisions of each firm may exert a significant influence on the other decisions of the firms in the industry. This corresponds to Option D, which is therefore the correct answer.Typically:
– There are just a few firms in an oligopolistic market, which contradicts Option A.
– There are significant barriers to entry in the market, which contradicts Option B.
– The firms have market power and thus are price makers, each with a downward-sloping demand curve, (unlike the price takers in perfect competition who face a perfectly elastic demand curve). This contradicts Option C. -
Question 747 of 999CB2031656
Question 747
FlagAn implicit or explicit agreement amongst firms in an industry NOT to compete with each other is known as:
Correct
Answer: B
A dominant firm (Option A) is likely to dictate rather than make agreements. Recall that a dominant firm may be a price leader, ie it sets the price for each product, which the other, typically smaller, firms then follow. So, Option A is not the correct answer.
A collusive oligopoly is defined as one in which the firms agree not to compete, which strongly suggests that Option B is the correct answer.
A non-cooperative (ie non-collusive or competitive) oligopoly (Option C) is not likely to cooperate to the extent of making agreements.
Product differentiation (Option D) has nothing to do with making agreements; it is about making a product different from other products, including those of other firms.
Incorrect
Answer: B
A dominant firm (Option A) is likely to dictate rather than make agreements. Recall that a dominant firm may be a price leader, ie it sets the price for each product, which the other, typically smaller, firms then follow. So, Option A is not the correct answer.
A collusive oligopoly is defined as one in which the firms agree not to compete, which strongly suggests that Option B is the correct answer.
A non-cooperative (ie non-collusive or competitive) oligopoly (Option C) is not likely to cooperate to the extent of making agreements.
Product differentiation (Option D) has nothing to do with making agreements; it is about making a product different from other products, including those of other firms.
-
Question 748 of 999CB2031657
Question 748
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is FALSE?
Correct
Answer B
Firms in perfect competition can make supernormal profit, normal profit or losses in the short run, but they will make only normal profit in the long run because of the freedom of firms to enter and leave the industry. This rules out Option A.
Firms in monopolistic competition produce heterogeneous products, so Option B is false and is the correct answer.
A key feature of oligopoly is that oligopolists are interdependent: their decisions depend on the likely actions of their competitors. This rules out Option C.
Any profit-maximising firm (including a monopoly) produces where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. This rules out Option D.
Incorrect
Answer B
Firms in perfect competition can make supernormal profit, normal profit or losses in the short run, but they will make only normal profit in the long run because of the freedom of firms to enter and leave the industry. This rules out Option A.
Firms in monopolistic competition produce heterogeneous products, so Option B is false and is the correct answer.
A key feature of oligopoly is that oligopolists are interdependent: their decisions depend on the likely actions of their competitors. This rules out Option C.
Any profit-maximising firm (including a monopoly) produces where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. This rules out Option D.
-
Question 749 of 999CB2031658
Question 749
FlagIn the kinked-demand curve theory of oligopoly the:
Correct
Answer B
The kinked demand curve diagram for the oligopolist is shown below, with the kink in the average revenue curve and the discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Note that the cost curves for an oligopoly will have the standard ‘ $U$ ‘ (and ‘ $J$ ‘) shape(s).
Incorrect
Answer B
The kinked demand curve diagram for the oligopolist is shown below, with the kink in the average revenue curve and the discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Note that the cost curves for an oligopoly will have the standard ‘ $U$ ‘ (and ‘ $J$ ‘) shape(s).
-
Question 750 of 999CB2031659
Question 750
FlagIn the long run, a firm in a monopolistic competition market structure will produce at:
Correct
Answer C
The long-run diagram representing a firm operating in monopolistic competition is shown below.The firm will produce the profit maximising output level $q^1$ (where $M R=M C$ ). At this output level, marginal cost is below average cost, and so average cost is decreasing. The correct answer is therefore Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C
The long-run diagram representing a firm operating in monopolistic competition is shown below.The firm will produce the profit maximising output level $q^1$ (where $M R=M C$ ). At this output level, marginal cost is below average cost, and so average cost is decreasing. The correct answer is therefore Option C.
-
Question 751 of 999CB2031660
Question 751
FlagUnder the Cournot model of duopoly, a firm:
Correct
Answer B
Of the different models of competition (ie non-collusion) within an oligopolistic market structure, the Cournot model is probably the second-most frequently tested (the first being the kinkeddemand model).
B The Cournot model is a model of duopoly where each firm makes its price and output decisions based on the assumption that its rival will produce a particular quantity. Hence the correct answer is Option B.
Option C describes the Bertrand model, where each firm is assumed to set a particular price and stick to it.
Option D describes a situation of collusive oligopoly, whereas the Cournot model (along with the Bertrand and kinked-demand models) are all theories of non-collusive oligopoly.
Incorrect
Answer B
Of the different models of competition (ie non-collusion) within an oligopolistic market structure, the Cournot model is probably the second-most frequently tested (the first being the kinkeddemand model).
B The Cournot model is a model of duopoly where each firm makes its price and output decisions based on the assumption that its rival will produce a particular quantity. Hence the correct answer is Option B.
Option C describes the Bertrand model, where each firm is assumed to set a particular price and stick to it.
Option D describes a situation of collusive oligopoly, whereas the Cournot model (along with the Bertrand and kinked-demand models) are all theories of non-collusive oligopoly.
-
Question 752 of 999CB2031661
Question 752
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a feature of monopolistic competition?
Correct
Answer A
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which there are no barriers to entry and each firm produces a differentiated product (Options B and C). If firms make supernormal profit in the short run, the absence of barriers to entry allows other firms to enter the market and compete away the supernormal profits, until only normal profits are made in the long run (Option D).
The profit-maximising condition (for any firm) is to produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost $(\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC})$. The demand curve for monopolistically competitive firms is downward-sloping. This results in an MR curve that is also downward-sloping, but is steeper than the demand curve, so at non-zero quantities, the MR curve is below the demand curve. So, MR will equal MC at an amount below the price level, since price is determined by the demand curve. Hence the equilibrium price will be above MC , and hence Option A is not true. This is shown on the diagram below:
Incorrect
Answer A
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which there are no barriers to entry and each firm produces a differentiated product (Options B and C). If firms make supernormal profit in the short run, the absence of barriers to entry allows other firms to enter the market and compete away the supernormal profits, until only normal profits are made in the long run (Option D).
The profit-maximising condition (for any firm) is to produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost $(\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC})$. The demand curve for monopolistically competitive firms is downward-sloping. This results in an MR curve that is also downward-sloping, but is steeper than the demand curve, so at non-zero quantities, the MR curve is below the demand curve. So, MR will equal MC at an amount below the price level, since price is determined by the demand curve. Hence the equilibrium price will be above MC , and hence Option A is not true. This is shown on the diagram below:
-
Question 753 of 999CB2031662
Question 753
FlagWhich of the following features is NOT a typical characteristic of oligopoly?
Correct
Answer A
Firms operating in oligopoly can make supernormal profits in both the short run and long run. This rules out Option B.
A key feature of oligopoly is that oligopolists are interdependent: their decisions depend on the likely actions of their competitors. This rules out Option C. Oligopolists also tend to use advertising and other forms of non-price competition, ruling out Option D.
Under the kinked-demand model of oligopoly, it is assumed that if a firm raises its price, its competitors will not match the price rise, but if a firm cuts its price, its competitors will match the cut. Option A is the opposite to this and therefore not a typical characteristic of oligopoly. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A
Firms operating in oligopoly can make supernormal profits in both the short run and long run. This rules out Option B.
A key feature of oligopoly is that oligopolists are interdependent: their decisions depend on the likely actions of their competitors. This rules out Option C. Oligopolists also tend to use advertising and other forms of non-price competition, ruling out Option D.
Under the kinked-demand model of oligopoly, it is assumed that if a firm raises its price, its competitors will not match the price rise, but if a firm cuts its price, its competitors will match the cut. Option A is the opposite to this and therefore not a typical characteristic of oligopoly. Option A is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 754 of 999CB2031663
Question 754
FlagIn the Cournot model of duopoly, when the two firms are at the equilibrium level of output, the:
Correct
Answer A
A duopoly is a type of oligopoly in which there are only two firms in the market. Under the Cournot model of duopoly, each firm has to choose an output level for a given period without knowing its rival’s production plans.
The following diagram shows the profit-maximising output level for Firm A (in a market consisting of Firm A and Firm B):
Firm A determines its demand curve $\left(D_A\right)$ according to the industry demand curve $\left(D_{\text {ind }}\right)$ and the assumed quantity that Firm $B$ produces $\left(Q_B\right)$. It then sets its price $\left(P_A\right)$ at the profit-maximising output level ( $Q_A$ ) where the marginal revenue and the marginal cost for Firm A are equal $\left(M R_A=M C_A\right)$.
The Cournot equilibrium is where each of two firms’ actual output is the same as what the other firm predicted it would produce. This is not necessarily where both firms produce the same amount of output, so this rules out Option D.
Perfect competition and monopoly are the two extreme market structures: perfect competition has lots of firms producing the same good and monopoly has only one firm. All else being equal, an industry characterised by perfect competition will produce more than an industry characterised by a monopoly. As a duopoly sits between these two extreme market structures, the answer is Option A.
Incorrect
Answer A
A duopoly is a type of oligopoly in which there are only two firms in the market. Under the Cournot model of duopoly, each firm has to choose an output level for a given period without knowing its rival’s production plans.
The following diagram shows the profit-maximising output level for Firm A (in a market consisting of Firm A and Firm B):
Firm A determines its demand curve $\left(D_A\right)$ according to the industry demand curve $\left(D_{\text {ind }}\right)$ and the assumed quantity that Firm $B$ produces $\left(Q_B\right)$. It then sets its price $\left(P_A\right)$ at the profit-maximising output level ( $Q_A$ ) where the marginal revenue and the marginal cost for Firm A are equal $\left(M R_A=M C_A\right)$.
The Cournot equilibrium is where each of two firms’ actual output is the same as what the other firm predicted it would produce. This is not necessarily where both firms produce the same amount of output, so this rules out Option D.
Perfect competition and monopoly are the two extreme market structures: perfect competition has lots of firms producing the same good and monopoly has only one firm. All else being equal, an industry characterised by perfect competition will produce more than an industry characterised by a monopoly. As a duopoly sits between these two extreme market structures, the answer is Option A.
-
Question 755 of 999CB2031664
Question 755
FlagIn the long run, a firm operating in an industry characterised by monopolistic competition will:
Correct
Answer B
The long-run diagram representing a firm operating in a monopolistic competition is shown below:
The firm will produce the profit maximising output level $Q^1$ (where $M R=M C$ ). At this level of output:
– average cost is decreasing, ruling out Option A
– the condition for the socially efficient output level $(A R=M C)$ is not met, ruling out Option C
– marginal cost is increasing, ruling out Option D.Firms operating in monopolistic competition are said to have excess capacity because they are not operating at minimum cost, ie by producing more, they would move to a lower point on their long-run average cost curve. So, the correct answer is Option B.
Incorrect
Answer B
The long-run diagram representing a firm operating in a monopolistic competition is shown below:
The firm will produce the profit maximising output level $Q^1$ (where $M R=M C$ ). At this level of output:
– average cost is decreasing, ruling out Option A
– the condition for the socially efficient output level $(A R=M C)$ is not met, ruling out Option C
– marginal cost is increasing, ruling out Option D.Firms operating in monopolistic competition are said to have excess capacity because they are not operating at minimum cost, ie by producing more, they would move to a lower point on their long-run average cost curve. So, the correct answer is Option B.
-
Question 756 of 999CB2031665
Question 756
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a feature of monopolistic competition?
Correct
Answer B
Under monopolistic competition, if supernormal profits are made in the short run, then as there is freedom of entry into the industry, new firms will enter and the increased competition will compete away the supernormal profits, leaving only normal profits in the long run. Therefore Option A is a feature of monopolistic competition, so is not the correct answer.
The profit-maximising output level will be determined by the $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$ condition, and the profit-maximising price will be the AR at that output level. As the firms are price makers and so face downward-sloping demand, ie average revenue (AR), curves and hence (steeper) downward-sloping marginal revenue (MR) curves (that sit below their AR curves, ie $A R>M R), P(=A R)>(M R=) M C$, ie price is greater than $M C$. Therefore Option $B$ is not a feature of monopolistic competition, so is the correct answer.
For any firm selling goods at a single price, it is always the case that price is equal to average revenue, so Option C is a feature of monopolistic competition, so is not the correct answer.
Firms in monopolistic competition face a downward-sloping demand curve. This means that each firm can raise its price without losing all its customers, so Option D is a feature of monopolistic competition, so is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B
Under monopolistic competition, if supernormal profits are made in the short run, then as there is freedom of entry into the industry, new firms will enter and the increased competition will compete away the supernormal profits, leaving only normal profits in the long run. Therefore Option A is a feature of monopolistic competition, so is not the correct answer.
The profit-maximising output level will be determined by the $\mathrm{MR}=\mathrm{MC}$ condition, and the profit-maximising price will be the AR at that output level. As the firms are price makers and so face downward-sloping demand, ie average revenue (AR), curves and hence (steeper) downward-sloping marginal revenue (MR) curves (that sit below their AR curves, ie $A R>M R), P(=A R)>(M R=) M C$, ie price is greater than $M C$. Therefore Option $B$ is not a feature of monopolistic competition, so is the correct answer.
For any firm selling goods at a single price, it is always the case that price is equal to average revenue, so Option C is a feature of monopolistic competition, so is not the correct answer.
Firms in monopolistic competition face a downward-sloping demand curve. This means that each firm can raise its price without losing all its customers, so Option D is a feature of monopolistic competition, so is not the correct answer.
-
Question 757 of 999CB2031666
Question 757
FlagWhich one of the following statements about market structure is TRUE?
Correct
Answer A
In the long run, perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive firms make normal profits only (due to the freedom of entry and exit to/from the industry). Therefore Option A is true, and so is the correct answer.
The only market structure that always produces an identical (homogeneous) product is perfect competition. Firms in other market structures, including monopolistic competition, can produce differentiated products, and so Option B is false, meaning it is not the correct answer.
Under oligopoly, firms make decisions taking into account the possible reactions of their competitors, so Option C is false, and so is not the correct answer.
A firm with positive marginal costs will have its profit-maximising level of output in the section of the graph where marginal revenues are also positive. This is in the left-hand half of the diagram, ie where demand is price-elastic. So Option D is false, and so is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A
In the long run, perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive firms make normal profits only (due to the freedom of entry and exit to/from the industry). Therefore Option A is true, and so is the correct answer.
The only market structure that always produces an identical (homogeneous) product is perfect competition. Firms in other market structures, including monopolistic competition, can produce differentiated products, and so Option B is false, meaning it is not the correct answer.
Under oligopoly, firms make decisions taking into account the possible reactions of their competitors, so Option C is false, and so is not the correct answer.
A firm with positive marginal costs will have its profit-maximising level of output in the section of the graph where marginal revenues are also positive. This is in the left-hand half of the diagram, ie where demand is price-elastic. So Option D is false, and so is not the correct answer.
-
Question 758 of 999CB2031667
Question 758
FlagThe prisoners’ dilemma, applied to a situation involving two oligopolistic firms, illustrates that:
Correct
Answer C
The prisoners’ dilemma is a scenario under which there are two or more firms (or prisoners) who, by attempting independently to choose the best strategy, based on what other(s) are likely to do, end up in a worse position than if they had co-operated from the start. Option C is the description that corresponds most closely with the prisoners’ dilemma and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
The prisoners’ dilemma is a scenario under which there are two or more firms (or prisoners) who, by attempting independently to choose the best strategy, based on what other(s) are likely to do, end up in a worse position than if they had co-operated from the start. Option C is the description that corresponds most closely with the prisoners’ dilemma and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 759 of 999CB2031668
Question 759
FlagA firm operating in an oligopoly differs from one operating in perfect competition because:
Correct
Answer C
Under perfect competition there are many firms, whereas in an oligopoly there are only a few firms, so Option A is false, and so is not the correct answer.
The (typical) demand (AR) curve faced by:
– a perfectly competitive firm is horizontal, ie it is a price taker
– an oligopolist is downward-sloping (and may be kinked), ie the firm is a price maker
and so Option B is false, and so is not the correct answer.In the short run, firms (from all market structures) may be able to make supernormal (ie abnormal) profits, normal profits or losses. In the long run:
– perfectly competitive firms make normal profits (due to the freedom of entry and exit to/from the industry)
– oligopolists and monopolists may be able to make supernormal profits.
and so Option C is true and is the correct answer. Barriers to entry are usually present in oligopoly and monopoly and so Option D is false.Incorrect
Answer C
Under perfect competition there are many firms, whereas in an oligopoly there are only a few firms, so Option A is false, and so is not the correct answer.
The (typical) demand (AR) curve faced by:
– a perfectly competitive firm is horizontal, ie it is a price taker
– an oligopolist is downward-sloping (and may be kinked), ie the firm is a price maker
and so Option B is false, and so is not the correct answer.In the short run, firms (from all market structures) may be able to make supernormal (ie abnormal) profits, normal profits or losses. In the long run:
– perfectly competitive firms make normal profits (due to the freedom of entry and exit to/from the industry)
– oligopolists and monopolists may be able to make supernormal profits.
and so Option C is true and is the correct answer. Barriers to entry are usually present in oligopoly and monopoly and so Option D is false. -
Question 760 of 999CB2031669
Question 760
FlagUnder the Cournot model of duopoly, equilibrium will occur when the:
Correct
Answer C
The Cournot model is a model of duopoly where each firm makes its price and output decisions based on the assumption that its rival will produce a particular quantity. (A duopoly is a type of oligopoly in which there are only two firms in the market.)
A reaction function (or curve) shows how a firm’s optimal output varies according to the output chosen by its rival (or rivals). Equilibrium will occur where the reaction functions of the two firms intersect (Option C).
According to the assumptions underlying the Cournot model, firms face the same costs and charge the same price. In other words, equilibrium will result in firms charging the same prices, however, firms charging the same prices won’t necessarily result in equilibrium, hence Option A is not correct. Similarly, although firms are assumed to face the same costs, this is also true at non-equilibrium positions and so Option B is not correct.
Incorrect
Answer C
The Cournot model is a model of duopoly where each firm makes its price and output decisions based on the assumption that its rival will produce a particular quantity. (A duopoly is a type of oligopoly in which there are only two firms in the market.)
A reaction function (or curve) shows how a firm’s optimal output varies according to the output chosen by its rival (or rivals). Equilibrium will occur where the reaction functions of the two firms intersect (Option C).
According to the assumptions underlying the Cournot model, firms face the same costs and charge the same price. In other words, equilibrium will result in firms charging the same prices, however, firms charging the same prices won’t necessarily result in equilibrium, hence Option A is not correct. Similarly, although firms are assumed to face the same costs, this is also true at non-equilibrium positions and so Option B is not correct.
-
Question 761 of 999CB2031670
Question 761
FlagAn example of second-degree price discrimination is a situation where:
Correct
Answer: A
Price discrimination occurs when a firm discriminates between customers by charging them different prices.
Remember that there are three different variations of price discrimination described in the course:
1. First-degree price discrimination is where each customer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay for each unit.
2. Second-degree price discrimination is where the firm offers customers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product. Consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the quantity of the product purchased.
3. Third-degree price discrimination is where different prices are charged to different groups of customers, though the same price is charged to everyone within each group.Option A is therefore an example of second-degree price discrimination.
Note that although different firms often charge different prices for the same product in practice (as in Option D), this isn’t what is meant by price discrimination, as each individual firm will typically charge the same price to all of its customers.Incorrect
Answer: A
Price discrimination occurs when a firm discriminates between customers by charging them different prices.
Remember that there are three different variations of price discrimination described in the course:
1. First-degree price discrimination is where each customer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay for each unit.
2. Second-degree price discrimination is where the firm offers customers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product. Consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the quantity of the product purchased.
3. Third-degree price discrimination is where different prices are charged to different groups of customers, though the same price is charged to everyone within each group.Option A is therefore an example of second-degree price discrimination.
Note that although different firms often charge different prices for the same product in practice (as in Option D), this isn’t what is meant by price discrimination, as each individual firm will typically charge the same price to all of its customers. -
Question 762 of 999CB2031671
Question 762
FlagThird-degree price discrimination refers to the situation where:
Correct
Answer: B
There are three forms of price discrimination:
1. first-degree price discrimination, where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that he or she is prepared to pay – this is Option C
2. second-degree price discrimination, where the firm offers consumers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product; consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the number of units purchased – this is Option A
3. third-degree price discrimination, where the firm divides consumers into different groups and charges a different price to each group of consumers – this is Option B.It is clear from this that Option B is the correct answer. Option D is just describing the usual practice of different firms charging different prices, so is irrelevant.
Incorrect
Answer: B
There are three forms of price discrimination:
1. first-degree price discrimination, where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that he or she is prepared to pay – this is Option C
2. second-degree price discrimination, where the firm offers consumers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product; consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the number of units purchased – this is Option A
3. third-degree price discrimination, where the firm divides consumers into different groups and charges a different price to each group of consumers – this is Option B.It is clear from this that Option B is the correct answer. Option D is just describing the usual practice of different firms charging different prices, so is irrelevant.
-
Question 763 of 999CB2031672
Question 763
FlagA necessary condition for a firm being able to engage in price discrimination is that:
Correct
Answer C
Recall that a perfectly elastic demand curve (ie one with an infinite elasticity of demand) is horizontal. This means that even a small increase price will lead to demand falling to zero. As such, it will not be possible for the firm to put up the price it charges to any of its customers and so it will be unable to discriminate between them by charging them different prices. So, Option A is not the correct answer.
Suppose that consumers of the firm’s product are willing and able to resell their purchase and that Consumer $A$ is being charged just $\$ 2$ for the product, whereas Consumer $B$ is being charged $\$ 4$. Then Consumer A could buy the product for \$2 and resell it to Consumer B for \$3. In doing so, it both makes a profit and undercuts the firm, which will therefore be unable to charge the higher price of \$4 to Consumer B. Consequently, the ability of consumers to resell generally reduces the ability of the firm to engage in price discrimination and so Option B is incorrect.
In order to charge different prices, the firm needs consumers who are prepared to pay different prices, ie some are prepared to pay more than others because they value the good more highly. This is consistent with a downward-sloping demand curve, whereby as price increases, consumers who value the good less highly will cease to buy it. Option C is therefore a necessary condition for price discrimination.
Finally, in order to charge different prices, the firm must be a price maker, with some degree of control over the price(s) that it charges, and not a price taker, which takes the market price as given. So, Option D is incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer C
Recall that a perfectly elastic demand curve (ie one with an infinite elasticity of demand) is horizontal. This means that even a small increase price will lead to demand falling to zero. As such, it will not be possible for the firm to put up the price it charges to any of its customers and so it will be unable to discriminate between them by charging them different prices. So, Option A is not the correct answer.
Suppose that consumers of the firm’s product are willing and able to resell their purchase and that Consumer $A$ is being charged just $\$ 2$ for the product, whereas Consumer $B$ is being charged $\$ 4$. Then Consumer A could buy the product for \$2 and resell it to Consumer B for \$3. In doing so, it both makes a profit and undercuts the firm, which will therefore be unable to charge the higher price of \$4 to Consumer B. Consequently, the ability of consumers to resell generally reduces the ability of the firm to engage in price discrimination and so Option B is incorrect.
In order to charge different prices, the firm needs consumers who are prepared to pay different prices, ie some are prepared to pay more than others because they value the good more highly. This is consistent with a downward-sloping demand curve, whereby as price increases, consumers who value the good less highly will cease to buy it. Option C is therefore a necessary condition for price discrimination.
Finally, in order to charge different prices, the firm must be a price maker, with some degree of control over the price(s) that it charges, and not a price taker, which takes the market price as given. So, Option D is incorrect.
-
Question 764 of 999CB2031673
Question 764
FlagThird-degree price discrimination refers to the situation where:
Correct
Answer: D
There are three forms of price discrimination:
1. first-degree price discrimination, where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that he or she is prepared to pay – this is Option B.
2. second-degree price discrimination, where the firm offers customers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product; consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the quantity of the product purchased – Option C is an example of this.
3. third-degree price discrimination, where the firm divides consumers into different groups and charges a different price to each group of consumers – this is Option D.It is clear from this that Option D is the correct answer. Option A is just describing the usual practice of different firms charging different prices (for the same product) and so is irrelevant.
Incorrect
Answer: D
There are three forms of price discrimination:
1. first-degree price discrimination, where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that he or she is prepared to pay – this is Option B.
2. second-degree price discrimination, where the firm offers customers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product; consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the quantity of the product purchased – Option C is an example of this.
3. third-degree price discrimination, where the firm divides consumers into different groups and charges a different price to each group of consumers – this is Option D.It is clear from this that Option D is the correct answer. Option A is just describing the usual practice of different firms charging different prices (for the same product) and so is irrelevant.
-
Question 765 of 999CB2031674
Question 765
FlagA firm that produces a main product and a by-product will maximise profits if it:
Correct
Answer B
A by-product is a good or a service that is produced as a result of producing another good or service. If a firm is producing a main product and a by-product, it will maximise profits at the output level where the combined $M C=$ combined $M R$. The answer is therefore Option B. Having decided on the output level, the firm should then use the relevant demand curves to determine the prices to be charged for each of the main product and the by-product.
Option D suggests using the ‘marginal rule’ for the by-product separately. However, production of the by-product is inextricably linked with the production of the main product. So, it is not possible to sell more of the by-product than the amount produced in the course of producing the desired amount of the main product, and selling less than the amount produced could be very costly and wasteful. By considering the profitability of the combined output, a firm might produce more of the main product than it otherwise would, because the profit from the by-product more than makes up for the lower profit on the main product.
Option A and C do not determine the profit-maximizing position
Incorrect
Answer B
A by-product is a good or a service that is produced as a result of producing another good or service. If a firm is producing a main product and a by-product, it will maximise profits at the output level where the combined $M C=$ combined $M R$. The answer is therefore Option B. Having decided on the output level, the firm should then use the relevant demand curves to determine the prices to be charged for each of the main product and the by-product.
Option D suggests using the ‘marginal rule’ for the by-product separately. However, production of the by-product is inextricably linked with the production of the main product. So, it is not possible to sell more of the by-product than the amount produced in the course of producing the desired amount of the main product, and selling less than the amount produced could be very costly and wasteful. By considering the profitability of the combined output, a firm might produce more of the main product than it otherwise would, because the profit from the by-product more than makes up for the lower profit on the main product.
Option A and C do not determine the profit-maximizing position
-
Question 766 of 999CB2031675
Question 766
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Answer: B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option C is true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option C isn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option C is true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option C isn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
-
Question 767 of 999CB2031676
Question 767
FlagThird-degree price discrimination refers to the situation where:
Correct
Answer: B
There are three forms of price discrimination:
1. first-degree price discrimination, where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that he or she is prepared to pay – this is Option C
2. second-degree price discrimination, where the firm offers customers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product; consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the quantity of the product purchased – Option A is an example of this
3. third-degree price discrimination, where the firm divides consumers into different groups and charges a different price to each group of consumers – this is Option B.It is clear from this that Option B is the correct answer. Option D is just describing the usual practice of different firms charging different prices (for the same product) and so is irrelevant.
Incorrect
Answer: B
There are three forms of price discrimination:
1. first-degree price discrimination, where the firm charges each consumer the maximum price that he or she is prepared to pay – this is Option C
2. second-degree price discrimination, where the firm offers customers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product; consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on the quantity of the product purchased – Option A is an example of this
3. third-degree price discrimination, where the firm divides consumers into different groups and charges a different price to each group of consumers – this is Option B.It is clear from this that Option B is the correct answer. Option D is just describing the usual practice of different firms charging different prices (for the same product) and so is irrelevant.
-
Question 768 of 999CB2031677
Question 768
FlagA firm operates in two markets, Market 1 and Market 2 , and price discriminates when profit maximising. In such circumstances, its marginal revenue in Market 1 is equal to the:
Correct
Answer C
Price discrimination is when a firm charges different prices to different people for the same product and the difference in price cannot be fully accounted for by any difference in the cost of supply. A firm must have significant market power to be able to price discriminate.
C The following diagram shows how a profit-maximising firm will practise TDPD by dividing its market into two distinct markets ( 1 and 2 ) with different demand elasticities:
Markets 1 and 2 face demand curves with different elasticities (Market 1 faces more inelastic demand and Market 2 more elastic demand). The $A R$ – and hence $M R$ – curve for the ‘total’ market is obtained by summing the quantity demanded at each price level in each market.
Total profit is maximised when $M R=M C$ in the ‘total’ market. Since the marginal cost of producing a certain level of output is irrelevant of which market it is sold in, $M C$ is assumed to be the same in both markets. The quantity to be sold in each market is set from $M R=M C$ in each market, and since $M C$ is assumed to be the same in each, $M R$ must also be the same in both Market 1 and Market 2, therefore Option C is correct. The price in each market is then set from its respective demand curve, which means that Options A and $B$ are not correct.
The diagram above doesn’t include the AC curve. It is possible that Option D could be true, however it is not necessarily the case. Therefore Option C is the best answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
Price discrimination is when a firm charges different prices to different people for the same product and the difference in price cannot be fully accounted for by any difference in the cost of supply. A firm must have significant market power to be able to price discriminate.
C The following diagram shows how a profit-maximising firm will practise TDPD by dividing its market into two distinct markets ( 1 and 2 ) with different demand elasticities:
Markets 1 and 2 face demand curves with different elasticities (Market 1 faces more inelastic demand and Market 2 more elastic demand). The $A R$ – and hence $M R$ – curve for the ‘total’ market is obtained by summing the quantity demanded at each price level in each market.
Total profit is maximised when $M R=M C$ in the ‘total’ market. Since the marginal cost of producing a certain level of output is irrelevant of which market it is sold in, $M C$ is assumed to be the same in both markets. The quantity to be sold in each market is set from $M R=M C$ in each market, and since $M C$ is assumed to be the same in each, $M R$ must also be the same in both Market 1 and Market 2, therefore Option C is correct. The price in each market is then set from its respective demand curve, which means that Options A and $B$ are not correct.
The diagram above doesn’t include the AC curve. It is possible that Option D could be true, however it is not necessarily the case. Therefore Option C is the best answer.
-
Question 769 of 999CB2031678
Question 769
FlagThe welfare consequences of third-degree price discrimination are to the benefit of:
Correct
Answer B or C
Third-degree price discrimination is where a firm divides consumers into different groups based on some characteristic that is relatively easy to observe and informative about how much consumers are willing to pay. The firm then charges a different price to consumers in different groups, but the same price to all the consumers within a group.
In the following diagram, the quantity $Q_1$ shows the quantity that will be sold if the firm charges a price of $P_1$ to all consumers. In this case, the consumer surplus is the area $A+B +C$. Let’s say the firm practises third-degree price discrimination and charges a higher price of $P_2$ to the subset of its customers that are willing to pay that much. This means that the quantity $Q_2$ is sold at the higher price, generating extra revenue for the firm equal to area $B$. This also transforms area $B$ from consumer surplus into producer surplus. Therefore, the examiners awarded credit for Option B.
However, it is also possible that when engaging in third-degree price discrimination, the firm opts to charge a price below $P_1$ for one or more groups, which will increase the total quantity sold to more than $Q_1$. These additional consumers who purchase the additional units over and above $Q_1$ will likely experience some consumer surplus. So, although there is always likely to be an increase in producer surplus, it is also possible that some consumers might benefit, so the examiners also awarded credit for Option C.
Incorrect
Answer B or C
Third-degree price discrimination is where a firm divides consumers into different groups based on some characteristic that is relatively easy to observe and informative about how much consumers are willing to pay. The firm then charges a different price to consumers in different groups, but the same price to all the consumers within a group.
In the following diagram, the quantity $Q_1$ shows the quantity that will be sold if the firm charges a price of $P_1$ to all consumers. In this case, the consumer surplus is the area $A+B +C$. Let’s say the firm practises third-degree price discrimination and charges a higher price of $P_2$ to the subset of its customers that are willing to pay that much. This means that the quantity $Q_2$ is sold at the higher price, generating extra revenue for the firm equal to area $B$. This also transforms area $B$ from consumer surplus into producer surplus. Therefore, the examiners awarded credit for Option B.
However, it is also possible that when engaging in third-degree price discrimination, the firm opts to charge a price below $P_1$ for one or more groups, which will increase the total quantity sold to more than $Q_1$. These additional consumers who purchase the additional units over and above $Q_1$ will likely experience some consumer surplus. So, although there is always likely to be an increase in producer surplus, it is also possible that some consumers might benefit, so the examiners also awarded credit for Option C.
-
Question 770 of 999CB2031679
Question 770
FlagCompany A is a manufacturer of high-quality men’s suits. To boost revenues, it is considering third-degree price discrimination.
Which statement best explains why such a strategy may not be possible to implement?
Correct
Answer C
Third-degree price discrimination involves the firm dividing consumers into different groups based on characteristics that are relatively easy to observe and informative about how much consumers are willing to pay.
Options A and C both relate to dividing consumers into different groups:
– Option A – by age
– Option C – by occupation.Although the inability to divide consumers into different groups based on each of age and occupation would limit the ability of Company A to implement a third-degree price discrimination strategy:
– it is arguably easier to group by age (than occupation) – age being both easier to observe, or easier to verify (eg using an identity card)
– occupation is arguably a greater indicator of a consumer’s willingness and ability to pay for a high-quality suit (than age).So in each case, being unable to group potential customers by occupation is more limiting if Company A wishes to implement a third-degree price discrimination strategy.
Option B appears to be more of a reason why Company A would be unable to implement a second-degree price discrimination strategy, and Option D doesn’t relate to price discrimination at all.
Incorrect
Answer C
Third-degree price discrimination involves the firm dividing consumers into different groups based on characteristics that are relatively easy to observe and informative about how much consumers are willing to pay.
Options A and C both relate to dividing consumers into different groups:
– Option A – by age
– Option C – by occupation.Although the inability to divide consumers into different groups based on each of age and occupation would limit the ability of Company A to implement a third-degree price discrimination strategy:
– it is arguably easier to group by age (than occupation) – age being both easier to observe, or easier to verify (eg using an identity card)
– occupation is arguably a greater indicator of a consumer’s willingness and ability to pay for a high-quality suit (than age).So in each case, being unable to group potential customers by occupation is more limiting if Company A wishes to implement a third-degree price discrimination strategy.
Option B appears to be more of a reason why Company A would be unable to implement a second-degree price discrimination strategy, and Option D doesn’t relate to price discrimination at all.
-
Question 771 of 999CB2031680
Question 771
FlagBigfirm is a monopolist in the market for household gas.
As part of a limit pricing strategy, Bigfirm is currently producing quantity Q and charging price P . However, NewCo has decided to enter the market.What is the most likely reason for NewCo’s decision?
Correct
Answer C
At:
– the profit-maximising output level, marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
– prices above the profit-maximising level, marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
– prices below the profit-maximising level, marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.Limit pricing is where a monopolist (or oligopolist) charges a price below the short-run profit-maximising level in order to deter new entrants. Since Bigfirm is currently producing using a limit pricing strategy, it must be the case that its current price $(P)$ is below the short-run profit-maximising level, therefore its marginal revenues must be less than its marginal costs. So Option B is not the correct answer.
If Bigfirm’s average costs are higher than the price $P$, then Bigfirm will be making a loss. If another firm sees the existing firms (in this case existing monopolist) making a loss, then it will be unlikely to choose to enter the market. So Option D is not the correct answer.
If NewCo has lower marginal costs than Bigfirm (Option A), it might be profitable for it to survive in the market, however since marginal costs reflect variable costs only, this does not take into account NewCo’s fixed costs – which for a firm entering the market are likely to be high.
However, average costs are made up of both fixed and variable costs, so if NewCo’s average costs are below P , then it would be able to make a supernormal profit by entering the market. Option C therefore seems the most likely reason and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
At:
– the profit-maximising output level, marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
– prices above the profit-maximising level, marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
– prices below the profit-maximising level, marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.Limit pricing is where a monopolist (or oligopolist) charges a price below the short-run profit-maximising level in order to deter new entrants. Since Bigfirm is currently producing using a limit pricing strategy, it must be the case that its current price $(P)$ is below the short-run profit-maximising level, therefore its marginal revenues must be less than its marginal costs. So Option B is not the correct answer.
If Bigfirm’s average costs are higher than the price $P$, then Bigfirm will be making a loss. If another firm sees the existing firms (in this case existing monopolist) making a loss, then it will be unlikely to choose to enter the market. So Option D is not the correct answer.
If NewCo has lower marginal costs than Bigfirm (Option A), it might be profitable for it to survive in the market, however since marginal costs reflect variable costs only, this does not take into account NewCo’s fixed costs – which for a firm entering the market are likely to be high.
However, average costs are made up of both fixed and variable costs, so if NewCo’s average costs are below P , then it would be able to make a supernormal profit by entering the market. Option C therefore seems the most likely reason and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 772 of 999CB2031681
Question 772
FlagWhich of the following is a feature of second-degree price discrimination?
Correct
Answer A
Price discrimination occurs when a firm sells the same product at different prices and the difference in price cannot be fully accounted for by any difference in the cost of supply.
Specifically, Second-degree price discrimination (SDPD) occurs when a firm offers consumers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product. Consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on some factor such as the quantity purchased.
The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Incorrect
Answer A
Price discrimination occurs when a firm sells the same product at different prices and the difference in price cannot be fully accounted for by any difference in the cost of supply.
Specifically, Second-degree price discrimination (SDPD) occurs when a firm offers consumers a range of different pricing options for the same or similar product. Consumers are then free to choose whichever option they wish, but the price is often dependent on some factor such as the quantity purchased.
The correct answer is therefore Option A.
-
Question 773 of 999CB2031682
Question 773
FlagA welfare loss occurs in a monopoly industry because the price is greater than the:
Correct
Answer: A
Recall that the socially efficient output level, which maximises social welfare, occurs when marginal social benefit (MSB) is equal to marginal social cost (MSC). Recall also that the monopolist’s average revenue (AR) or demand curve tells us the maximum price each successive consumer is prepared to pay for the marginal unit of the good and hence the marginal private benefit (MB) of that unit of output. In the absence of any external costs or benefits of consumption, the marginal private benefit will equal the MSB. Likewise, in the absence of any external costs or benefits of production, the firm’s marginal private cost (MC) of production will equal the MSC. In the absence of externalities, social efficiency therefore occurs when AR (or demand) = MC, ie when price is equal to marginal cost.
However, a profit-maximising monopolist will set its output to maximise its profits where $M C=M R$ (marginal revenue) and then charge the corresponding price for that output level from its $A R /$ demand curve. Since the $A R$ curve is above the $M R$ curve for a monopolist (as they are both downward-sloping), this means price will be set above MC at the profit-maximising output whereas price is set equal to MC at the socially efficient output. (It also means that the monopoly’s profit-maximising output is less than the socially efficient output.) Option A is therefore the correct answer.
All of this is most easily seen by considering the following diagram:
The monopolist maximises profits where $M C=M R$ and consequently sells quantity $Q_M$ at price $P_M$, which is greater than the $M C$ at $Q_M$. This contrasts with the socially efficient output of $Q_{P G}$, where price is set equal to MC, which would be attained under a perfectly competitive market with the same industry MC as the monopolist. This is because the industry supply curve under perfect competition $\left(S_{P C}\right)$ is equal to the industry MC curve and the industry demand curve has been taken to be the same $D=A R$ curve as for the monopoly.
Under perfect competition, the consumer surplus is $a+b+c$ and the producer surplus is $d+e$. Under monopoly, the consumer surplus is a and the producer surplus is $b+d$, so the welfare loss is equivalent to the area $c+e$, and arises because $M S B>M S C$ for output levels between $Q_{\infty}$ and $Q_M$.
In practice, economies of scale mean that the industry MC curve is likely to be lower for a monopoly than for a perfectly competitive market.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Recall that the socially efficient output level, which maximises social welfare, occurs when marginal social benefit (MSB) is equal to marginal social cost (MSC). Recall also that the monopolist’s average revenue (AR) or demand curve tells us the maximum price each successive consumer is prepared to pay for the marginal unit of the good and hence the marginal private benefit (MB) of that unit of output. In the absence of any external costs or benefits of consumption, the marginal private benefit will equal the MSB. Likewise, in the absence of any external costs or benefits of production, the firm’s marginal private cost (MC) of production will equal the MSC. In the absence of externalities, social efficiency therefore occurs when AR (or demand) = MC, ie when price is equal to marginal cost.
However, a profit-maximising monopolist will set its output to maximise its profits where $M C=M R$ (marginal revenue) and then charge the corresponding price for that output level from its $A R /$ demand curve. Since the $A R$ curve is above the $M R$ curve for a monopolist (as they are both downward-sloping), this means price will be set above MC at the profit-maximising output whereas price is set equal to MC at the socially efficient output. (It also means that the monopoly’s profit-maximising output is less than the socially efficient output.) Option A is therefore the correct answer.
All of this is most easily seen by considering the following diagram:
The monopolist maximises profits where $M C=M R$ and consequently sells quantity $Q_M$ at price $P_M$, which is greater than the $M C$ at $Q_M$. This contrasts with the socially efficient output of $Q_{P G}$, where price is set equal to MC, which would be attained under a perfectly competitive market with the same industry MC as the monopolist. This is because the industry supply curve under perfect competition $\left(S_{P C}\right)$ is equal to the industry MC curve and the industry demand curve has been taken to be the same $D=A R$ curve as for the monopoly.
Under perfect competition, the consumer surplus is $a+b+c$ and the producer surplus is $d+e$. Under monopoly, the consumer surplus is a and the producer surplus is $b+d$, so the welfare loss is equivalent to the area $c+e$, and arises because $M S B>M S C$ for output levels between $Q_{\infty}$ and $Q_M$.
In practice, economies of scale mean that the industry MC curve is likely to be lower for a monopoly than for a perfectly competitive market.
-
Question 774 of 999CB2031683
Question 774
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Answer: B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option Cis true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option C isn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Collusion between firms is most likely to occur in oligopolistic markets, which rules out Option A.
Under perfect competition, each firm faces a horizontal demand curve, ie it faces an infinitely or perfectly elastic demand curve. Option B is therefore definitely a false statement and the correct answer.In monopolistic competition, it is typically assumed there are no barriers to entry and therefore firms earn only normal profit in the long run. This implies that the statement in Option Cis true.
First-degree price discrimination (FDPD), whereby each consumer is charged the maximum price they are prepared to pay, means that the firm’s demand curve without price discrimination becomes its MR curve under FDPD. Thus, profit-maximising firms which produce at the level of output where MC is equal to MR will unwittingly also produce at the level of output where MC is equal to price. This is the socially efficient output level, assuming the absence of externalities. For this reason, Option D can therefore also be considered a true statement.
Note that under monopolistic competition, some firms may be able to earn supernormal profits even in the long run if:
– information is not perfect, so other firms do not enter the market
– firms differ in their size and cost structures as well as their product
– there isn’t complete freedom of entry
– entry of new firms would reduce the profits of all firms below the normal profit level.So, the statement in Option C isn’t always true.
Also, the socially efficient output level is unlikely to be attained under second-degree and thirddegree price discrimination and so the statement in Option D is not always true.However, the statement in Option B is always false, which is why it is the correct answer.
-
Question 775 of 999CB2031684
Question 775
FlagThe socially efficient output for a monopoly is at the point where:
Correct
Answer: B
The social optimum is the level of output at which welfare is maximised. When determining the optimum (in the absence of externalities), it is possible to consider the extra utility that an extra unit would give the consumer (which is assumed to be reflected in the maximum price, $P$, the consumer is prepared to pay), along with the extra costs incurred in making that unit (ie the marginal cost, MC). It follows that:
– if $P>M C$, welfare increases if output increases
– if $P<M C$, welfare increases if output decreases
– if $P=M C$, welfare is maximised.The maximum price that consumers are prepared to pay is shown by the demand curve, so the social optimum occurs where the marginal cost curve cuts the demand curve. Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note that, as with previous similar multiple-choice questions, this question assumes that there are no external costs or benefits associated with either production or consumption.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The social optimum is the level of output at which welfare is maximised. When determining the optimum (in the absence of externalities), it is possible to consider the extra utility that an extra unit would give the consumer (which is assumed to be reflected in the maximum price, $P$, the consumer is prepared to pay), along with the extra costs incurred in making that unit (ie the marginal cost, MC). It follows that:
– if $P>M C$, welfare increases if output increases
– if $P<M C$, welfare increases if output decreases
– if $P=M C$, welfare is maximised.The maximum price that consumers are prepared to pay is shown by the demand curve, so the social optimum occurs where the marginal cost curve cuts the demand curve. Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note that, as with previous similar multiple-choice questions, this question assumes that there are no external costs or benefits associated with either production or consumption.
-
Question 776 of 999CB2031685
Question 776
FlagWhich of the following could explain why a country’s aggregate demand curve might shift inwards to the left?
Correct
Answer: B
This question is testing the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model.
$A D$ is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where:
C $=$ consumption
| = investment
G = government expenditure
$X-M=\quad$ net exports (exports less imports)
Note that the AD curve will shift inwards to the left if any of these components decreases.Given this, it is possible to work through the four options and consider the impact of each on the components of AD.
A decrease in interest rates will affect C and I. Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so consumption (C) might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase $C$ and $I$, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option A is not the correct answer.
A rise in exchange rates will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper. So, there is likely to be a decrease in exports $(X)$ and an increase in imports $(M)$. If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to a decrease in net exports $(X-M)$ and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
A rise in government expenditure ( $G$ ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
An increase in business confidence is likely to increase the level of business investment (l) and hence increase AD. So Option D is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
This question is testing the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model.
$A D$ is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where:
C $=$ consumption
| = investment
G = government expenditure
$X-M=\quad$ net exports (exports less imports)
Note that the AD curve will shift inwards to the left if any of these components decreases.Given this, it is possible to work through the four options and consider the impact of each on the components of AD.
A decrease in interest rates will affect C and I. Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so consumption (C) might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase $C$ and $I$, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option A is not the correct answer.
A rise in exchange rates will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper. So, there is likely to be a decrease in exports $(X)$ and an increase in imports $(M)$. If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to a decrease in net exports $(X-M)$ and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
A rise in government expenditure ( $G$ ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
An increase in business confidence is likely to increase the level of business investment (l) and hence increase AD. So Option D is not the correct answer.
-
Question 777 of 999CB2031686
Question 777
FlagWhich of the following statements about real variables in the economy is FALSE?
Correct
Answer: D
When asked to identify whether a statement is true or false, it is good practice to go through all four options thoroughly. This should help reduce the risk of making a silly mistake.
Basically, a real quantity has had inflation stripped out of it, ie it is equal to the nominal quantity less inflation. Equivalently, a real quantity plus inflation is equal to the nominal quantity.
Option A – If there is no inflation, then a rise in nominal GDP of 5\% corresponds to a rise in real GDP of 5\%. Therefore Option A is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option B-Recall that:
The nominal exchange rate is the actual rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
The real exchange rate is the nominal exchange rate adjusted for inflation in export and import prices.For example:
the real \$/£ exchange rate
$$
=\text { nominal } \$ / £ \text { exchange rate } \text { × } \frac{\text { index of prices of UK exports to US }}{\text { index of prices of UK imports from US }}
$$The ratio of the prices of exports and imports is a measure of the relative inflation rates in the UK and the US.
This means that the real $\$ / £$ exchange rate will decrease, ie depreclate, if:
– the nominal $\$ / £$ exchange rate decreases and/or
– the prices of UK exports to the US fall relative to the prices of UK imports from the US, perhaps because the UK inflation rate is lower than the US inflation rate.This suggests that Option B is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option C-In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transaction purposes. Therefore Option C is true, and so is not the correct answer. (Note that the textbook considers the nominal demand for money (rather than the real demand for money), and this will be affected by both nominal income and inflation.)Option D – Recall that the ex ante (before the event) real interest rate is equal to nominal interest rates less the expected rate of inflation. Therefore, the ex ante real interest rate will be positive if the expected rate of inflation is less than the nominal interest rate. For example, if the nominal interest rate is 5\% pa and inflation is expected to be 3\% pa, then the ex ante real interest rate is 2\% pa. Therefore Option D is false, and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
When asked to identify whether a statement is true or false, it is good practice to go through all four options thoroughly. This should help reduce the risk of making a silly mistake.
Basically, a real quantity has had inflation stripped out of it, ie it is equal to the nominal quantity less inflation. Equivalently, a real quantity plus inflation is equal to the nominal quantity.
Option A – If there is no inflation, then a rise in nominal GDP of 5\% corresponds to a rise in real GDP of 5\%. Therefore Option A is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option B-Recall that:
The nominal exchange rate is the actual rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
The real exchange rate is the nominal exchange rate adjusted for inflation in export and import prices.For example:
the real \$/£ exchange rate
$$
=\text { nominal } \$ / £ \text { exchange rate } \text { × } \frac{\text { index of prices of UK exports to US }}{\text { index of prices of UK imports from US }}
$$The ratio of the prices of exports and imports is a measure of the relative inflation rates in the UK and the US.
This means that the real $\$ / £$ exchange rate will decrease, ie depreclate, if:
– the nominal $\$ / £$ exchange rate decreases and/or
– the prices of UK exports to the US fall relative to the prices of UK imports from the US, perhaps because the UK inflation rate is lower than the US inflation rate.This suggests that Option B is true, and so is not the correct answer.
Option C-In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transaction purposes. Therefore Option C is true, and so is not the correct answer. (Note that the textbook considers the nominal demand for money (rather than the real demand for money), and this will be affected by both nominal income and inflation.)Option D – Recall that the ex ante (before the event) real interest rate is equal to nominal interest rates less the expected rate of inflation. Therefore, the ex ante real interest rate will be positive if the expected rate of inflation is less than the nominal interest rate. For example, if the nominal interest rate is 5\% pa and inflation is expected to be 3\% pa, then the ex ante real interest rate is 2\% pa. Therefore Option D is false, and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 778 of 999CB2031687
Question 778
FlagIn the circular flow of income model:
Correct
This is a standard question on the circular flow model.
The injections into the circular flow are investment (I), government spending (G) and exports (X), whereas the withdrawals from the circular flow are savings (S), taxation (T) and imports (M).
Consumption on domestic goods ( $C_d$ ) is considered as neither an injection into nor a withdrawal from the circular flow of income, but is part of the circular flow itself.Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Answer: B
Incorrect
This is a standard question on the circular flow model.
The injections into the circular flow are investment (I), government spending (G) and exports (X), whereas the withdrawals from the circular flow are savings (S), taxation (T) and imports (M).
Consumption on domestic goods ( $C_d$ ) is considered as neither an injection into nor a withdrawal from the circular flow of income, but is part of the circular flow itself.Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
Answer: B
-
Question 779 of 999CB2031688
Question 779
FlagIf a country has a positive balance of net income from abroad then:
Correct
Recall that:
gross national income = gross domestic product + net income from abroadSo, if net income from abroad is positive, gross national income must be more than gross domestic product, ie gross domestic product is less than gross national income. Thus, Option B is the correct answer.
Answer: B
Incorrect
Recall that:
gross national income = gross domestic product + net income from abroadSo, if net income from abroad is positive, gross national income must be more than gross domestic product, ie gross domestic product is less than gross national income. Thus, Option B is the correct answer.
Answer: B
-
Question 780 of 999CB2031689
Question 780
FlagTo obtain a measure of net national income from gross domestic product it is necessary to:
Correct
the following relationships:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& N N Y=\text { gross national income }(G N Y)-\text { capital depreciation } \\
& G N Y=G D P+\text { net income from abroad }
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore:
$$
\text { NNY }=\text { GDP }+ \text { net income from abroad – capital depreciation }
$$Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Answer: D
Incorrect
the following relationships:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& N N Y=\text { gross national income }(G N Y)-\text { capital depreciation } \\
& G N Y=G D P+\text { net income from abroad }
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore:
$$
\text { NNY }=\text { GDP }+ \text { net income from abroad – capital depreciation }
$$Hence, Option D is the correct answer.
Answer: D
-
Question 781 of 999CB2031690
Question 781
FlagA country with a population of 38 million has 32 million in employment and 2 million unemployed. What is the unemployment rate?
Correct
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}
$$Here there are 32 million people in employment and 2 million unemployed, which means that the total labour force is 34 million people. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$$
\frac{2}{34} \times 100 \%=5.9 \%
$$The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
Answer: C
Incorrect
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}
$$Here there are 32 million people in employment and 2 million unemployed, which means that the total labour force is 34 million people. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$$
\frac{2}{34} \times 100 \%=5.9 \%
$$The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
Answer: C
-
Question 782 of 999CB2031691
Question 782
FlagAssuming all other variables remain constant, a decrease in the average price level will result in a:
Correct
Answer: A
By definition, real variables are related to their respective nominal variables by inflation. More specifically, the real rate of a variable is approximately equal to the nominal rate less inflation (actual inflation if we’re looking retrospectively, or expected inflation if we’re looking forward in time). In addition, the real value of a quantity (such as GDP) is found by dividing or deflating the nominal value by a suitable price index.
If there is a fall in the average price level, the real value of wages will rise, ie the purchasing power of wages will rise. So Option A is the correct answer.
Let’s consider the other options. If there is a fall in the average price level, the real interest rate will rise, not fall, so Option B is incorrect. The nominal wage rate and the nominal interest rate are not directly affected by the change in the average price level, so Options C and D are incorrect.
Note that the changes in the average price level may indirectly affect the level of nominal variables. For example, a fall in the average price level might lead to a fall in nominal wages as trade unions and employers take inflation into account when setting wages. Similarly, central banks will take inflation into account when setting nominal interest rates.
Incorrect
Answer: A
By definition, real variables are related to their respective nominal variables by inflation. More specifically, the real rate of a variable is approximately equal to the nominal rate less inflation (actual inflation if we’re looking retrospectively, or expected inflation if we’re looking forward in time). In addition, the real value of a quantity (such as GDP) is found by dividing or deflating the nominal value by a suitable price index.
If there is a fall in the average price level, the real value of wages will rise, ie the purchasing power of wages will rise. So Option A is the correct answer.
Let’s consider the other options. If there is a fall in the average price level, the real interest rate will rise, not fall, so Option B is incorrect. The nominal wage rate and the nominal interest rate are not directly affected by the change in the average price level, so Options C and D are incorrect.
Note that the changes in the average price level may indirectly affect the level of nominal variables. For example, a fall in the average price level might lead to a fall in nominal wages as trade unions and employers take inflation into account when setting wages. Similarly, central banks will take inflation into account when setting nominal interest rates.
-
Question 783 of 999CB2031692
Question 783
FlagWhich one of the following will have net exports directly measured in the method used to calculate gross domestic product (GDP)?
Correct
Answer: B
Remember that gross domestic product (GDP) is one of the commonly used measures of national income. The circular flow of income shows that output is produced, factors of production earn income from that production, and then the output is bought.
It can therefore be calculated in three different ways:
1. The product (or output) method sums up the ‘value added’ across all industries, where the value added by each firm is equal to its total revenue less the cost of intermediate goods purchased from other firms.
2. The income method sums the incomes paid to the owners of factors of production, ie wages, rents, interests, profits. It adds up incomes before tax and excludes transfer payments such as pensions, so as to avoid double counting and to ensure that only incomes earned for the year’s production are included.
3. The expenditure method sums the different types of aggregate expenditure on domestically produced goods and services, namely (total) consumption, investment, government spending (excluding transfer payments) and net exports. As it includes, net exports, Option B is the correct answer.These are three methods by which GDP can be calculated – there is no ‘investment method’.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Remember that gross domestic product (GDP) is one of the commonly used measures of national income. The circular flow of income shows that output is produced, factors of production earn income from that production, and then the output is bought.
It can therefore be calculated in three different ways:
1. The product (or output) method sums up the ‘value added’ across all industries, where the value added by each firm is equal to its total revenue less the cost of intermediate goods purchased from other firms.
2. The income method sums the incomes paid to the owners of factors of production, ie wages, rents, interests, profits. It adds up incomes before tax and excludes transfer payments such as pensions, so as to avoid double counting and to ensure that only incomes earned for the year’s production are included.
3. The expenditure method sums the different types of aggregate expenditure on domestically produced goods and services, namely (total) consumption, investment, government spending (excluding transfer payments) and net exports. As it includes, net exports, Option B is the correct answer.These are three methods by which GDP can be calculated – there is no ‘investment method’.
-
Question 784 of 999CB2031693
Question 784
FlagTo obtain a measure of net national income from gross domestic product it is necessary to:
Correct
Answer: B
Recall:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { gross national income }=\text { gross domestic product }+ \text { net income from abroad } \\
& \text { net national income }=\text { gross national income }- \text { capital depreciation }
\end{aligned}
$$Hence:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { net national income }=\text { gross domestic product } \\
& \qquad \begin{aligned}
+ & \text { net income from abroad } \\
– & \text { capital depreciation }
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned}
$$So, Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Recall:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { gross national income }=\text { gross domestic product }+ \text { net income from abroad } \\
& \text { net national income }=\text { gross national income }- \text { capital depreciation }
\end{aligned}
$$Hence:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { net national income }=\text { gross domestic product } \\
& \qquad \begin{aligned}
+ & \text { net income from abroad } \\
– & \text { capital depreciation }
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned}
$$So, Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 785 of 999CB2031694
Question 785
FlagIf the gross domestic product (GDP) in an economy rises and the unemployment rate falls then:
Correct
Answer: D
Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is the GDP per head of population. It therefore gives an indication of the average income across the whole population.
Here the question states that GDP has risen. However, it does not say whether the population has increased, decreased or remained unchanged. Therefore, it is not possible to say whether GDP per capita has increased, decreased or remained unchanged, and so Option D is the correct answer.
Changes in the unemployment rate have no direct link to GDP per capita. However, there may be an indirect link in that it is possible that a fall in the unemployment rate may be associated with higher national output and hence a rise in (overall) GDP.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is the GDP per head of population. It therefore gives an indication of the average income across the whole population.
Here the question states that GDP has risen. However, it does not say whether the population has increased, decreased or remained unchanged. Therefore, it is not possible to say whether GDP per capita has increased, decreased or remained unchanged, and so Option D is the correct answer.
Changes in the unemployment rate have no direct link to GDP per capita. However, there may be an indirect link in that it is possible that a fall in the unemployment rate may be associated with higher national output and hence a rise in (overall) GDP.
-
Question 786 of 999CB2031695
Question 786
FlagWhich of the following could explain why a country’s aggregate demand curve might shift inwards to the left?
Correct
Answer A
$A D$ is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where, as usual, $C$ denotes consumption, $I$ is investment, $G$ is government expenditure and $X-M$ refers to net exports (exports less imports).Note that the AD curve will shift inwards to the left if any of these components decreases. Given this, it is possible to work through the four options and consider the impact of each on the components of AD.
An appreciation of the domestic currency will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheap. So, there is likely to be a decrease in the volume of exports $(X)$ and an increase in the volume of imports (M). If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, this will lead to a decrease in the value of net exports ( $X-M$ ) and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
A decrease in interest rates will affect consumption ( $C$ ) and investment (I). Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so C might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase C and I, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option B is not the correct answer.
A rise in government expenditure ( $G$ ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
An increase in business confidence is likely to increase the level of business investment (1) and hence increase AD. So Option D is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer A
$A D$ is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where, as usual, $C$ denotes consumption, $I$ is investment, $G$ is government expenditure and $X-M$ refers to net exports (exports less imports).Note that the AD curve will shift inwards to the left if any of these components decreases. Given this, it is possible to work through the four options and consider the impact of each on the components of AD.
An appreciation of the domestic currency will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheap. So, there is likely to be a decrease in the volume of exports $(X)$ and an increase in the volume of imports (M). If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, this will lead to a decrease in the value of net exports ( $X-M$ ) and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option A is the correct answer.
A decrease in interest rates will affect consumption ( $C$ ) and investment (I). Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so C might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase C and I, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option B is not the correct answer.
A rise in government expenditure ( $G$ ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
An increase in business confidence is likely to increase the level of business investment (1) and hence increase AD. So Option D is not the correct answer.
-
Question 787 of 999CB2031696
Question 787
FlagThe short-run aggregate supply curves show that an increase in the average price level will encourage firms to:
Correct
Answer: B
Recall that a short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve shows how total output varies with the average price level, assuming that factor prices (such as wages), technology and the total supply of factors of production are fixed.
As long as there is spare capacity in the economy, the SRAS is typically assumed to slope upwards, suggesting that an increase in the average price level will encourage firms to increase output in the short run. This is because, assuming wages are fixed, profitability will increase with increases in the price level. Options $A$ and $D$ can therefore be ruled out.
In addition, an increase in output will usually require the employment of more workers in order to produce the additional output and so employment would also be expected to increase. The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Recall that a short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve shows how total output varies with the average price level, assuming that factor prices (such as wages), technology and the total supply of factors of production are fixed.
As long as there is spare capacity in the economy, the SRAS is typically assumed to slope upwards, suggesting that an increase in the average price level will encourage firms to increase output in the short run. This is because, assuming wages are fixed, profitability will increase with increases in the price level. Options $A$ and $D$ can therefore be ruled out.
In addition, an increase in output will usually require the employment of more workers in order to produce the additional output and so employment would also be expected to increase. The correct answer is therefore Option B.
-
Question 788 of 999CB2031697
Question 788
FlagWhich of the following does NOT form part of a country’s gross domestic product?
Correct
Answer: C
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12-month period in terms of the prices actually paid. It can be calculated using:
– the product method, which sums the value added by firms at the different stages of production
– the income method, which sums the incomes paid to the owners of factors of production and includes wages (eg salaries of school teachers, Option D), interest, rent and company profits (Option A)
– the expenditure method, which sums the different types of aggregate expenditure and includes consumption, investment (Option B), government spending and net exports.Therefore the only option that does not form part of GDP is Option C – net income from abroad. Note that this would be included in the calculation of gross national income.
Incorrect
Answer: C
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12-month period in terms of the prices actually paid. It can be calculated using:
– the product method, which sums the value added by firms at the different stages of production
– the income method, which sums the incomes paid to the owners of factors of production and includes wages (eg salaries of school teachers, Option D), interest, rent and company profits (Option A)
– the expenditure method, which sums the different types of aggregate expenditure and includes consumption, investment (Option B), government spending and net exports.Therefore the only option that does not form part of GDP is Option C – net income from abroad. Note that this would be included in the calculation of gross national income.
-
Question 789 of 999CB2031698
Question 789
FlagThe aggregate demand curve slopes downwards because at higher price levels the real money supply:
Correct
Answer A
four distinct reasons why the aggregate demand schedule slopes downwards, none of them seems particularly helpful here. The aggregate demand schedule is plotted on a graph of price vs national income, and the question states that it is downward sloping, so higher price levels will be associated with lower levels of national income (and vice versa). This rules out Options B and D.
Module 15 discusses the nominal money market model. This question is using a model of the real money market, which is not covered explicitly in the textbook. However, the examiners were expecting students to apply their knowledge of the relationship between real and nominal variables. For a given nominal money supply, higher prices will lead to a decreased real money supply. This rules out Options C and D.
We have now ruled out Options B, C and D and so the correct answer must be Option A.
The logic for Option $A$ is that (as mentioned above), an increase in the price level leads to a decrease in the real money supply. This causes an increase in the equilibrium interest rate which, in turn, leads to a reduction in aggregate demand and hence national income. This is the Intertemporal substitution effect, explained in Module 10, in terms of the nominal money market, ie an increase in the price level leads to an increase in the demand for money to pay for the more expensive goods and services, and with a given money supply, this increases interest rates. Higher interest rates lead to a reduction in aggregate demand and hence a fall in national income.Incorrect
Answer A
four distinct reasons why the aggregate demand schedule slopes downwards, none of them seems particularly helpful here. The aggregate demand schedule is plotted on a graph of price vs national income, and the question states that it is downward sloping, so higher price levels will be associated with lower levels of national income (and vice versa). This rules out Options B and D.
Module 15 discusses the nominal money market model. This question is using a model of the real money market, which is not covered explicitly in the textbook. However, the examiners were expecting students to apply their knowledge of the relationship between real and nominal variables. For a given nominal money supply, higher prices will lead to a decreased real money supply. This rules out Options C and D.
We have now ruled out Options B, C and D and so the correct answer must be Option A.
The logic for Option $A$ is that (as mentioned above), an increase in the price level leads to a decrease in the real money supply. This causes an increase in the equilibrium interest rate which, in turn, leads to a reduction in aggregate demand and hence national income. This is the Intertemporal substitution effect, explained in Module 10, in terms of the nominal money market, ie an increase in the price level leads to an increase in the demand for money to pay for the more expensive goods and services, and with a given money supply, this increases interest rates. Higher interest rates lead to a reduction in aggregate demand and hence a fall in national income. -
Question 790 of 999CB2031699
Question 790
FlagIf the total output of goods and services increases and the price index falls then the nominal gross domestic product (GDP):
Correct
This question starts ‘If total output of goods and services increases …’. Initially, it may be unclear whether this increase in GDP will be in nominal or real terms. However, the question then asks for the effect on nominal GDP, so the increase in total output must be in real terms. So, real GDP will rise and this rules out Option A.
The question also states that the price index falls, ie inflation is negative. Recall that the change in nominal GDP will be approximately equal to the change in real GDP plus inflation. So, real GDP growth will be positive and inflation will be negative but the question doesn’t give the magnitude of either and so it is not possible to say whether nominal GDP will rise or fall. Therefore, Option D is the correct answer.
Answer: D
Incorrect
This question starts ‘If total output of goods and services increases …’. Initially, it may be unclear whether this increase in GDP will be in nominal or real terms. However, the question then asks for the effect on nominal GDP, so the increase in total output must be in real terms. So, real GDP will rise and this rules out Option A.
The question also states that the price index falls, ie inflation is negative. Recall that the change in nominal GDP will be approximately equal to the change in real GDP plus inflation. So, real GDP growth will be positive and inflation will be negative but the question doesn’t give the magnitude of either and so it is not possible to say whether nominal GDP will rise or fall. Therefore, Option D is the correct answer.
Answer: D
-
Question 791 of 999CB2031700
Question 791
FlagIf a country has a current account deficit then:
Correct
This question is asking for the effect of a current account deficit on the relationship between gross domestic product and gross national product.
Recall that gross domestic product (GDP) is the total value of output produced domestically, or equivalently, the total income earned from domestic production, and that gross national income (GNY) is the total income earned by the nation’s residents from current production. The relationship is:
GNP = GDP + net income from abroadA current account deficit or surplus has no effect on this relationship, so the answer must be Option D.
Answer: D
Incorrect
This question is asking for the effect of a current account deficit on the relationship between gross domestic product and gross national product.
Recall that gross domestic product (GDP) is the total value of output produced domestically, or equivalently, the total income earned from domestic production, and that gross national income (GNY) is the total income earned by the nation’s residents from current production. The relationship is:
GNP = GDP + net income from abroadA current account deficit or surplus has no effect on this relationship, so the answer must be Option D.
Answer: D
-
Question 792 of 999CB2031701
Question 792
FlagThe nominal rate of interest is $2 \%$ and the rate of inflation is negative at $-3 \%$. Which one of the following is TRUE?
Correct
The real rate of interest is approximately equal to the nominal rate of interest minus the inflation rate. Thus:
$$
\text { real rate of interest }=2 \%-(-3 \%)=5 \%
$$So the real interest rate is greater than the nominal rate of interest and Option A is correct.
Answer: A
Incorrect
The real rate of interest is approximately equal to the nominal rate of interest minus the inflation rate. Thus:
$$
\text { real rate of interest }=2 \%-(-3 \%)=5 \%
$$So the real interest rate is greater than the nominal rate of interest and Option A is correct.
Answer: A
-
Question 793 of 999CB2031702
Question 793
FlagThe nominal rate of interest is 2% and the expected rate of inflation is positive at 3%. Which one of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer: D
Remember that real variables are adjusted for inflation. So, for example, the increase in real GDP represents the increase in money GDP adjusted for inflation. So, if money GDP increases by say 4%, whereas the general level of prices increases by 3%, then the real value of GDP has increased by approximately 1%.
A similar argument applies here, where the real interest rate is normally interpreted as the excess (or shortfall) of the actual, or nominal, interest rate over and above (or indeed below) inflation.
So, here, as the nominal interest rate is 2% pa and the expected inflation rate is 3% pa, the real interest rate is approximately -1% pa, which corresponds to Option D.
Note that here expected inflation is used, as the question is looking at what the real return on borrowing or lending is expected to be over the next year. Conversely, to work out the real return that was actually achieved over the previous year, then it would be necessary to use the actual inflation rate experienced over the past year to do so.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Remember that real variables are adjusted for inflation. So, for example, the increase in real GDP represents the increase in money GDP adjusted for inflation. So, if money GDP increases by say 4%, whereas the general level of prices increases by 3%, then the real value of GDP has increased by approximately 1%.
A similar argument applies here, where the real interest rate is normally interpreted as the excess (or shortfall) of the actual, or nominal, interest rate over and above (or indeed below) inflation.
So, here, as the nominal interest rate is 2% pa and the expected inflation rate is 3% pa, the real interest rate is approximately -1% pa, which corresponds to Option D.
Note that here expected inflation is used, as the question is looking at what the real return on borrowing or lending is expected to be over the next year. Conversely, to work out the real return that was actually achieved over the previous year, then it would be necessary to use the actual inflation rate experienced over the past year to do so.
-
Question 794 of 999CB2031703
Question 794
FlagThe unemployment rate, expressed as a percentage, is given by the number of unemployed divided by:
Correct
Recall that the unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}
$$
where the total labour force is simply the total of the employed plus the unemployed, the latter being defined as those people of working age without jobs who are available to work at current wage rates.Answer: B
Incorrect
Recall that the unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}
$$
where the total labour force is simply the total of the employed plus the unemployed, the latter being defined as those people of working age without jobs who are available to work at current wage rates.Answer: B
-
Question 795 of 999CB2031704
Question 795
FlagWhich of the following does NOT form part of a country’s gross domestic product (GDP)?
Correct
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12-month period. It can be calculated using:
– the product (or output) method
– the income method – this includes wages (ie salaries of school teachers), interest, rent and (company) profits
– the expenditure method – this includes consumption, investment, government spending and net exports.Therefore the only option that does not form part of GDP is Option B – net income from abroad. Note that this would be included in the calculation of gross national income, which is the value of income earned by the nation’s residents in a year.
Answer: B
Incorrect
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12-month period. It can be calculated using:
– the product (or output) method
– the income method – this includes wages (ie salaries of school teachers), interest, rent and (company) profits
– the expenditure method – this includes consumption, investment, government spending and net exports.Therefore the only option that does not form part of GDP is Option B – net income from abroad. Note that this would be included in the calculation of gross national income, which is the value of income earned by the nation’s residents in a year.
Answer: B
-
Question 796 of 999CB2031705
Question 796
FlagTo calculate gross national income, you need to know all of the following EXCEPT:
Correct
Answer B
Gross domestic product (GDP) at market prices is a measure of a nation’s output and can be calculated using the expenditure method as:
– consumption (expenditure)
– investment (also known as gross fixed capital formation)
– government spending
– net exports of goods and services (exports less imports).Hence Options A and C are part of the calculation of GDP.
Gross national income ( $G N Y$ ) is the value of income earned by the nation’s resources, and can be calculated as:GNY at market prices = GDP at market prices + net income from abroad
Hence Options A, C and D are part of the calculation of GNY, so the correct answer is Option B. Note that Option B, capital depreciation, (along with all of the other options) is part of the calculation of net national income ( $N N Y$ ).Incorrect
Answer B
Gross domestic product (GDP) at market prices is a measure of a nation’s output and can be calculated using the expenditure method as:
– consumption (expenditure)
– investment (also known as gross fixed capital formation)
– government spending
– net exports of goods and services (exports less imports).Hence Options A and C are part of the calculation of GDP.
Gross national income ( $G N Y$ ) is the value of income earned by the nation’s resources, and can be calculated as:GNY at market prices = GDP at market prices + net income from abroad
Hence Options A, C and D are part of the calculation of GNY, so the correct answer is Option B. Note that Option B, capital depreciation, (along with all of the other options) is part of the calculation of net national income ( $N N Y$ ). -
Question 797 of 999CB2031706
Question 797
FlagA country with a population of 38 million has 32 million in employment and 2 million unemployed. What is the unemployment rate?
Correct
Answer A
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { totallabour force }}
$$Here there are 32 million people in employment and 2 million unemployed, which means that the total labour force is 34 million people. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$$
\frac{2}{34} \times 100 \%=5.9 \%
$$The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
Incorrect
Answer A
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { totallabour force }}
$$Here there are 32 million people in employment and 2 million unemployed, which means that the total labour force is 34 million people. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$$
\frac{2}{34} \times 100 \%=5.9 \%
$$The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
-
Question 798 of 999CB2031707
Question 798
FlagWhich of the following might explain why a country’s aggregate demand curve might shift inwards to the left?
Correct
Answer B
AD is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government expenditure and $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$ is net exports (exports less imports).Note that the AD curve will shift inwards to the left if any of these components decreases. Given this, it is possible to work through the four options and consider the impact of each on the components of $A D$.
A decrease in interest rates will affect C and I . Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so consumption ( C ) might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase C and I, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option A is not the correct answer.
An appreciation of the domestic currency will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper. So, there is likely to be a decrease in exports ( X ) and an increase in imports (M). If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to a decrease in net exports $(X-M)$ and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
A rise in government expenditure ( G ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
An increase in business confidence is likely to increase the level of business investment (I) and hence increase AD . So Option D is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer B
AD is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government expenditure and $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$ is net exports (exports less imports).Note that the AD curve will shift inwards to the left if any of these components decreases. Given this, it is possible to work through the four options and consider the impact of each on the components of $A D$.
A decrease in interest rates will affect C and I . Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so consumption ( C ) might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase C and I, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option A is not the correct answer.
An appreciation of the domestic currency will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper. So, there is likely to be a decrease in exports ( X ) and an increase in imports (M). If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to a decrease in net exports $(X-M)$ and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
A rise in government expenditure ( G ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
An increase in business confidence is likely to increase the level of business investment (I) and hence increase AD . So Option D is not the correct answer.
-
Question 799 of 999CB2031708
Question 799
FlagThe short-run aggregate supply curve shows that an increase in the average price level will encourage firms to:
Correct
Answer D
The short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve shows how total output varies with the average price level, assuming that factor prices (such as wages), technology and the total supply of factors of production are fixed.
The moderate view is that the SRAS slopes upwards, suggesting that an increase in the average price level will encourage firms to increase output in the short run. This is because, assuming wages are fixed, profitability will increase with increases in the price level. Options B and A can therefore be ruled out.
In addition, an increase in output will usually require the employment of more workers in order to produce the additional output and so employment would also be expected to increase. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Incorrect
Answer D
The short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve shows how total output varies with the average price level, assuming that factor prices (such as wages), technology and the total supply of factors of production are fixed.
The moderate view is that the SRAS slopes upwards, suggesting that an increase in the average price level will encourage firms to increase output in the short run. This is because, assuming wages are fixed, profitability will increase with increases in the price level. Options B and A can therefore be ruled out.
In addition, an increase in output will usually require the employment of more workers in order to produce the additional output and so employment would also be expected to increase. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
-
Question 800 of 999CB2031709
Question 800
FlagWhich of the following statements helps explain why the aggregate demand curve has a negative slope? As the price level falls:
Correct
Answer D
Demand curves typically slope down because of the income and substitution effects. In the case of the aggregate demand curve, the income effect describes how a rise (fall) in prices leads to a fall (rise) in real incomes and therefore people will spend less (more). This is Option D.
(For the aggregate demand curve, there are actually three substitution effects (the intertemporal substitution effect, the real balance effect and the international substitution effect), but none of these relate to any of the other options.)In terms of the other options, as the price level falls:
– it is not necessarily true that shareholders’ dividends will increase – in fact, as the price level falls, firms might experience reduced profits, and so pay out a lower dividend (Option A)
– it is not necessarily true that the central bank will have to increase the money supply – the quantity theory of money states that an increase in the money supply will lead to an increase in the price level, but a fall in the price level will not necessarily necessitate an increase in the money supply (Option B)
– it will not necessarily be the case that the government will have to reduce taxes the government’s fiscal policy will depend on its objectives (Option C).Incorrect
Answer D
Demand curves typically slope down because of the income and substitution effects. In the case of the aggregate demand curve, the income effect describes how a rise (fall) in prices leads to a fall (rise) in real incomes and therefore people will spend less (more). This is Option D.
(For the aggregate demand curve, there are actually three substitution effects (the intertemporal substitution effect, the real balance effect and the international substitution effect), but none of these relate to any of the other options.)In terms of the other options, as the price level falls:
– it is not necessarily true that shareholders’ dividends will increase – in fact, as the price level falls, firms might experience reduced profits, and so pay out a lower dividend (Option A)
– it is not necessarily true that the central bank will have to increase the money supply – the quantity theory of money states that an increase in the money supply will lead to an increase in the price level, but a fall in the price level will not necessarily necessitate an increase in the money supply (Option B)
– it will not necessarily be the case that the government will have to reduce taxes the government’s fiscal policy will depend on its objectives (Option C). -
Question 801 of 999CB2031710
Question 801
FlagGiven the gross domestic product (GDP) at basic prices cost we can calculate the GDP at market prices by:
Correct
Answer B
Recall that the difference between market prices and basic prices is that the former includes taxes on products less subsidies. Option B is therefore correct.
Incorrect
Answer B
Recall that the difference between market prices and basic prices is that the former includes taxes on products less subsidies. Option B is therefore correct.
-
Question 802 of 999CB2031711
Question 802
FlagThe nominal rate of interest is $7 \%$ and the expected rate of inflation is $4 \%$. Which one of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D
When the expected rate of inflation is less than the nominal rate of interest, savings will be gaining value, ie the real rate of interest will be positive. Here, the nominal interest rate is $7 \% p a$ and inflation is expected to be $4 \% p a$, so the real interest rate is approximately $3 \% p a$. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D
When the expected rate of inflation is less than the nominal rate of interest, savings will be gaining value, ie the real rate of interest will be positive. Here, the nominal interest rate is $7 \% p a$ and inflation is expected to be $4 \% p a$, so the real interest rate is approximately $3 \% p a$. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 803 of 999CB2031712
Question 803
FlagIn a country with a population of 25 million, there are 16 million employed and 2 million unemployed. What is the rate of unemployment?
Correct
Answer B
The unemployment rate is defined as the number unemployed expressed as a percentage of the labour force.
Here, there are 16 million people in the labour force and 2 million unemployed. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$\frac{2}{18} \times 100 \%=11.1 \%$, and so Option B is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer B
The unemployment rate is defined as the number unemployed expressed as a percentage of the labour force.
Here, there are 16 million people in the labour force and 2 million unemployed. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$\frac{2}{18} \times 100 \%=11.1 \%$, and so Option B is the correct answer. -
Question 804 of 999CB2031713
Question 804
FlagAssuming all other variables remain constant, a decrease in the average price level will result in a:
Correct
Answer C
Real variables are related to their respective nominal variables by inflation. More specifically, the real rate of a variable is approximately equal to the nominal rate less inflation. In addition, the real value of a quantity (such as GDP) is found by deflating the nominal value by a suitable price index.
If there is a fall in the average price level, the real value of wages will rise, ie the purchasing power of wages will rise. So Option C is the correct answer.
If there is a fall in the average price level, the real interest rate will rise, not fall, so Option A is incorrect. The nominal wage rate and the nominal interest rate are not directly affected by the change in the average price level, so Options B and D are incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer C
Real variables are related to their respective nominal variables by inflation. More specifically, the real rate of a variable is approximately equal to the nominal rate less inflation. In addition, the real value of a quantity (such as GDP) is found by deflating the nominal value by a suitable price index.
If there is a fall in the average price level, the real value of wages will rise, ie the purchasing power of wages will rise. So Option C is the correct answer.
If there is a fall in the average price level, the real interest rate will rise, not fall, so Option A is incorrect. The nominal wage rate and the nominal interest rate are not directly affected by the change in the average price level, so Options B and D are incorrect.
-
Question 805 of 999CB2031715
Question 805
FlagWhich of the following is most likely to lead to a rise in aggregate demand?
Correct
Answer D
AD is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government expenditure and $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$ is net exports (exports less imports.AD will rise if any of its components ( $\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{I}, \mathrm{G}$ and $(\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M})$ ) increases:
– An increase in the income tax rate will reduce the disposable income available to households. This is likely to reduce C, so reduce AD. Hence Option A is incorrect.
– A decrease in government expenditure will directly reduce AD. Hence Option B is incorrect.
– A decrease in the value of exports will directly reduce AD. Hence Option C is incorrect.
– A decrease in the rate of interest will make saving unattractive and should lead to cheaper borrowing. This should increase C and I and hence increase AD. Therefore Option D is correct.Incorrect
Answer D
AD is made up of the following components:
$$
A D=C+I+G+(X-M)
$$
where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government expenditure and $\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M}$ is net exports (exports less imports.AD will rise if any of its components ( $\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{I}, \mathrm{G}$ and $(\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M})$ ) increases:
– An increase in the income tax rate will reduce the disposable income available to households. This is likely to reduce C, so reduce AD. Hence Option A is incorrect.
– A decrease in government expenditure will directly reduce AD. Hence Option B is incorrect.
– A decrease in the value of exports will directly reduce AD. Hence Option C is incorrect.
– A decrease in the rate of interest will make saving unattractive and should lead to cheaper borrowing. This should increase C and I and hence increase AD. Therefore Option D is correct. -
Question 806 of 999CB2031716
Question 806
FlagThe following transactions take place in a simple closed economy. A company producing Good X sells its output for $£ 2$ million. In producing Good $X$, the company buys raw materials for $£ 800,000$, uses $£ 200,000$ worth of electricity and has labour costs of $£ 400,000$. What is the contribution of the company to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
Correct
Answer C
The product method for measuring national income is:
GDP = value added by each firm in the production process.
Without adjustment, this will give GDP at basic prices (ie GVA), as these figures will not reflect indirect taxes net of subsidiesHere, the company uses resources worth $£ 800,000+£ 200,000+£ 400,000=£ 1,400,000$ in order to produce a good that is worth $£ 2 m$.
It has therefore added value of $£ 2,000,000-£ 1,400,000=£ 600,000$.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer C
The product method for measuring national income is:
GDP = value added by each firm in the production process.
Without adjustment, this will give GDP at basic prices (ie GVA), as these figures will not reflect indirect taxes net of subsidiesHere, the company uses resources worth $£ 800,000+£ 200,000+£ 400,000=£ 1,400,000$ in order to produce a good that is worth $£ 2 m$.
It has therefore added value of $£ 2,000,000-£ 1,400,000=£ 600,000$.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer. -
Question 807 of 999CB2031717
Question 807
FlagIf nominal GDP per capita is $£ 30,000$ and the GDP deflator is 150 , then real GDP is (given the base year index of 100):
Correct
Answer D
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices.
Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year.Nominal values can be calculated as:
$$
\text { nominal values }=\text { real values } \times(1+\text { inflation }) \text {. }
$$Inflation may be calculated using price index figures (in this case the GDP deflator) at certain points in time:
$$
(1+\text { inflation })=\frac{150}{100}=1.50
$$So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { real value } & =\frac{\text { nominal value }}{(1+\text { inflation })} \\
& =\frac{30,000}{1.50} \\
& =20,000
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices.
Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year.Nominal values can be calculated as:
$$
\text { nominal values }=\text { real values } \times(1+\text { inflation }) \text {. }
$$Inflation may be calculated using price index figures (in this case the GDP deflator) at certain points in time:
$$
(1+\text { inflation })=\frac{150}{100}=1.50
$$So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { real value } & =\frac{\text { nominal value }}{(1+\text { inflation })} \\
& =\frac{30,000}{1.50} \\
& =20,000
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 808 of 999CB2031718
Question 808
FlagWhich one of the following does NOT form part of the UK GDP:
Correct
Answer A
The expenditure method for calculating GDP is:
$$
G D P=C+I+G+X-M,
$$
and the income method is:
$$
\text { GDP }=\text { wages }+ \text { interest }+ \text { rents }+ \text { profits. }
$$Investment expenditure ( $I$ ) and export revenue ( $X$ ) are incorporated within the expenditure method of calculating GDP, and this corresponds to Options B and C.
Option D – government expenditure on employing teachers – refers mainly to teacher salaries. Salaries are incorporated within the income method of calculating GDP.
Option A – investment income from abroad – is the only option that does not form part of GDP, and therefore this is the correct answer.
Option A – investment income from abroad – does not represent domestic economic activity and so is not included in the calculation of GDP. However it would be included in the UK’s gross national income calculation.
Incorrect
Answer A
The expenditure method for calculating GDP is:
$$
G D P=C+I+G+X-M,
$$
and the income method is:
$$
\text { GDP }=\text { wages }+ \text { interest }+ \text { rents }+ \text { profits. }
$$Investment expenditure ( $I$ ) and export revenue ( $X$ ) are incorporated within the expenditure method of calculating GDP, and this corresponds to Options B and C.
Option D – government expenditure on employing teachers – refers mainly to teacher salaries. Salaries are incorporated within the income method of calculating GDP.
Option A – investment income from abroad – is the only option that does not form part of GDP, and therefore this is the correct answer.
Option A – investment income from abroad – does not represent domestic economic activity and so is not included in the calculation of GDP. However it would be included in the UK’s gross national income calculation.
-
Question 809 of 999CB2031719
Question 809
FlagIf the real rate of interest is $5 \%$ and the expected inflation rate is $4 \%$, then the nominal rate of interest is approximately:
Correct
Answer C
The formula we need is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { nominal interest rate } & \approx \text { real interest rate }+ \text { inflation } \\
& =5 \%+4 \% \\
& =9 \%
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
The formula we need is:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { nominal interest rate } & \approx \text { real interest rate }+ \text { inflation } \\
& =5 \%+4 \% \\
& =9 \%
\end{aligned}
$$Hence Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 810 of 999CB2031720
Question 810
FlagThe circular flow of the income model assumes that injections:
Correct
Answer D
The diagram below shows the circular flow of income in an open economy with a government:
According to the diagram, injections represent income re-entering the economy, so Option C is not the correct answer.
Aggregate demand is made up of the quantities that different parties are willing to and able to buy, in particular:
-firms(investment)
-consumers (consumption)
– the government (government spending)
– the rest of the world (exports minus imports).It is therefore equal to injections plus consumption on domestically produced goods, (ie total consumption minus imports). Since injections are a component of aggregate demand, they increase it (rather than reduce it) and so Option B is not the correct answer.
Injections are usually assumed to be independent of the current level of income. (This is in contrast to withdrawals, which are usually assumed to be a function of income.) This suggests that Option A is not the correct answer.
Option D looks somewhat similar to Option A, however its wording suggests a looser link between the injections and the level of income. For example, if income is low, this might have an impact on the level that firms choose to spend or invest, or the amount that governments might choose to spend. However, while Option A suggests an explicit relationship between the injections and the level of income, Option D is vaguer, suggesting that the relationship isn’t explicit, just that there might be some link. The link could also be in the other direction, eg an increase in injections increases aggregate demand and so is likely to also increase income. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D
The diagram below shows the circular flow of income in an open economy with a government:
According to the diagram, injections represent income re-entering the economy, so Option C is not the correct answer.
Aggregate demand is made up of the quantities that different parties are willing to and able to buy, in particular:
-firms(investment)
-consumers (consumption)
– the government (government spending)
– the rest of the world (exports minus imports).It is therefore equal to injections plus consumption on domestically produced goods, (ie total consumption minus imports). Since injections are a component of aggregate demand, they increase it (rather than reduce it) and so Option B is not the correct answer.
Injections are usually assumed to be independent of the current level of income. (This is in contrast to withdrawals, which are usually assumed to be a function of income.) This suggests that Option A is not the correct answer.
Option D looks somewhat similar to Option A, however its wording suggests a looser link between the injections and the level of income. For example, if income is low, this might have an impact on the level that firms choose to spend or invest, or the amount that governments might choose to spend. However, while Option A suggests an explicit relationship between the injections and the level of income, Option D is vaguer, suggesting that the relationship isn’t explicit, just that there might be some link. The link could also be in the other direction, eg an increase in injections increases aggregate demand and so is likely to also increase income. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.
-
Question 811 of 999CB2031721
Question 811
FlagIn order to determine real national income, the nominal national income is adjusted for:
Correct
Answer D
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices.
Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year. Inflation may be calculated using price index figures at certain points in time. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.Option A – adjusting for indirect taxes (and subsidies) – gives the difference between market and basic prices.
Option B – adjusting for depreciation – gives the difference between gross and net national income.
Option C – adjusting for population size – gives national income per capita. This is national income per head of the population.
Incorrect
Answer D
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices.
Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year. Inflation may be calculated using price index figures at certain points in time. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.Option A – adjusting for indirect taxes (and subsidies) – gives the difference between market and basic prices.
Option B – adjusting for depreciation – gives the difference between gross and net national income.
Option C – adjusting for population size – gives national income per capita. This is national income per head of the population.
-
Question 812 of 999CB2031722
Question 812
FlagTwo firms operate in a duopoly but do not collude. Given the profit pay-off matrix of output options to firms A and B below, what is the dominant strategy for the firms?
\begin{array}{lccc}
& & \textbf{Firm B} \\[4pt]
& & \textit{Low} & \textit{High} \\[6pt]
\textbf{Firm A} & \textit{Low} & (50,50) & (10,70) \\
& \textit{High} & (70,10) & (30,30) \\
\end{array}Note: Profit pay-offs are (Profit A, Profit B) and ‘high’ and ‘low’ refer to the output decision.
Correct
Answer B
A dominant strategy is a strategy that is the best strategy for one player, no matter what strategy the other player follows.
Firm A
Suppose Firm B goes high, what should Firm A do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 30 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 10 . So Firm A should go high.Suppose Firm B goes low, what should Firm A do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 70 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 50 . So Firm A should go high.
Since Firm A should go high no matter what Firm B does, high is a dominant strategy for Firm A. This rules out Options C and D.
Firm B
Suppose Firm A goes high, what should Firm B do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 30 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 10 . So Firm B should go high.Suppose Firm A goes low, what should Firm B do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 70 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 50 . So Firm B should go high.
Since Firm B should go high no matter what Firm A does, high is a dominant strategy for Firm B. This rules out Options A and C.
Hence the answer is Option B.
Incorrect
Answer B
A dominant strategy is a strategy that is the best strategy for one player, no matter what strategy the other player follows.
Firm A
Suppose Firm B goes high, what should Firm A do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 30 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 10 . So Firm A should go high.Suppose Firm B goes low, what should Firm A do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 70 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 50 . So Firm A should go high.
Since Firm A should go high no matter what Firm B does, high is a dominant strategy for Firm A. This rules out Options C and D.
Firm B
Suppose Firm A goes high, what should Firm B do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 30 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 10 . So Firm B should go high.Suppose Firm A goes low, what should Firm B do? If it goes high, it will get a payoff of 70 . If it goes low, it will get a payoff of 50 . So Firm B should go high.
Since Firm B should go high no matter what Firm A does, high is a dominant strategy for Firm B. This rules out Options A and C.
Hence the answer is Option B.
-
Question 813 of 999CB2031723
Question 813
FlagTwo firms operate in a duopoly but do not collude. Given the profit pay-off matrix of output options to firms A and B below, what is the dominant strategy for the firms?
\begin{array}{lccc}
& & \textbf{Firm B} \\[4pt]
& & \textit{Low} & \textit{High} \\[6pt]
\textbf{Firm A} & \textit{Low} & (60,60) & (20,90) \\
& \textit{High} & (90,20) & (40,40) \\
\end{array}Note: Profit pay-offs are (Profit A, Profit B) and ‘high’ and ‘low’ refer to the price decision.
Correct
Answer C
Firm A
Suppose Firm B goes high. If Firm A:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 60
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 90 .So Firm A should go low.
Suppose Firm B goes low. If Firm A:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 20
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 40 .So Firm A should go low.
Since Firm $A$ should go low no matter what Firm $B$ does, low is a dominant strategy for Firm A. This rules out Options A and B.Firm B
Suppose Firm A goes high. If Firm B:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 60
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 90 .So Firm B should go low.
Suppose Firm A goes low. If Firm B:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 20
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 40 .So Firm B should go low.
Since Firm B should go low no matter what Firm A does, low is a dominant strategy for Firm B. This rules out Options B and D.Hence the answer is Option C.
Incorrect
Answer C
Firm A
Suppose Firm B goes high. If Firm A:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 60
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 90 .So Firm A should go low.
Suppose Firm B goes low. If Firm A:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 20
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 40 .So Firm A should go low.
Since Firm $A$ should go low no matter what Firm $B$ does, low is a dominant strategy for Firm A. This rules out Options A and B.Firm B
Suppose Firm A goes high. If Firm B:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 60
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 90 .So Firm B should go low.
Suppose Firm A goes low. If Firm B:
– goes high, it will get a payoff of 20
– goes low, it will get a payoff of 40 .So Firm B should go low.
Since Firm B should go low no matter what Firm A does, low is a dominant strategy for Firm B. This rules out Options B and D.Hence the answer is Option C.
-
Question 814 of 999CB2031725
Question 814
FlagWhich one of the following is likely to lead to cost-push inflation?
Correct
Answer: C
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of producing and/or supplying goods and services. In practice there are number of factors that might lead production costs to increase, including:
1. increased trade union power, perhaps resulting from higher union membership or a relaxation of the laws governing their actions. Conversely, a decrease in union powers, is likely to contribute to lower cost-push inflation, meaning that Option A is not the correct answer.
2. a depreciation of the domestic currency, which will increase the cost of imported raw materials and components. So, an appreciation of the currency is likely to reduce cost-push inflationary pressures, implying that Option B is incorrect.
3. a fall in labour productivity, which will mean that more labour is needed to produce each unit of output and hence the cost of each unit of output is higher. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
4. an increase in firms’ profit margins, which will increase the prices they charge to consumers and other firms. So, a decrease in profit margins will tend to reduce prices and hence costpush inflation. Option D is therefore incorrect.Incorrect
Answer: C
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of producing and/or supplying goods and services. In practice there are number of factors that might lead production costs to increase, including:
1. increased trade union power, perhaps resulting from higher union membership or a relaxation of the laws governing their actions. Conversely, a decrease in union powers, is likely to contribute to lower cost-push inflation, meaning that Option A is not the correct answer.
2. a depreciation of the domestic currency, which will increase the cost of imported raw materials and components. So, an appreciation of the currency is likely to reduce cost-push inflationary pressures, implying that Option B is incorrect.
3. a fall in labour productivity, which will mean that more labour is needed to produce each unit of output and hence the cost of each unit of output is higher. Option C is therefore the correct answer.
4. an increase in firms’ profit margins, which will increase the prices they charge to consumers and other firms. So, a decrease in profit margins will tend to reduce prices and hence costpush inflation. Option D is therefore incorrect. -
Question 815 of 999CB2031726
Question 815
FlagStructural unemployment is unemployment that:
Correct
Option B is the correct answer.
Structural unemployment is (equilibrium) unemployment that arises from changes in the pattern of demand or supply in the economy. In other words, it is caused by a change in the structure of industry, because of either changes in the demand for a product, or in the methods of production.
Option A describes unemployment that exists in a recession when demand for labour is low across the whole economy. As such, it does not relate to a specific industry. This is a description of demand-deficient (or cyclical unemployment) rather than structural unemployment and so is not the correct answer.
Option B describes a situation in which the unemployed lack the skills needed by newly created jobs. This is a structural issue and consequently this is likely to be the correct answer. If one industry goes into decline and subsequently new industries spring up creating new jobs, then the former workers in the declining industry may not have appropriate skills for the newly created jobs.
Option C – the unemployed giving up hope of finding a job – is most likely to arise for the long-term unemployed. Individuals may be unemployed for a long time for a number of reasons – it need not necessarily be a structural issue. So this is unlikely to be the correct answer.
Option D describes frictional unemployment and so is incorrect.
Hence Option B is the correct answer.Incorrect
Option B is the correct answer.
Structural unemployment is (equilibrium) unemployment that arises from changes in the pattern of demand or supply in the economy. In other words, it is caused by a change in the structure of industry, because of either changes in the demand for a product, or in the methods of production.
Option A describes unemployment that exists in a recession when demand for labour is low across the whole economy. As such, it does not relate to a specific industry. This is a description of demand-deficient (or cyclical unemployment) rather than structural unemployment and so is not the correct answer.
Option B describes a situation in which the unemployed lack the skills needed by newly created jobs. This is a structural issue and consequently this is likely to be the correct answer. If one industry goes into decline and subsequently new industries spring up creating new jobs, then the former workers in the declining industry may not have appropriate skills for the newly created jobs.
Option C – the unemployed giving up hope of finding a job – is most likely to arise for the long-term unemployed. Individuals may be unemployed for a long time for a number of reasons – it need not necessarily be a structural issue. So this is unlikely to be the correct answer.
Option D describes frictional unemployment and so is incorrect.
Hence Option B is the correct answer. -
Question 816 of 999CB2031727
Question 816
FlagWhich one of the following is most likely to be the best method of reducing long-term structural unemployment?
Correct
Answer: D
Structural unemployment is unemployment caused by a change in the structure of industry, because of either changes in the demand for a product, or in the methods of production.
Options A and B (expansionary fiscal and monetary policies) are both possible ways of increasing aggregate demand. An increase in aggregate demand should lead to an increase in the aggregate demand for labour, and so should reduce demand-deficient unemployment. However, these methods are unlikely to help the unemployment in any specific industry. Therefore Options $A$ and $B$ are not correct.
Option C is a method of reducing real-wage unemployment. This type of unemployment might arise as a result of a fall in aggregate demand without a corresponding fall in average real wages. One reason why wages might not be allowed to fall is trade union power, which tends to keep wages artificially high. Alternatively, trade unions might have bid up real wages above their equilibrium level without any change in the aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply of labour. Therefore by reducing trade union power, wages will be more flexible downwards. So Option C also deals with economy-wide unemployment, but does not help with structural unemployment in a specific industry.
Structural unemployment tends to persist because the individuals who have become structurally unemployed do not possess appropriate skills for the jobs that are available. Option D – better education and training – should help overcome this, and so this is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Structural unemployment is unemployment caused by a change in the structure of industry, because of either changes in the demand for a product, or in the methods of production.
Options A and B (expansionary fiscal and monetary policies) are both possible ways of increasing aggregate demand. An increase in aggregate demand should lead to an increase in the aggregate demand for labour, and so should reduce demand-deficient unemployment. However, these methods are unlikely to help the unemployment in any specific industry. Therefore Options $A$ and $B$ are not correct.
Option C is a method of reducing real-wage unemployment. This type of unemployment might arise as a result of a fall in aggregate demand without a corresponding fall in average real wages. One reason why wages might not be allowed to fall is trade union power, which tends to keep wages artificially high. Alternatively, trade unions might have bid up real wages above their equilibrium level without any change in the aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply of labour. Therefore by reducing trade union power, wages will be more flexible downwards. So Option C also deals with economy-wide unemployment, but does not help with structural unemployment in a specific industry.
Structural unemployment tends to persist because the individuals who have become structurally unemployed do not possess appropriate skills for the jobs that are available. Option D – better education and training – should help overcome this, and so this is the correct answer.
-
Question 817 of 999CB2031728
Question 817
FlagWhich of the following is likely to be the most effective method of reducing the natural rate of unemployment?
Correct
Answer: D
The natural level of unemployment is the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work.
In the diagram, $A B$ is the equilibrium or natural level of unemployment. It arises because some people who are in the labour force (shown by $N$ ) are not immediately willing or able to accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $\mathrm{AS}_{\mathrm{L}}$ ). These might be, for example, the structurally unemployed who may not be perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or they might be frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
The disequilibrium level of unemployment is the excess supply of labour resulting from the wage rate being above the equilibrium, ie CD above. This type of unemployment is usually caused by a reduction in the level of aggregate demand (demand-deficient unemployment) and by a reluctance of real wages to fall (real-wage unemployment).
Policies to reduce equilibrium unemployment need to address the particular type of unemployment that exists. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option D is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option A) could increase equilibrium unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in government expenditure (Option B) and an increase in the money supply (Option C) would increase aggregate demand and be appropriate policies to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The natural level of unemployment is the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work.
In the diagram, $A B$ is the equilibrium or natural level of unemployment. It arises because some people who are in the labour force (shown by $N$ ) are not immediately willing or able to accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $\mathrm{AS}_{\mathrm{L}}$ ). These might be, for example, the structurally unemployed who may not be perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or they might be frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
The disequilibrium level of unemployment is the excess supply of labour resulting from the wage rate being above the equilibrium, ie CD above. This type of unemployment is usually caused by a reduction in the level of aggregate demand (demand-deficient unemployment) and by a reluctance of real wages to fall (real-wage unemployment).
Policies to reduce equilibrium unemployment need to address the particular type of unemployment that exists. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option D is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option A) could increase equilibrium unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in government expenditure (Option B) and an increase in the money supply (Option C) would increase aggregate demand and be appropriate policies to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
-
Question 818 of 999CB2031729
Question 818
FlagIf, due to pollution concerns, consumers switch from travelling to work by car to travelling by public transport, the resulting unemployment in the car industry is:
Correct
Answer: C
Frictional (search) unemployment is (equilibrium) unemployment resulting from imperfect information about the labour market, so that employers and employees take time to search for the ‘right’ employee and the ‘right’ job. This is not relevant to the situation outlined in the question, which revolves around a change in consumer tastes.
Seasonal unemployment is unemployment caused by a decrease in the demand for particular goods and services, and hence the labour used to produce and/or supply them, at particular times of the year. As there is no seasonal element involved in the switch from car travel to using public transport, this too is not relevant to the situation outlined.
Structural unemployment is (equilibrium) unemployment caused by a change in the structure of an industry, either because of a fall in the demand for a product, eg coal, or because of changes in the methods of production, eg internet banking. The question describes a reduction in the demand for driving and a consequent fall in the demand for cars that results in unemployment. It is, therefore, an example of structural unemployment and so Option C is the correct answer.
For the sake of completeness, recall that technological unemployment, which is what the question means by technical unemployment, is a type of structural unemployment that results from the introduction of labour-saving technology, which is not relevant to the situation outlined in the question.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Frictional (search) unemployment is (equilibrium) unemployment resulting from imperfect information about the labour market, so that employers and employees take time to search for the ‘right’ employee and the ‘right’ job. This is not relevant to the situation outlined in the question, which revolves around a change in consumer tastes.
Seasonal unemployment is unemployment caused by a decrease in the demand for particular goods and services, and hence the labour used to produce and/or supply them, at particular times of the year. As there is no seasonal element involved in the switch from car travel to using public transport, this too is not relevant to the situation outlined.
Structural unemployment is (equilibrium) unemployment caused by a change in the structure of an industry, either because of a fall in the demand for a product, eg coal, or because of changes in the methods of production, eg internet banking. The question describes a reduction in the demand for driving and a consequent fall in the demand for cars that results in unemployment. It is, therefore, an example of structural unemployment and so Option C is the correct answer.
For the sake of completeness, recall that technological unemployment, which is what the question means by technical unemployment, is a type of structural unemployment that results from the introduction of labour-saving technology, which is not relevant to the situation outlined in the question.
-
Question 819 of 999CB2031730
Question 819
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT likely to lead to cost-push inflation?
Correct
Answer: B
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of producing and/or supplying goods and services. In practice there are number of factors that might lead production costs to increase, including:
1. increased trade union power, perhaps resulting from higher union membership or a relaxation of the laws governing their actions, meaning that Option A is not the correct answer.
2. a depreciation of the domestic currency, which will increase the cost of imported raw materials and components in domestic currency terms.
3. an increase in interest rates, which increases the cost of borrowing by firms to fund production. Option C is therefore not the correct answer.
4. an increase in firms’ profit margins, which will increase the prices they charge to consumers and other firms. Option D is therefore incorrect.In contrast to a depreciation, an appreciation of the currency is likely to reduce cost-push inflationary pressures. So, as the question has asked for a factor that will not lead to cost-push inflation, Option B is correct.
Incorrect
Answer: B
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of producing and/or supplying goods and services. In practice there are number of factors that might lead production costs to increase, including:
1. increased trade union power, perhaps resulting from higher union membership or a relaxation of the laws governing their actions, meaning that Option A is not the correct answer.
2. a depreciation of the domestic currency, which will increase the cost of imported raw materials and components in domestic currency terms.
3. an increase in interest rates, which increases the cost of borrowing by firms to fund production. Option C is therefore not the correct answer.
4. an increase in firms’ profit margins, which will increase the prices they charge to consumers and other firms. Option D is therefore incorrect.In contrast to a depreciation, an appreciation of the currency is likely to reduce cost-push inflationary pressures. So, as the question has asked for a factor that will not lead to cost-push inflation, Option B is correct.
-
Question 820 of 999CB2031731
Question 820
FlagThe short-run Phillips curve shows:
Correct
Answer: C
The Phillips curve shows an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Note that in the monetarist model of inflation, the expectations-augmented Phillips curves are sometimes referred to as short-run Phillips curves, in contrast to the long-run Phillips curve, which is vertical in that model.
Incorrect
Answer: C
The Phillips curve shows an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation. Hence Option C is the correct answer.
Note that in the monetarist model of inflation, the expectations-augmented Phillips curves are sometimes referred to as short-run Phillips curves, in contrast to the long-run Phillips curve, which is vertical in that model.
-
Question 821 of 999CB2031732
Question 821
FlagThe need to employ workers with certain skills may decline even if the industry as a whole is not in decline. This form of unemployment is called:
Correct
Answer: C
In this instance, the unemployment described in the question is caused not by a decline in demand for the industry’s product, but by a decline in the demand for certain skills. This rules out structural unemployment (Option B), which occurs directly as a result of a decline in a particular industry, and regional unemployment (Option A), which arises when that industry is located in a particular area.
It also rules out demand-deficient unemployment (Option D), which is widespread unemployment across the economy as a whole caused by a fall in aggregate demand.
The answer must therefore be technological unemployment (Option C), which results from the introduction of labour-saving technology. For example, skilled carpenters might lose their jobs with the introduction of assembly-line production.
Incorrect
Answer: C
In this instance, the unemployment described in the question is caused not by a decline in demand for the industry’s product, but by a decline in the demand for certain skills. This rules out structural unemployment (Option B), which occurs directly as a result of a decline in a particular industry, and regional unemployment (Option A), which arises when that industry is located in a particular area.
It also rules out demand-deficient unemployment (Option D), which is widespread unemployment across the economy as a whole caused by a fall in aggregate demand.
The answer must therefore be technological unemployment (Option C), which results from the introduction of labour-saving technology. For example, skilled carpenters might lose their jobs with the introduction of assembly-line production.
-
Question 822 of 999CB2031733
Question 822
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a cause of cost-push inflation?
Correct
Answer: A
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of production independent of the level of aggregate demand. Possible sources of cost-push inflation include:
– an increase in raw materials costs (Option B)
– an increase in profit margins applied by firms (Option C)
– an increase in wages above increases in labour productivity (Option D).An appreciation of the exchange rate (Option A) reduces import prices and so reduces the cost of imported supplies. This is likely to reduce any cost-push pressures and so is not a cause of costpush inflation. Consequently, Option A is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of production independent of the level of aggregate demand. Possible sources of cost-push inflation include:
– an increase in raw materials costs (Option B)
– an increase in profit margins applied by firms (Option C)
– an increase in wages above increases in labour productivity (Option D).An appreciation of the exchange rate (Option A) reduces import prices and so reduces the cost of imported supplies. This is likely to reduce any cost-push pressures and so is not a cause of costpush inflation. Consequently, Option A is the correct answer.
-
Question 823 of 999CB2031734
Question 823
FlagWhich one of the following is likely to lead to cost-push inflation?
Correct
Answer: B
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of producing and/or supplying goods and services. In practice, there are number of factors that might lead production costs to increase, including:
– increased trade union power, perhaps resulting from higher union membership or a relaxation of the laws governing their actions. Conversely, a decrease in trade union power, is likely to contribute to lower cost-push inflation, meaning that Option A is not the correct answer.
– a depreciation of the domestic currency, which will increase the cost of imported raw materials and components. So, Option B is the correct answer.
– a fall in labour productivity, which will mean that more labour is needed to produce each unit of output and hence the cost of each unit of output is higher. Conversely, a rise in labour productivity will reduce costs and hence cost-push inflation. So, Option C is incorrect.
– an increase in firms’ profit margins, which will increase the prices they charge to consumers and other firms. On the other hand, a decrease in profit margins will tend to reduce prices and hence cost-push inflation. Option D is therefore incorrect.Incorrect
Answer: B
Cost-push inflation is caused by persistent increases in the costs of producing and/or supplying goods and services. In practice, there are number of factors that might lead production costs to increase, including:
– increased trade union power, perhaps resulting from higher union membership or a relaxation of the laws governing their actions. Conversely, a decrease in trade union power, is likely to contribute to lower cost-push inflation, meaning that Option A is not the correct answer.
– a depreciation of the domestic currency, which will increase the cost of imported raw materials and components. So, Option B is the correct answer.
– a fall in labour productivity, which will mean that more labour is needed to produce each unit of output and hence the cost of each unit of output is higher. Conversely, a rise in labour productivity will reduce costs and hence cost-push inflation. So, Option C is incorrect.
– an increase in firms’ profit margins, which will increase the prices they charge to consumers and other firms. On the other hand, a decrease in profit margins will tend to reduce prices and hence cost-push inflation. Option D is therefore incorrect. -
Question 824 of 999CB2031735
Question 824
FlagThe need to employ workers with certain skills may decline even if the industry as a whole is not in decline. This form of unemployment is called:
Correct
Answer: C
In this instance, the unemployment described in the question is caused not by a decline in demand for the industry’s product, but by a decline in the demand for certain skills. This rules out structural unemployment (Option B), which typically occurs directly as a result of a decline in a particular industry, and regional unemployment (Option A), which arises when that industry is located in a particular area.
It also rules out demand-deficient unemployment (Option D), which is widespread unemployment across the economy as a whole caused by a fall in aggregate demand.
The answer must therefore be technological unemployment (Option C), which results from the introduction of labour-saving technology. For example, some actuaries might lose their jobs with the introduction of more powerful modelling packages, even if the demand for actuarial services remains unchanged.
Incorrect
Answer: C
In this instance, the unemployment described in the question is caused not by a decline in demand for the industry’s product, but by a decline in the demand for certain skills. This rules out structural unemployment (Option B), which typically occurs directly as a result of a decline in a particular industry, and regional unemployment (Option A), which arises when that industry is located in a particular area.
It also rules out demand-deficient unemployment (Option D), which is widespread unemployment across the economy as a whole caused by a fall in aggregate demand.
The answer must therefore be technological unemployment (Option C), which results from the introduction of labour-saving technology. For example, some actuaries might lose their jobs with the introduction of more powerful modelling packages, even if the demand for actuarial services remains unchanged.
-
Question 825 of 999CB2031736
Question 825
FlagWhich one of the following is likely to be the most effective method of reducing the natural rate of unemployment?
Correct
Answer: D
The natural rate (or level) of unemployment is the rate (or level) of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work. It is also referred to as the equilibrium rate or level of unemployment.
In the diagram, $A B$ is the natural or equilibrium level of unemployment. It arises because of the difference between the total number of workers in the labour force (shown by $N$ ) and the number of people who are willing and able to immediately accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $A S_L$ ). This difference might be due to, for example, the structurally unemployed who are not perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or it might be due to frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
Policies to reduce natural (or equilibrium) unemployment need to address the particular cause of the unemployment. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities (Option D)
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option D is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option B) could actually increase the natural rate of unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in government expenditure (Option C) and an increase in the money supply (Option A) would increase aggregate demand and be appropriate policies to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
Incorrect
Answer: D
The natural rate (or level) of unemployment is the rate (or level) of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work. It is also referred to as the equilibrium rate or level of unemployment.
In the diagram, $A B$ is the natural or equilibrium level of unemployment. It arises because of the difference between the total number of workers in the labour force (shown by $N$ ) and the number of people who are willing and able to immediately accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $A S_L$ ). This difference might be due to, for example, the structurally unemployed who are not perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or it might be due to frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
Policies to reduce natural (or equilibrium) unemployment need to address the particular cause of the unemployment. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities (Option D)
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option D is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option B) could actually increase the natural rate of unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in government expenditure (Option C) and an increase in the money supply (Option A) would increase aggregate demand and be appropriate policies to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
-
Question 826 of 999CB2031737
Question 826
FlagThe business cycle is defined as:
Correct
Answer: B
The term business cycle refers to the short-run fluctuations in national output around the long-run trend, which sounds like Option B and rules out Options A and D.
In practice, business cycles typically last for several years, although the actual length varies from cycle to cycle. Hence Option C is also incorrect and Option B is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The term business cycle refers to the short-run fluctuations in national output around the long-run trend, which sounds like Option B and rules out Options A and D.
In practice, business cycles typically last for several years, although the actual length varies from cycle to cycle. Hence Option C is also incorrect and Option B is the correct answer.
-
Question 827 of 999CB2031738
Question 827
FlagWhich of the following is a potential source of cost-push inflation?
Correct
Answer: C
cost-push inflation is caused by a persistent increase in costs independent of the level of aggregate demand. It corresponds to an upward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
A decrease in direct taxes, such as income tax, would have the effect of increasing consumer spending and hence aggregate demand, which might result in demand-pull inflation. In addition, it might also enable firms to reduce gross salaries, without reducing net-of-tax salaries, which would tend to reduce cost-push inflation. Either way, Option A cannot be the correct answer.
As mentioned above, an increase in consumer expenditure could lead to inflation, but this would be demand-pull inflation due to excess demand bidding up prices, rather than cost-push inflation.
So Option B is incorrect.
A depreciation of the domestic currency would increase the domestic currency price of imported goods and services, including raw materials and components. This would therefore push up firms’ production costs, leading to cost-push inflation. So, Option C is the correct answer.Conversely, a decrease in imported commodity prices would reduce production costs and costpush inflation, meaning that Option D cannot be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
cost-push inflation is caused by a persistent increase in costs independent of the level of aggregate demand. It corresponds to an upward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
A decrease in direct taxes, such as income tax, would have the effect of increasing consumer spending and hence aggregate demand, which might result in demand-pull inflation. In addition, it might also enable firms to reduce gross salaries, without reducing net-of-tax salaries, which would tend to reduce cost-push inflation. Either way, Option A cannot be the correct answer.
As mentioned above, an increase in consumer expenditure could lead to inflation, but this would be demand-pull inflation due to excess demand bidding up prices, rather than cost-push inflation.
So Option B is incorrect.
A depreciation of the domestic currency would increase the domestic currency price of imported goods and services, including raw materials and components. This would therefore push up firms’ production costs, leading to cost-push inflation. So, Option C is the correct answer.Conversely, a decrease in imported commodity prices would reduce production costs and costpush inflation, meaning that Option D cannot be the correct answer.
-
Question 828 of 999CB2031739
Question 828
FlagWhich of the following types of unemployment would exist even in a well-functioning free market economy?
Correct
Answer: B
The term ‘classical unemployment’ (Option A) is not mentioned in the course and so is unlikely to be the correct answer. However, the classical economists blamed the high unemployment in the 1930s on real wages being too high. This type of unemployment is now more often known as ‘real-wage’ unemployment. It is one of the two causes of disequilibrium unemployment (the other being ‘demand-deficient’ unemployment). If the economy is in disequilibrium, it is unlikely to be considered ‘well-functioning’, so this is not likely to be the correct answer.
One difficulty is that the term ‘well-functioning economy’ is not defined in the course. In the absence of further information, we might assume that the labour market in a well-functioning economy may be in equilibrium, ie the aggregate demand for and supply of labour are equal.
In such a situation we would expect five main types of equilibrium unemployment to be present:
– Frictional (search) unemployment, ie unemployment resulting from imperfect information about the labour market, so that employers and employees take time to search for the ‘right’ employee and the ‘right’ job. This is Option B.
– Technological unemployment, ie structural unemployment resulting from the introduction of labour-saving technology, which reduces the demand for labour in certain industries. This is Option C.
– Structural unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a change in the structure of industry, either because of changes in the demand for a product, eg coal, or because of changes in the methods of production, eg internet banking.This is Option D.
– Regional unemployment, ie structural unemployment that is concentrated in a particular region of the country in which the industries undergoing structural change are located.
– Seasonal unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a decrease in the demand for labour in certain industries (eg skiing) at particular times of the year.In the absence of further information, it is difficult to choose between Options B, C and D; indeed, it seems strange to call an economy ‘well-functioning’ when it has any of these types of unemployment. However, possibly the least serious of these is frictional unemployment (Option B) – in fact, it is thought that an economy that has a workforce that is prepared to give up a job and be temporarily unemployed while looking for a better one, is a more adaptable and mobile workforce and one that will bring greater economic growth in the long run.
The examiners also accepted Options C and D when this question appeared in this exam. However, when the same question appeared in the April 2020 exam, Options C and D were not accepted.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The term ‘classical unemployment’ (Option A) is not mentioned in the course and so is unlikely to be the correct answer. However, the classical economists blamed the high unemployment in the 1930s on real wages being too high. This type of unemployment is now more often known as ‘real-wage’ unemployment. It is one of the two causes of disequilibrium unemployment (the other being ‘demand-deficient’ unemployment). If the economy is in disequilibrium, it is unlikely to be considered ‘well-functioning’, so this is not likely to be the correct answer.
One difficulty is that the term ‘well-functioning economy’ is not defined in the course. In the absence of further information, we might assume that the labour market in a well-functioning economy may be in equilibrium, ie the aggregate demand for and supply of labour are equal.
In such a situation we would expect five main types of equilibrium unemployment to be present:
– Frictional (search) unemployment, ie unemployment resulting from imperfect information about the labour market, so that employers and employees take time to search for the ‘right’ employee and the ‘right’ job. This is Option B.
– Technological unemployment, ie structural unemployment resulting from the introduction of labour-saving technology, which reduces the demand for labour in certain industries. This is Option C.
– Structural unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a change in the structure of industry, either because of changes in the demand for a product, eg coal, or because of changes in the methods of production, eg internet banking.This is Option D.
– Regional unemployment, ie structural unemployment that is concentrated in a particular region of the country in which the industries undergoing structural change are located.
– Seasonal unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a decrease in the demand for labour in certain industries (eg skiing) at particular times of the year.In the absence of further information, it is difficult to choose between Options B, C and D; indeed, it seems strange to call an economy ‘well-functioning’ when it has any of these types of unemployment. However, possibly the least serious of these is frictional unemployment (Option B) – in fact, it is thought that an economy that has a workforce that is prepared to give up a job and be temporarily unemployed while looking for a better one, is a more adaptable and mobile workforce and one that will bring greater economic growth in the long run.
The examiners also accepted Options C and D when this question appeared in this exam. However, when the same question appeared in the April 2020 exam, Options C and D were not accepted.
-
Question 829 of 999CB2031740
Question 829
FlagWhich of the following is least likely to lead to an increase in long-run economic growth?
Correct
Answer: A
Supply-side policies aim to increase the quantity and / or productivity of the nation’s resources and so increase potential output and long-run economic growth. Options B, C and D are all examples of supply-side policies.
Demand-side policies aim to stimulate aggregate demand in order to attain potential output. For example, an increase in the money supply (Option A) will decrease interest rates, making it cheaper and easier to borrow, and should therefore increase consumption and investment. Lower interest rates will lead to a depreciation of the currency (if it is floating) and therefore increase net exports. This expansion of aggregate demand might increase business confidence and therefore further encourage investment. This investment, especially if it incorporates new technology, may increase potential output (by increasing the quantity and / or productivity of resources).
However, Options B, C and D are more direct ways of stimulating economic growth in the long run. Hence Option A is least likely to lead to an increase in long-run economic growth, and is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Supply-side policies aim to increase the quantity and / or productivity of the nation’s resources and so increase potential output and long-run economic growth. Options B, C and D are all examples of supply-side policies.
Demand-side policies aim to stimulate aggregate demand in order to attain potential output. For example, an increase in the money supply (Option A) will decrease interest rates, making it cheaper and easier to borrow, and should therefore increase consumption and investment. Lower interest rates will lead to a depreciation of the currency (if it is floating) and therefore increase net exports. This expansion of aggregate demand might increase business confidence and therefore further encourage investment. This investment, especially if it incorporates new technology, may increase potential output (by increasing the quantity and / or productivity of resources).
However, Options B, C and D are more direct ways of stimulating economic growth in the long run. Hence Option A is least likely to lead to an increase in long-run economic growth, and is the correct answer.
-
Question 830 of 999CB2031741
Question 830
FlagUnanticipated inflation:
Correct
Answer: B
It’s easiest to determine the impact of unanticipated inflation by considering the impact on two parties who agree a loan at a fixed interest rate. However, the same argument can be extended to loans that are at a variable rate of interest that fails to change to reflect fully any changes in inflation.
Lenders and borrowers of capital agree the fixed-rate terms at which they exchange funds based on their expectations of future inflation over the term of the loan.
If actual inflation subsequently turns out to be higher than anticipated, then the real value of the loan granted will be lower than anticipated at the outset. In effect there is an unanticipated redistribution of wealth from fixed-rate lenders (savers) – whose asset has a lower real value than anticipated – to borrowers, whose corresponding liability to repay the loan likewise has a lower real value than anticipated.
The correct answer is therefore $B$.
Incorrect
Answer: B
It’s easiest to determine the impact of unanticipated inflation by considering the impact on two parties who agree a loan at a fixed interest rate. However, the same argument can be extended to loans that are at a variable rate of interest that fails to change to reflect fully any changes in inflation.
Lenders and borrowers of capital agree the fixed-rate terms at which they exchange funds based on their expectations of future inflation over the term of the loan.
If actual inflation subsequently turns out to be higher than anticipated, then the real value of the loan granted will be lower than anticipated at the outset. In effect there is an unanticipated redistribution of wealth from fixed-rate lenders (savers) – whose asset has a lower real value than anticipated – to borrowers, whose corresponding liability to repay the loan likewise has a lower real value than anticipated.
The correct answer is therefore $B$.
-
Question 831 of 999CB2031742
Question 831
FlagThe Phillips curve shows that:
Correct
Answer: B
Recall that the original and simpler Phillips curve slopes downwards, suggesting a trade-off between the rates of inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment.
The first of these corresponds to Option B, which is therefore the correct answer.
Remember that prices and inflation are not the same thing, as inflation is the rate of growth of prices.Incorrect
Answer: B
Recall that the original and simpler Phillips curve slopes downwards, suggesting a trade-off between the rates of inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment.
The first of these corresponds to Option B, which is therefore the correct answer.
Remember that prices and inflation are not the same thing, as inflation is the rate of growth of prices. -
Question 832 of 999CB2031743
Question 832
FlagWhich of the following could explain why a country’s aggregate demand curve may shift inwards to the left?
Correct
Answer B
The AD curve will shift if any of its components ( $C, I, G, X$ or $M$ ) change (assuming that the change was not caused by a general change in the price). More specifically, it will shift inwards to the left if any of its components ( $C, I, G$ and $(X-M)$ ) decrease:
– A decrease in interest rates (Option A) will affect $C$ and $I$. Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so $C$ might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase $C$ and $I$, and hence increase AD . Therefore Option A is not the correct answer.
– An appreciation of the domestic currency (Option B) will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper. So, there is likely to be a decrease in $X$ and an increase in $M$. If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to a decrease in net exports ( $X-M$ ) and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
– A rise in $G$ (Option C ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
– An increase in business confidence (Option D) is likely to increase the level of I and hence increase AD. So Option D is not the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer B
The AD curve will shift if any of its components ( $C, I, G, X$ or $M$ ) change (assuming that the change was not caused by a general change in the price). More specifically, it will shift inwards to the left if any of its components ( $C, I, G$ and $(X-M)$ ) decrease:
– A decrease in interest rates (Option A) will affect $C$ and $I$. Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so $C$ might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase $C$ and $I$, and hence increase AD . Therefore Option A is not the correct answer.
– An appreciation of the domestic currency (Option B) will make exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper. So, there is likely to be a decrease in $X$ and an increase in $M$. If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to a decrease in net exports ( $X-M$ ) and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option B is the correct answer.
– A rise in $G$ (Option C ) will lead to a direct increase in AD, therefore Option C is not the correct answer.
– An increase in business confidence (Option D) is likely to increase the level of I and hence increase AD. So Option D is not the correct answer. -
Question 833 of 999CB2031744
Question 833
FlagOne way of reducing the natural rate of unemployment would be to increase:
Correct
Answer: C
The natural rate (or level) of unemployment is also referred to as the equilibrium rate or level of unemployment.
In the diagram, AB is the natural or equilibrium level of unemployment. It arises because of the difference between the total number of workers in the labour force (shown by N ) and the number of people who are willing and able to immediately accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $A S_L$ ). This difference might be due to, for example, the structurally unemployed who are not perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or it might be due to frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
Policies to reduce natural (or equilibrium) unemployment need to address the particular cause of the unemployment. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities (Option C)
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option C is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option A) could actually increase the natural rate of unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in government expenditure (Option B) and an increase in the money supply (Option D) would increase aggregate demand and be appropriate policies to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
Incorrect
Answer: C
The natural rate (or level) of unemployment is also referred to as the equilibrium rate or level of unemployment.
In the diagram, AB is the natural or equilibrium level of unemployment. It arises because of the difference between the total number of workers in the labour force (shown by N ) and the number of people who are willing and able to immediately accept a job at the current wage rate (shown by $A S_L$ ). This difference might be due to, for example, the structurally unemployed who are not perfectly mobile occupationally, industrially and geographically; or it might be due to frictionally unemployed young people who are searching for an appropriate first job.
Policies to reduce natural (or equilibrium) unemployment need to address the particular cause of the unemployment. For example:
– a lack of occupational or geographical mobility can be overcome by retraining or mobility incentives
– the job search process can be speeded up by providing improved information about job opportunities (Option C)
– unemployment can be made less attractive by reducing unemployment benefit.Consequently, Option C is the correct answer.
An increase in unemployment benefit (Option A) could actually increase the natural rate of unemployment by making unemployment more attractive.An increase in government expenditure (Option B) and an increase in the money supply (Option D) would increase aggregate demand and be appropriate policies to deal with demand-deficient unemployment, which is a type of disequilibrium unemployment.
-
Question 834 of 999CB2031745
Question 834
FlagWhich of the following statements about real variables in the economy is TRUE?
Correct
Answer D
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices. Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year.
Inflation may be calculated using price index figures at certain points in time. Nominal values can be calculated as real values $\times(1+$ inflation $)$. This is often approximated as nominal values $\simeq$ real values + inflation.
Option A relates to growth in GDP:
nominal GDP growth $\simeq$ real GDP growth + inflation
If nominal GDP growth is $3 \%$, then it is impossible to say what has happened to real GDP growth without having information on inflation. So Option A is false, and so is not the correct answer.Option B also relates to growth in GDP. The GDP deflator is a way of measuring / calculating inflation. If there is a rise in the GDP deflator, this corresponds to positive inflation:
nominal GDP growth $\simeq$ real GDP growth+inflation
inflation $\simeq$ nominal GDP growth – real GDP growth $>0$
At an initial glance, it would appear to be true that positive inflation implies that the nominal GDP must change by a bigger percentage than the real GDP, and indeed this is the case for positive changes. However, consider the case where nominal GDP falls by $1 \%$. If inflation is $1 \%$ then this would lead to:$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { real GDP growth } & \approx \text { nominal GDP growth-inflation } \\
& =-1 \%-1 \% \\
& =-2 \%
\end{aligned}
$$
ie real GDP falls by a bigger percentage than nominal GDP. So Option B is false, and so is not the correct answer.Option C relates to the relationship between real income and the demand for real money balances. In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transactions purposes. Therefore Option C is false, and so is not a correct answer.
The textbook considers the nominal demand for money (rather than the real demand for money), and this will be affected by both nominal income and inflation.
Option D relates to interest rates:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { nominal interest rate } \approx \text { real interest rate }+ \text { inflation } \\
& \quad \text { real interest rate } \approx \text { nominal interest rate }- \text { inflation }
\end{aligned}
$$Real interest rates can be negative if the expected rate of inflation is greater than nominal interest rates. Option D is therefore true, and so is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer D
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices. Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year.
Inflation may be calculated using price index figures at certain points in time. Nominal values can be calculated as real values $\times(1+$ inflation $)$. This is often approximated as nominal values $\simeq$ real values + inflation.
Option A relates to growth in GDP:
nominal GDP growth $\simeq$ real GDP growth + inflation
If nominal GDP growth is $3 \%$, then it is impossible to say what has happened to real GDP growth without having information on inflation. So Option A is false, and so is not the correct answer.Option B also relates to growth in GDP. The GDP deflator is a way of measuring / calculating inflation. If there is a rise in the GDP deflator, this corresponds to positive inflation:
nominal GDP growth $\simeq$ real GDP growth+inflation
inflation $\simeq$ nominal GDP growth – real GDP growth $>0$
At an initial glance, it would appear to be true that positive inflation implies that the nominal GDP must change by a bigger percentage than the real GDP, and indeed this is the case for positive changes. However, consider the case where nominal GDP falls by $1 \%$. If inflation is $1 \%$ then this would lead to:$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { real GDP growth } & \approx \text { nominal GDP growth-inflation } \\
& =-1 \%-1 \% \\
& =-2 \%
\end{aligned}
$$
ie real GDP falls by a bigger percentage than nominal GDP. So Option B is false, and so is not the correct answer.Option C relates to the relationship between real income and the demand for real money balances. In real terms, the more income people have, the more cash they will want for transactions purposes. Therefore Option C is false, and so is not a correct answer.
The textbook considers the nominal demand for money (rather than the real demand for money), and this will be affected by both nominal income and inflation.
Option D relates to interest rates:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { nominal interest rate } \approx \text { real interest rate }+ \text { inflation } \\
& \quad \text { real interest rate } \approx \text { nominal interest rate }- \text { inflation }
\end{aligned}
$$Real interest rates can be negative if the expected rate of inflation is greater than nominal interest rates. Option D is therefore true, and so is the correct answer.
-
Question 835 of 999CB2031746
Question 835
FlagWhich of the following is an example of disequilibrium unemployment?
Correct
There are three main causes of disequilibrium unemployment:
1. demand-deficient (or cyclical) unemployment
2. real-wage unemployment
3. growth in the labour supply.Therefore the correct answer is Option B.
Note that there are three causes of equilibrium unemployment:
1. frictional unemployment-Option A
2. structural unemployment, which includes technological and regional unemployment) – Option D
3. seasonal unemployment-Option C.Incorrect
There are three main causes of disequilibrium unemployment:
1. demand-deficient (or cyclical) unemployment
2. real-wage unemployment
3. growth in the labour supply.Therefore the correct answer is Option B.
Note that there are three causes of equilibrium unemployment:
1. frictional unemployment-Option A
2. structural unemployment, which includes technological and regional unemployment) – Option D
3. seasonal unemployment-Option C. -
Question 836 of 999CB2031747
Question 836
FlagWhich of the following is a potential source of cost push inflation?
Correct
Answer: A
A depreciation of the domestic currency would increase the domestic currency price of imported goods and services, including raw materials and components. This would therefore push up firms’ production costs, leading to cost-push inflation. So, Option A is the correct answer.
Conversely, a decrease in imported commodity prices would reduce production costs and cost-push inflation, meaning that Option B cannot be the correct answer.
An increase in consumer expenditure, and hence aggregate demand, could lead to demand-pull inflation due to excess demand bidding up prices, but this is not cost-push inflation. So Option C is incorrect.
A decrease in direct taxes, such as income tax, would have the effect of increasing consumer spending, which might result in demand-pull inflation (as above). In addition, it might also enable firms to reduce gross salaries, without reducing net-of-tax salaries, which would tend to reduce cost-push inflation. Either way, Option D cannot be the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: A
A depreciation of the domestic currency would increase the domestic currency price of imported goods and services, including raw materials and components. This would therefore push up firms’ production costs, leading to cost-push inflation. So, Option A is the correct answer.
Conversely, a decrease in imported commodity prices would reduce production costs and cost-push inflation, meaning that Option B cannot be the correct answer.
An increase in consumer expenditure, and hence aggregate demand, could lead to demand-pull inflation due to excess demand bidding up prices, but this is not cost-push inflation. So Option C is incorrect.
A decrease in direct taxes, such as income tax, would have the effect of increasing consumer spending, which might result in demand-pull inflation (as above). In addition, it might also enable firms to reduce gross salaries, without reducing net-of-tax salaries, which would tend to reduce cost-push inflation. Either way, Option D cannot be the correct answer.
-
Question 837 of 999CB2031748
Question 837
FlagGiven the information in the table below, calculate Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at market prices using the income method:
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline & \$ million \\
\hline \text{Mixed incomes} & 200 \\
\hline \text{Exports of goods and services} & 700 \\
\hline \text{Imports of goods and services} & 550 \\
\hline \text{Taxes} & 150 \\
\hline \text{Wages and salaries} & 850 \\
\hline \text{Consumption expenditure} & 975 \\
\hline \text{Subsidies} & 25 \\
\hline \text{Gross capital formation} & 350 \\
\hline \text{Operating surplus} & 450 \\
\hline
\end{array}Correct
Answer A
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12 -month period. It can be calculated using the product (or output) method, the income method or the expenditure method.
This question specifically asks for the income method to be used, which involves summing wages, interest, rent and profits. However, this will give GDP at basic prices (or GVA), whereas the question asks for it at market prices:
– GDP at market prices is the value of output (or income or expenditure) in terms of the prices actually paid.
– GDP at basic prices is the sum of all the values added by all industries in the economy over a year, rather than the prices paid for them; these figures exclude taxes on products (such as VAT) and subsidies on products. GDP at basic prices is also known as gross value added (GVA).So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GDP at market prices } & =\text { GDP at basic prices (GVA) } \\
& + \text { taxes on products } \\
& \text {-subsidies on products }
\end{aligned}
$$Substituting in the numbers from the question:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GDP at market prices } & =850+450+200 \\
& +150 \\
& -25 \\
& =1,625
\end{aligned}
$$This assumes that:
– operating surplus is another name for profit
– mixed incomes should be included (and may be made up of items such as interest and rent)
– taxes are indirect taxes, ie taxes on expenditure rather than income.Consumption expenditure, gross capital formation (ie investment) and exports less imports of goods and services would form part of the expenditure method for calculating national income. However:
– this cannot be used here as government expenditure information has not been given
– the question has stated that the income method should be used.Incorrect
Answer A
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12 -month period. It can be calculated using the product (or output) method, the income method or the expenditure method.
This question specifically asks for the income method to be used, which involves summing wages, interest, rent and profits. However, this will give GDP at basic prices (or GVA), whereas the question asks for it at market prices:
– GDP at market prices is the value of output (or income or expenditure) in terms of the prices actually paid.
– GDP at basic prices is the sum of all the values added by all industries in the economy over a year, rather than the prices paid for them; these figures exclude taxes on products (such as VAT) and subsidies on products. GDP at basic prices is also known as gross value added (GVA).So:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GDP at market prices } & =\text { GDP at basic prices (GVA) } \\
& + \text { taxes on products } \\
& \text {-subsidies on products }
\end{aligned}
$$Substituting in the numbers from the question:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GDP at market prices } & =850+450+200 \\
& +150 \\
& -25 \\
& =1,625
\end{aligned}
$$This assumes that:
– operating surplus is another name for profit
– mixed incomes should be included (and may be made up of items such as interest and rent)
– taxes are indirect taxes, ie taxes on expenditure rather than income.Consumption expenditure, gross capital formation (ie investment) and exports less imports of goods and services would form part of the expenditure method for calculating national income. However:
– this cannot be used here as government expenditure information has not been given
– the question has stated that the income method should be used. -
Question 838 of 999CB2031749
Question 838
FlagUnanticipated inflation:
Correct
correct answer: B
Lenders and borrowers of capital agree the fixed-rate terms at which they exchange funds based on their expectations of future inflation over the term of the loan.
If actual inflation subsequently turns out to be higher than anticipated, then the real value of the loan granted will be lower than anticipated at the outset. In effect there is an unanticipated redistribution of wealth from fixed-rate lenders (savers) – whose asset has a lower real value than anticipated – to borrowers, whose corresponding liability to repay the loan likewise has a lower real value than anticipated. This rules out Options A and C .
The opportunity cost of holding money could be measured in terms of the goods and services that the money could purchase. Unanticipated inflation reduces the purchasing power and so increases the opportunity cost of money being held.
The correct answer is therefore B.
Incorrect
correct answer: B
Lenders and borrowers of capital agree the fixed-rate terms at which they exchange funds based on their expectations of future inflation over the term of the loan.
If actual inflation subsequently turns out to be higher than anticipated, then the real value of the loan granted will be lower than anticipated at the outset. In effect there is an unanticipated redistribution of wealth from fixed-rate lenders (savers) – whose asset has a lower real value than anticipated – to borrowers, whose corresponding liability to repay the loan likewise has a lower real value than anticipated. This rules out Options A and C .
The opportunity cost of holding money could be measured in terms of the goods and services that the money could purchase. Unanticipated inflation reduces the purchasing power and so increases the opportunity cost of money being held.
The correct answer is therefore B.
-
Question 839 of 999CB2031750
Question 839
FlagWhich of the following is an injection in the circular flow of income model?
Correct
Answer C
The diagram below shows the circular flow of income in an open economy with a government:
The three injections into the circular flow of income are investment, government expenditure and exports. Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 840 of 999CB2031751
Question 840
FlagWhich of the following types of unemployment would exist even in a well-functioning free-market economy?
Correct
Answer: B
‘Classical (or real-wage)’ unemployment is one of the two types of disequilibrium unemployment (the other being ‘demand-deficient’ unemployment). If the labour market is in disequilibrium, it is unlikely to be considered a ‘well-functioning’ economy, so this is not likely to be the correct answer.
If the labour market is in equilibrium, the types of unemployment that might be present are:
– Frictional (search) unemployment, ie unemployment resulting from imperfect information about the labour market, so that employers and employees take time to search for the ‘right’ employee and the ‘right’ job. This is Option B.
– Structural unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a change in the structure of industry, either because of changes in the demand for a product, eg coal, or because of changes in the methods of production, eg internet banking. This is Option D.
– Technological unemployment, ie structural unemployment resulting from the introduction of labour-saving technology, which reduces the demand for labour in certain industries. This is Option C.
– Regional unemployment, ie structural unemployment that is concentrated in a particular region of the country in which the industries undergoing structural change are located.
– Seasonal unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a decrease in the demand for labour in certain industries (eg skiing) at particular times of the year.In the absence of further information, it is difficult to choose between Options B, C and D; indeed, it seems strange to call an economy ‘well-functioning’ when it has any of these types of unemployment. However, possibly the least serious of these is frictional unemployment (Option B) – in fact, it is thought that an economy that has a workforce that is prepared to give up a job and be temporarily unemployed while looking for a better one, is a more adaptable and mobile workforce and one that will bring greater economic growth in the long run.
Incorrect
Answer: B
‘Classical (or real-wage)’ unemployment is one of the two types of disequilibrium unemployment (the other being ‘demand-deficient’ unemployment). If the labour market is in disequilibrium, it is unlikely to be considered a ‘well-functioning’ economy, so this is not likely to be the correct answer.
If the labour market is in equilibrium, the types of unemployment that might be present are:
– Frictional (search) unemployment, ie unemployment resulting from imperfect information about the labour market, so that employers and employees take time to search for the ‘right’ employee and the ‘right’ job. This is Option B.
– Structural unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a change in the structure of industry, either because of changes in the demand for a product, eg coal, or because of changes in the methods of production, eg internet banking. This is Option D.
– Technological unemployment, ie structural unemployment resulting from the introduction of labour-saving technology, which reduces the demand for labour in certain industries. This is Option C.
– Regional unemployment, ie structural unemployment that is concentrated in a particular region of the country in which the industries undergoing structural change are located.
– Seasonal unemployment, ie unemployment caused by a decrease in the demand for labour in certain industries (eg skiing) at particular times of the year.In the absence of further information, it is difficult to choose between Options B, C and D; indeed, it seems strange to call an economy ‘well-functioning’ when it has any of these types of unemployment. However, possibly the least serious of these is frictional unemployment (Option B) – in fact, it is thought that an economy that has a workforce that is prepared to give up a job and be temporarily unemployed while looking for a better one, is a more adaptable and mobile workforce and one that will bring greater economic growth in the long run.
-
Question 841 of 999CB2031752
Question 841
FlagIn an economy where the working population increasingly undertake activities themselves rather than employing someone else to undertake the task, then national income:
Correct
Answer C
National income measures the value of the nation’s output per year, ie it is an attempt to quantify the economic activity of that nation over the year. Whether it is calculated according to the product, the income or the expenditure method, it will only include items that have been recorded.
When individuals undertake activities themselves:
– this activity will not form part of the output by firms (as the activity has been carried out by individuals (households)), so it will not be included in the product method calculation
– they will not receive an income for undertaking the activity, so it will not be included in the income method calculation
– they will not go on to sell the output from the activity, so it will not be included in the expenditure method calculation.Since the unreported component of output is growing, national income overall must be growing at a faster rate than reported. Therefore Option C is true and Option A is false.
Options B and D may also be true, but with no information on what is happening to reported output it is impossible to know with certainty. Therefore these options are not correct.
Incorrect
Answer C
National income measures the value of the nation’s output per year, ie it is an attempt to quantify the economic activity of that nation over the year. Whether it is calculated according to the product, the income or the expenditure method, it will only include items that have been recorded.
When individuals undertake activities themselves:
– this activity will not form part of the output by firms (as the activity has been carried out by individuals (households)), so it will not be included in the product method calculation
– they will not receive an income for undertaking the activity, so it will not be included in the income method calculation
– they will not go on to sell the output from the activity, so it will not be included in the expenditure method calculation.Since the unreported component of output is growing, national income overall must be growing at a faster rate than reported. Therefore Option C is true and Option A is false.
Options B and D may also be true, but with no information on what is happening to reported output it is impossible to know with certainty. Therefore these options are not correct.
-
Question 842 of 999CB2031753
Question 842
FlagThe business cycle is defined as:
Correct
Answer: C
The term business cycle refers to the periodic fluctuations of national output round its long-run trend, which sounds like Option C, and rules out Option B.
In practice, business cycles typically last for several years, although the actual length varies from cycle to cycle. Hence Option A is also incorrect and Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
The term business cycle refers to the periodic fluctuations of national output round its long-run trend, which sounds like Option C, and rules out Option B.
In practice, business cycles typically last for several years, although the actual length varies from cycle to cycle. Hence Option A is also incorrect and Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 843 of 999CB2031754
Question 843
FlagIf nominal GDP increased by $11 \%$ in the last year, while real GDP rose by $5 \%$ then the GDP deflator has:
Correct
Answer A
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices.
Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year.Inflation may be calculated using price index figures at certain points in time.
Nominal values can be calculated as real values $\times(1+\inf$ lation $)$.
For percentage changes, this is often approximated as:
$$
\text { nominal values } \simeq \text { real values }+ \text { inf lation } .
$$Therefore:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { inf lation } & \approx \text { nominal values }- \text { real values } \\
& =11 \%-5 \% \\
& =6 \%
\end{aligned}
$$
and so Option A is the correct answer.Incorrect
Answer A
Nominal measures of national income are measured at current prices.
Real measures of national income are measured after allowing for inflation, ie real variables are measured in constant prices, or in other words, in terms of the prices ruling in some base year.Inflation may be calculated using price index figures at certain points in time.
Nominal values can be calculated as real values $\times(1+\inf$ lation $)$.
For percentage changes, this is often approximated as:
$$
\text { nominal values } \simeq \text { real values }+ \text { inf lation } .
$$Therefore:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { inf lation } & \approx \text { nominal values }- \text { real values } \\
& =11 \%-5 \% \\
& =6 \%
\end{aligned}
$$
and so Option A is the correct answer. -
Question 844 of 999CB2031755
Question 844
FlagWhich of the following is a potential source of demand-pull inflation?
Correct
Demand-pull inflation is caused by a persistent increase in the level of aggregate demand. The excess demand in the economy bids up prices. In contrast, cost-push inflation is a situation in which input costs increase independently of aggregate demand, leading to a rise in the general level of prices.
A fall in wages, which may be caused by an increase in direct (eg income) taxes, will mean that individuals have less money to spend on goods and services, leading to lower demand. This rules out Options A and D.
An increase in the price of imported commodities may lead to cost-push inflation. This rules out Option B.
An increase in consumer expenditure will lead to an increase in aggregate demand and therefore could lead to demand-pull inflation.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Demand-pull inflation is caused by a persistent increase in the level of aggregate demand. The excess demand in the economy bids up prices. In contrast, cost-push inflation is a situation in which input costs increase independently of aggregate demand, leading to a rise in the general level of prices.
A fall in wages, which may be caused by an increase in direct (eg income) taxes, will mean that individuals have less money to spend on goods and services, leading to lower demand. This rules out Options A and D.
An increase in the price of imported commodities may lead to cost-push inflation. This rules out Option B.
An increase in consumer expenditure will lead to an increase in aggregate demand and therefore could lead to demand-pull inflation.
Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 845 of 999CB2031756
Question 845
FlagThe aggregate demand curve may shift to the right following:
Correct
Answer C
The AD curve will shift if there is a change in any of its components. More specifically, it will shift outwards to the right if any of its components ( $\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{I}, \mathrm{G}$ and $(\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M})$ ) increase:
– An appreciation of the domestic currency will make $X$ less competitive and $M$ relatively cheap. So, there is likely to be a decrease in $X$ and an increase in $M$. If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to an decrease in net exports $(X-M)$ and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option A is not a correct answer.
– A decrease in business confidence is likely to decrease the level of I and hence decrease AD. So Option B is not a correct answer.
– A fall in interest rates will affect C and I . Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so C might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase C and I, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
– An increase in the rate of income tax will reduce households’ disposable income. This is likely to reduce C, and hence decrease AD. Therefore Option D is not a correct answer.Incorrect
Answer C
The AD curve will shift if there is a change in any of its components. More specifically, it will shift outwards to the right if any of its components ( $\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{I}, \mathrm{G}$ and $(\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M})$ ) increase:
– An appreciation of the domestic currency will make $X$ less competitive and $M$ relatively cheap. So, there is likely to be a decrease in $X$ and an increase in $M$. If demand for exports and imports is sufficiently elastic, then this will lead to an decrease in net exports $(X-M)$ and hence a decrease in AD. Therefore Option A is not a correct answer.
– A decrease in business confidence is likely to decrease the level of I and hence decrease AD. So Option B is not a correct answer.
– A fall in interest rates will affect C and I . Lower interest rates will make saving less attractive for individuals, so C might increase. Furthermore, borrowing (for both individuals and firms) will be cheaper, so there might be an increase in borrowing and hence spending. This will increase C and I, and hence increase AD. Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
– An increase in the rate of income tax will reduce households’ disposable income. This is likely to reduce C, and hence decrease AD. Therefore Option D is not a correct answer. -
Question 846 of 999CB2031757
Question 846
FlagWhich of the following is added to the gross domestic product to arrive at gross national income?
Correct
A Gross domestic product (GDP) is concerned only with incomes generated within the country, irrespective of ownership. Gross national income (GNY) also incorporates ‘net income from abroad’ (ie these inflows minus outflows), ie:
$$
G N Y=G D P+\text { net income from abroad }
$$Therefore the correct answer is Option A.
Incorrect
A Gross domestic product (GDP) is concerned only with incomes generated within the country, irrespective of ownership. Gross national income (GNY) also incorporates ‘net income from abroad’ (ie these inflows minus outflows), ie:
$$
G N Y=G D P+\text { net income from abroad }
$$Therefore the correct answer is Option A.
-
Question 847 of 999CB2031758
Question 847
FlagWhich of the following is NOT one of the main macroeconomic objectives of a government?
Correct
High employment (or low unemployment), high and stable economic growth and low and stable inflation (ie Options B, C and D) are among the major macroeconomic objectives in the box above.
The correct answer must therefore be Option A.
As to whether a balanced fiscal budget is an objective of a government depends on the beliefs of the government itself. Keynesian economists argue that a balanced fiscal budget is not important in the short term, whereas classical economists deem it to be more so.Incorrect
High employment (or low unemployment), high and stable economic growth and low and stable inflation (ie Options B, C and D) are among the major macroeconomic objectives in the box above.
The correct answer must therefore be Option A.
As to whether a balanced fiscal budget is an objective of a government depends on the beliefs of the government itself. Keynesian economists argue that a balanced fiscal budget is not important in the short term, whereas classical economists deem it to be more so. -
Question 848 of 999CB2031759
Question 848
FlagWhich of the following is most likely to be negatively correlated to an increase in real national income in a country?
Correct
Answer C
As real national income increases, this is likely to increase aggregate demand and consumer expenditure. The increase in aggregate demand will likely mean firms increasing their output and therefore employing more staff. This will generally lead to an increase in employment, and so a decrease in unemployment. This corresponds to Option C.
As it is the real national income that is increasing there may not be a direct impact on the rate of inflation (Option A), although the increased aggregate demand may lead to an increase in demand-pull inflation.
Any increase in inflation, coupled with higher aggregate demand, will likely push domestic prices up. This is likely to reduce exports (which become comparatively more expensive for those in other countries) and increase imports (which may be comparatively cheap). The impact may be to increase any deficit on the international trade account (Option B).
Increased real national income is likely to lead to greater real tax income for the government, who may also need to pay out less in benefits, resulting in a surplus in the government budget (Option D).
Incorrect
Answer C
As real national income increases, this is likely to increase aggregate demand and consumer expenditure. The increase in aggregate demand will likely mean firms increasing their output and therefore employing more staff. This will generally lead to an increase in employment, and so a decrease in unemployment. This corresponds to Option C.
As it is the real national income that is increasing there may not be a direct impact on the rate of inflation (Option A), although the increased aggregate demand may lead to an increase in demand-pull inflation.
Any increase in inflation, coupled with higher aggregate demand, will likely push domestic prices up. This is likely to reduce exports (which become comparatively more expensive for those in other countries) and increase imports (which may be comparatively cheap). The impact may be to increase any deficit on the international trade account (Option B).
Increased real national income is likely to lead to greater real tax income for the government, who may also need to pay out less in benefits, resulting in a surplus in the government budget (Option D).
-
Question 849 of 999CB2031760
Question 849
FlagIf the price level in 2024 for a country is 180 and the rate of inflation between 2023 and 2024 has been $20 \%$, then the price level in 2023 was:
Correct
Answer C
With price levels, as with any other financial quantity, nominal values can be calculated as real values $\times(1+\mathrm{inf}$ lation $)$.
The relevant nominal values can therefore be calculated as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { price level }(2024) & =\text { price level }(2023) \times(1+\mathrm{inf} \text { lation }) \\
\text { price level }(2023) & =\frac{\text { price level }(2024)}{(1+\mathrm{inf} \text { lation })} \\
& =\frac{180}{(1+20 \%)} \\
& =150
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer C
With price levels, as with any other financial quantity, nominal values can be calculated as real values $\times(1+\mathrm{inf}$ lation $)$.
The relevant nominal values can therefore be calculated as:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { price level }(2024) & =\text { price level }(2023) \times(1+\mathrm{inf} \text { lation }) \\
\text { price level }(2023) & =\frac{\text { price level }(2024)}{(1+\mathrm{inf} \text { lation })} \\
& =\frac{180}{(1+20 \%)} \\
& =150
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 850 of 999CB2031761
Question 850
FlagThe Phillips curve shows that the:
Correct
Answer : B
The Phillips curve suggests a trade-off between the rates of inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment.
The first of these corresponds to Option B, which is therefore the correct answer.
Remember that prices and inflation are not the same thing, as inflation is the rate of growth of prices.Incorrect
Answer : B
The Phillips curve suggests a trade-off between the rates of inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment.
The first of these corresponds to Option B, which is therefore the correct answer.
Remember that prices and inflation are not the same thing, as inflation is the rate of growth of prices. -
Question 851 of 999CB2031762
Question 851
FlagThe Phillips curve shows:
Correct
The Phillips curve suggests a trade-off between the rates of inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment.
Option C is therefore the correct answer.
Incorrect
The Phillips curve suggests a trade-off between the rates of inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment.
Option C is therefore the correct answer.
-
Question 852 of 999CB2031763
Question 852
FlagIn a country with a population of 50 million, there are 30 million employed and 7 million unemployed. Calculate the rate of unemployment to the nearest whole percentage.
Correct
Answer B
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}=\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { number employed }+ \text { number unemployed }}
$$
where the total labour force is simply the total of the employed plus the unemployed, the latter being defined as those people of working age without jobs who are available to work at current wage rates.The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
Here, there are 30 million people in employment and 7 million unemployed. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$$
\frac{7}{37} \times 100 \%=18.9 \%
$$The correct answer is therefore Option B.
Incorrect
Answer B
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}=\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { number employed }+ \text { number unemployed }}
$$
where the total labour force is simply the total of the employed plus the unemployed, the latter being defined as those people of working age without jobs who are available to work at current wage rates.The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
Here, there are 30 million people in employment and 7 million unemployed. The unemployment rate is therefore:
$$
\frac{7}{37} \times 100 \%=18.9 \%
$$The correct answer is therefore Option B.
-
Question 853 of 999CB2031764
Question 853
FlagWhich of the following costs of inflation occurs because of the possibility of unanticipated extrahigh inflation?
Correct
Answer: D
Unanticipated inflation erodes the real value of money (ie the value of money measured in terms of what it can buy). This is good for those who have borrowed money, since the real value of what they owe falls, but not good for those who have saved (ie lent) money, since the real value of their savings falls. Option A is therefore incorrect and Option D is the correct answer.
Menu costs (Option B) refer to any costs incurred by firms when changing prices. Shoe-leather costs (Option C), which are not described in the course, refer to the time and effort people take to reduce the effects of inflation. Both menu costs and shoe-leather costs occur even if the inflation has been anticipated.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Unanticipated inflation erodes the real value of money (ie the value of money measured in terms of what it can buy). This is good for those who have borrowed money, since the real value of what they owe falls, but not good for those who have saved (ie lent) money, since the real value of their savings falls. Option A is therefore incorrect and Option D is the correct answer.
Menu costs (Option B) refer to any costs incurred by firms when changing prices. Shoe-leather costs (Option C), which are not described in the course, refer to the time and effort people take to reduce the effects of inflation. Both menu costs and shoe-leather costs occur even if the inflation has been anticipated.
-
Question 854 of 999CB2031765
Question 854
FlagAn unexpected increase in the price level, which causes a temporary reduction in the real wage rate, may:
Correct
Answer: B
A reduction in the real wage (wages adjusted for the price level) corresponds to a decrease in firms’ marginal costs relative to their marginal revenues. They may therefore be willing to employ more workers to produce more output. Hence, the actual rate of unemployment may fall below the natural rate in the short term – ie temporarily.
Option B is therefore the correct answer.
Changes to the natural rate of unemployment are generally difficult to achieve and are unlikely to be temporary, so Options C and D can be ruled out.Incorrect
Answer: B
A reduction in the real wage (wages adjusted for the price level) corresponds to a decrease in firms’ marginal costs relative to their marginal revenues. They may therefore be willing to employ more workers to produce more output. Hence, the actual rate of unemployment may fall below the natural rate in the short term – ie temporarily.
Option B is therefore the correct answer.
Changes to the natural rate of unemployment are generally difficult to achieve and are unlikely to be temporary, so Options C and D can be ruled out. -
Question 855 of 999CB2031766
Question 855
FlagIf the government imposes a minimum wage that is above the market equilibrium wage, we would expect:
Correct
Answer: C
A minimum wage or price floor above the market equilibrium wage will not shift the labour demand or supply curves, so Options B and D are incorrect. It will, however, result in a wage rate above the equilibrium wage rate, so reducing the quantity of labour demanded and increasing the quantity of labour supplied.
Thus, Option A is incorrect and Option C is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
A minimum wage or price floor above the market equilibrium wage will not shift the labour demand or supply curves, so Options B and D are incorrect. It will, however, result in a wage rate above the equilibrium wage rate, so reducing the quantity of labour demanded and increasing the quantity of labour supplied.
Thus, Option A is incorrect and Option C is the correct answer.
-
Question 856 of 999CB2031767
Question 856
FlagOther things being equal, the natural rate of unemployment would increase if the:
Correct
Answer: A
The natural level of unemployment is the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work.
Frictional unemployment is one type of equilibrium unemployment that is associated with imperfect information in the labour market and the time it takes for workers to find jobs, even when there are vacancies. An increase in this time to search for a job will therefore increase frictional (and so equilibrium) unemployment, and so Option A is the correct answer.
A decrease in unemployment benefits (Option B) and an increase in labour productivity (Option C) are both likely to decrease the natural rate of unemployment. The rate of inflation (Option D) is not directly relevant.
Incorrect
Answer: A
The natural level of unemployment is the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium, ie when at a particular wage rate, the demand for labour is equal to the supply of people willing and able to work.
Frictional unemployment is one type of equilibrium unemployment that is associated with imperfect information in the labour market and the time it takes for workers to find jobs, even when there are vacancies. An increase in this time to search for a job will therefore increase frictional (and so equilibrium) unemployment, and so Option A is the correct answer.
A decrease in unemployment benefits (Option B) and an increase in labour productivity (Option C) are both likely to decrease the natural rate of unemployment. The rate of inflation (Option D) is not directly relevant.
-
Question 857 of 999CB2031771
Question 857
FlagThe conventional Phillips curve indicates that the authorities face a:
Correct
The short-run Phillips curve is downward-sloping, so shows an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment. Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
Incorrect
The short-run Phillips curve is downward-sloping, so shows an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. In other words, a higher rate of inflation is associated with a lower rate of unemployment, whereas a lower rate of inflation is associated with a higher rate of unemployment. Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
-
Question 858 of 999CB2031794
Question 858
FlagStructural unemployment most commonly arises:
Correct
Answer: C
Unemployment is defined as the people of working age who are actively looking for work but are currently without a job.
Equilibrium (or ‘natural’) unemployment is the difference between those who would like employment at the current wage rate and those willing and able to take a job. It includes:
– frictional (search) unemployment, which occurs as a result of imperfect information in the labour market; it often takes time for workers to find jobs (even though there are vacancies) and in the meantime they are unemployed.
– structural unemployment, which arises from changes in the pattern of demand (Option C) or supply in the economy; people made redundant in one part of the economy cannot immediately take up jobs in other parts (even though there are vacancies); it includes:
– technological unemployment, which occurs as a result of the introduction of labour-saving technology
– regional unemployment, which occurs in specific regions of the country
– seasonal unemployment, which is associated with industries or regions where the demand for labour is lower at certain times of the year (Option B).Incorrect
Answer: C
Unemployment is defined as the people of working age who are actively looking for work but are currently without a job.
Equilibrium (or ‘natural’) unemployment is the difference between those who would like employment at the current wage rate and those willing and able to take a job. It includes:
– frictional (search) unemployment, which occurs as a result of imperfect information in the labour market; it often takes time for workers to find jobs (even though there are vacancies) and in the meantime they are unemployed.
– structural unemployment, which arises from changes in the pattern of demand (Option C) or supply in the economy; people made redundant in one part of the economy cannot immediately take up jobs in other parts (even though there are vacancies); it includes:
– technological unemployment, which occurs as a result of the introduction of labour-saving technology
– regional unemployment, which occurs in specific regions of the country
– seasonal unemployment, which is associated with industries or regions where the demand for labour is lower at certain times of the year (Option B). -
Question 859 of 999CB2031796
Question 859
FlagGiven a population of 24 million people, with 12 million employed and 2 million unemployed, what is the size of the labour force?
Correct
Answer: B
The labour force is made up of the employed and the unemployed.
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}=\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { number employed }+ \text { number unemployed }}
$$
where the total labour force is simply the total of the employed plus the unemployed, the latter being defined as those people of working age without jobs who are available to work at current wage rates.The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
The labour force is therefore $12 m+2 m=14 m$, so the correct answer is Option B.Incorrect
Answer: B
The labour force is made up of the employed and the unemployed.
The unemployment rate is defined as:
$$
\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { total labour force }}=\frac{\text { number unemployed }}{\text { number employed }+ \text { number unemployed }}
$$
where the total labour force is simply the total of the employed plus the unemployed, the latter being defined as those people of working age without jobs who are available to work at current wage rates.The total population of the country is irrelevant when calculating the unemployment rate.
The labour force is therefore $12 m+2 m=14 m$, so the correct answer is Option B. -
Question 860 of 999CB2031798
Question 860
FlagCost-push inflation may be likely to arise following:
Correct
Answer: D
Inflation refers to a general rise in the level of prices throughout the economy.
Cost-push inflation is inflation that is caused by persistent rises in costs of production (independently of demand).Rises in the cost of production may be the result of:
– an increase in the price of raw materials, which – in the case of imported raw materials – may be the result of a depreciation of the domestic currency
– an increase in wages above labour productivity, which may be due to an increase in the power of trade unions
– an increase in energy prices (Option D)
– an increase in interest rates, which increases the cost of borrowing by firms to fund production, ruling out Option B
– an increase in the profit margins applied by firms (bearing in mind that firms are required to make profits, so they can in this sense be thought of as costs that need to be covered).A cut in the rate of income tax would have the effect of increasing consumer spending, which might result in demand-pull inflation; it might also enable firms to reduce gross salaries, without reducing net-of-tax salaries, which would tend to reduce cost-push inflation; so Option A is incorrect.
A reduction in interest rates would make saving unattractive while borrowing would be relatively cheap, thus increasing consumption and investment, and hence aggregate demand, leading to demand-pull inflation, so Option B is incorrect.
An increase in government spending would directly increase aggregate demand, leading to demand-pull inflation, so Option C is incorrect.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Inflation refers to a general rise in the level of prices throughout the economy.
Cost-push inflation is inflation that is caused by persistent rises in costs of production (independently of demand).Rises in the cost of production may be the result of:
– an increase in the price of raw materials, which – in the case of imported raw materials – may be the result of a depreciation of the domestic currency
– an increase in wages above labour productivity, which may be due to an increase in the power of trade unions
– an increase in energy prices (Option D)
– an increase in interest rates, which increases the cost of borrowing by firms to fund production, ruling out Option B
– an increase in the profit margins applied by firms (bearing in mind that firms are required to make profits, so they can in this sense be thought of as costs that need to be covered).A cut in the rate of income tax would have the effect of increasing consumer spending, which might result in demand-pull inflation; it might also enable firms to reduce gross salaries, without reducing net-of-tax salaries, which would tend to reduce cost-push inflation; so Option A is incorrect.
A reduction in interest rates would make saving unattractive while borrowing would be relatively cheap, thus increasing consumption and investment, and hence aggregate demand, leading to demand-pull inflation, so Option B is incorrect.
An increase in government spending would directly increase aggregate demand, leading to demand-pull inflation, so Option C is incorrect.
-
Question 861 of 999CB2031801
Question 861
FlagWhich one of the following is most likely to lead to cost-push inflation?
Correct
Answer: A
Cost-push inflation is inflation that is caused by persistent rises in costs of production (independently of demand).
Rises in the cost of production may be the result of:
– an increase in wages above labour productivity, which may be due to an increase in the power of trade unions, and so Option A is correct
– an increase in the price of raw materials, which – in the case of imported raw materials – may be the result of a depreciation of the domestic currency, and so Option B is not a correct answer
– a rise in labour productivity means that less labour is needed to produce each unit of output and hence the cost of each unit of output is lower, which would reduce cost-push pressures, so Option C is not a correct answer
– an increase in the cost of capital invested, which is consistent with an increase in the profit margins applied by firms (bearing in mind that firms are required to make profits, so they can in this sense be thought of as costs that need to be covered), so Option D is not a correct answer.Incorrect
Answer: A
Cost-push inflation is inflation that is caused by persistent rises in costs of production (independently of demand).
Rises in the cost of production may be the result of:
– an increase in wages above labour productivity, which may be due to an increase in the power of trade unions, and so Option A is correct
– an increase in the price of raw materials, which – in the case of imported raw materials – may be the result of a depreciation of the domestic currency, and so Option B is not a correct answer
– a rise in labour productivity means that less labour is needed to produce each unit of output and hence the cost of each unit of output is lower, which would reduce cost-push pressures, so Option C is not a correct answer
– an increase in the cost of capital invested, which is consistent with an increase in the profit margins applied by firms (bearing in mind that firms are required to make profits, so they can in this sense be thought of as costs that need to be covered), so Option D is not a correct answer. -
Question 862 of 999CB2031804
Question 862
FlagAn individual who is not actively looking for work after having lost their job due to a change in the availability of jobs in their local area is:
Correct
Answer: D
Unemployment is defined as the people of working age who are actively looking for work but are currently without a job. In this question, the individual is not actively looking for work, so is (currently) not part of the labour force. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Unemployment is defined as the people of working age who are actively looking for work but are currently without a job. In this question, the individual is not actively looking for work, so is (currently) not part of the labour force. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
-
Question 863 of 999CB2031806
Question 863
FlagWhich of the following is likely to raise the natural rate of unemployment?
Correct
Answer: B
The natural level of unemployment is the difference between those who would like employment at the current wage rate and those willing and able to take a job, ie the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium.
A rise in unemployment benefits is likely to reduce the number of people who are willing to take a job, so increasing the natural rate of unemployment. So Option B is the correct answer.
Improved information flows on job availability (Option A) will tend to reduce frictional unemployment, so reducing the natural rate of unemployment. So Option A is not correct.
A general fall in government expenditure (Option C) and a decrease in the money supply (Option D) will not directly affect the specific types of unemployment that make up natural unemployment. Furthermore, any indirect effect of these variables is likely to increase unemployment, rather than reducing it.
Incorrect
Answer: B
The natural level of unemployment is the difference between those who would like employment at the current wage rate and those willing and able to take a job, ie the amount of unemployment that exists when the labour market is in equilibrium.
A rise in unemployment benefits is likely to reduce the number of people who are willing to take a job, so increasing the natural rate of unemployment. So Option B is the correct answer.
Improved information flows on job availability (Option A) will tend to reduce frictional unemployment, so reducing the natural rate of unemployment. So Option A is not correct.
A general fall in government expenditure (Option C) and a decrease in the money supply (Option D) will not directly affect the specific types of unemployment that make up natural unemployment. Furthermore, any indirect effect of these variables is likely to increase unemployment, rather than reducing it.
-
Question 864 of 999CB2031809
Question 864
FlagThe impact of setting the minimum wage above the market equilibrium wage is most likely to be:
Correct
Answer: D
Below is a diagram representing the labour market.
where:
– $A D_l$ is the aggregate demand for labour curve
– $A S_L$ is the aggregate supply of labour curve
– $\quad N$ is the total labour force curve.The labour market is in equilibrium at Point $C$, where the $A S_L$ curve and the $A D_L$ curve intersect. This gives an equilibrium real wage rate of $w_1$ and an equilibrium number of workers of $Q_1$. The equilibrium (or natural) level of unemployment is the difference between those who would like employment at the current wage rate (represented by the total labour force curve $(N)$ ) and those willing and able to take a job (represented by the aggregate supply of labour curve $\left.\left(A S_l\right)\right)$ at the equilibrium wage, which is $D-C$ in the diagram.
A minimum wage above the market equilibrium wage, $e g$ at $w_2$ in the diagram above, will result in a wage rate above the equilibrium wage rate, so reducing the quantity of labour demanded and increasing the quantity of labour supplied. This rules out Option C.
A lower quantity of labour demanded and a higher quantity of labour supplied will lead to excess supply of labour (ruling out Option A), and a surplus in the supply of labour (ruling out Option B).
This excess supply over demand for labour will increase unemployment and so Option D is the correct answer. This is a form of disequilibrium unemployment.
Incorrect
Answer: D
Below is a diagram representing the labour market.

where:
– $A D_l$ is the aggregate demand for labour curve
– $A S_L$ is the aggregate supply of labour curve
– $\quad N$ is the total labour force curve.The labour market is in equilibrium at Point $C$, where the $A S_L$ curve and the $A D_L$ curve intersect. This gives an equilibrium real wage rate of $w_1$ and an equilibrium number of workers of $Q_1$. The equilibrium (or natural) level of unemployment is the difference between those who would like employment at the current wage rate (represented by the total labour force curve $(N)$ ) and those willing and able to take a job (represented by the aggregate supply of labour curve $\left.\left(A S_l\right)\right)$ at the equilibrium wage, which is $D-C$ in the diagram.
A minimum wage above the market equilibrium wage, $e g$ at $w_2$ in the diagram above, will result in a wage rate above the equilibrium wage rate, so reducing the quantity of labour demanded and increasing the quantity of labour supplied. This rules out Option C.
A lower quantity of labour demanded and a higher quantity of labour supplied will lead to excess supply of labour (ruling out Option A), and a surplus in the supply of labour (ruling out Option B).
This excess supply over demand for labour will increase unemployment and so Option D is the correct answer. This is a form of disequilibrium unemployment.
-
Question 865 of 999CB2031810
Question 865
FlagWhich of the following does NOT explain why wages for skilled workers are greater than the wages paid to unskilled workers?
Correct
Answer: C
Training costs for skilled workers are likely to be higher than for unskilled workers, so Option A is a possible explanation, so is not the correct answer.
The marginal revenue product of skilled workers is likely to be higher than that of unskilled workers, ie the output of skilled workers can be sold for more, so skilled workers can (and should) be paid more. So Option B is a possible explanation, so is not the correct answer.
The supply of skilled workers may be greater or smaller than the supply of unskilled workers, however, a greater supply results in a lower price (ie wage). So Option C is not a possible explanation, so is the correct answer.
Human capital is defined as ‘the qualifications, skills and expertise that contribute to a worker’s productivity’, so it is true that skilled workers have accumulated more human capital than unskilled workers. Greater productivity is also another reason for paying these workers more, so Option D is a possible explanation, so is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: C
Training costs for skilled workers are likely to be higher than for unskilled workers, so Option A is a possible explanation, so is not the correct answer.
The marginal revenue product of skilled workers is likely to be higher than that of unskilled workers, ie the output of skilled workers can be sold for more, so skilled workers can (and should) be paid more. So Option B is a possible explanation, so is not the correct answer.
The supply of skilled workers may be greater or smaller than the supply of unskilled workers, however, a greater supply results in a lower price (ie wage). So Option C is not a possible explanation, so is the correct answer.
Human capital is defined as ‘the qualifications, skills and expertise that contribute to a worker’s productivity’, so it is true that skilled workers have accumulated more human capital than unskilled workers. Greater productivity is also another reason for paying these workers more, so Option D is a possible explanation, so is not the correct answer.
-
Question 866 of 999CB2031811
Question 866
FlagAn anticipated increase in the rate of inflation is:
Correct
Answer: D
When inflation is high, the opportunity cost of holding cash (rather than investing it in an asset whose value increases in line with inflation, ie real assets) is high. This means that:
– Option B is not the correct answer
– individuals will choose to keep as much of their wealth invested in real assets, for example, bank accounts that pay interest in excess of the rate of inflation. A desire to keep wealth invested for as long as possible will lead to individuals making more frequent, smaller cash withdrawals, which is arguably not an efficient use of time. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.Redistribution of income / wealth from lenders to borrowers is generally a cost of unanticipated inflation, so Option A is not the correct answer.
If contracts can be readily adjusted, then a change in the anticipated rate of inflation should not be costly. However, some contracts may be fixed for a number of years, in which case they cannot be adjusted in response to a change in the anticipated rate of inflation. So Option C is not the correct answer.
Incorrect
Answer: D
When inflation is high, the opportunity cost of holding cash (rather than investing it in an asset whose value increases in line with inflation, ie real assets) is high. This means that:
– Option B is not the correct answer
– individuals will choose to keep as much of their wealth invested in real assets, for example, bank accounts that pay interest in excess of the rate of inflation. A desire to keep wealth invested for as long as possible will lead to individuals making more frequent, smaller cash withdrawals, which is arguably not an efficient use of time. Therefore Option D is the correct answer.Redistribution of income / wealth from lenders to borrowers is generally a cost of unanticipated inflation, so Option A is not the correct answer.
If contracts can be readily adjusted, then a change in the anticipated rate of inflation should not be costly. However, some contracts may be fixed for a number of years, in which case they cannot be adjusted in response to a change in the anticipated rate of inflation. So Option C is not the correct answer.
-
Question 867 of 999CB2031969
Question 867
FlagYou are given the following information for an economy:
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Consumer expenditure } & £ 80 \text { million } \\
\text { Investment expenditure } & £ 20 \text { million } \\
\text { Government expenditure } & £ 40 \text { million } \\
\text { Exports } & £ 20 \text { million } \\
\text { Imports } & £ 30 \text { million } \\
\text { Net income from abroad } & £ 10 \text { million }
\end{array}what is the value of economy’s gross domestic product?
Correct
Answer: A
Gross domestic product or GDP is the total value of output produced within the domestic economy over a 12-month period. Using the expenditure method, it can be found as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
G D P & =C+I+G+X-M \\
& =80+20+40+20-30 \\
& =130
\end{aligned}
$$Remember that imports ( $M$ ) are deducted from total consumption as the latter includes all expenditure, ie expenditure on items produced domestically and those produced abroad.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Gross domestic product or GDP is the total value of output produced within the domestic economy over a 12-month period. Using the expenditure method, it can be found as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
G D P & =C+I+G+X-M \\
& =80+20+40+20-30 \\
& =130
\end{aligned}
$$Remember that imports ( $M$ ) are deducted from total consumption as the latter includes all expenditure, ie expenditure on items produced domestically and those produced abroad.
-
Question 868 of 999CB2031970
Question 868
FlagYou are given the following data for an economy:
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline & £ millions \\
\hline \text{Consumer expenditure (including taxes on products)} & 120 \\
\hline \text{Investment} & 60 \\
\hline \text{Government expenditure (including transfer payments)} & 70 \\
\hline \text{Exports} & 40 \\
\hline \text{Imports} & 20 \\
\hline \text{Taxes on products (Indirect taxes)} & 10 \\
\hline \text{Capital depreciation} & 20 \\
\hline \text{Transfer payments} & 10 \\
\hline \text{Net income from abroad} & 10 \\
\hline
\end{array}The value of the economy’s gross national income at market prices is:
Correct
Answer: C
Gross domestic product (GDP) at market prices (ie in terms of the prices actually paid for goods and services) using the expenditure method:
$$
\begin{aligned}
G D P \text { (market prices) } & =C+I+G+X-M \\
& =120+60+(70-10)+40-20 \\
& =260
\end{aligned}
$$Remember that GDP should only include expenditure on goods and services, so it is necessary to deduct the government expenditure on transfer payments, which should not be included. Also, note that the consumer expenditure figure includes taxes on products, which means that it is expressed in terms of market prices.
Gross national income (GNY) at market prices can then be obtained by adding net income from abroad to GDP:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GNY(market prices) } & =\text { GDP(market prices) }+ \text { net income from abroad } \\
& =260+10 \\
& =270
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer: C
Gross domestic product (GDP) at market prices (ie in terms of the prices actually paid for goods and services) using the expenditure method:
$$
\begin{aligned}
G D P \text { (market prices) } & =C+I+G+X-M \\
& =120+60+(70-10)+40-20 \\
& =260
\end{aligned}
$$Remember that GDP should only include expenditure on goods and services, so it is necessary to deduct the government expenditure on transfer payments, which should not be included. Also, note that the consumer expenditure figure includes taxes on products, which means that it is expressed in terms of market prices.
Gross national income (GNY) at market prices can then be obtained by adding net income from abroad to GDP:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GNY(market prices) } & =\text { GDP(market prices) }+ \text { net income from abroad } \\
& =260+10 \\
& =270
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 869 of 999CB2031971
Question 869
FlagYou are given the following information for an economy:
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Consumer expenditure } & £ 70 \text { million } \\
\text { Investment expenditure } & £ 20 \text { million } \\
\text { Government expenditure } & £ 40 \text { million } \\
\text { Exports } & £ 20 \text { million } \\
\text { Imports } & £ 30 \text { million } \\
\text { Net income from abroad } & £ 10 \text { million }
\end{array}what is the value of gross national income?
Correct
Answer B
Gross domestic income or product (GDP) is found as:
$$
C+I+G+X-M=70+20+40+20-30=120
$$Gross national income (GNY) is found as:
$$
\text { GDP + net income from abroad }=120+10=130
$$So GNY is $£ 130$ million.
Incorrect
Answer B
Gross domestic income or product (GDP) is found as:
$$
C+I+G+X-M=70+20+40+20-30=120
$$Gross national income (GNY) is found as:
$$
\text { GDP + net income from abroad }=120+10=130
$$So GNY is $£ 130$ million.
-
Question 870 of 999CB2031972
Question 870
FlagWhich of the following does NOT form part of a country’s gross domestic product?
Correct
Answer B
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12 -month period. It can be calculated using:
– the product (or output) method
– the income method – this includes wages (ie salaries of school teachers), interest, rent and (company) profits
– the expenditure method – this includes consumption, investment, government spending and net exports.Therefore the only option that does not form part of GDP is Option B – net income from abroad.
Note that this would be included in the calculation of gross national income, which is the value of income earned by the nation’s residents in a year.
Incorrect
Answer B
GDP is the value of output produced within a country over a 12 -month period. It can be calculated using:
– the product (or output) method
– the income method – this includes wages (ie salaries of school teachers), interest, rent and (company) profits
– the expenditure method – this includes consumption, investment, government spending and net exports.Therefore the only option that does not form part of GDP is Option B – net income from abroad.
Note that this would be included in the calculation of gross national income, which is the value of income earned by the nation’s residents in a year.
-
Question 871 of 999CB2031973
Question 871
FlagYou are given the following data for an economy:
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline & £ millions \\
\hline \text{Consumer expenditure (including indirect taxes)} & 120 \\
\hline \text{Investment} & 60 \\
\hline \text{Government expenditure (including transfer payments)} & 70 \\
\hline \text{Exports} & 40 \\
\hline \text{Imports} & 30 \\
\hline \text{Net income from abroad} & 20 \\
\hline \text{Indirect taxes} & 10 \\
\hline \text{Capital depreciation} & 20 \\
\hline \text{Transfer payments} & 10 \\
\hline
\end{array}The value of the economy’s gross national income at market prices is:
Correct
Answer C
Using the expenditure method, gross domestic product (GDP) at market prices can be calculated as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GDP (market prices) } & =\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M} \\
& =120+60+(70-10)+40-30 \\
& =250
\end{aligned}
$$Remember that GDP should only include expenditure on goods and services produced, so government expenditure on transfer payments should not be included. Also, if consumer expenditure includes sales taxes, then the figure given is at market prices, ie prices paid in the shops.
Gross national income (GNY) can then be obtained by adding net income from abroad:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GNY (market prices) } & =\text { GDP (market prices) }+ \text { net income from abroad } \\
& =250+20 \\
& =270
\end{aligned}
$$Incorrect
Answer C
Using the expenditure method, gross domestic product (GDP) at market prices can be calculated as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GDP (market prices) } & =\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M} \\
& =120+60+(70-10)+40-30 \\
& =250
\end{aligned}
$$Remember that GDP should only include expenditure on goods and services produced, so government expenditure on transfer payments should not be included. Also, if consumer expenditure includes sales taxes, then the figure given is at market prices, ie prices paid in the shops.
Gross national income (GNY) can then be obtained by adding net income from abroad:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { GNY (market prices) } & =\text { GDP (market prices) }+ \text { net income from abroad } \\
& =250+20 \\
& =270
\end{aligned}
$$ -
Question 872 of 999CB2031974
Question 872
FlagThe following table contains output and expenditure data for an economy:
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline & £billions \\
\hline \text{Consumption (at market prices)} & 300 \\
\hline \text{Investment (at market prices)} & 80 \\
\hline \text{Government spending (at market prices)} & 85 \\
\hline \text{Net exports (at market prices)} & -10 \\
\hline \text{Net income from abroad} & 5 \\
\hline \text{Indirect taxes} & 60 \\
\hline
\end{array}GDP at basic prices and gross national income at market prices are respectively (in £ billions):
Correct
A The expenditure method for calculating GDP is:
$$
\mathrm{GDP}=\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M} .
$$Without adjustment, this will give GDP at market prices, as these are the prices actually paid by customers. Here:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{GDP} & =\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M} \\
& =300+80+85-10 \\
& =455
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore:
– GDP at basic prices is:GDP (market prices)-indirect taxes (net of subsidies)
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =455-60 \\
& =395
\end{aligned}
$$
– GNY at market prices is:GDP (market prices) + net income from abroad
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =455+5 \\
& =460
\end{aligned}
$$This means that the answer is 395, 460, which corresponds to Option A.
Incorrect
A The expenditure method for calculating GDP is:
$$
\mathrm{GDP}=\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M} .
$$Without adjustment, this will give GDP at market prices, as these are the prices actually paid by customers. Here:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{GDP} & =\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{X}-\mathrm{M} \\
& =300+80+85-10 \\
& =455
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore:
– GDP at basic prices is:GDP (market prices)-indirect taxes (net of subsidies)
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =455-60 \\
& =395
\end{aligned}
$$
– GNY at market prices is:GDP (market prices) + net income from abroad
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =455+5 \\
& =460
\end{aligned}
$$This means that the answer is 395, 460, which corresponds to Option A.
-
Question 873 of 999CB2031975
Question 873
FlagThe profit payoffs to Firm $X$ from combining the various strategies of $X(1,2,3,4)$ and the presumed response of the other firm ( $\mathrm{S}, \mathrm{P}, \mathrm{Q}, \mathrm{R}$ ) in a duopoly industry is given below:
\begin{array}{cccccc}
&{ Other firm’s response } \\
& & S & P & Q & R \\
& 1 & 90 & 40 & -10 & 100 \\
Strategy of & 2 & 40 & 70 & -20 & -80 \\
Firm X & 3 & 25 & 50 & 120 & 130 \\
& 4 & 10 & 40 & 70 & 60
\end{array}Which one of the following represents the maximin strategy of Firm $X$ ?
Correct
Answer: C
A maximin strategy is one that chooses the policy which maximises the minimum, or worst, possible payoff. So, to identify the maximin strategy for Firm $X$, you first need to identify the worst possibly payoff that might be obtained from pursuing each of Strategies 1 to 4. These are as follows:
– Strategy 1 has a worst possible payoff of -10.
– Strategy 2 has a worst possible payoff of -80.
– Strategy 3 has a worst possible payoff of 25.
– Strategy 4 has a worst possible payoff of 10.The maximum of these four possible (worst) payoffs is 25, from Strategy 3. Consequently, Strategy 3 (Option C) is Firm X’s maximin strategy.
Incorrect
Answer: C
A maximin strategy is one that chooses the policy which maximises the minimum, or worst, possible payoff. So, to identify the maximin strategy for Firm $X$, you first need to identify the worst possibly payoff that might be obtained from pursuing each of Strategies 1 to 4. These are as follows:
– Strategy 1 has a worst possible payoff of -10.
– Strategy 2 has a worst possible payoff of -80.
– Strategy 3 has a worst possible payoff of 25.
– Strategy 4 has a worst possible payoff of 10.The maximum of these four possible (worst) payoffs is 25, from Strategy 3. Consequently, Strategy 3 (Option C) is Firm X’s maximin strategy.
-
Question 874 of 999CB2031983
Question 874
FlagAll else being equal, the real exchange rate will increase if:
Correct
Option A. The real exchange rate is defined as:
$$
\text { real exchange rate }=\text { nominal exchange rate } \times \frac{\text { export prices }}{\text { import prices }}
$$Changes in the real exchange rate measure changes in the competitiveness of a country’s exports.
Incorrect
Option A. The real exchange rate is defined as:
$$
\text { real exchange rate }=\text { nominal exchange rate } \times \frac{\text { export prices }}{\text { import prices }}
$$Changes in the real exchange rate measure changes in the competitiveness of a country’s exports.
-
Question 875 of 999CB2031984
Question 875
FlagImperfect competition is the collective name for:
Correct
Option D. Imperfect competition is the collective name for monopolistic competition and oligopoly (by definition).
Incorrect
Option D. Imperfect competition is the collective name for monopolistic competition and oligopoly (by definition).
-
Question 876 of 999CB2031985
Question 876
FlagAn adjustable peg is defined as:
Correct
Option B. This is the definition of an adjustable peg.
Options A and C define a crawling peg and a devaluation respectively. Option D describes an exchange rate band.Incorrect
Option B. This is the definition of an adjustable peg.
Options A and C define a crawling peg and a devaluation respectively. Option D describes an exchange rate band. -
Question 877 of 999CB2031986
Question 877
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an assumption underlying perfect competition?
Correct
Option B.
Options A, C and D are three of the assumptions underlying perfect competition. In perfect competition, it is the individual firm’s demand curve that is horizontal. The industry demand curve is a normal downward-sloping demand curve
Incorrect
Option B.
Options A, C and D are three of the assumptions underlying perfect competition. In perfect competition, it is the individual firm’s demand curve that is horizontal. The industry demand curve is a normal downward-sloping demand curve
-
Question 878 of 999CB2031987
Question 878
FlagWhich of the following is a Keynesian criticism of fixed exchange rates?
Correct
Option A.
A key Keynesian criticism of fixed exchange rates is that faced by a balance of payments deficit, the government may need to reduce aggregate demand to reduce imports, with adverse consequences for output and employment. {In practice, an alternative approach to reducing a deficit might be to impose restrictions on trade such as tariffs and quotas.
However, these reduce trade and may be prohibited under World Trade Organisation rules.) Options B and Care new classical criticisms of fixed exchange rates. The certainty fixed exchange rates provide for international investors, which will encourage international trade, investment and growth, is a key advantage of fixed exchange rates.
Incorrect
Option A.
A key Keynesian criticism of fixed exchange rates is that faced by a balance of payments deficit, the government may need to reduce aggregate demand to reduce imports, with adverse consequences for output and employment. {In practice, an alternative approach to reducing a deficit might be to impose restrictions on trade such as tariffs and quotas.
However, these reduce trade and may be prohibited under World Trade Organisation rules.) Options B and Care new classical criticisms of fixed exchange rates. The certainty fixed exchange rates provide for international investors, which will encourage international trade, investment and growth, is a key advantage of fixed exchange rates.
-
Question 879 of 999CB2031988
Question 879
FlagThe short-run industry supply curve in a perfectly competitive market is the:
Correct
Option D
The short-run supply curve in the market for a good is the total quantity supplied at each price level. In the short run, each firm in a perfectly competitive market will produce at a level of output where P =MR= MC, as long as the price it receives is sufficient to at least cover its short-run average variable costs. Therefore for each individual firm, the MC curve above the minimum average variable cost represents its short-run supply curve and to find the industry short-run supply curve, we need the horizontal sum of the MC curves from above the point where
they cut the respective A VC curves.Incorrect
Option D
The short-run supply curve in the market for a good is the total quantity supplied at each price level. In the short run, each firm in a perfectly competitive market will produce at a level of output where P =MR= MC, as long as the price it receives is sufficient to at least cover its short-run average variable costs. Therefore for each individual firm, the MC curve above the minimum average variable cost represents its short-run supply curve and to find the industry short-run supply curve, we need the horizontal sum of the MC curves from above the point where
they cut the respective A VC curves. -
Question 880 of 999CB2031989
Question 880
FlagThe purchasing power parity theory implies that if UK inflation is persistently lower than US inflation, then over time:
I the UK pound will appreciate against the US dollar.
II the real exchange rate between pounds and dollars will be unchanged.
Ill the UK pound will depreciate against the US dollar.Correct
Option C.
The purchasing power parity (PPP) theory implies that if UK inflation is persistently lower than US inflation, then over time the UK pound will appreciate against the US dollar – Statement I. (This is because as UK exports become more competitive, demand for them will increase, leading to an increased demand for UK pounds.). In fact, PPP suggests the UK pound will appreciate so that the decrease in relative prices will be exactly offset by an increase in the value of the pound versus the dollar, so that the real exchange rate is unchanged – Statement II. For example, if UK price fall by 10% relative to US prices, then the pound should rise by 10% in value against the dollar.
Incorrect
Option C.
The purchasing power parity (PPP) theory implies that if UK inflation is persistently lower than US inflation, then over time the UK pound will appreciate against the US dollar – Statement I. (This is because as UK exports become more competitive, demand for them will increase, leading to an increased demand for UK pounds.). In fact, PPP suggests the UK pound will appreciate so that the decrease in relative prices will be exactly offset by an increase in the value of the pound versus the dollar, so that the real exchange rate is unchanged – Statement II. For example, if UK price fall by 10% relative to US prices, then the pound should rise by 10% in value against the dollar.
-
Question 881 of 999CB2031990
Question 881
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a barrier to entry?
Correct
Option B. In some industries, the opportunities for economies of scale are limited. Hence the minimum efficient scale is low. This means that large firms do not enjoy cost advantages and so there is room in the industry for both small and large firms, eg brewing.
Incorrect
Option B. In some industries, the opportunities for economies of scale are limited. Hence the minimum efficient scale is low. This means that large firms do not enjoy cost advantages and so there is room in the industry for both small and large firms, eg brewing.
-
Question 882 of 999CB2031991
Question 882
FlagWhich of the following statements about free-floating exchange rates is NOT true?
Correct
Option A.
Having a free-floating exchange rate diminishes the effectiveness offiscal policy. For example, suppose the government increases its spending in order to increase aggregate demand and output. Assuming a fixed money supply schedule, the resulting increased demand for money will cause interest rates to rise, leading to financial inflows, and a rise in the exchange rate. This will make exports less competitive, so reducing net exports and hence aggregate demand.
Options Band Care both true statements, although bear in mind that speculation can also be stabilising. Option Dis true because the exchange rate automatically changes to correct balance of payments disequilibria without the need for government intervention.Incorrect
Option A.
Having a free-floating exchange rate diminishes the effectiveness offiscal policy. For example, suppose the government increases its spending in order to increase aggregate demand and output. Assuming a fixed money supply schedule, the resulting increased demand for money will cause interest rates to rise, leading to financial inflows, and a rise in the exchange rate. This will make exports less competitive, so reducing net exports and hence aggregate demand.
Options Band Care both true statements, although bear in mind that speculation can also be stabilising. Option Dis true because the exchange rate automatically changes to correct balance of payments disequilibria without the need for government intervention. -
Question 883 of 999CB2031992
Question 883
FlagWhich of the following has NOT contributed the increased volatility of exchange rates?
Correct
Option D.
The J-curve effect refers to the fact that a devaluation may initially cause a deterioration in the balance of payments before it subsequently improves (once trade has fully adjusted to the new lower exchange rate).
The use of inflation and money supply targets has resulted in larger interest rate changes, which have caused greater exchange rate fluctuations. The growth in information technology has made it much quicker and easier to make large international financial transfers. Increased currency speculation has led to huge increases in the trading of currenciesIncorrect
Option D.
The J-curve effect refers to the fact that a devaluation may initially cause a deterioration in the balance of payments before it subsequently improves (once trade has fully adjusted to the new lower exchange rate).
The use of inflation and money supply targets has resulted in larger interest rate changes, which have caused greater exchange rate fluctuations. The growth in information technology has made it much quicker and easier to make large international financial transfers. Increased currency speculation has led to huge increases in the trading of currencies -
Question 884 of 999CB2031993
Question 884
FlagA monopolist in a perfectly contestable market will:
I produce as efficiently as possible and only make normal profits
II keep prices down, but produce supernormal profits
Ill produce as efficiently as possible and make supernormal profitsCorrect
Option C. According to the theory, a monopolist in a perfectly contestable market will keep prices down so that it is only making normal profits, and will produce as efficiently as possible.
Incorrect
Option C. According to the theory, a monopolist in a perfectly contestable market will keep prices down so that it is only making normal profits, and will produce as efficiently as possible.
-
Question 885 of 999CB2031994
Question 885
FlagIf the US Federal Reserve Bank wished to raise the exchange rate of the dollar against other currencies, then appropriate measures would include
I selling dollars and buying yen on the foreign exchange market.
II recommending reduced tariffs on imported products.
Ill raising interest rates through its open market operations in the money market.Correct
Option D.
Raising interest rates would increase deposits in the USA and the demand for dollars, which would increase the exchange rate.
Selling dollars would increase the supply of dollars and reduce the exchange rate. Reducing tariffs would increase imports and the supply of dollars, which would reduce the exchange rateIncorrect
Option D.
Raising interest rates would increase deposits in the USA and the demand for dollars, which would increase the exchange rate.
Selling dollars would increase the supply of dollars and reduce the exchange rate. Reducing tariffs would increase imports and the supply of dollars, which would reduce the exchange rate -
Question 886 of 999CB2031995
Question 886
FlagWhich of the following CANNOT be true for a profit-maximising monopolist?
Correct
Option D.
A profit-maximising monopolist will produce where MR = MC. If marginal revenue is negative, then marginal cost must be negative, which is impossible.Incorrect
Option D.
A profit-maximising monopolist will produce where MR = MC. If marginal revenue is negative, then marginal cost must be negative, which is impossible. -
Question 887 of 999CB2031996
Question 887
FlagWhich of the following is TRUE?
Correct
Option D.
Options A and Care incorrect as floating exchange rates automatically correct a balance of payments deficit, which means there is no need for governments to hold reserves.
Option B is incorrect as if speculators believe the fixed rate cannot be maintained, their actions could cause a devaluation or a revaluation.
Under Option D, the government may need to decrease demand in the economy to reduce downward pressures on the exchange rate at a time when the economy would benefit from measures to increase demand, eg to increase GDP and employment. Alternatively, the government might introduce import controls, which prevent the most efficient allocation of the world’ s resources. So, Option Dis true.Incorrect
Option D.
Options A and Care incorrect as floating exchange rates automatically correct a balance of payments deficit, which means there is no need for governments to hold reserves.
Option B is incorrect as if speculators believe the fixed rate cannot be maintained, their actions could cause a devaluation or a revaluation.
Under Option D, the government may need to decrease demand in the economy to reduce downward pressures on the exchange rate at a time when the economy would benefit from measures to increase demand, eg to increase GDP and employment. Alternatively, the government might introduce import controls, which prevent the most efficient allocation of the world’ s resources. So, Option Dis true. -
Question 888 of 999CB2031998
Question 888
FlagWhich one of the following is NOT a feature of monopolistic competition?
Correct
Option A. Marginal cost equals marginal revenue, which is below the downward-sloping demand curve. Thus the equilibrium price is above marginal cost and so the monopolistically competitive firm produces less than the optimum level of output.
Incorrect
Option A. Marginal cost equals marginal revenue, which is below the downward-sloping demand curve. Thus the equilibrium price is above marginal cost and so the monopolistically competitive firm produces less than the optimum level of output.
-
Question 889 of 999CB2031999
Question 889
FlagSuppose that the current exchange rate is $1.20 = £1. Suppose that over the next five years, UK prices increase by 20%, whereas US prices increase by 10%. According to the purchasing power parity theory, the exchange rate in five years’ time should be:
Correct
Option B.
According to purchasing power parity, the nominal exchange rate should change so as to exactly offset the change in the relative prices {so keeping the real exchange rate constant). So, the exchange rate in five years’ time should be:1.20 x (1.10 /1.20) = 1.10, i.e $1.10 = £1.00
Incorrect
Option B.
According to purchasing power parity, the nominal exchange rate should change so as to exactly offset the change in the relative prices {so keeping the real exchange rate constant). So, the exchange rate in five years’ time should be:1.20 x (1.10 /1.20) = 1.10, i.e $1.10 = £1.00
-
Question 890 of 999CB2032000
Question 890
FlagIf the centra I bank has to intervene in the foreign exchange markets to prevent the domestic currency from depreciating, then its foreign exchange reserves will:
Correct
Option B.
If the exchange rate is in danger of depreciating, there must be a decrease in demand for and/or an increase in supply of the currency. To prevent the depreciation, the central bank will have to buy the excess supply of domestic currency, which it will finance by selling foreign currency. Consequently, the domestic money supply and the country’s foreign exchange reserves will both decrease
Incorrect
Option B.
If the exchange rate is in danger of depreciating, there must be a decrease in demand for and/or an increase in supply of the currency. To prevent the depreciation, the central bank will have to buy the excess supply of domestic currency, which it will finance by selling foreign currency. Consequently, the domestic money supply and the country’s foreign exchange reserves will both decrease
-
Question 891 of 999CB2032001
Question 891
FlagWhat is oligopoly?
Correct
Option C. This is by definition. Collusive behaviour is a possible feature of oligopoly but does not always occur.
Incorrect
Option C. This is by definition. Collusive behaviour is a possible feature of oligopoly but does not always occur.
-
Question 892 of 999CB2032002
Question 892
FlagCartels are best described as:
Correct
Option B. This is a definition.
Incorrect
Option B. This is a definition.
-
Question 893 of 999CB2032003
Question 893
FlagWhich of the following are advantages of the single currency?
I increased competition and efficiency
II lower inflation and interest rates
Ill the adoption of a common monetary policyCorrect
Option B.
A key argument against the single currency is that the countries that use the euro lose the ability to have an independent monetary policy tailored to their own economic circumstances and problems. For example, as the economies of Germany and Greece are very different, the monetary policy that is suitable for Germany may be very unsuitable for Greece and vice versa
Incorrect
Option B.
A key argument against the single currency is that the countries that use the euro lose the ability to have an independent monetary policy tailored to their own economic circumstances and problems. For example, as the economies of Germany and Greece are very different, the monetary policy that is suitable for Germany may be very unsuitable for Greece and vice versa
-
Question 894 of 999CB2032004
Question 894
FlagThe kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly implies that the oligopolist:
Correct
Option B. The kink in the oligopolist’s demand (= average revenue) curve gives rise to a discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve at the level of output corresponding to the kink.
Incorrect
Option B. The kink in the oligopolist’s demand (= average revenue) curve gives rise to a discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve at the level of output corresponding to the kink.
-
Question 895 of 999CB2032005
Question 895
FlagThe possible arguments against the single currency within the EMU include:
I The eurozone isn’t an optimal currency area.
II The fiscal rules of the Stability and Growth Pact have not been adequately enforced.
Ill It removes the ability of countries to depreciate their currencies in the event of recessionCorrect
Option D.
All three alternatives are possible arguments against the single currency.
Incorrect
Option D.
All three alternatives are possible arguments against the single currency.
-
Question 896 of 999CB2032006
Question 896
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option D.
The euro eliminates uncertainty due to exchange rate fluctuations within the eurozone, as members all use the same currency. However, it does not remove such uncertainty with respect to financial flows into and out of the eurozone, as the euro fluctuates in value against other currencies
Incorrect
Option D.
The euro eliminates uncertainty due to exchange rate fluctuations within the eurozone, as members all use the same currency. However, it does not remove such uncertainty with respect to financial flows into and out of the eurozone, as the euro fluctuates in value against other currencies
-
Question 897 of 999CB2032092
Question 897
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Statement 1 (Assertion)} & & \text{Statement 2 (Reason)} \\
\hline \text{Firms in perfect and monopolistic competition can make supernormal profits in the short and long run.} & BECAUSE & \text{Industries with barriers to entry are at lower risk of other firms entering the market to compete away supernormal profits.} \\
\hline
\end{array}Correct
Option D.
Firms in perfect and monopolistic competition may be able to make supernormal profits in the short run, but will make only normal profits in the long run. This is because firms are free to enter the industry and these firms will then compete away any supernormal profits.
Incorrect
Option D.
Firms in perfect and monopolistic competition may be able to make supernormal profits in the short run, but will make only normal profits in the long run. This is because firms are free to enter the industry and these firms will then compete away any supernormal profits.
-
Question 898 of 999CB2032093
Question 898
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Statement 1 (Assertion)} & & \text{Statement 2 (Reason)} \\
\hline \text{A profit-maximising monopolist will aim to maximise total revenue if the marginal cost of the product supplied is zero at all output levels.} & BECAUSE & \text{Profit maximisation occurs where $M R$ equals $M C$, or in this case $M R=0$, which is also the output level at which total revenue will be maximised.} \\
\hline
\end{array}Correct
Option A.
Profit maximisation occurs where $M R=M C$. So in this case, profit maximisation means equating $M R$ with zero. When $M R$ is zero, total revenue is at a maximum. So, in this case, profit maximisation is equivalent to revenue maximisation.
Incorrect
Option A.
Profit maximisation occurs where $M R=M C$. So in this case, profit maximisation means equating $M R$ with zero. When $M R$ is zero, total revenue is at a maximum. So, in this case, profit maximisation is equivalent to revenue maximisation.
-
Question 899 of 999CB2032097
Question 899
Flag‘Once a firm observes that its rival has broken some agreed behaviour it will never co-operate with them ever again.’
This is a description of which type of strategy?
Correct
Option A. This is a definition.
Incorrect
Option A. This is a definition.
-
Question 900 of 999CB2032098
Question 900
FlagA market in which firms produce differentiated products and enjoy normal profits could be described as:
Correct
Option C. Differentiated products are often produced by firms in an oligopoly and always under conditions of monopolistic competition. (Monopolists may also produce differentiated products as well, to cover all market niches.) Normal profits are enjoyed only by firms under monopolistic competition and perfect competition – due to the absence of barriers to entry. Thus, monopolistic competition is the only market type consistent with both differentiated products and normal profits.
Incorrect
Option C. Differentiated products are often produced by firms in an oligopoly and always under conditions of monopolistic competition. (Monopolists may also produce differentiated products as well, to cover all market niches.) Normal profits are enjoyed only by firms under monopolistic competition and perfect competition – due to the absence of barriers to entry. Thus, monopolistic competition is the only market type consistent with both differentiated products and normal profits.
-
Question 901 of 999CB2032099
Question 901
FlagAn industry has the following characteristics:
– large numbers of buyers and sellers
– slightly differentiated products
– no entry barriers
– supernormal profits made by all firms.The market conditions of this industry are those of:
Correct
Option B. The first three characteristics describe monopolistic competition. However, in the long run, most firms in monopolistic competition can only make normal profits. Therefore, this must be a short-run scenario.
Incorrect
Option B. The first three characteristics describe monopolistic competition. However, in the long run, most firms in monopolistic competition can only make normal profits. Therefore, this must be a short-run scenario.
-
Question 902 of 999CB2032100
Question 902
FlagThe market structure in which price is likely to be furthest from marginal cost is known as:
Correct
Option A.
In perfect competition, demand for the products of each firm is totally elastic and $P=M C$. However, under each of the other three market structures, $M R=M C$ at the profit-maximising output level, and the demand curve is above the $M R$ curve. Consequently, $P>M C$.
The more inelastic demand is (ie the steeper the demand curve), the further $M R$ is below the demand curve, and hence the further $M R=M C$ is below price. Typically, the absence of substitutes means that a monopolist faces more inelastic demand than both an oligopolist and each firm under monopolistic competition. Hence, the excess of price over MC will be greater.
Incorrect
Option A.
In perfect competition, demand for the products of each firm is totally elastic and $P=M C$. However, under each of the other three market structures, $M R=M C$ at the profit-maximising output level, and the demand curve is above the $M R$ curve. Consequently, $P>M C$.
The more inelastic demand is (ie the steeper the demand curve), the further $M R$ is below the demand curve, and hence the further $M R=M C$ is below price. Typically, the absence of substitutes means that a monopolist faces more inelastic demand than both an oligopolist and each firm under monopolistic competition. Hence, the excess of price over MC will be greater.
-
Question 903 of 999CB2032101
Question 903
FlagIn the long run, a firm operating under conditions of monopolistic competition will produce at an output at which:
Correct
Option A. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will make normal profits. This is at the point which average (total) cost equals average revenue. Due to the downward-sloping demand curve, the firm will not produce at the minimum average total cost.
Incorrect
Option A. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will make normal profits. This is at the point which average (total) cost equals average revenue. Due to the downward-sloping demand curve, the firm will not produce at the minimum average total cost.
-
Question 904 of 999CB2032102
Question 904
FlagLimit pricing describes the strategy under which a monopolist (or oligopolist) charges a price that may be below what level in order to deter new entrants?
I the short-run profit-maximising price
II the minimum average cost for a new entrant
Ill its own minimum average costCorrect
Option A
A new entrant is likely to have higher average costs than an existing company, eg due to economies of scale. So, if the existing firm charges a price that is lower than a new entrant’s minimum average cost, then the potential new entrant will not be attracted into the industry. This may well be below the existing firm’s short-run profit maximising price. This describes limit pricing and this covers Options I and II. Option III describes predatory pricing, which is covered in the next section.
Incorrect
Option A
A new entrant is likely to have higher average costs than an existing company, eg due to economies of scale. So, if the existing firm charges a price that is lower than a new entrant’s minimum average cost, then the potential new entrant will not be attracted into the industry. This may well be below the existing firm’s short-run profit maximising price. This describes limit pricing and this covers Options I and II. Option III describes predatory pricing, which is covered in the next section.
-
Question 905 of 999CB2032103
Question 905
FlagFirst-degree price discrimination (FDPD) refers to the situation where:
Correct
Option C.
First-degree price discrimination means the firm charges each individual customer their maximum willingness to pay.
A refers to second-degree, B to third-degree, and D is simply price variation across firms.
Incorrect
Option C.
First-degree price discrimination means the firm charges each individual customer their maximum willingness to pay.
A refers to second-degree, B to third-degree, and D is simply price variation across firms.
-
Question 906 of 999CB2032104
Question 906
FlagWhich of the following situations describes a form of second-degree price discrimination (SDPD)?
Correct
Option A.
An example of SDPD in practice is ‘buy-one-get-one-free’ offers.
Incorrect
Option A.
An example of SDPD in practice is ‘buy-one-get-one-free’ offers.
-
Question 907 of 999CB2032105
Question 907
FlagWhen a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good it means that the country:
Correct
Option B.
Option A describes absolute advantage.Incorrect
Option B.
Option A describes absolute advantage. -
Question 908 of 999CB2032106
Question 908
FlagThe table below shows the quantities of cars and bicycles that one unit of input can produce in the UK and the USA. Assume that these are the only two goods that the countries produce.
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \textbf{One unit of input produces:} \\ \hline
& \textbf{Bicycles} & \textbf{Cars} \\ \hline
\textbf{UK} & 20 & 2 \\ \hline
\textbf{USA} & 30 & 4 \\ \hline
\end{array}Given the table above, which of the following is true?
Correct
Option D.
As the USA can produce more units of each good per unit of input, it can produce both goods at a lower cost. It thus has an absolute advantage in both goods, so Option D is correct.The UK has a comparative advantage in bicycles because the UK’s opportunity cost of bicycles is only $2 / 20$ cars compared with the USA’s opportunity cost of $4 / 30$. Conversely, the USA has a comparative advantage in cars, as its opportunity cost is $30 / 4$ compared to 20/2 for the UK. The USA is therefore likely to export cars to the UK in return for imports of bicycles.
Incorrect
Option D.
As the USA can produce more units of each good per unit of input, it can produce both goods at a lower cost. It thus has an absolute advantage in both goods, so Option D is correct.The UK has a comparative advantage in bicycles because the UK’s opportunity cost of bicycles is only $2 / 20$ cars compared with the USA’s opportunity cost of $4 / 30$. Conversely, the USA has a comparative advantage in cars, as its opportunity cost is $30 / 4$ compared to 20/2 for the UK. The USA is therefore likely to export cars to the UK in return for imports of bicycles.
-
Question 909 of 999CB2032107
Question 909
FlagThird-degree price discrimination (TDPD) refers to the situation where:
Correct
Option B.
Option D does not describe price discrimination. It is just describing the practice of different firms charging different prices that might be true in any imperfect market.Incorrect
Option B.
Option D does not describe price discrimination. It is just describing the practice of different firms charging different prices that might be true in any imperfect market. -
Question 910 of 999CB2032108
Question 910
FlagWhich of the following are barriers to trade designed to protect a nation’s domestic industries?
I tariffs on imports
II restrictions on the amount of goods that the nation can export
III excessive paperwork for imported goodsCorrect
Option A. Restrictions on the amount of goods that can be imported would help protect a nation’s domestic industries. Both tariffs and excessive paperwork would achieve this.
Incorrect
Option A. Restrictions on the amount of goods that can be imported would help protect a nation’s domestic industries. Both tariffs and excessive paperwork would achieve this.
-
Question 911 of 999CB2032110
Question 911
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a reason to restrict international trade?
Correct
Option D. International competition may put outdated industries out of business very quickly. The government may restrict trade to decrease the speed at which outdated industries decline in order to reduce structural unemployment.
Incorrect
Option D. International competition may put outdated industries out of business very quickly. The government may restrict trade to decrease the speed at which outdated industries decline in order to reduce structural unemployment.
-
Question 912 of 999CB2032112
Question 912
FlagWhich of the following statements relating to limit pricing is/are TRUE?
I Limit pricing is a pricing strategy where a firm deliberately keeps its prices below its average cost to deter new entrants to the market.II Limit pricing relies on the existing firm having lower average costs than potential new entrants.
III Limit pricing may result in reduced profits in the short run.
Correct
Option C.
Limit pricing is a pricing strategy where an existing firm deliberately keeps its prices below the level that would maximise profits in the short run to deter new entrants to the market. Although the price would need to be below the average cost of potential new entrants to prevent them for entering the market, it does not mean that the price needs to be below the average cost of the existing firm itself, and so Statement I is false.Limit pricing relies on the existing firm having lower average costs than potential new entrants (Statement II), eg due to economies of scale.
The firm’s profits may be reduced in the short run (Statement III). However, this strategy may lead to greater long-run profits if new entrants are successfully deterred, and competition thereby reduced.
Incorrect
Option C.
Limit pricing is a pricing strategy where an existing firm deliberately keeps its prices below the level that would maximise profits in the short run to deter new entrants to the market. Although the price would need to be below the average cost of potential new entrants to prevent them for entering the market, it does not mean that the price needs to be below the average cost of the existing firm itself, and so Statement I is false.Limit pricing relies on the existing firm having lower average costs than potential new entrants (Statement II), eg due to economies of scale.
The firm’s profits may be reduced in the short run (Statement III). However, this strategy may lead to greater long-run profits if new entrants are successfully deterred, and competition thereby reduced.
-
Question 913 of 999CB2032113
Question 913
Flag$P_{\mathrm{x}} / P_{\mathrm{m}}$ is the terms of trade and $M C_{\mathrm{x}} / M C_{\mathrm{m}}$ is the opportunity cost ratio for a country. The country will have maximised the gain from specialisation and trade when:
Correct
Option C.
If the terms of trade is greater than the opportunity cost ratio ie $\boldsymbol{P}_{\mathrm{x}} / \boldsymbol{P}_{\mathrm{m}}>\boldsymbol{M} \boldsymbol{C}_{\mathrm{x}} / \boldsymbol{M} \boldsymbol{C}_{\mathrm{m}}$ (Option B ), it will benefit the country to produce more exports in return for imports, since the relative value of production is greater than the relative cost.
As more exports are produced, opportunity costs will increase until the relative value of production is equal to the relative cost le $P_{\mathrm{x}} / P_{\mathrm{m}}=M C_{\mathrm{x}} / M C_{\mathrm{m}}$ (Option C ). At this point, there can be no more gain from further specialisation and trade.
Incorrect
Option C.
If the terms of trade is greater than the opportunity cost ratio ie $\boldsymbol{P}_{\mathrm{x}} / \boldsymbol{P}_{\mathrm{m}}>\boldsymbol{M} \boldsymbol{C}_{\mathrm{x}} / \boldsymbol{M} \boldsymbol{C}_{\mathrm{m}}$ (Option B ), it will benefit the country to produce more exports in return for imports, since the relative value of production is greater than the relative cost.
As more exports are produced, opportunity costs will increase until the relative value of production is equal to the relative cost le $P_{\mathrm{x}} / P_{\mathrm{m}}=M C_{\mathrm{x}} / M C_{\mathrm{m}}$ (Option C ). At this point, there can be no more gain from further specialisation and trade.
-
Question 914 of 999CB2032114
Question 914
FlagFollowing the imposition of a tariff:
Correct
Option C. The imposition of a tariff increases the price to the consumers, so the consumer surplus decreases. The producers receive the higher price and extend their supply, so the producer surplus increases. The government receives revenue from the tariff on imported goods, so the government surplus increases.
Incorrect
Option C. The imposition of a tariff increases the price to the consumers, so the consumer surplus decreases. The producers receive the higher price and extend their supply, so the producer surplus increases. The government receives revenue from the tariff on imported goods, so the government surplus increases.
-
Question 915 of 999CB2032117
Question 915
FlagWhich TWO of the following are NOT necessary in order for a firm to practise third-degree price discrimination:
Correct
Options A and C.
Third-degree price discrimination is the practice of dividing consumers into different groups based on some characteristic that is relatively easy to observe and informative about how much consumers are willing to pay.In order to practise third-degree price discrimination:
– The firm must have some control over the price it sets (Option B), ie it must face a downward-sloping demand curve. A monopoly firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve and so could practise third degree price discrimination. Therefore, Option A is not necessary.
– It must be possible (and not prohibitively expensive) to identify the different groups of consumers (Option D) and their different elasticities of demand.
– It must not be possible for consumers to buy a good and then to resell it on to other consumers at a higher price (Option E).
– The elasticity of demand for the good must differ between different groups of consumers. However, each could still be relatively elastic and so Option C is not necessary.
– It must be possible to find a characteristic with which to differentiate groups of consumers that is relatively easy to observe, informative about consumers’ willingness to pay, legal and acceptable to the consumers.Incorrect
Options A and C.
Third-degree price discrimination is the practice of dividing consumers into different groups based on some characteristic that is relatively easy to observe and informative about how much consumers are willing to pay.In order to practise third-degree price discrimination:
– The firm must have some control over the price it sets (Option B), ie it must face a downward-sloping demand curve. A monopoly firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve and so could practise third degree price discrimination. Therefore, Option A is not necessary.
– It must be possible (and not prohibitively expensive) to identify the different groups of consumers (Option D) and their different elasticities of demand.
– It must not be possible for consumers to buy a good and then to resell it on to other consumers at a higher price (Option E).
– The elasticity of demand for the good must differ between different groups of consumers. However, each could still be relatively elastic and so Option C is not necessary.
– It must be possible to find a characteristic with which to differentiate groups of consumers that is relatively easy to observe, informative about consumers’ willingness to pay, legal and acceptable to the consumers. -
Question 916 of 999CB2032118
Question 916
FlagWhich of the following would give rise to a ‘ + ‘ in the USA’s balance of payments?
Correct
Option C.
Option A: if the Federal Reserve Bank buys more gold, it will be increasing the supply of dollars, which would be recorded as a ‘ – ‘ in the balance of payments.Option B: an increase in the sterling value of the dollar will not directly affect the balance of payments now, although it may influence the subsequent volume and value of exports and imports to and from the USA.
Option C: this will be recorded as a ‘ + ‘ in the financial account.
Option D: as with Option B, there will be no direct effect on the balance of payments. The subsequent effect will depend on the elasticity of demand for US exports.Incorrect
Option C.
Option A: if the Federal Reserve Bank buys more gold, it will be increasing the supply of dollars, which would be recorded as a ‘ – ‘ in the balance of payments.Option B: an increase in the sterling value of the dollar will not directly affect the balance of payments now, although it may influence the subsequent volume and value of exports and imports to and from the USA.
Option C: this will be recorded as a ‘ + ‘ in the financial account.
Option D: as with Option B, there will be no direct effect on the balance of payments. The subsequent effect will depend on the elasticity of demand for US exports. -
Question 917 of 999CB2032119
Question 917
FlagWhich of the following would NOT appear in the UK’s balance of trade?
Correct
Option D. The balance of trade includes exports and imports of goods and services. Option D is a transaction that would appear in the capital account.
‘Debt forgiveness’ refers to the writing-off of a portion of one or more loans to a financially troubled government by its lender(s) – in this case, the UK government. The objective is to help that government in its debt restructuring so that it remains viable and is able to pay off the remaining part of the loan(s). This would appear as a negative item in the UK’s capital account, as money equal to the value of the debt written off is leaving the UK.Incorrect
Option D. The balance of trade includes exports and imports of goods and services. Option D is a transaction that would appear in the capital account.
‘Debt forgiveness’ refers to the writing-off of a portion of one or more loans to a financially troubled government by its lender(s) – in this case, the UK government. The objective is to help that government in its debt restructuring so that it remains viable and is able to pay off the remaining part of the loan(s). This would appear as a negative item in the UK’s capital account, as money equal to the value of the debt written off is leaving the UK. -
Question 918 of 999CB2032120
Question 918
FlagWhich of the following is most likely to result from the depreciation of a country’s exchange rate?
Correct
Option C. Depreciation means that the domestic currency will now be worth less in terms of the overseas currency it can buy, therefore exports will become more competitive and imports will become more expensive, which is likely to decrease the volume of imports. However, inflation is likely to rise through cost-push pressures (more expensive imports) and demand-pull pressures (an increased demand for (cheaper) exports).
Incorrect
Option C. Depreciation means that the domestic currency will now be worth less in terms of the overseas currency it can buy, therefore exports will become more competitive and imports will become more expensive, which is likely to decrease the volume of imports. However, inflation is likely to rise through cost-push pressures (more expensive imports) and demand-pull pressures (an increased demand for (cheaper) exports).
-
Question 919 of 999CB2032121
Question 919
FlagA firm that produces a main product and a by-product will maximise profits if it:
Correct
Option C.
Profit is maximised when marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
A by-product is good or a service that is produced as a result of producing another good or service. If a firm is producing a main product and a by-product, it will maximise profits at the combined output where:combined $M C=$ combined $M R$
The answer is therefore Option C. Having decided on the combined output and split this into the individual outputs of each product, the firm will then use the individual demand curves to determine the price to be charged for the main product and the by-product.Option B suggests using the ‘marginal rule’ for the by-product separately. However, production of the by-product is inextricably linked with the production of the main product. It is not possible to sell more of the by-product than the amount produced in the course of producing the desired amount of the main product, and selling less than the amount produced could be very costly and wasteful. By considering the profitability of the combined output, a firm might produce more of the main product than it otherwise would, because the profit from the by-product more than makes up for the lower profit on the main product.
Incorrect
Option C.
Profit is maximised when marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
A by-product is good or a service that is produced as a result of producing another good or service. If a firm is producing a main product and a by-product, it will maximise profits at the combined output where:combined $M C=$ combined $M R$
The answer is therefore Option C. Having decided on the combined output and split this into the individual outputs of each product, the firm will then use the individual demand curves to determine the price to be charged for the main product and the by-product.Option B suggests using the ‘marginal rule’ for the by-product separately. However, production of the by-product is inextricably linked with the production of the main product. It is not possible to sell more of the by-product than the amount produced in the course of producing the desired amount of the main product, and selling less than the amount produced could be very costly and wasteful. By considering the profitability of the combined output, a firm might produce more of the main product than it otherwise would, because the profit from the by-product more than makes up for the lower profit on the main product.
-
Question 920 of 999CB2032122
Question 920
FlagWhich of the following are assets of a bank?
I cash
II repos
III mortgagesCorrect
Option B. Repos (sale and repurchase agreements) involve a bank selling bonds in return for cash, at the same time agreeing to rebuy the bonds at some future date. They therefore create a financial obligation for the bank and as such are a liability of the bank. However, they are an asset of the counterparty, usually the central bank or another bank, which is said to have a reverse repo position.
Incorrect
Option B. Repos (sale and repurchase agreements) involve a bank selling bonds in return for cash, at the same time agreeing to rebuy the bonds at some future date. They therefore create a financial obligation for the bank and as such are a liability of the bank. However, they are an asset of the counterparty, usually the central bank or another bank, which is said to have a reverse repo position.
-
Question 921 of 999CB2032123
Question 921
FlagWhich of the following are functions of money?
I a means of measuring future payments
II a unit of account
III a means of savingCorrect
Option D. All three of the above are functions of money.
Remember that:
– a unit of account means a way of measuring the value of goods, services and assets
– the fourth and main function of money is as a medium of exchange.Incorrect
Option D. All three of the above are functions of money.
Remember that:
– a unit of account means a way of measuring the value of goods, services and assets
– the fourth and main function of money is as a medium of exchange. -
Question 922 of 999CB2032124
Question 922
FlagIf the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost then:
Correct
Option A.
If $M S B>M S C$, then the addition to total benefit from the extra unit of output exceeds the addition to total cost from the extra unit of output, so that total welfare will increase from producing the additional unit of output.
Incorrect
Option A.
If $M S B>M S C$, then the addition to total benefit from the extra unit of output exceeds the addition to total cost from the extra unit of output, so that total welfare will increase from producing the additional unit of output.
-
Question 923 of 999CB2032126
Question 923
FlagWhich of the following statements is NOT true?
Correct
Option B. There are many different definitions of money. The broader definitions of money include not just notes and coins but also various types of bank accounts and other financial assets.
Incorrect
Option B. There are many different definitions of money. The broader definitions of money include not just notes and coins but also various types of bank accounts and other financial assets.
-
Question 924 of 999CB2032128
Question 924
FlagWhich of these would NOT be included in the social costs of the petroleum industry?
Correct
Option B.
The social costs include the private costs (eg wages, raw materials, admin costs, finance costs (Option C)) plus the external costs (ie the costs imposed on third parties, such as health effects (Option A) and accidents and disruption (Option D)). Surplus profits, ie supernormal profits (Option B), are not included in private costs.
Incorrect
Option B.
The social costs include the private costs (eg wages, raw materials, admin costs, finance costs (Option C)) plus the external costs (ie the costs imposed on third parties, such as health effects (Option A) and accidents and disruption (Option D)). Surplus profits, ie supernormal profits (Option B), are not included in private costs.
-
Question 925 of 999CB2032131
Question 925
FlagA bank’s decision to reduce loans and advances to customers and increase its reserve balances at the central bank whilst holdings of other liquid assets are held constant will:
Correct
Option B.
A reduction in loans and advances to customers and an increase in the reserve balances at the central bank will increase the bank’s holdings of liquid assets and will increase the liquidity ratio (liquid assets/total assets).
The average maturity of the bank’s loans will decrease, since it will have a smaller proportion of long-term loans (to customers), so the maturity gap (the difference in the average maturity of loans and deposits) will decrease.
Incorrect
Option B.
A reduction in loans and advances to customers and an increase in the reserve balances at the central bank will increase the bank’s holdings of liquid assets and will increase the liquidity ratio (liquid assets/total assets).
The average maturity of the bank’s loans will decrease, since it will have a smaller proportion of long-term loans (to customers), so the maturity gap (the difference in the average maturity of loans and deposits) will decrease.
-
Question 926 of 999CB2032133
Question 926
FlagWhich of the following is NOT a tool that the Bank of England uses to provide liquidity insurance for the banking system?
Correct
Option B. As lender of last resort, the Bank of England uses a variety of methods (such as Options $\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{C}$ and D ) to try to ensure that individual banks and the banking system as a whole has sufficient liquidity to meet customers’ demand. Quantitative easing aims to increase the money supply.
Incorrect
Option B. As lender of last resort, the Bank of England uses a variety of methods (such as Options $\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{C}$ and D ) to try to ensure that individual banks and the banking system as a whole has sufficient liquidity to meet customers’ demand. Quantitative easing aims to increase the money supply.
-
Question 927 of 999CB2032134
Question 927
FlagWhich of the following ratios is the ratio of a company’s borrowed capital to shares?
Correct
Option B.
The capital adequacy ratio is the ratio of a bank’s capital (reserves and shares) to its risk-weighted assets, the liquidity ratio is the proportion of a bank’s total assets held in liquid form, and the net stable funding ratio is the ratio of stable liabilities to assets likely to require funding (ie assets where there is a likelihood of default.
Incorrect
Option B.
The capital adequacy ratio is the ratio of a bank’s capital (reserves and shares) to its risk-weighted assets, the liquidity ratio is the proportion of a bank’s total assets held in liquid form, and the net stable funding ratio is the ratio of stable liabilities to assets likely to require funding (ie assets where there is a likelihood of default.
-
Question 928 of 999CB2032135
Question 928
FlagWhich of the following is NOT one of the main functions of the central bank?
Correct
Option B.
The central bank has the following functions:
1. it issues notes
2. it acts as banker to the government
3. it acts as banker to the banks
4. it acts as banker to overseas central banks
5. it operates the government’s monetary policy
6. it provides liquidity to the banks
6. it oversees (ie regulates) the activities of banks and other financial institutions
7. it operates the government’s exchange rate policy.Incorrect
Option B.
The central bank has the following functions:
1. it issues notes
2. it acts as banker to the government
3. it acts as banker to the banks
4. it acts as banker to overseas central banks
5. it operates the government’s monetary policy
6. it provides liquidity to the banks
6. it oversees (ie regulates) the activities of banks and other financial institutions
7. it operates the government’s exchange rate policy. -
Question 929 of 999CB2032136
Question 929
FlagThe Bank of England has a number of functions including operating the government’s monetary policy, providing liquidity to banks and operating the government’s exchange rate policy. Following are either true or false statements:
1 The Bank of England’s operational standing facility deposit rate is set above the bank rate to encourage banks to make use of the facility.
II Repo arrangements occur when the Bank of England buys back Treasury bills from the banks before maturity (and therefore at a price below the face value).
III The management of foreign currency reserves is done through the exchange equalisation account.
Which of the statements is/are TRUE?
Correct
Option B.
The Bank of England’s operational standing facility deposit rate is set below the bank rate to discourage banks from making use of the facility (by incentivising them to trade with other banks instead), so Statement I is false. Statement II describes the process of rediscounting (rather than repo arrangements) and so is also false.
Incorrect
Option B.
The Bank of England’s operational standing facility deposit rate is set below the bank rate to discourage banks from making use of the facility (by incentivising them to trade with other banks instead), so Statement I is false. Statement II describes the process of rediscounting (rather than repo arrangements) and so is also false.
-
Question 930 of 999CB2032137
Question 930
FlagThe principle of non-rivalry applied to public goods means that:
Correct
Option D.
Non-rivalry means that one person’s consumption does not impede another person’s consumption. Unlike private goods, people do not compete with each other for a public good. Therefore, once it is provided for one person, no extra resources are needed to provide it for another. For example, once street lighting is provided, there is no extra cost when an additional person walks down the street.
Incorrect
Option D.
Non-rivalry means that one person’s consumption does not impede another person’s consumption. Unlike private goods, people do not compete with each other for a public good. Therefore, once it is provided for one person, no extra resources are needed to provide it for another. For example, once street lighting is provided, there is no extra cost when an additional person walks down the street.
-
Question 931 of 999CB2032138
Question 931
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Statement 1 (Assertion)} & & \text{Statement 2 (Reason)} \\
\hline \text{Securitisation reduces the systemic risk of a banking collapse.} & BECAUSE & \text{Securitisation enables banks to manage their exposures to default risk (by selling on risky assets) and liquidity risk (by selling illiquid assets for cash).} \\
\hline
\end{array}Correct
Option D.
Securitisation increases the systematic risk of a banking collapse because the fortunes of the banks become even more intertwined. Ultimately, many financial institutions may end up being exposed to the risk of the original bank’s lending policy.
Securitisation does help banks to manage their own risks and so the reason is true.
Incorrect
Option D.
Securitisation increases the systematic risk of a banking collapse because the fortunes of the banks become even more intertwined. Ultimately, many financial institutions may end up being exposed to the risk of the original bank’s lending policy.
Securitisation does help banks to manage their own risks and so the reason is true.
-
Question 932 of 999CB2032139
Question 932
FlagThe production of a good results in a negative externality. It is likely that there will be an improvement in economic welfare if the government:
Correct
Option D.
The existence of a negative production externality (an external cost) means that MSC > MPC. This implies that the profit-maximising level of output (determined on the basis of private costs and benefits alone) will be in excess of the socially optimal output level. To reduce output to the socially optimal output level, the external cost will need to be internalised, ie the producer will have to absorb this external cost. Therefore, a tax needs to be imposed that is equal to the marginal external cost at the socially efficient output level.
Incorrect
Option D.
The existence of a negative production externality (an external cost) means that MSC > MPC. This implies that the profit-maximising level of output (determined on the basis of private costs and benefits alone) will be in excess of the socially optimal output level. To reduce output to the socially optimal output level, the external cost will need to be internalised, ie the producer will have to absorb this external cost. Therefore, a tax needs to be imposed that is equal to the marginal external cost at the socially efficient output level.
-
Question 933 of 999CB2032140
Question 933
FlagAccording to classical theory, withdrawals should equal injections because:
Correct
Option D.
Classical theory says that withdrawals should equal injections because:
– the rate of interest in the market for loanable funds will ensure that savings equals investment
– the gold standard mechanism ensures that exports equals imports
– the government should ensure that it balances its own budget, ie government spending equals taxation.Incorrect
Option D.
Classical theory says that withdrawals should equal injections because:
– the rate of interest in the market for loanable funds will ensure that savings equals investment
– the gold standard mechanism ensures that exports equals imports
– the government should ensure that it balances its own budget, ie government spending equals taxation. -
Question 934 of 999CB2032141
Question 934
FlagIn the quantity theory of money, which of the following is assumed?
Correct
Option C.
In the quantity theory of money $(M \bar{V}=P \bar{Y})$, velocity of circulation ( $V$ ) and real output $(Y)$ are assumed to be fixed.
$\_\_\_\_$Incorrect
Option C.
In the quantity theory of money $(M \bar{V}=P \bar{Y})$, velocity of circulation ( $V$ ) and real output $(Y)$ are assumed to be fixed.
$\_\_\_\_$ -
Question 935 of 999CB2032142
Question 935
FlagUnder the gold standard, a balance of payments deficit would lead to:
Correct
Option B.
Under the gold standard, a country’s deficit was paid in gold from its reserves, so a deficit would lead to an outflow of gold. The domestic money supply was backed by gold, so if the gold reserves fell, the money supply had to fall. According to the quantity theory, if the money supply fell, prices fell. This would make exports more competitive and imports less competitive, therefore the sale of exports would rise and the sales of imports would fall.
Incorrect
Option B.
Under the gold standard, a country’s deficit was paid in gold from its reserves, so a deficit would lead to an outflow of gold. The domestic money supply was backed by gold, so if the gold reserves fell, the money supply had to fall. According to the quantity theory, if the money supply fell, prices fell. This would make exports more competitive and imports less competitive, therefore the sale of exports would rise and the sales of imports would fall.
-
Question 936 of 999CB2032143
Question 936
FlagAccording to the classical view of the labour market, an increase in aggregate demand causes:
Correct
Option B.
Classical economists argue that an increase in aggregate demand will lead to an increase in the price level and hence a reduction in real wages in the short run. However, since at lower real wages, there is excess demand for labour, there will be an increase in nominal wages so that real wages return to the original equilibrium level in the long run
Incorrect
Option B.
Classical economists argue that an increase in aggregate demand will lead to an increase in the price level and hence a reduction in real wages in the short run. However, since at lower real wages, there is excess demand for labour, there will be an increase in nominal wages so that real wages return to the original equilibrium level in the long run
-
Question 937 of 999CB2032144
Question 937
FlagAccording to the classical view:
Correct
Option C
Classical economists argue that the economy will settle at a long-run equilibrium at its natural level (or potential) level of output, $Y_p$.
As the diagram above shows, an increase in aggregate demand will, in the short run, lead to an increase in the price level from $p_1$ to $p_2$ and an increase in output beyond its potential output from $Y_p$ to $Y_2$.
However, over time, the increase in the price level will lead to an increase in nominal wages, which will increase firms’ costs, so the SRAS curve shifts upwards to the left. This increases the price further to $p_3$ and reduces output back to its potential output $Y_p$. Therefore, although output increases in the short run in response to an increase in aggregate demand, in the long run output is fixed at $Y_p$.
As mentioned earlier, the AD-AS model is a recently developed model and therefore was not used by the classical economists. Notice that this vertical LRAS curve accords with the quantity theory of money if we assume that the quantity theory is a long-run theory, ie output $Y$ is fixed in the long run.
Incorrect
Option C
Classical economists argue that the economy will settle at a long-run equilibrium at its natural level (or potential) level of output, $Y_p$.
As the diagram above shows, an increase in aggregate demand will, in the short run, lead to an increase in the price level from $p_1$ to $p_2$ and an increase in output beyond its potential output from $Y_p$ to $Y_2$.
However, over time, the increase in the price level will lead to an increase in nominal wages, which will increase firms’ costs, so the SRAS curve shifts upwards to the left. This increases the price further to $p_3$ and reduces output back to its potential output $Y_p$. Therefore, although output increases in the short run in response to an increase in aggregate demand, in the long run output is fixed at $Y_p$.
As mentioned earlier, the AD-AS model is a recently developed model and therefore was not used by the classical economists. Notice that this vertical LRAS curve accords with the quantity theory of money if we assume that the quantity theory is a long-run theory, ie output $Y$ is fixed in the long run.
-
Question 938 of 999CB2032145
Question 938
FlagKeynes rejected the classical view that in a recession real wages would fall to clear the labour market because:
I wages are sticky downwards.
II a fall in real wages would decrease consumption and further decrease the demand for labour.
Ill a fall in wages cuts costs, reduces prices and increases export demand.Which of the above are correct?
Correct
Option B.
Keynes did not think it would be easy to reduce wages. Wages tend to be inflexible, especially downwards. They are usually set for a whole year, even in non-unionised firms, and wage cuts would be resisted by workers. (Nowadays, it is thought that wage cuts are resisted by employers too because the ‘economy of high wages’ suggests that productivity might fall if wages were reduced.) Even if wages did fall, it might take a long time, during which workers and the economy would suffer. Also, this essentially micro vision of the labour market overlooks macroeconomic considerations. If real wages in general fall, there will be a decrease in real incomes in the economy, which will lead to a decrease in aggregate demand and hence a decrease in the demand for labour. Option Ill is the classical argument, not a criticism of it.
Incorrect
Option B.
Keynes did not think it would be easy to reduce wages. Wages tend to be inflexible, especially downwards. They are usually set for a whole year, even in non-unionised firms, and wage cuts would be resisted by workers. (Nowadays, it is thought that wage cuts are resisted by employers too because the ‘economy of high wages’ suggests that productivity might fall if wages were reduced.) Even if wages did fall, it might take a long time, during which workers and the economy would suffer. Also, this essentially micro vision of the labour market overlooks macroeconomic considerations. If real wages in general fall, there will be a decrease in real incomes in the economy, which will lead to a decrease in aggregate demand and hence a decrease in the demand for labour. Option Ill is the classical argument, not a criticism of it.
-
Question 939 of 999CB2032146
Question 939
FlagKeynesian theory predicts that:
Correct
Option B.
A decrease in withdrawals (savings, taxation, imports) increases consumption on domestically produced goods and services and therefore increases aggregate demand, which increases real output (real national income) and employment. Therefore, an increase in taxation (Option C) would decrease national income. An increase in injections (investment, government spending, exports) (Option A) increases aggregate demand and hence increases real national income and employment. A decrease in interest rates (Option D) would increase borrowing and increase consumption and investment, hence leading to an increase in real national income and employment.
Incorrect
Option B.
A decrease in withdrawals (savings, taxation, imports) increases consumption on domestically produced goods and services and therefore increases aggregate demand, which increases real output (real national income) and employment. Therefore, an increase in taxation (Option C) would decrease national income. An increase in injections (investment, government spending, exports) (Option A) increases aggregate demand and hence increases real national income and employment. A decrease in interest rates (Option D) would increase borrowing and increase consumption and investment, hence leading to an increase in real national income and employment.
-
Question 940 of 999CB2032147
Question 940
FlagThe production of a good results in a negative externality. It is likely that there will be an improvement in economic welfare if the government:
Correct
Option D.
The existence of a negative production externality (an external cost) means that MSC > MPC. This implies that the profit-maximising level of output (determined on the basis of private costs and benefits alone) will be in excess of the socially optimal output level. To reduce output to the socially optimal output level, the external cost will need to be internalised, ie the producer will have to absorb this external cost. Therefore, a tax needs to be imposed that is equal to the marginal external cost at the socially efficient output level.
Incorrect
Option D.
The existence of a negative production externality (an external cost) means that MSC > MPC. This implies that the profit-maximising level of output (determined on the basis of private costs and benefits alone) will be in excess of the socially optimal output level. To reduce output to the socially optimal output level, the external cost will need to be internalised, ie the producer will have to absorb this external cost. Therefore, a tax needs to be imposed that is equal to the marginal external cost at the socially efficient output level.
-
Question 941 of 999CB2032148
Question 941
FlagThe monetary base is £ 300 billion and the broad money supply is £ 1,500 billion. Assuming that the money multiplier and the bank deposits multiplier are equal in value, what is the liquidity ratio of the banking system?
Correct
Option D. The money multiplier $m$ shows the relationship between the monetary base and the (broad) money supply and can be found as follows:
$$
m=\frac{\mathrm{M} 4}{\text { monetary base }}=\frac{1500}{300}=5
$$Assuming the money multiplier and the bank deposits multiplier (b) are equal in value we have:
$$
m=b=\frac{1}{L}=5
$$
where $L$ is the banks’ liquidity ratio.
Hence $\boldsymbol{L}=0.2$.Incorrect
Option D. The money multiplier $m$ shows the relationship between the monetary base and the (broad) money supply and can be found as follows:
$$
m=\frac{\mathrm{M} 4}{\text { monetary base }}=\frac{1500}{300}=5
$$Assuming the money multiplier and the bank deposits multiplier (b) are equal in value we have:
$$
m=b=\frac{1}{L}=5
$$
where $L$ is the banks’ liquidity ratio.
Hence $\boldsymbol{L}=0.2$. -
Question 942 of 999CB2032149
Question 942
FlagThe opportunity cost of holding money is the:
Correct
Option D. The main alternative to holding low-risk and low-return money is holding higher-risk and higher-return shares and bonds, so the opportunity cost of holding money is the interest rate foregone by not holding shares and bonds. For example, if the rate of interest on a bank account is $12 \%$ and that on the best alternative is $6 \%$, the opportunity cost is $51 / 2 \%$.
Incorrect
Option D. The main alternative to holding low-risk and low-return money is holding higher-risk and higher-return shares and bonds, so the opportunity cost of holding money is the interest rate foregone by not holding shares and bonds. For example, if the rate of interest on a bank account is $12 \%$ and that on the best alternative is $6 \%$, the opportunity cost is $51 / 2 \%$.
-
Question 943 of 999CB2032150
Question 943
FlagWhich of the following is NOT likely to lead to an increase in investment?
Correct
Option C.
One of the major sources of funds for investment is profit that is ploughed back into the business rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends. A fall in profit would mean that businesses would have to look elsewhere to finance any investment. A fall in interest rates (Option A) would make it cheaper to borrow to invest. A rise in consumption (Option B) would raise business expectations and confidence in the economy (Option D) and therefore businesses would increase investment to give them the capacity they need to cope with increased demand.
Incorrect
Option C.
One of the major sources of funds for investment is profit that is ploughed back into the business rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends. A fall in profit would mean that businesses would have to look elsewhere to finance any investment. A fall in interest rates (Option A) would make it cheaper to borrow to invest. A rise in consumption (Option B) would raise business expectations and confidence in the economy (Option D) and therefore businesses would increase investment to give them the capacity they need to cope with increased demand.
-
Question 944 of 999CB2032151
Question 944
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an advantage of the free market?
Correct
Option B.
Monopolies and oligopolies can form in a free market and, since barriers to entry prevent new firms entering the market, high levels of supernormal profits can be earned in the long run.
Incorrect
Option B.
Monopolies and oligopolies can form in a free market and, since barriers to entry prevent new firms entering the market, high levels of supernormal profits can be earned in the long run.
-
Question 945 of 999CB2032152
Question 945
FlagEquilibrium in the Keynesian model occurs where:
I injections = withdrawals
II aggregate demand = GDP
III $C_d+J=Y$Correct
Option D.
The equilibrium level of income occurs where aggregate demand or expenditure ( $E$ ) is equal to GDP or income $(Y)$. (Recall that GDP is a measure of national income.) Therefore Statement II is correct. Since $E=C_{\mathrm{d}}+J$, Statement III is also correct. Alternatively, since $E=C_{\mathrm{d}}+J$ and $Y=C_{\mathrm{d}}+W, J=W$ is also a condition for equilibrium, so Statement $I$ is also correct.
Incorrect
Option D.
The equilibrium level of income occurs where aggregate demand or expenditure ( $E$ ) is equal to GDP or income $(Y)$. (Recall that GDP is a measure of national income.) Therefore Statement II is correct. Since $E=C_{\mathrm{d}}+J$, Statement III is also correct. Alternatively, since $E=C_{\mathrm{d}}+J$ and $Y=C_{\mathrm{d}}+W, J=W$ is also a condition for equilibrium, so Statement $I$ is also correct.
-
Question 946 of 999CB2032153
Question 946
FlagWhich of the following approaches would NOT be used by a central bank that wishes to avoid increasing the money supply?
Correct
Option C. Funding government borrowing by selling Treasury bills will increase the banks’ holdings of liquid assets, so increasing their willingness and ability to lend. The money supply will therefore increase.
This contrasts with funding the borrowing by selling government bonds, which will likely have no overall effect on the money supply. This is because the government spends the money borrowed on goods and services, which is then redeposited back in the banks, and so there is no overall change in banks’ holdings of cash and hence in their ability to create credit.
Options A, B and D will all lead to a contraction in the money supply.
Incorrect
Option C. Funding government borrowing by selling Treasury bills will increase the banks’ holdings of liquid assets, so increasing their willingness and ability to lend. The money supply will therefore increase.
This contrasts with funding the borrowing by selling government bonds, which will likely have no overall effect on the money supply. This is because the government spends the money borrowed on goods and services, which is then redeposited back in the banks, and so there is no overall change in banks’ holdings of cash and hence in their ability to create credit.
Options A, B and D will all lead to a contraction in the money supply.
-
Question 947 of 999CB2032154
Question 947
FlagGovernment attempts to increase the monetary base are likely to cause short-term interest rates to:
Correct
Option D. Increasing the monetary base will initially lead to an excess of money supply over money demand leading to a fall in short-term interest rates. As money demand depends negatively upon interest rates, this fall in interest rates will also lead to an increase in the quantity of money demanded, ie a movement along the demand for money curve.
This corresponds to a rightward shift of the money supply curve on the money market equilibrium diagram.
Incorrect
Option D. Increasing the monetary base will initially lead to an excess of money supply over money demand leading to a fall in short-term interest rates. As money demand depends negatively upon interest rates, this fall in interest rates will also lead to an increase in the quantity of money demanded, ie a movement along the demand for money curve.
This corresponds to a rightward shift of the money supply curve on the money market equilibrium diagram.
-
Question 948 of 999CB2032155
Question 948
FlagThe multiplier is:
I the ratio of the change in equilibrium output to the original change in injections that caused the change in output.
II the inverse of the marginal propensity to withdraw.
Ill the ratio of aggregate demand to investment demanCorrect
Option A.
Statement I is the definition of the injections multiplier. Statement II is one of the ways of calculating the injections multiplier in practice. Statement Ill is wrong.
Incorrect
Option A.
Statement I is the definition of the injections multiplier. Statement II is one of the ways of calculating the injections multiplier in practice. Statement Ill is wrong.
-
Question 949 of 999CB2032156
Question 949
FlagWhich of the following is the definition of exploitative abuse?
Correct
Option A.
Options B, C and D are definitions of exclusionary abuses, restrictive practices and bid rigging respectively.
Incorrect
Option A.
Options B, C and D are definitions of exclusionary abuses, restrictive practices and bid rigging respectively.
-
Question 950 of 999CB2032157
Question 950
FlagThe marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods is 0.8 and the government decides to increase public spending by $\mathbf{£ 1 0 0}$ million. According to Keynesian analysis, what is likely to be the total change in national income resulting from this increased government expenditure?
Correct
Option D.
In this case the injections multiplier is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}=\frac{1}{1-0.8}=5
$$Therefore:
$$
\Delta Y=k \times \Delta=5 \times 100=500
$$Incorrect
Option D.
In this case the injections multiplier is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}=\frac{1}{1-0.8}=5
$$Therefore:
$$
\Delta Y=k \times \Delta=5 \times 100=500
$$ -
Question 951 of 999CB2032158
Question 951
FlagSuppose that a 10,000 increase in monetary base results in a 40,000 increase in M4. If the public hold all their money in bank accounts, then the banks’ reserve ratio is equal to:
Correct
Option D.
The value of the money multiplier, $m$, is:
$$
\frac{\Delta \text { total money supply }}{\Delta \text { monetary base }}=4
$$However, $m$ can also be calculated in terms of the banks’ reserve ratio, $r$, as:
$$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}
$$Since the public hold all their money in banks, ie $c=0$, this is equal to:
$$
m=\frac{1}{r}
$$So:
$$
r=\frac{1}{m}=\frac{1}{4}=0.25
$$Incorrect
Option D.
The value of the money multiplier, $m$, is:
$$
\frac{\Delta \text { total money supply }}{\Delta \text { monetary base }}=4
$$However, $m$ can also be calculated in terms of the banks’ reserve ratio, $r$, as:
$$
m=\frac{1+c}{r+c}
$$Since the public hold all their money in banks, ie $c=0$, this is equal to:
$$
m=\frac{1}{r}
$$So:
$$
r=\frac{1}{m}=\frac{1}{4}=0.25
$$ -
Question 952 of 999CB2032159
Question 952
FlagWhich of the following statements is NOT true?
Correct
Option D.
If investors expect share prices to rise, they will switch some of their investments from cash to shares. So, their holdings of money balances as an asset will decrease.
Recall that active money balances refers to money held for transactions and precautionary purposes, whereas idle money balances refers to money held as an asset and/or for speculative purposes.
Incorrect
Option D.
If investors expect share prices to rise, they will switch some of their investments from cash to shares. So, their holdings of money balances as an asset will decrease.
Recall that active money balances refers to money held for transactions and precautionary purposes, whereas idle money balances refers to money held as an asset and/or for speculative purposes.
-
Question 953 of 999CB2032160
Question 953
FlagUnemployment and inflation can co-exist because of:
I structural unemployment.
II cost-push inflation.
Ill firms operating with different degrees of slack.Correct
Option D.
Whereas demand-deficient unemployment and demand-pull inflation are unlikely to occur at the same time (since one is caused by too little demand and the other by too much), structural unemployment can occur at any level of inflation, and cost-push inflation can occur at any level of unemployment.
If firms operate at different levels of capacity, it is possible that an increase in aggregate demand in a depressed economy might result in most firms increasing output to satisfy the demand but other firms increasing prices because they have no spare capacity. This will be more likely as the economy as a whole approaches full capacity_ A consequence of this is that the AS curve is likely to slope upwards and to become steeper as output approaches its full-employment level.Incorrect
Option D.
Whereas demand-deficient unemployment and demand-pull inflation are unlikely to occur at the same time (since one is caused by too little demand and the other by too much), structural unemployment can occur at any level of inflation, and cost-push inflation can occur at any level of unemployment.
If firms operate at different levels of capacity, it is possible that an increase in aggregate demand in a depressed economy might result in most firms increasing output to satisfy the demand but other firms increasing prices because they have no spare capacity. This will be more likely as the economy as a whole approaches full capacity_ A consequence of this is that the AS curve is likely to slope upwards and to become steeper as output approaches its full-employment level. -
Question 954 of 999CB2032161
Question 954
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an example of an abuse of market power performed by a monopoly?
Correct
Option D.
Bid rigging requires two or more firms to secretly agree the prices they will tender for a contract.
Incorrect
Option D.
Bid rigging requires two or more firms to secretly agree the prices they will tender for a contract.
-
Question 955 of 999CB2032162
Question 955
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for money balances is interest-elastic and the demand for investment is interest-inelastic. A change in the money supply will result in a relatively:
Correct
Option A. To see this, consider an increase in the money supply. This will reduce interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium. The fact that the demand for money is interest-elastic, ie the money demand curve is relatively flat, means that this can happen with only a small reduction in interest rates. Almost by definition, if investment is interest-inelastic it would not be increased much even by a large reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
Incorrect
Option A. To see this, consider an increase in the money supply. This will reduce interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium. The fact that the demand for money is interest-elastic, ie the money demand curve is relatively flat, means that this can happen with only a small reduction in interest rates. Almost by definition, if investment is interest-inelastic it would not be increased much even by a large reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option A.
-
Question 956 of 999CB2032163
Question 956
FlagAn increase in injections will:
Correct
Option C.
An increase in injections (investment, government spending and/or exports) will increase aggregate demand, increase sales (including sales of imports), increase employment and increase national income. As aggregate demand increases, the rate of inflation will tend to increase. The extent of demand-pull inflationary pressure will be greater, the closer the economy is to full capacity, and hence, the greater the difficulty firms have in trying to meet the demand.
Incorrect
Option C.
An increase in injections (investment, government spending and/or exports) will increase aggregate demand, increase sales (including sales of imports), increase employment and increase national income. As aggregate demand increases, the rate of inflation will tend to increase. The extent of demand-pull inflationary pressure will be greater, the closer the economy is to full capacity, and hence, the greater the difficulty firms have in trying to meet the demand.
-
Question 957 of 999CB2032164
Question 957
FlagFunding and minimum reserve requirements are techniques that the monetary authorities of a country can use to expand or contract the money supply. Following are either true or false statements:
I Funding is concerned with the structure of government debt, ie the mix of short-term liquid Treasury bills and long-term illiquid government bonds used to fund a given level of public sector borrowing.
II If the central bank wishes to create credit, it will issue a higher proportion of Treasury bills and a lower proportion of government bonds.
III A decrease in the minimum reserve requirement is likely to expand the money supply.
Which of the statements is/are TRUE?Correct
Option D.
Funding is concerned with the structure of government debt (Statement I).
Treasury bills have a shorter term and are more liquid than government bonds and so banks can lend more and create more credit when holding treasury bills. The central bank is therefore more likely to issue Treasury Bills rather than government bonds when wanting to create credit (Statement II).If the reserve ratio is greater than the liquidity ratio banks would choose if left to their own devices, then reserve requirements restrict banks’ ability to expand the money supply through lending. So a decrease in reserve requirements increases the banks’ ability to lend and expands the money supply (Statement III).
Incorrect
Option D.
Funding is concerned with the structure of government debt (Statement I).
Treasury bills have a shorter term and are more liquid than government bonds and so banks can lend more and create more credit when holding treasury bills. The central bank is therefore more likely to issue Treasury Bills rather than government bonds when wanting to create credit (Statement II).If the reserve ratio is greater than the liquidity ratio banks would choose if left to their own devices, then reserve requirements restrict banks’ ability to expand the money supply through lending. So a decrease in reserve requirements increases the banks’ ability to lend and expands the money supply (Statement III).
-
Question 958 of 999CB2032165
Question 958
FlagAccording to the accelerator theory, investment expenditure will:
Correct
Option A.
According to the accelerator theory, small fluctuations in national income, of which consumer expenditure is a significant part, can lead to large fluctuations in investment demand. The correct answer is therefore Option A. Investment expenditure might rise when interest rates fall (Option B) but this has nothing to do with the accelerator. Options C and Dare red herrings with the word ‘accelerate’ thrown in.
Incorrect
Option A.
According to the accelerator theory, small fluctuations in national income, of which consumer expenditure is a significant part, can lead to large fluctuations in investment demand. The correct answer is therefore Option A. Investment expenditure might rise when interest rates fall (Option B) but this has nothing to do with the accelerator. Options C and Dare red herrings with the word ‘accelerate’ thrown in.
-
Question 959 of 999CB2032166
Question 959
FlagWhich of the following explains the way in which borrowing amplifies the business cycle?
Correct
Option B.
The financial sector can accelerate a boom and a slump because of the way in which it responds to the state of the economy, eg by becoming more willing to lend in a boom.
Consumption smoothing and the banks’ role in this (Option A) reduces the volatility in consumption relative to the volatility in income. A fall in the value of financial and non-financial assets can encourage households to decrease spending (Option C) to restore their balance sheets and hence help to bring about a recession, but this is not a result of a change in borrowing.Option D describes the accelerator.
Incorrect
Option B.
The financial sector can accelerate a boom and a slump because of the way in which it responds to the state of the economy, eg by becoming more willing to lend in a boom.
Consumption smoothing and the banks’ role in this (Option A) reduces the volatility in consumption relative to the volatility in income. A fall in the value of financial and non-financial assets can encourage households to decrease spending (Option C) to restore their balance sheets and hence help to bring about a recession, but this is not a result of a change in borrowing.Option D describes the accelerator.
-
Question 960 of 999CB2032167
Question 960
FlagThe accelerator effect will not be as great as that predicted by the accelerator theory for all of the following reasons except:
Correct
Option B.
The accelerator theory assumes that the capital goods sector has plenty of slack to meet the needs of the consumer goods industry for new machinery etc. This enables firms to invest as the theory predicts. The theory also assumes that firms producing consumer goods have no slack (and therefore must invest to cope with new demand). However, if the consumer goods sector has some slack (Option A), it will be able to meet demand without new investment. Similarly, if firms have anticipated a change in demand (Option C), they might have made the necessary investment prior to the change in national income. Finally, firms may make long-term plans for investment (Option D) and be unable to change them in response to a change in national income
Incorrect
Option B.
The accelerator theory assumes that the capital goods sector has plenty of slack to meet the needs of the consumer goods industry for new machinery etc. This enables firms to invest as the theory predicts. The theory also assumes that firms producing consumer goods have no slack (and therefore must invest to cope with new demand). However, if the consumer goods sector has some slack (Option A), it will be able to meet demand without new investment. Similarly, if firms have anticipated a change in demand (Option C), they might have made the necessary investment prior to the change in national income. Finally, firms may make long-term plans for investment (Option D) and be unable to change them in response to a change in national income
-
Question 961 of 999CB2032168
Question 961
FlagA recession will tend to come to an end when:
Correct
Option D.
Consumer durables, such as washing machines and cars, last many years, so in a recession, people often ‘make-do’ with what they have rather than buy new versions at an uncertain time. The same is true of capital equipment. However, eventually, these will need to be replaced, and this ‘echo effect’ can trigger a recovery. The other three options are characteristics of the end of a boom period.
Incorrect
Option D.
Consumer durables, such as washing machines and cars, last many years, so in a recession, people often ‘make-do’ with what they have rather than buy new versions at an uncertain time. The same is true of capital equipment. However, eventually, these will need to be replaced, and this ‘echo effect’ can trigger a recovery. The other three options are characteristics of the end of a boom period.
-
Question 962 of 999CB2032169
Question 962
FlagWhich of the following is NOT an approach to the environment and sustainability?
Correct
Option D.
The four approaches to the environment and sustainability are the free-market approach, the social efficiency approach, the conservationist approach and the Gaia approach.
Incorrect
Option D.
The four approaches to the environment and sustainability are the free-market approach, the social efficiency approach, the conservationist approach and the Gaia approach.
-
Question 963 of 999CB2032170
Question 963
FlagThe quantity theory of money assumes that the:
Correct
Option D.
In the quantity theory of money $(M \bar{V}=P \bar{Y})$, velocity of circulation ( V ) and real output ( Y ) are assumed to be relatively stable. (The theory therefore predicts that an increase in the money supply will lead to the same percentage increase in prices.
Incorrect
Option D.
In the quantity theory of money $(M \bar{V}=P \bar{Y})$, velocity of circulation ( V ) and real output ( Y ) are assumed to be relatively stable. (The theory therefore predicts that an increase in the money supply will lead to the same percentage increase in prices.
-
Question 964 of 999CB2032171
Question 964
FlagKarl Marx predicted that the capitalist system would collapse because:
Correct
Option D. Marx believed that Options A, B and C are also true, but these would not, of themselves, cause the capitalist system to collapse.
Incorrect
Option D. Marx believed that Options A, B and C are also true, but these would not, of themselves, cause the capitalist system to collapse.
-
Question 965 of 999CB2032172
Question 965
FlagWhich THREE of the following might confer an external benefit of production?
Correct
Options A, B and E.
An external benefit of production is a benefit from production experienced by people other than the producer directly involved in the transaction.The external benefits of the correct options are described below:
– forestry – planting new woodlands benefits the world through a reduction of $\mathrm{CO}_2$ in the atmosphere
– construction of train station – newly created jobs such as engineers and other technicians
– beekeeping – as a result of a beekeeper keeping bees, there will be an increased level of pollination of surrounding crops (and flowers).Travelling by train confers external benefits of consumption, as it is when the train is being used (rather than built) that others benefit from less congestion, lower levels of exhaust fumes and fewer accidents on the road. Using deodorant also confers external benefits of consumption rather than production.
Incorrect
Options A, B and E.
An external benefit of production is a benefit from production experienced by people other than the producer directly involved in the transaction.The external benefits of the correct options are described below:
– forestry – planting new woodlands benefits the world through a reduction of $\mathrm{CO}_2$ in the atmosphere
– construction of train station – newly created jobs such as engineers and other technicians
– beekeeping – as a result of a beekeeper keeping bees, there will be an increased level of pollination of surrounding crops (and flowers).Travelling by train confers external benefits of consumption, as it is when the train is being used (rather than built) that others benefit from less congestion, lower levels of exhaust fumes and fewer accidents on the road. Using deodorant also confers external benefits of consumption rather than production.
-
Question 966 of 999CB2032173
Question 966
FlagWhich of the following are views of the Austrian school?
I Governments should control the money supply so as to avoid distortions of the economy and inflation.II Supply-side shocks are a key influence on economic growth.
III Self regulation of markets is preferable to government regulation.Correct
Option C. The second statement is a key element of the new classical school.
Incorrect
Option C. The second statement is a key element of the new classical school.
-
Question 967 of 999CB2032174
Question 967
FlagKeynes rejected the classical view that people should be encouraged to save to get out of recession because increased savings will:
Correct
Option C.
Classical theory suggested that an increase in savings would lead to a fall in interest rates and therefore an increase in demand for loanable funds for investment. The extra demand for investment goods would increase output and hence employment. However, according to Keynes, increased savings would mean reduced consumption. Also, investment is not very responsive to a fall in interest rates. It is more likely to be affected by business confidence, and the fall in business confidence arising from a reduction in consumption would be likely to lead to a decrease in investment. Consumption and investment are two key components of aggregate demand, so there would be a decrease in output and hence employment.Incorrect
Option C.
Classical theory suggested that an increase in savings would lead to a fall in interest rates and therefore an increase in demand for loanable funds for investment. The extra demand for investment goods would increase output and hence employment. However, according to Keynes, increased savings would mean reduced consumption. Also, investment is not very responsive to a fall in interest rates. It is more likely to be affected by business confidence, and the fall in business confidence arising from a reduction in consumption would be likely to lead to a decrease in investment. Consumption and investment are two key components of aggregate demand, so there would be a decrease in output and hence employment. -
Question 968 of 999CB2032175
Question 968
FlagA merit good:
Correct
Option B.
By definition, a merit good provides benefits that are not fully appreciated by the user (Option B). For example, not everyone appreciates their education at the time. It also has strong positive externalities, (ruling out Option C).A merit good is a private good, ie it is rival and excludable. It therefore could be provided by the market, eg private schools (ruling out Option D) or by the government at a subsidised price (ruling out Option A).
Incorrect
Option B.
By definition, a merit good provides benefits that are not fully appreciated by the user (Option B). For example, not everyone appreciates their education at the time. It also has strong positive externalities, (ruling out Option C).A merit good is a private good, ie it is rival and excludable. It therefore could be provided by the market, eg private schools (ruling out Option D) or by the government at a subsidised price (ruling out Option A).
-
Question 969 of 999CB2032176
Question 969
FlagWhich of the following schools of thought believes that the free-market economy will NOT automatically recover from a recession?
Correct
Option C. Keynes believed that there is no reason to suppose that the free-market economy will automatically settle at a level of output that is sufficient to generate enough jobs for everyone that wants one. He said that the government should manage the level of aggregate demand in the economy so that it is sufficient to generate full employment.
Incorrect
Option C. Keynes believed that there is no reason to suppose that the free-market economy will automatically settle at a level of output that is sufficient to generate enough jobs for everyone that wants one. He said that the government should manage the level of aggregate demand in the economy so that it is sufficient to generate full employment.
-
Question 970 of 999CB2032177
Question 970
FlagCorrect
Option D
The diagram above reproduces the consumption function and adds a $45^{\circ}$ line, which shows the locus of points at which $C_{\mathrm{d}}=Y$. We can see that at an income level of $Y^*, C_{\mathrm{d}}=Y$; at levels of income below $Y^*, C_{\mathrm{d}}>Y$ and $W<0$; and at levels of income above $Y^*, C_{\mathrm{d}}<Y$ and $W>0$.
This tells us that the proportion of income spent on domestically produced goods $\left(C_{\mathrm{d}} / Y\right)$ falls as income increases (so Option C is not correct); that consumption on domestically produced goods is greater than income at some income levels (so Option D is correct); and that savings and taxes are not positive at all income levels (so Option B is not correct). The $m p c_{\mathbf{d}}$ is equal to the slope of the consumption function. Since it is a straight line, the $m p c_{\mathrm{d}}$ must be constant (so Option A is not correct).
Incorrect
Option D
The diagram above reproduces the consumption function and adds a $45^{\circ}$ line, which shows the locus of points at which $C_{\mathrm{d}}=Y$. We can see that at an income level of $Y^*, C_{\mathrm{d}}=Y$; at levels of income below $Y^*, C_{\mathrm{d}}>Y$ and $W<0$; and at levels of income above $Y^*, C_{\mathrm{d}}<Y$ and $W>0$.
This tells us that the proportion of income spent on domestically produced goods $\left(C_{\mathrm{d}} / Y\right)$ falls as income increases (so Option C is not correct); that consumption on domestically produced goods is greater than income at some income levels (so Option D is correct); and that savings and taxes are not positive at all income levels (so Option B is not correct). The $m p c_{\mathbf{d}}$ is equal to the slope of the consumption function. Since it is a straight line, the $m p c_{\mathrm{d}}$ must be constant (so Option A is not correct).
-
Question 971 of 999CB2032178
Question 971
FlagWhich two schools of economists are regarded as heterodox economists?
Correct
Option A. Heterodox economists are those who reject neoclassical equilibrium analysis, especially assumptions of rational optimising behaviour. Post-Keynesian and Austrian economists focus on the difficulty of making decisions in conditions of uncertainty.
Incorrect
Option A. Heterodox economists are those who reject neoclassical equilibrium analysis, especially assumptions of rational optimising behaviour. Post-Keynesian and Austrian economists focus on the difficulty of making decisions in conditions of uncertainty.
-
Question 972 of 999CB2032179
Question 972
FlagAccording the Marxist theory of value, the value of a product is determined by the:
Correct
Option B. This is the basis of Marx’s labour theory of value.
Incorrect
Option B. This is the basis of Marx’s labour theory of value.
-
Question 973 of 999CB2032180
Question 973
FlagWhen national income is less than full-employment national income, by how much must aggregate demand be increased to achieve full employment?
Correct
Option C
The economy is in equilibrium at less than full-employment national income. This is shown in the diagram by $Y_{\mathbf{e}}$.
Option A describes the amount by which national income must increase. However, as a result of the multiplier effect, aggregate demand does not have to increase by as much as this. The amount by which aggregate demand must increase is the deflationary or recessionary gap.
Option C gives the amount by which aggregate demand is deficient; the distance between $a$ and $b$ on the diagram. An increase in injections of this amount will, as a result of the multiplier effect, lead to the required increase in income.
Option B describes an inflationary gap. Option D only considers exports and imports, rather than the full picture of injections and withdrawals.
Incorrect
Option C
The economy is in equilibrium at less than full-employment national income. This is shown in the diagram by $Y_{\mathbf{e}}$.
Option A describes the amount by which national income must increase. However, as a result of the multiplier effect, aggregate demand does not have to increase by as much as this. The amount by which aggregate demand must increase is the deflationary or recessionary gap.
Option C gives the amount by which aggregate demand is deficient; the distance between $a$ and $b$ on the diagram. An increase in injections of this amount will, as a result of the multiplier effect, lead to the required increase in income.
Option B describes an inflationary gap. Option D only considers exports and imports, rather than the full picture of injections and withdrawals.
-
Question 974 of 999CB2032181
Question 974
FlagWhich of the following statements is correct in relation to the Austrian school of economic thought?
The Austrian school:
Correct
Option A. The Austrian school believes that economists must focus on the uncertain environment in which businesses operate.
Incorrect
Option A. The Austrian school believes that economists must focus on the uncertain environment in which businesses operate.
-
Question 975 of 999CB2032182
Question 975
FlagConsider both Statement 1 and Statement 2 and decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false.
If, and only if, you consider both statements to be true, you must decide whether Statement 2 is a valid explanation as to why Statement 1 is true.
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text{Statement 1 (Assertion)} & & \text{Statement 2 (Reason)} \\
\hline \text{Car insurance can be considered a merit good.} & BECAUSE & \text{Car insurance might be under consumed if left to the free market without some form of government intervention. }\\
\hline
\end{array}Correct
Option A.
Merit goods are goods that the government feels people will under consume and therefore ought to be subsidised, provided free, or alternatively, made compulsory.Car insurance may be under consumed as its benefits are not fully appreciated by the user (perhaps because people do not understand the risks or believe they will not need to make a claim) and because it confers external benefits (in that it offers protection for other people who might be injured and whose cars might be damaged by the insured driver).
Car insurance is therefore often compulsory.
Incorrect
Option A.
Merit goods are goods that the government feels people will under consume and therefore ought to be subsidised, provided free, or alternatively, made compulsory.Car insurance may be under consumed as its benefits are not fully appreciated by the user (perhaps because people do not understand the risks or believe they will not need to make a claim) and because it confers external benefits (in that it offers protection for other people who might be injured and whose cars might be damaged by the insured driver).
Car insurance is therefore often compulsory.
-
Question 976 of 999CB2032183
Question 976
FlagConsumption on domestically produced goods and services $\left(C_{\mathrm{d}}\right)$ is given by:
$$
C_{\mathrm{d}}=£ 100 m+0.8(Y-T)
$$
where $Y=$ income
$$
T=\text { tax revenue }
$$If both government expenditure and taxes are raised by $£ 10$ million each, the equilibrium level of national income will:
Correct
Option C.
We can see from the consumption function that tax is unrelated to income, ie it is a lump-sum tax. We could rewrite it as:
$$
C_d=£ 100 m-0.8 T+0.8 Y
$$This means that an increase in taxation of $£ 10$ million would decrease consumption by $£ 8$ million. If, at the same time, government spending increases by $£ 10$ million, then overall there would be a net increase in spending of $£ 2$ million. This would be subject to the multiplier, which is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}=\frac{1}{1-0.8}=5
$$So national income would increase by $£ 10$ million.
Alternatively:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{1-0.8}=5 \text { and so a } £ 10 \mathrm{~m} \text { increase in } G \text { leads to a } £ 50 \mathrm{~m} \text { increase in } Y \\
& k_{\mathrm{t}}=\frac{m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}{1-m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}=k-1=4 \text { and so a } £ 10 \mathrm{~m} \text { increase in } T \text { leads to a } £ 40 \mathrm{~m} \text { decrease in } Y
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore a $£ 10 m$ increase in $G$ and $T$ leads to a $£ 10 m$ increase in $Y$.
Incorrect
Option C.
We can see from the consumption function that tax is unrelated to income, ie it is a lump-sum tax. We could rewrite it as:
$$
C_d=£ 100 m-0.8 T+0.8 Y
$$This means that an increase in taxation of $£ 10$ million would decrease consumption by $£ 8$ million. If, at the same time, government spending increases by $£ 10$ million, then overall there would be a net increase in spending of $£ 2$ million. This would be subject to the multiplier, which is:
$$
k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}=\frac{1}{1-0.8}=5
$$So national income would increase by $£ 10$ million.
Alternatively:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& k=\frac{1}{1-m p c_d}=\frac{1}{1-0.8}=5 \text { and so a } £ 10 \mathrm{~m} \text { increase in } G \text { leads to a } £ 50 \mathrm{~m} \text { increase in } Y \\
& k_{\mathrm{t}}=\frac{m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}{1-m p c_{\mathrm{d}}}=k-1=4 \text { and so a } £ 10 \mathrm{~m} \text { increase in } T \text { leads to a } £ 40 \mathrm{~m} \text { decrease in } Y
\end{aligned}
$$Therefore a $£ 10 m$ increase in $G$ and $T$ leads to a $£ 10 m$ increase in $Y$.
-
Question 977 of 999CB2032184
Question 977
FlagWhich of the following is inconsistent with the co-existence of unemployment and inflation?
Correct
Option D.
The AS curve shows the relationship between the price level (on the vertical axis) and the total output produced (on the horizontal axis). If the AS curve is horizontal, it means that output can increase or decrease without there being any change in the price level. This means that the level of unemployment could change as output changes but there would be no inflation.The other three options are consistent with the experience of unemployment and inflation at the same time:
– Even when there is high aggregate demand and no demand-deficient unemployment, there could be structural unemployment co-existing with inflation.
– The Phillips curve shows an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation, suggesting that when aggregate demand is low, unemployment will be high and inflation will be low; and when aggregate demand is high, unemployment will be low and inflation will be high. This relationship does not suggest that when aggregate demand is low, unemployment will be high and inflation will be zero; and when aggregate demand is high, unemployment will be zero and inflation will be high.If an increase in aggregate demand can lead to an increase in the price level as well as an increase in real output, an injection will not increase real output by the full extent of the multiplier. This corresponds to an upward-sloping AS curve (and does not preclude the co-existence of unemployment and inflation).
Incorrect
Option D.
The AS curve shows the relationship between the price level (on the vertical axis) and the total output produced (on the horizontal axis). If the AS curve is horizontal, it means that output can increase or decrease without there being any change in the price level. This means that the level of unemployment could change as output changes but there would be no inflation.The other three options are consistent with the experience of unemployment and inflation at the same time:
– Even when there is high aggregate demand and no demand-deficient unemployment, there could be structural unemployment co-existing with inflation.
– The Phillips curve shows an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation, suggesting that when aggregate demand is low, unemployment will be high and inflation will be low; and when aggregate demand is high, unemployment will be low and inflation will be high. This relationship does not suggest that when aggregate demand is low, unemployment will be high and inflation will be zero; and when aggregate demand is high, unemployment will be zero and inflation will be high.If an increase in aggregate demand can lead to an increase in the price level as well as an increase in real output, an injection will not increase real output by the full extent of the multiplier. This corresponds to an upward-sloping AS curve (and does not preclude the co-existence of unemployment and inflation).
-
Question 978 of 999CB2032185
Question 978
FlagThe standardised unemployment rate:
Correct
Option A. The standardised rate is generally higher, since it includes people who are seeking work but are not eligible for unemployment benefit. The claimant rate is a measure of those in receipt of unemployment benefits.
Incorrect
Option A. The standardised rate is generally higher, since it includes people who are seeking work but are not eligible for unemployment benefit. The claimant rate is a measure of those in receipt of unemployment benefits.
-
Question 979 of 999CB2032186
Question 979
FlagWhich of the following could be a potential source of demand-pull inflation?
Correct
Option D. Demand-pull inflation occurs when there is a persistent increase in the level of aggregate demand. Options A and C would lead to a decrease in aggregate demand. Option B would lead to cost-push inflation
Incorrect
Option D. Demand-pull inflation occurs when there is a persistent increase in the level of aggregate demand. Options A and C would lead to a decrease in aggregate demand. Option B would lead to cost-push inflation
-
Question 980 of 999CB2032187
Question 980
FlagThe accelerator principle states that:
Correct
Option C.
According to the accelerator principle, investment expenditure is determined by the rate of change of national income. Although Option A is generally true, it isn’t a statement of the accelerator principle. Option B is concerned with the effect of a change in investment on output (income), rather than the effect of a change in income on investment, ie the direction of causation is incorrect. Finally, Option D contradicts Option A and so generally isn’t true.
Incorrect
Option C.
According to the accelerator principle, investment expenditure is determined by the rate of change of national income. Although Option A is generally true, it isn’t a statement of the accelerator principle. Option B is concerned with the effect of a change in investment on output (income), rather than the effect of a change in income on investment, ie the direction of causation is incorrect. Finally, Option D contradicts Option A and so generally isn’t true.
-
Question 981 of 999CB2032188
Question 981
FlagWhich THREE of the following reasons explain why training might be underprovided in a free-market economy relative to the social optimum, assuming that training is paid for by the recipients of the training:
Correct
Options B, E and F.
Training confers external benefits (Option B), eg the skills passed on to other workers, and the benefits to present and future employers who profit from the workers’ higher productivity.Training might be undervalued by the recipients (Option F) due to the fact that it incurs opportunity costs in the short run (including lost leisure time) but the benefits are only seen in the longer run.
At the free-market output level, $M S B>M S C$ (Option E). The socially optimal output level is where $M S B=M S C$.
This is illustrated in the following diagram, where:
– the free-market output level is $Q_1$.
– the socially optimal output level is $Q_2$.Incorrect
Options B, E and F.
Training confers external benefits (Option B), eg the skills passed on to other workers, and the benefits to present and future employers who profit from the workers’ higher productivity.Training might be undervalued by the recipients (Option F) due to the fact that it incurs opportunity costs in the short run (including lost leisure time) but the benefits are only seen in the longer run.
At the free-market output level, $M S B>M S C$ (Option E). The socially optimal output level is where $M S B=M S C$.
This is illustrated in the following diagram, where:
– the free-market output level is $Q_1$.
– the socially optimal output level is $Q_2$. -
Question 982 of 999CB2032189
Question 982
FlagIn the diagram below, S1 is the supply curve for cigarettes before an indirect tax is imposed and
S2 is the supply curve after the indirect tax has been imposed.The annual revenue collected by the government in taxation is :
Correct
Option B.
The imposition of an indirect tax raises firms’ costs by the amount of that tax.
Therefore the supply curve shifts vertically upwards by the amount of the tax. The vertical
distance between the supply curves is DF . The equilibrium quantity sold after the imposition of
the tax is G. Therefore, the tax revenue is DF x G = ACDF .Incorrect
Option B.
The imposition of an indirect tax raises firms’ costs by the amount of that tax.
Therefore the supply curve shifts vertically upwards by the amount of the tax. The vertical
distance between the supply curves is DF . The equilibrium quantity sold after the imposition of
the tax is G. Therefore, the tax revenue is DF x G = ACDF . -
Question 983 of 999CB2032190
Question 983
FlagA liquidity trap occurs when:
Correct
Option C.
When interest rates fall (and bond prices rise), the speculative (or idle) demand for money will increase (ie there is a movement along the demand for money curve) as the opportunity cost of holding savings in money falls. People think it’s not worth buying bonds; they might as well hold their savings in money form. When interest rates are at their floor, people expect interest rates to rise and bond prices to fall, so no-one wants to buy bonds and any additional money is held.
Incorrect
Option C.
When interest rates fall (and bond prices rise), the speculative (or idle) demand for money will increase (ie there is a movement along the demand for money curve) as the opportunity cost of holding savings in money falls. People think it’s not worth buying bonds; they might as well hold their savings in money form. When interest rates are at their floor, people expect interest rates to rise and bond prices to fall, so no-one wants to buy bonds and any additional money is held.
-
Question 984 of 999CB2032191
Question 984
FlagAccording to the portfolio balance theory, which of the following statements in FALSE?
Correct
Option D.
The first three explain the logic of the theory. People hold wealth in a portfolio of assets including money, financial assets (eg bonds, shares) and physical assets (eg property, cars). An increase in the money supply means that people might find that their portfolios are too liquid. As a result, people will spend excess liquid balances on both financial assets and goods and services. This increase in consumption therefore increases aggregate demand.
Incorrect
Option D.
The first three explain the logic of the theory. People hold wealth in a portfolio of assets including money, financial assets (eg bonds, shares) and physical assets (eg property, cars). An increase in the money supply means that people might find that their portfolios are too liquid. As a result, people will spend excess liquid balances on both financial assets and goods and services. This increase in consumption therefore increases aggregate demand.
-
Question 985 of 999CB2032192
Question 985
FlagWhich of the following statements about the velocity of circulation is TRUE?
Correct
Option B.
The fall in interest rates as a result of a rise in the money supply will cause a movement downwards along the demand for money curve and result in higher holdings of money. This is because the fall in interest rates reduces the attraction of holding bonds etc. Higher holdings of speculative (or idle) money result in a lower velocity of circulation.Let’s consider why the other options are false:
– Option A: In the short run, the demand for money is unstable and unpredictable (eg changing because of changing expectations of price changes) and hence the velocity of circulation is unstable.
– Option C: The financial crisis caused people to increase their holdings of money and hence contributed to a fall in the velocity of circulation.
– Option D: Monetarists recommend a long-term approach to monetary policy using targets for the growth of the money supply because they believe that, in the long run, the velocity of circulation is stable and predictable, and therefore the effect of a change in the money supply on aggregate demand and national income is predictable.Incorrect
Option B.
The fall in interest rates as a result of a rise in the money supply will cause a movement downwards along the demand for money curve and result in higher holdings of money. This is because the fall in interest rates reduces the attraction of holding bonds etc. Higher holdings of speculative (or idle) money result in a lower velocity of circulation.Let’s consider why the other options are false:
– Option A: In the short run, the demand for money is unstable and unpredictable (eg changing because of changing expectations of price changes) and hence the velocity of circulation is unstable.
– Option C: The financial crisis caused people to increase their holdings of money and hence contributed to a fall in the velocity of circulation.
– Option D: Monetarists recommend a long-term approach to monetary policy using targets for the growth of the money supply because they believe that, in the long run, the velocity of circulation is stable and predictable, and therefore the effect of a change in the money supply on aggregate demand and national income is predictable. -
Question 986 of 999CB2032193
Question 986
FlagWhich of these statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option C.
The capital account records the stock of non-financial (physical) wealth, such as property and machinery. The financial account records the stock of financial assets and liabilities in the balance sheet.
Incorrect
Option C.
The capital account records the stock of non-financial (physical) wealth, such as property and machinery. The financial account records the stock of financial assets and liabilities in the balance sheet.
-
Question 987 of 999CB2032194
Question 987
FlagThe (original) Phillips curve shows:
Correct
Option D. The (original) Phillips curve shows a trade-off between higher inflation and lower unemployment.
Incorrect
Option D. The (original) Phillips curve shows a trade-off between higher inflation and lower unemployment.
-
Question 988 of 999CB2032195
Question 988
FlagFollowing an expansionary fiscal policy to boost national income, a government can avoid crowding out by:
Correct
Option D.
Increasing government expenditure increases aggregate demand and increases national income. The resulting increase in demand for active money increases interest rates if we assume the supply of money curve is fixed. Higher interest rates reduce consumption and investment and possibly net exports, hence crowding out some of the initial increase in aggregate demand. However, increasing the money supply puts an offsetting downward pressure on interest rates so that consumption and investment will not fall.
Incorrect
Option D.
Increasing government expenditure increases aggregate demand and increases national income. The resulting increase in demand for active money increases interest rates if we assume the supply of money curve is fixed. Higher interest rates reduce consumption and investment and possibly net exports, hence crowding out some of the initial increase in aggregate demand. However, increasing the money supply puts an offsetting downward pressure on interest rates so that consumption and investment will not fall.
-
Question 989 of 999CB2032196
Question 989
FlagKeynesian economists believe that crowding out following a rise in injections is likely to be small because:
Correct
Option A
A rise in injections will lead to an increase in national income and hence an increase in the demand for money. If the demand for money and supply of money are both elastic, ie the two curves are relatively flat, then the resulting increase in interest rates will be relatively small. If the demand for investment is interest-inelastic, the demand for investment will not fall very much in response to the slightly higher interest rates.
Incorrect
Option A
A rise in injections will lead to an increase in national income and hence an increase in the demand for money. If the demand for money and supply of money are both elastic, ie the two curves are relatively flat, then the resulting increase in interest rates will be relatively small. If the demand for investment is interest-inelastic, the demand for investment will not fall very much in response to the slightly higher interest rates.
-
Question 990 of 999CB2032197
Question 990
FlagWhich of the following would cause the IS curve to shift to the right?
Correct
Option A.
The IS curve will shift to the right if there is an increase in any of the injections for reasons other than a fall in interest rates. An increase in business confidence (Option A) will increase investment and hence increase injections. A decrease in interest rates (Option B) will cause a downward movement along the IS curve. An appreciation of the currency (Option C) will make exports more expensive and imports less expensive so there is likely to be a decrease in net exports and the IS curve will shift to the left. A decrease in expected inflation (Option D) is likely to allow the central bank to choose a lower real interest rate for each level of national income which would cause the MP curve to shift downwards / to the right.
Incorrect
Option A.
The IS curve will shift to the right if there is an increase in any of the injections for reasons other than a fall in interest rates. An increase in business confidence (Option A) will increase investment and hence increase injections. A decrease in interest rates (Option B) will cause a downward movement along the IS curve. An appreciation of the currency (Option C) will make exports more expensive and imports less expensive so there is likely to be a decrease in net exports and the IS curve will shift to the left. A decrease in expected inflation (Option D) is likely to allow the central bank to choose a lower real interest rate for each level of national income which would cause the MP curve to shift downwards / to the right.
-
Question 991 of 999CB2032198
Question 991
FlagIf a country has negative net income from abroad then:
Correct
Option A.
This is because, by definition, GNY = GDP + net income from abroad.
Incorrect
Option A.
This is because, by definition, GNY = GDP + net income from abroad.
-
Question 992 of 999CB2032199
Question 992
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option D.
For positive ex ante real interest rates, the nominal interest rate is always above the expected inflation rate. In order for the real interest rate to rise, the nominal interest rate must be increased relative to the expected inflation rate.
Incorrect
Option D.
For positive ex ante real interest rates, the nominal interest rate is always above the expected inflation rate. In order for the real interest rate to rise, the nominal interest rate must be increased relative to the expected inflation rate.
-
Question 993 of 999CB2032200
Question 993
FlagThe MP curve slopes upwards because:
Correct
Option D.
Assuming that inflation is at its target level and that potential output is constant, an increase in aggregate demand will raise national income pushing the economy closer to its potential output. This will increase inflation, taking it above its target rate, and therefore cause the central bank to increase interest rates to bring inflation back to target. (Remember that MP stands for monetary policy.)Option A is the explanation of the upward-sloping LM curve – different to the MP curve and no longer part of the Core Reading. Options B and C are not explanations of the upward-sloping MP curve, and they are also incorrect statements. A rise in national income would cause an increase in imports, not exports. A rise in interest rates would cause a decrease in aggregate demand.
Incorrect
Option D.
Assuming that inflation is at its target level and that potential output is constant, an increase in aggregate demand will raise national income pushing the economy closer to its potential output. This will increase inflation, taking it above its target rate, and therefore cause the central bank to increase interest rates to bring inflation back to target. (Remember that MP stands for monetary policy.)Option A is the explanation of the upward-sloping LM curve – different to the MP curve and no longer part of the Core Reading. Options B and C are not explanations of the upward-sloping MP curve, and they are also incorrect statements. A rise in national income would cause an increase in imports, not exports. A rise in interest rates would cause a decrease in aggregate demand.
-
Question 994 of 999CB2032201
Question 994
FlagWhich of the following will result in a decrease in aggregate demand, other things being equal?
Correct
Option A.
Aggregate demand will decrease if any of its components ( $C, I, G$ or $(X-M)$ ) decrease. A rise in imports will reduce net exports and so reduce aggregate demand. All of the other options cause an increase in aggregate demand: a fall in savings will typically lead to a rise in consumption; a fall in interest rates will make saving unattractive and borrowing (for consumption and investment) more attractive; and a fall in economic and business uncertainty will tend to increase consumption and investment.
Incorrect
Option A.
Aggregate demand will decrease if any of its components ( $C, I, G$ or $(X-M)$ ) decrease. A rise in imports will reduce net exports and so reduce aggregate demand. All of the other options cause an increase in aggregate demand: a fall in savings will typically lead to a rise in consumption; a fall in interest rates will make saving unattractive and borrowing (for consumption and investment) more attractive; and a fall in economic and business uncertainty will tend to increase consumption and investment.
-
Question 995 of 999CB2032202
Question 995
FlagWhich of the following would cause a rightward/downward shift in the $M P$ curve?
I a lower target inflation rate
II an oil price increase
III an increase in potential national incomeCorrect
Option D.
An increase in potential national income (Statement III) means that a given inflation rate (and therefore a given interest rate) will be associated with a higher level of national income.Conversely, a lower inflation target (Statement I) means that a given level of national income will be associated with higher interest rates to achieve the lower target, ie the MP curve shifts leftwards (or upwards).
An oil price increase (Statement II) is a source of cost-push inflation, so for any level of national income, there will be a higher rate of inflation and hence higher interest rates will be required to reduce it. This would therefore also cause a leftward (or upward) shift in the MP curve.
Incorrect
Option D.
An increase in potential national income (Statement III) means that a given inflation rate (and therefore a given interest rate) will be associated with a higher level of national income.Conversely, a lower inflation target (Statement I) means that a given level of national income will be associated with higher interest rates to achieve the lower target, ie the MP curve shifts leftwards (or upwards).
An oil price increase (Statement II) is a source of cost-push inflation, so for any level of national income, there will be a higher rate of inflation and hence higher interest rates will be required to reduce it. This would therefore also cause a leftward (or upward) shift in the MP curve.
-
Question 996 of 999CB2032203
Question 996
FlagWhich of the following statements is FALSE?
Correct
Option C.
A higher target for inflation (eg $4 \%$ rather than $2 \%$ ) means that a given level of national income requires a lower interest rate to keep inflation on target, so the MP curve shifts downwards. This causes interest rates to fall, investment to rise and a movement along the $I S$ curve to a higher level of national income.A looser monetary policy (Option B) means that the central bank sets a lower interest rate for a given national income.
Incorrect
Option C.
A higher target for inflation (eg $4 \%$ rather than $2 \%$ ) means that a given level of national income requires a lower interest rate to keep inflation on target, so the MP curve shifts downwards. This causes interest rates to fall, investment to rise and a movement along the $I S$ curve to a higher level of national income.A looser monetary policy (Option B) means that the central bank sets a lower interest rate for a given national income.
-
Question 997 of 999CB2032204
Question 997
FlagIn the short run, a decrease in exports is likely to lead to:
Correct
Option C.
A decrease in exports will decrease aggregate demand and cause the AD curve to shift to the left. In the short run, this will cause a fall in the price level and a fall in output, as can be seen in the following diagram.
-
Question 998 of 999CB2032205
Question 998
FlagConsider an economy where the demand for real money balances and the demand for investment are both highly interest-elastic. A change in the money supply will give:
Correct
Option D.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a decrease in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium.The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If, as in this question, money demand is elastic, ie the demand curve is flattish, then only a relatively small fall in interest rates is required. This means that one of Options A and D must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if the demand for investment is highly interest-elastic, ie very sensitive to interest rates, then it will change considerably in response to even a small reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
Incorrect
Option D.
For illustration, consider an increase in the money supply. As shown on the diagram below, this will lead to a decrease in interest rates so that the supply and demand for money can be brought back into equilibrium.The extent to which interest rates will change in response to a change in the money supply depends upon the slope of the money demand curve. If, as in this question, money demand is elastic, ie the demand curve is flattish, then only a relatively small fall in interest rates is required. This means that one of Options A and D must be the correct answer.
Let’s now consider the effect of a change in interest rates on investment by firms. Almost by definition, if the demand for investment is highly interest-elastic, ie very sensitive to interest rates, then it will change considerably in response to even a small reduction in interest rates. The correct answer is therefore Option D.
-
Question 999 of 999CB2032206
Question 999
FlagAn increase in government expenditure financed by government borrowing from the non-bank private sector is most likely to:
Correct
Option C.
If the government finances its expenditure by borrowing from the non-bank private sector, there will be no change in the money supply curve. By increasing government expenditure, injections increase, so national income will increase. However, the resulting increase in the demand for active money will increase interest rates (given that the money supply curve is unchanged) and hence cause a fall in investment. Option D gives the outcome of an increase in government expenditure financed by borrowing from the central bank or in the form of bills from the commercial banks, both of which increase the money supply.
Incorrect
Option C.
If the government finances its expenditure by borrowing from the non-bank private sector, there will be no change in the money supply curve. By increasing government expenditure, injections increase, so national income will increase. However, the resulting increase in the demand for active money will increase interest rates (given that the money supply curve is unchanged) and hence cause a fall in investment. Option D gives the outcome of an increase in government expenditure financed by borrowing from the central bank or in the form of bills from the commercial banks, both of which increase the money supply.